Smart Electricity Meter Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-electricity-meter
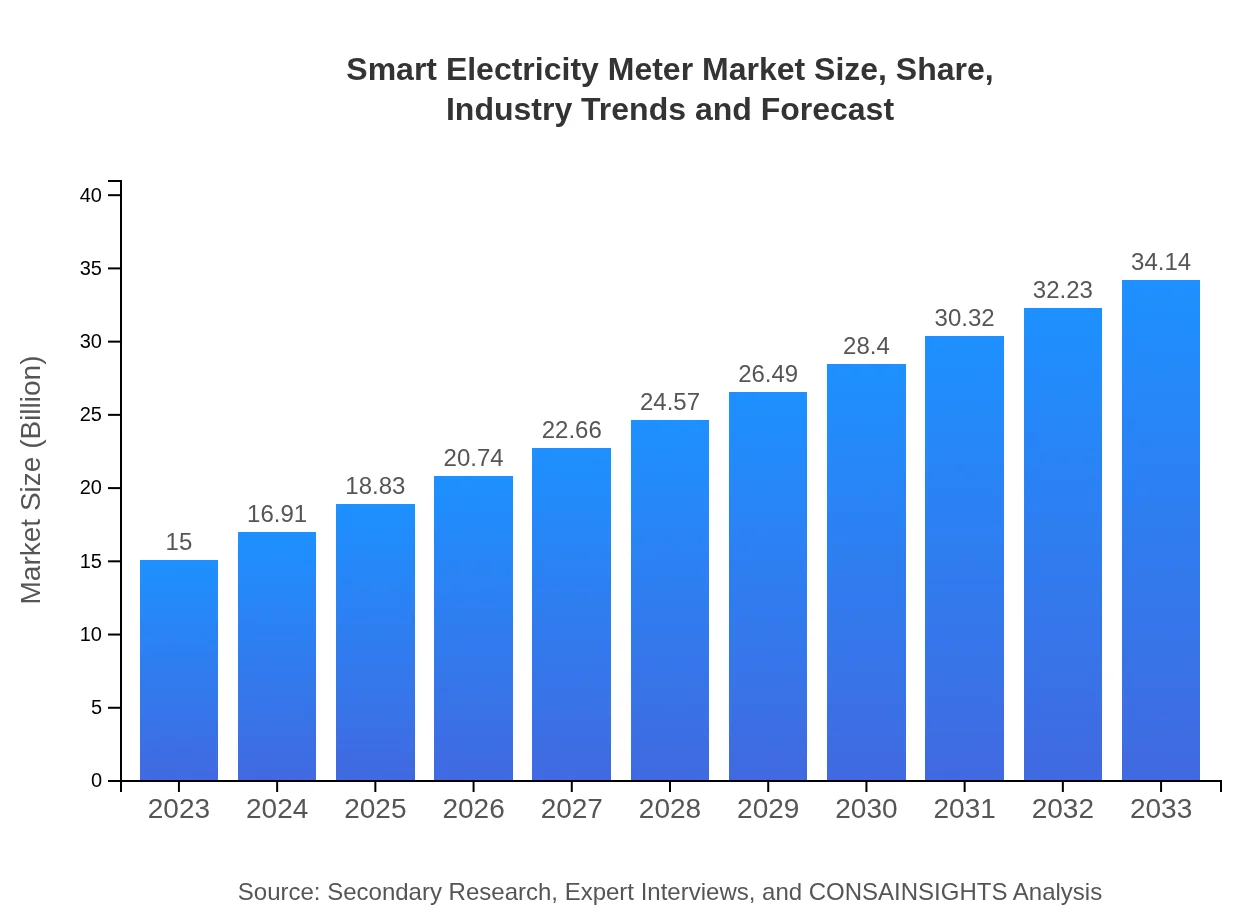
Smart Electricity Meter Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Smart Electricity Meter market, covering insights on market size, trends, technologies, and forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $15.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $34.14 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Itron, Inc., Landis+Gyr, Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Electricity Meter Market Overview
Customize Smart Electricity Meter Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Electricity Meter market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Electricity Meter's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Electricity Meter
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Electricity Meter market in 2023?
