Smart Factory Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-factory
Smart Factory Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive report provides insights into the Smart Factory market from 2023 to 2033, focusing on market size, growth trends, technological advancements, key players, and regional dynamics. It aims to equip stakeholders with essential data for informed decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
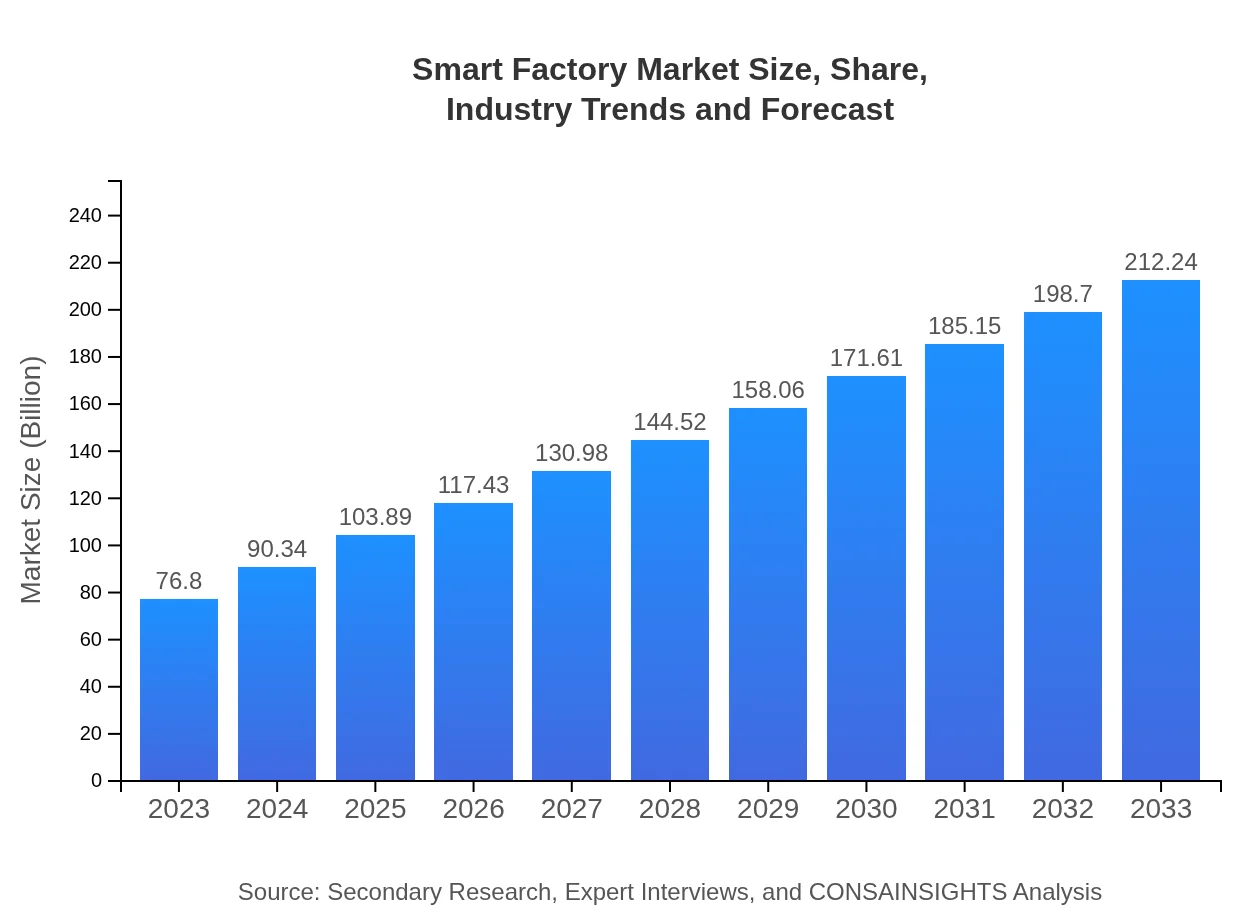
| 2023 Market Size | $76.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 10.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $212.24 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Honeywell International, General Electric |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Factory Market Overview
Customize Smart Factory Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Factory market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Factory's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Factory
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Factory market in 2023?