Smart Electricity Meter Industry Analysis
Smart Electricity Meter Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Electricity Meter Market Report:
Europe's market for Smart Electricity Meters is anticipated to grow from $4.53 billion in 2023 to $10.31 billion in 2033, driven by stringent energy regulations, carbon reduction targets, and high government investments in smart grid technologies.Asia Pacific Smart Electricity Meter Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is witnessing rapid growth, driven by increasing urbanization and investments in smart city initiatives. With a market size projected to grow from $2.60 billion in 2023 to $5.91 billion in 2033, countries like China and India lead the adoption of smart meters to enhance grid efficiency.North America Smart Electricity Meter Market Report:
North America is anticipated to dominate the market, growing from $5.85 billion in 2023 to $13.32 billion in 2033. The growth is attributed to advanced infrastructure and a progressive regulatory environment promoting energy efficiency and smart technology.South America Smart Electricity Meter Market Report:
In South America, the Smart Electricity Meter market is expanding due to governmental support and a push for renewable energy management. The market is expected to grow from $1.14 billion in 2023 to $2.60 billion in 2033, with Brazil and Argentina as key players.Middle East & Africa Smart Electricity Meter Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is expected to expand from $0.88 billion in 2023 to $2.00 billion in 2033. Regional initiatives aimed at energy conservation and improvements in grid infrastructure increase demand for smart electricity meters.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
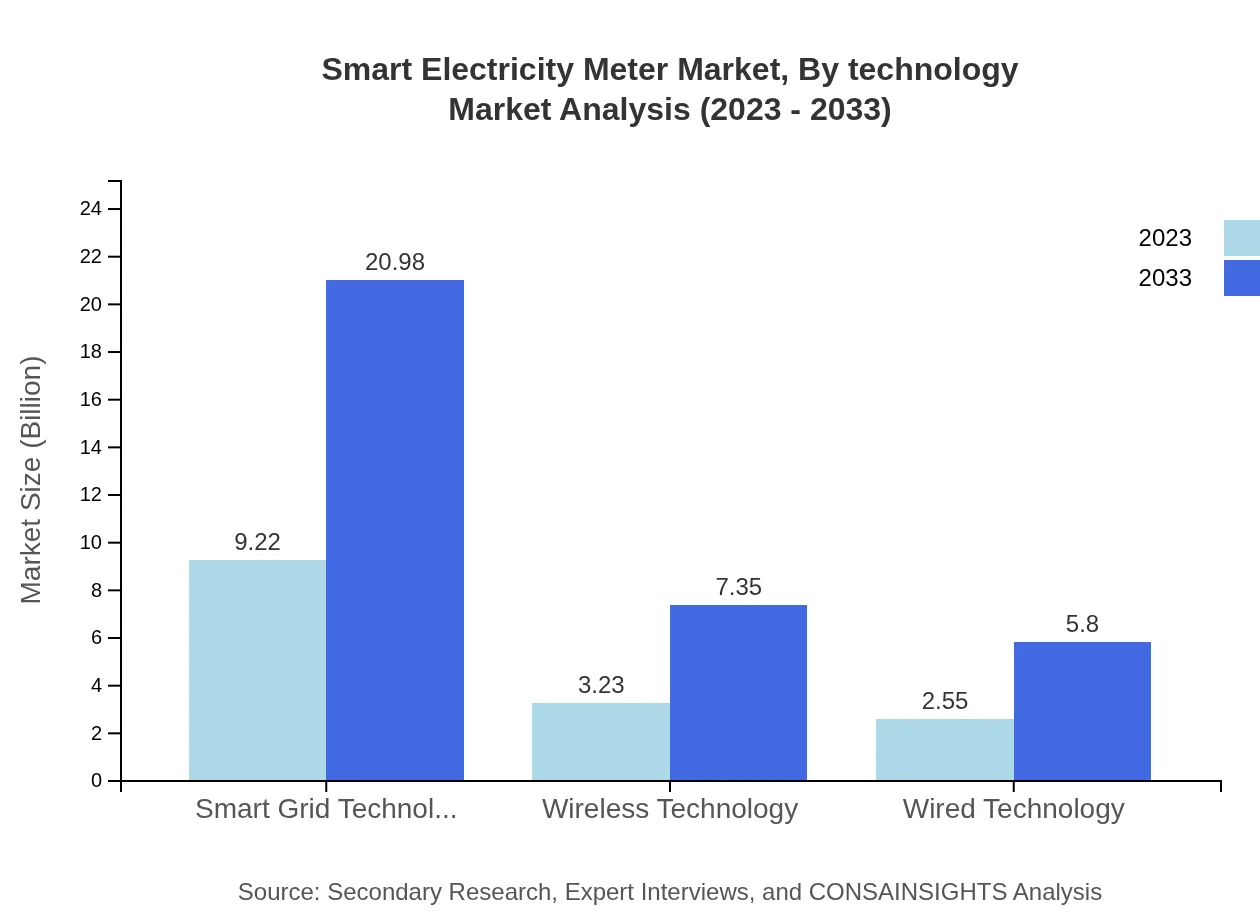
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis By Technology
The market is predominantly driven by Smart Grid Technology, which constitutes 61.46% market share. Wireless technology, accounting for 21.54%, is essential for remote monitoring and control, whereas wired technology, with 17% share, remains relevant for established infrastructures.
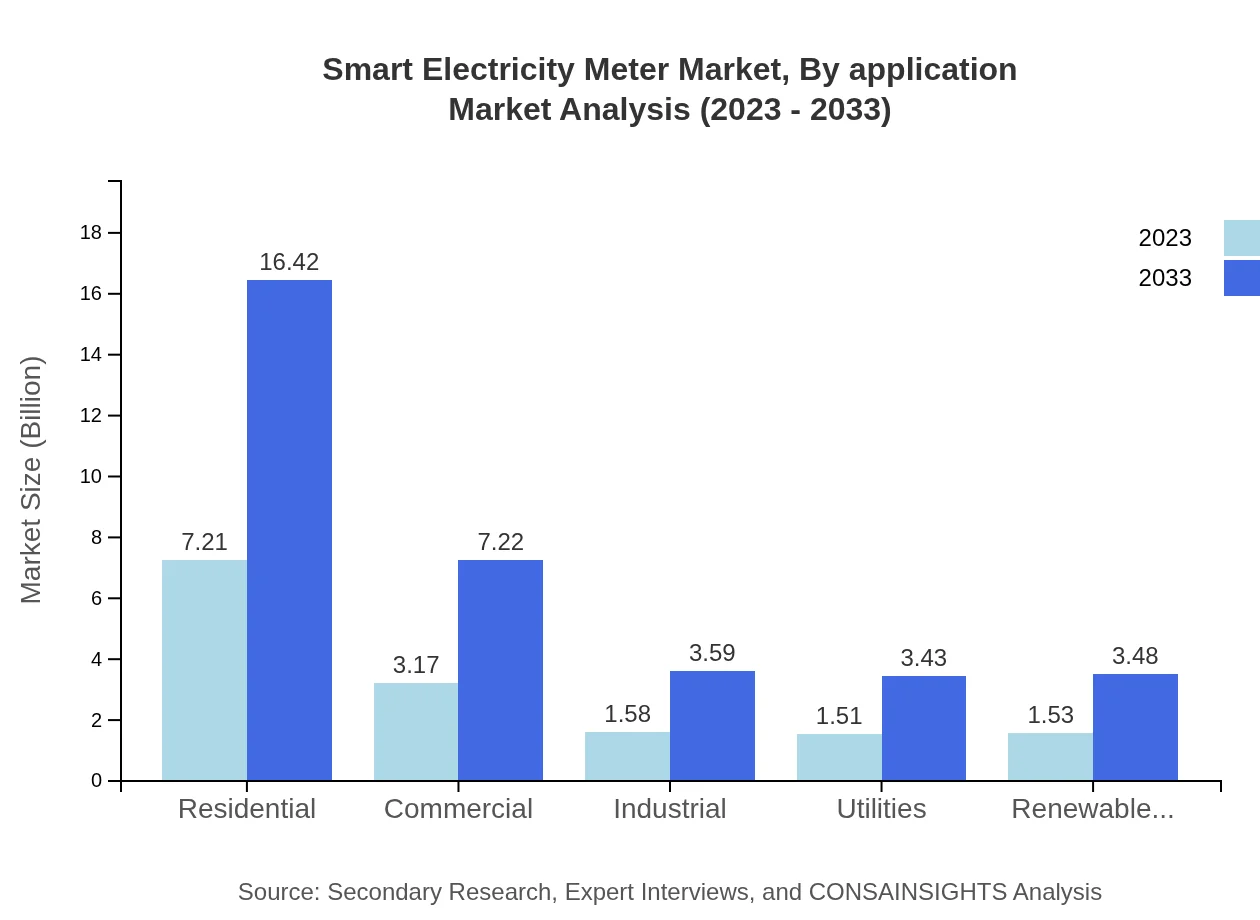
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis By Application
The residential sector holds 48.09% of the market share, while commercial and industrial applications contribute 21.14% and 10.52% respectively. The demand for smart meters in residential applications is largely fueled by consumer preferences for energy monitoring and savings.
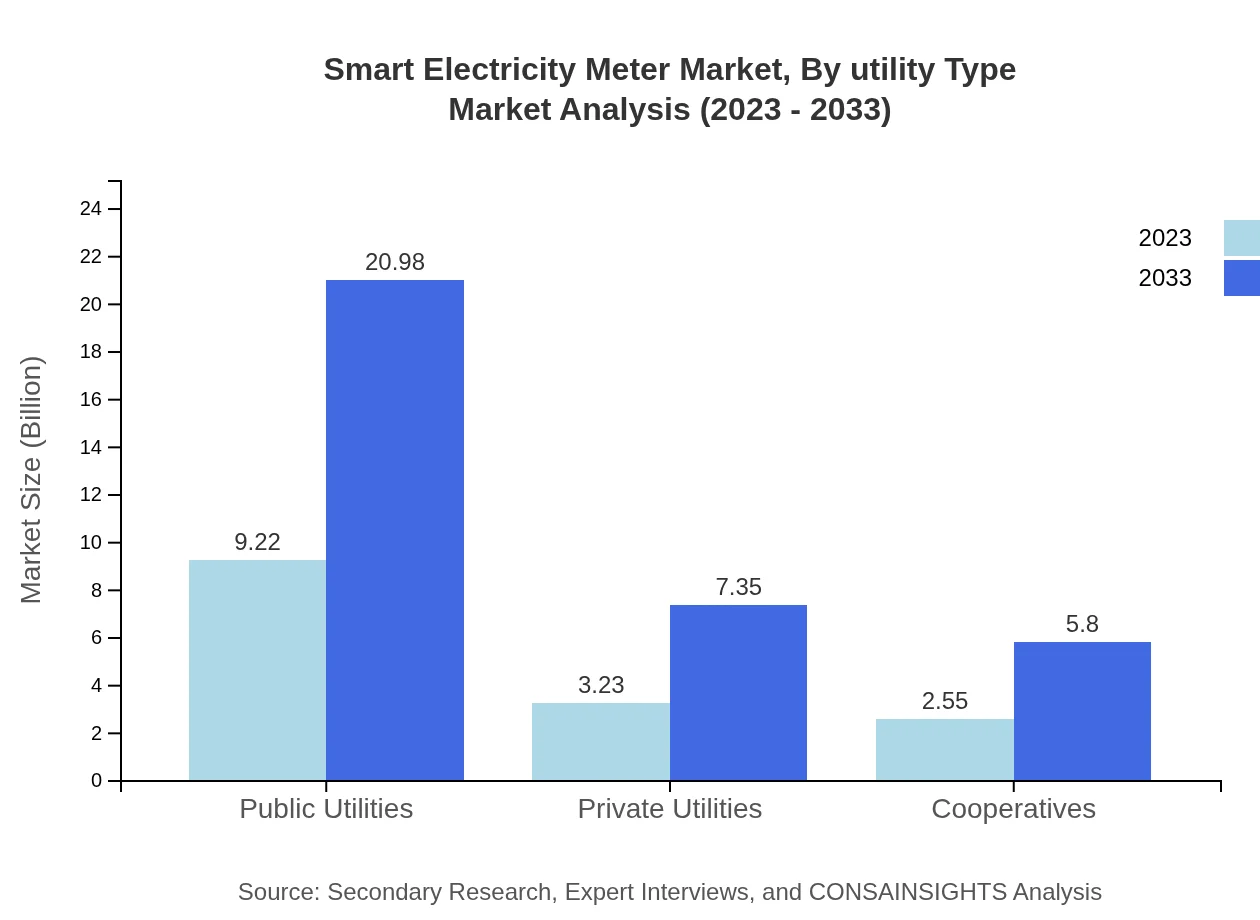
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis By Utility Type
Public Utilities dominate the market with a share of 61.46% due to extensive regulatory frameworks supporting energy efficiency. Private Utilities and Cooperatives also play significant roles, contributing 21.54% and 17% respectively.
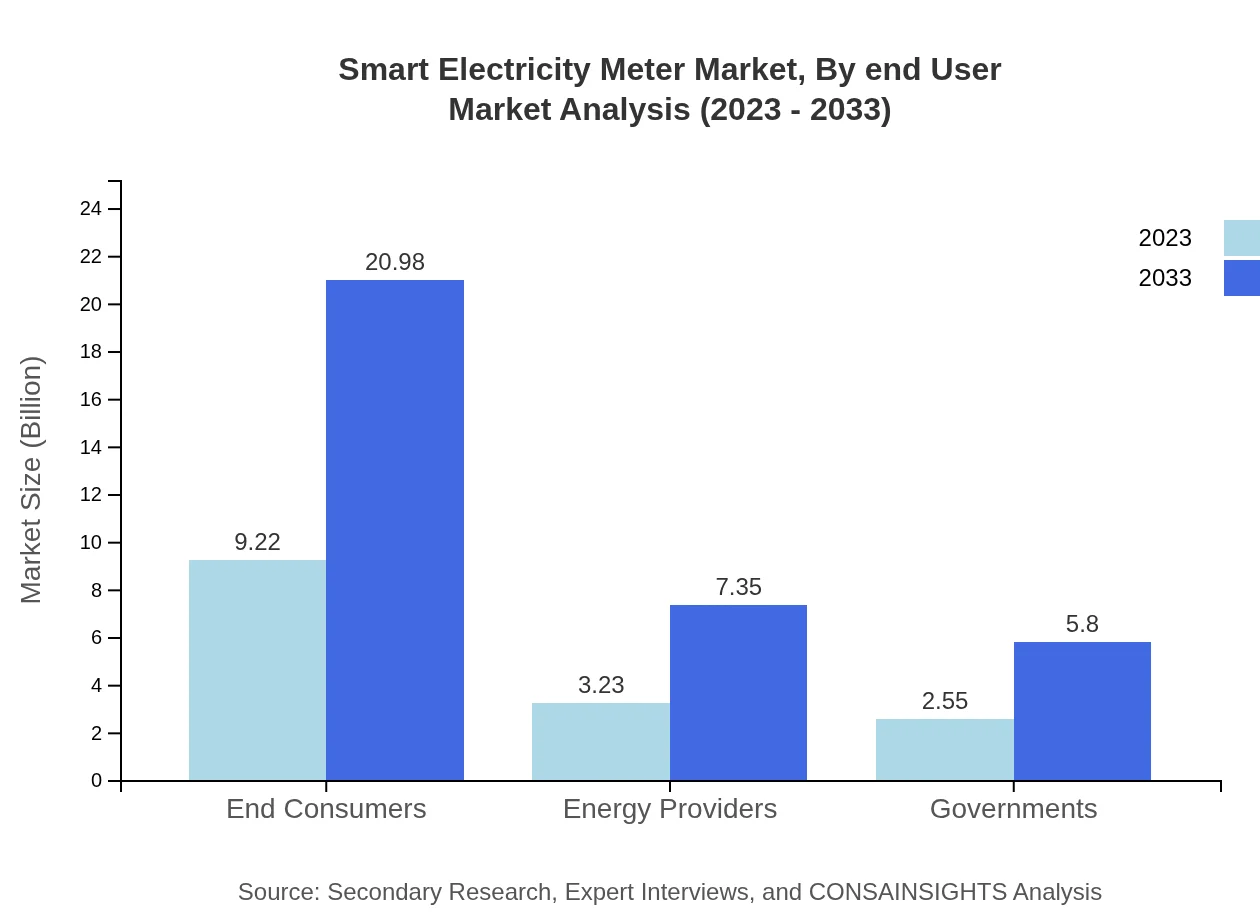
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis By End User
End consumers represent a remarkable 61.46% market share and are expected to drive further technological advancement towards energy efficiency and sustainability in the upcoming decade.
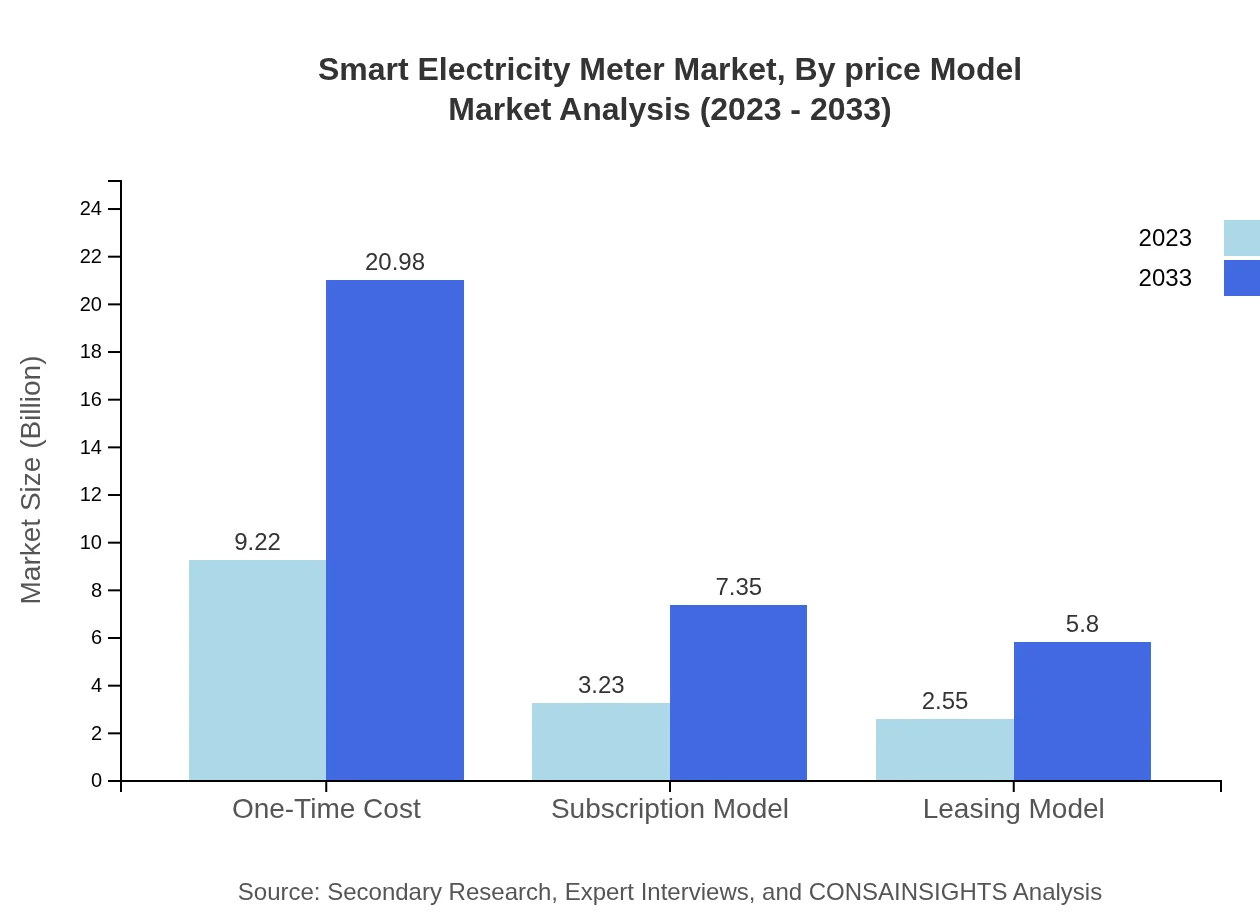
Smart Electricity Meter Market Analysis By Price Model