Smart Factory Industry Analysis
Smart Factory Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Factory Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Factory Market Report:
In Europe, the Smart Factory market is forecasted to grow from $24.93 billion in 2023 to $68.89 billion by 2033. The region is spearheading technological advancements, particularly in manufacturing processes and automation technologies, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and substantial investments in research and development.Asia Pacific Smart Factory Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Smart Factory market is projected to grow from $14.51 billion in 2023 to $40.09 billion by 2033, driven by manufacturing hubs like China, Japan, and South Korea, which are investing heavily in automation technologies to meet production demands. The emphasis on export-oriented industrialization and technological upgradation significantly contributes to this growth.North America Smart Factory Market Report:
North America holds a prominent share in the Smart Factory market, with a value of $26.43 billion in 2023 projected to rise to $73.05 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a strong technology infrastructure and significant investment in automation across industries such as automotive and consumer electronics, driven by demand for increased operational efficiency and supply chain optimization.South America Smart Factory Market Report:
The South American Smart Factory market is expected to expand from $4.85 billion in 2023 to $13.41 billion by 2033. Countries like Brazil and Argentina are increasingly adopting smart manufacturing practices, supported by government initiatives aimed at enhancing industrial competitiveness through technology integration.Middle East & Africa Smart Factory Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa Smart Factory market will grow from $6.07 billion in 2023 to $16.79 billion by 2033. Increased focus on digital transformation in sectors like oil and gas, and manufacturing is driving the adoption of smart factory technologies, with governments promoting initiatives to enhance industry productivity sustainably.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Factory Market Analysis By Technology
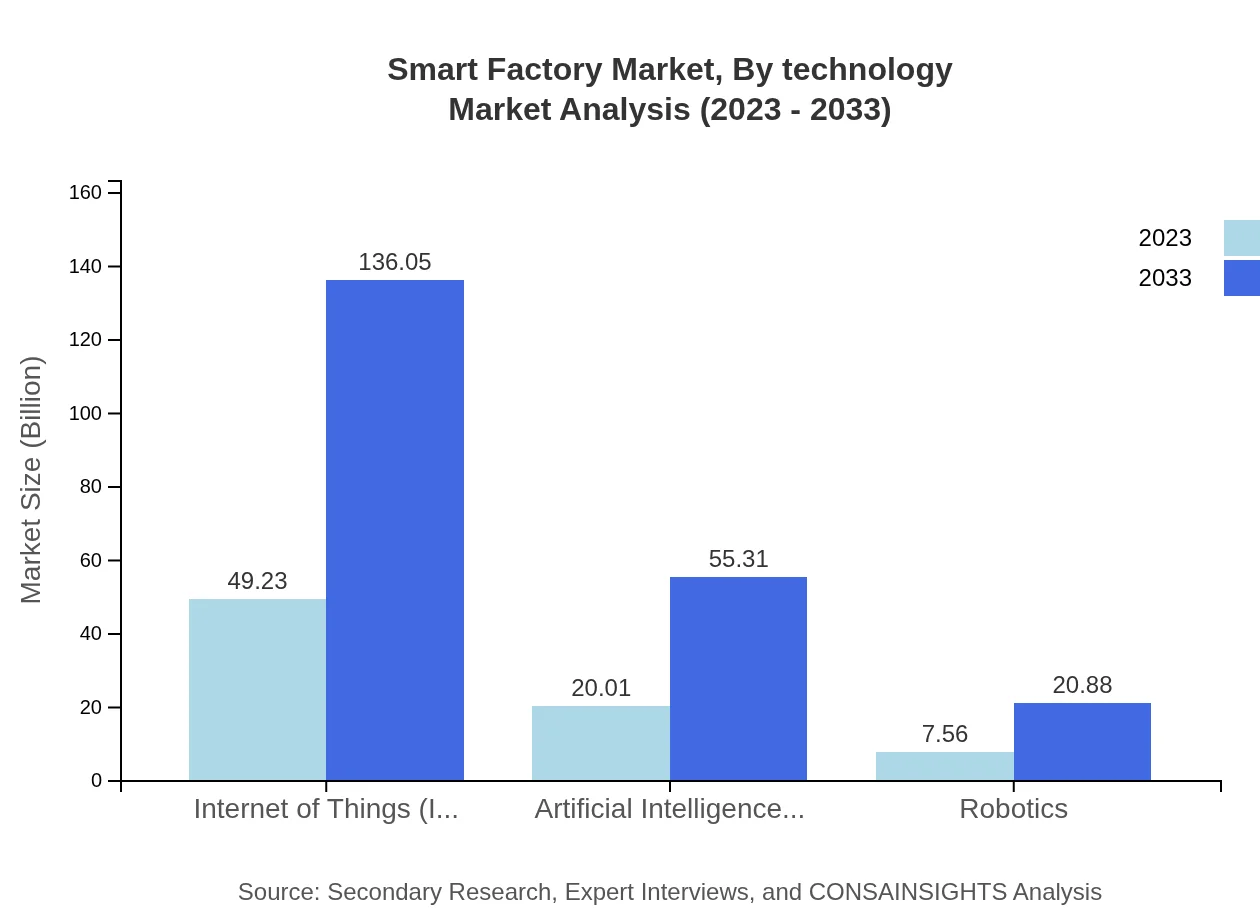
The Smart Factory market by technology includes various segments such as IoT, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotics, Automation Solutions, and Data Management Solutions. Notably, IoT holds a significant market share, projected to grow from $49.23 billion in 2023 to $136.05 billion by 2033, highlighting its essential role in networked manufacturing environments.
Smart Factory Market Analysis By Solution
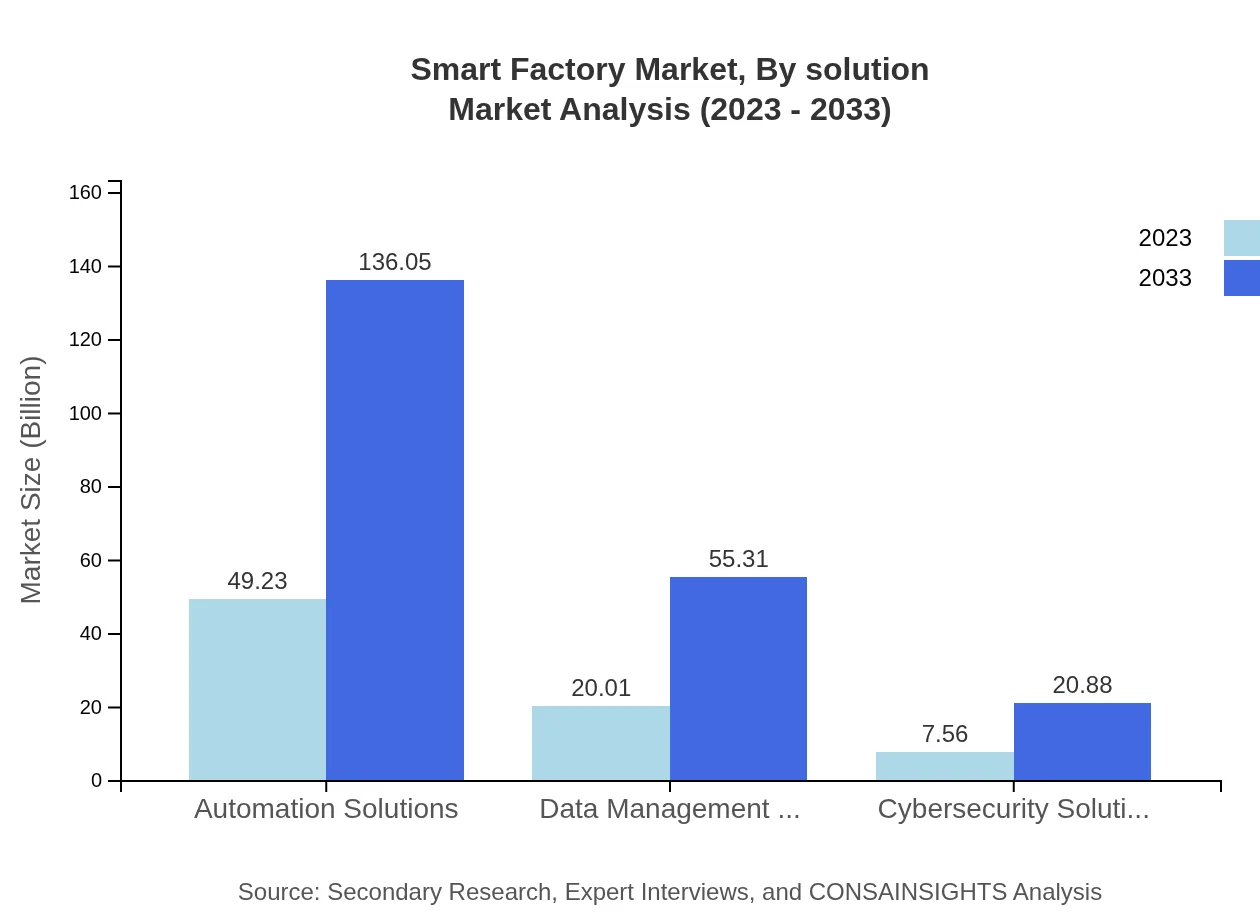
Solutions in the Smart Factory sector comprise Consulting Services, Integration Services, Support Services, and more. Consulting Services are expected to dominate the market, with a size of $49.23 billion in 2023, growing to $136.05 billion by 2033, indicating the vital role of expert consultants in driving smart factory implementations.
Smart Factory Market Analysis By End User
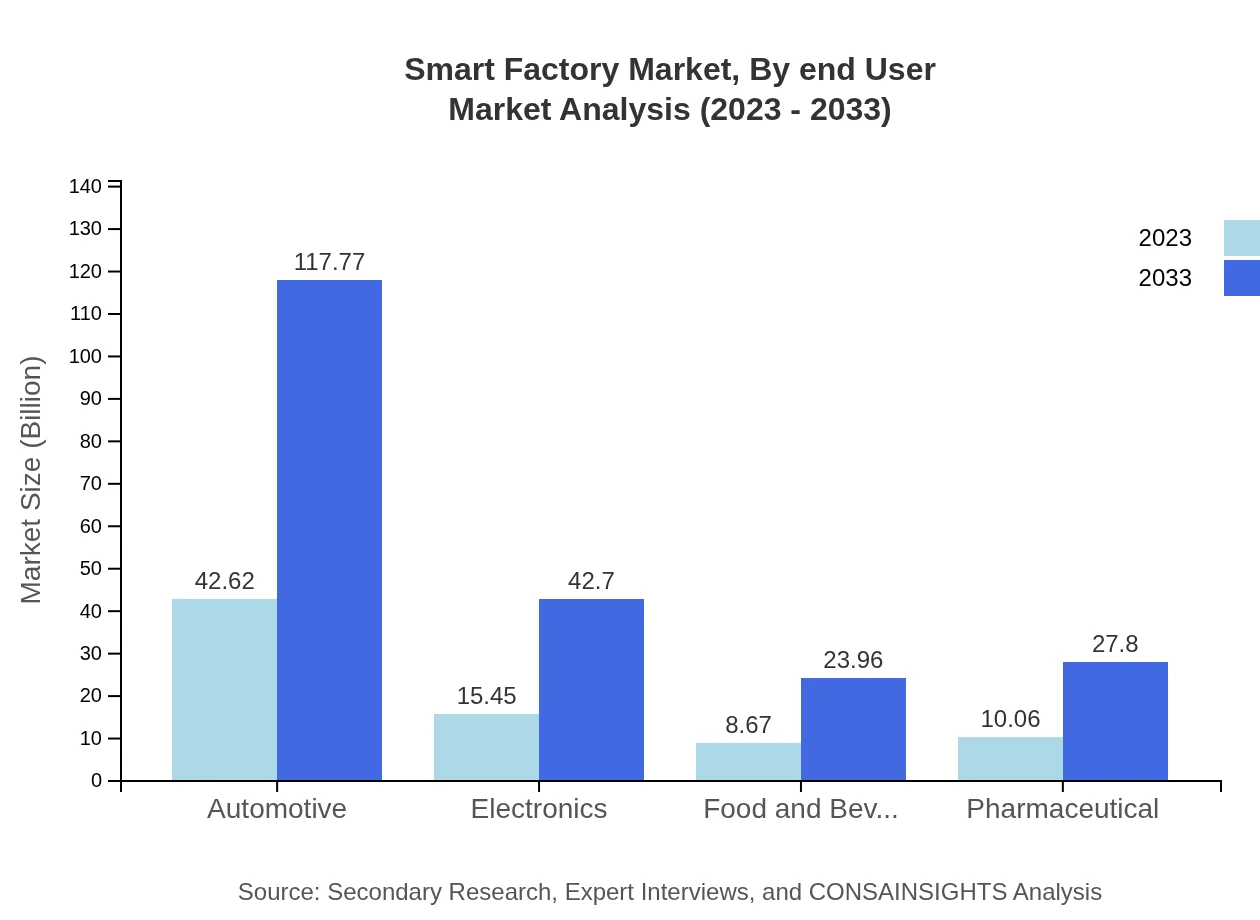
The major industries engaging in Smart Factory solutions include Automotive, Electronics, Food and Beverage, and Pharmaceuticals. The Automotive sector is projected to maintain its lead, growing from $42.62 billion in 2023 to $117.77 billion by 2033, showcasing the critical dependency of automotive manufacturing on automation technologies.
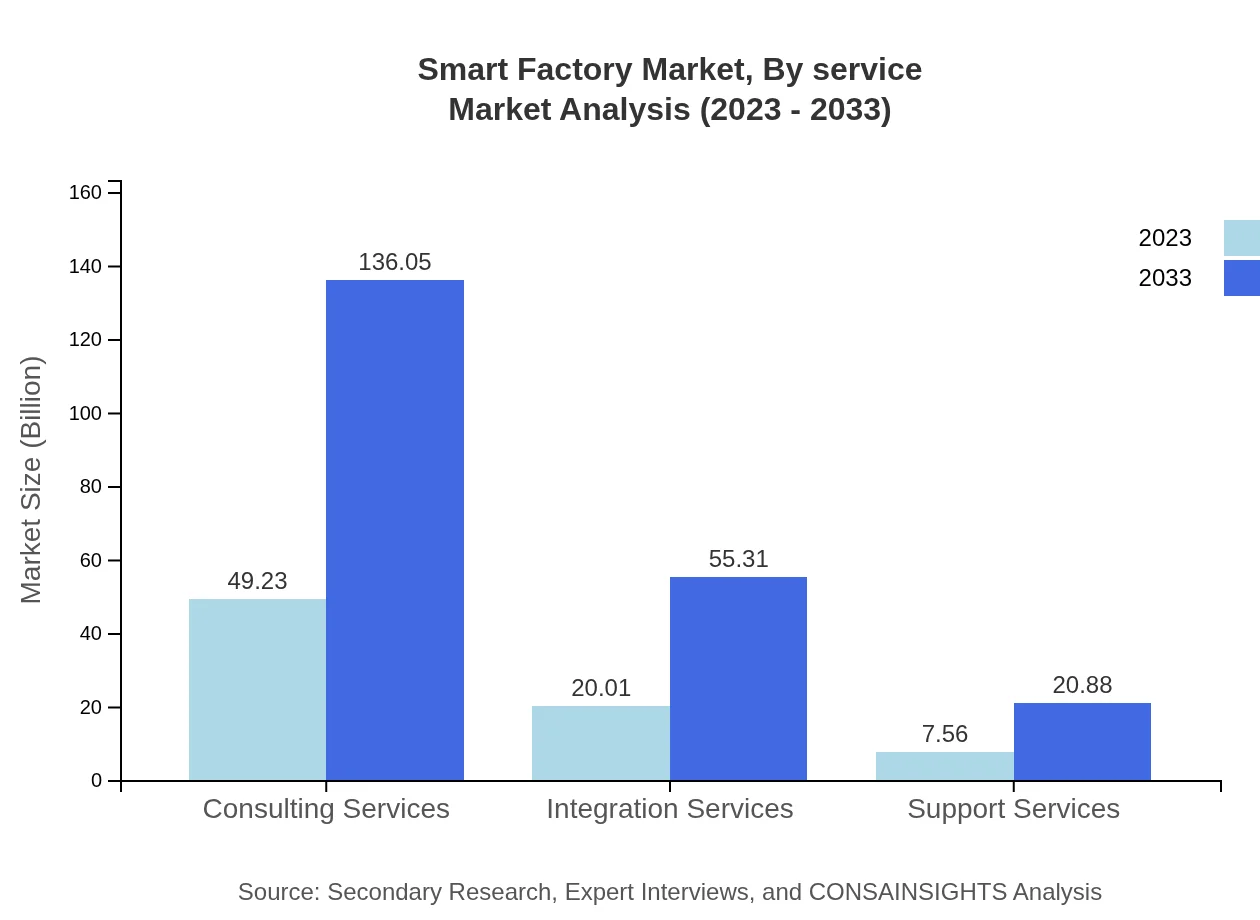
Smart Factory Market Analysis By Service