The One-Time Cost model is widely adopted, representing 61.46% of the market. Subscription models account for 21.54%, while leasing options add 17%, providing flexibility for consumers and utilities alike.
Smart Electricity Meter Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Electricity Meter Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG provides a broad range of smart metering solutions, enhancing grid operations and consumer engagement through advanced technology and IoT integration.Itron, Inc.:
Itron is a prominent player offering innovative smart metering solutions focused on improving energy efficiency and driving sustainability across the utility sector.Landis+Gyr:
Landis+Gyr specializes in smart metering technologies and solutions that enable utility providers to better manage resources and improve customer service.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell provides advanced technology for better energy management, focusing on smart meters and systems that enhance energy usage insights.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Electricity Meter?
The global smart electricity meter market is valued at approximately $15 billion in 2023, with a promising CAGR of 8.3% projected through 2033. This growth reflects an increasing adoption of smart meters across various segments.
What are the key market players or companies in this smart Electricity Meter industry?
The smart electricity meter industry features key players such as Siemens, Landis+Gyr, Itron, and Honeywell, all of which are instrumental in driving innovation and market expansion by offering comprehensive solutions in smart metering technologies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart Electricity Meter industry?
Growth in the smart electricity meter market is primarily driven by rising energy efficiency mandates, increased renewable energy integration, and growing demand for real-time data analytics to help utilities manage energy distribution effectively.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart Electricity Meter?
The fastest-growing region for smart electricity meters is North America, expecting to rise from $5.85 billion in 2023 to $13.32 billion by 2033, supported by robust infrastructure investment and energy efficiency initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart Electricity Meter industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific requirements in the smart electricity meter industry, enabling detailed insights into regional trends, market size segmentation, and competitive analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart Electricity Meter market research project?
Deliverables from the smart electricity meter market research project include comprehensive reports covering market analysis, insights into key players, growth forecasts, and segmentation data across various regions and market segments.
What are the market trends of smart Electricity Meter?
Market trends for smart electricity meters indicate a shift towards advanced technologies such as IoT integration, wireless communication enhancements, and consumer-centric functionalities aimed at increasing user engagement and energy management efficiency.