Services in the Smart Factory domain, including Automation, Data Management, Cybersecurity, and Support Services, are imperative for sustained operational efficiency. Automation Solutions are forecasted to experience the highest growth, with market size expanding from $49.23 billion in 2023 to $136.05 billion by 2033.
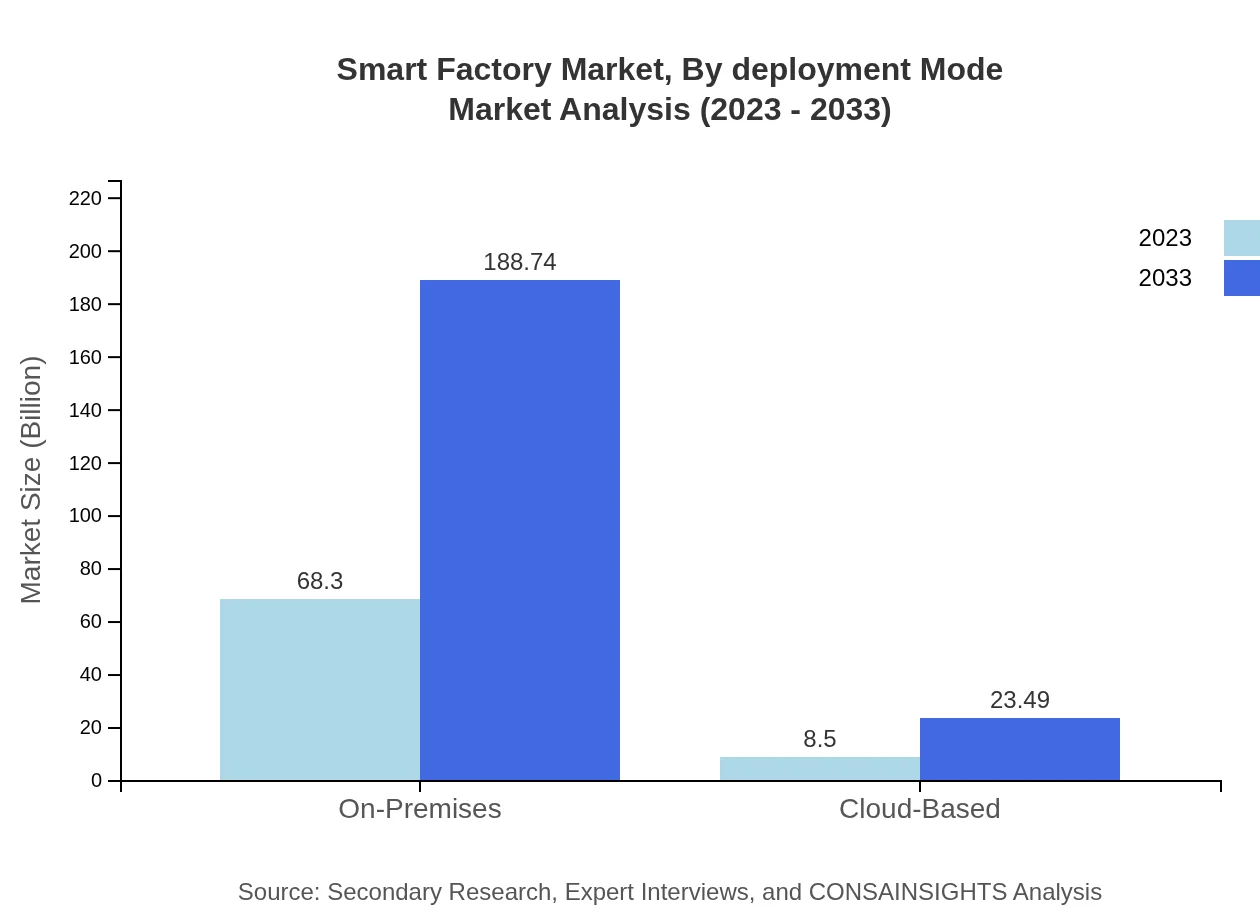
Smart Factory Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
Deployment modes in the Smart Factory landscape cover On-Premises and Cloud-Based solutions. On-Premises solutions are anticipated to grow significantly from $68.30 billion in 2023 to $188.74 billion by 2033, indicating a strong preference for in-house control over manufacturing processes.
Smart Factory Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Factory Industry
Siemens AG:
A leader in industrial automation, Siemens provides advanced engineering and technological solutions that facilitate the implementation of smart factory concepts across diverse industries.Rockwell Automation:
Rockwell Automation specializes in automation and control technologies, focusing on intelligent devices and connected services to enhance manufacturing efficiency.Schneider Electric:
Known for its energy management solutions, Schneider Electric integrates automation systems and IoT into smart factory frameworks to boost operational sustainability.Honeywell International:
Honeywell offers comprehensive automation solutions, ranging from safety systems to industrial software analytics, supporting the transformation of conventional factories into smart manufacturing facilities.General Electric:
GE plays a pivotal role in smart manufacturing by providing advanced industrial IoT platforms that connect machines, systems, and people for greater productivity.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Factory?
The global smart factory market is projected to reach $76.8 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2023. This robust growth reflects the increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in the smart Factory industry?
Key players in the smart factory industry include Siemens AG, General Electric, Honeywell, Rockwell Automation, and ABB. These companies dominate the market with their innovative technologies and comprehensive service offerings.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart factory industry?
Growth in the smart factory sector is driven by advancements in IoT and AI technologies, increased automation and robotics adoption, demand for operational efficiency, and the need for sustainable manufacturing practices in various industries.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart factory?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the smart factory market, with a projected market size of $40.09 billion by 2033, up from $14.51 billion in 2023, reflecting a surge in manufacturing and IoT investments.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart factory industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customizable market report data tailored to client needs within the smart factory industry, ensuring relevant insights and detailed analysis for strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart factory market research project?
Deliverables from the smart factory market research project include detailed reports on market size, growth forecasts, competitive landscape, regional analysis, and insights into key trends and segments within the industry.
What are the market trends of smart factory?
Current trends in the smart factory market include increased integration of AI and ML, the growth of automation solutions, enhanced focus on cybersecurity, and the shift toward cloud-based and on-premises solutions for flexible manufacturing environments.