Smart Food Packaging Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-food-packaging
Smart Food Packaging Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Smart Food Packaging market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting market trends, forecasts, and insights into the industry’s dynamics. It reviews market size, segmentation, regional analysis, and profiles of key players within the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
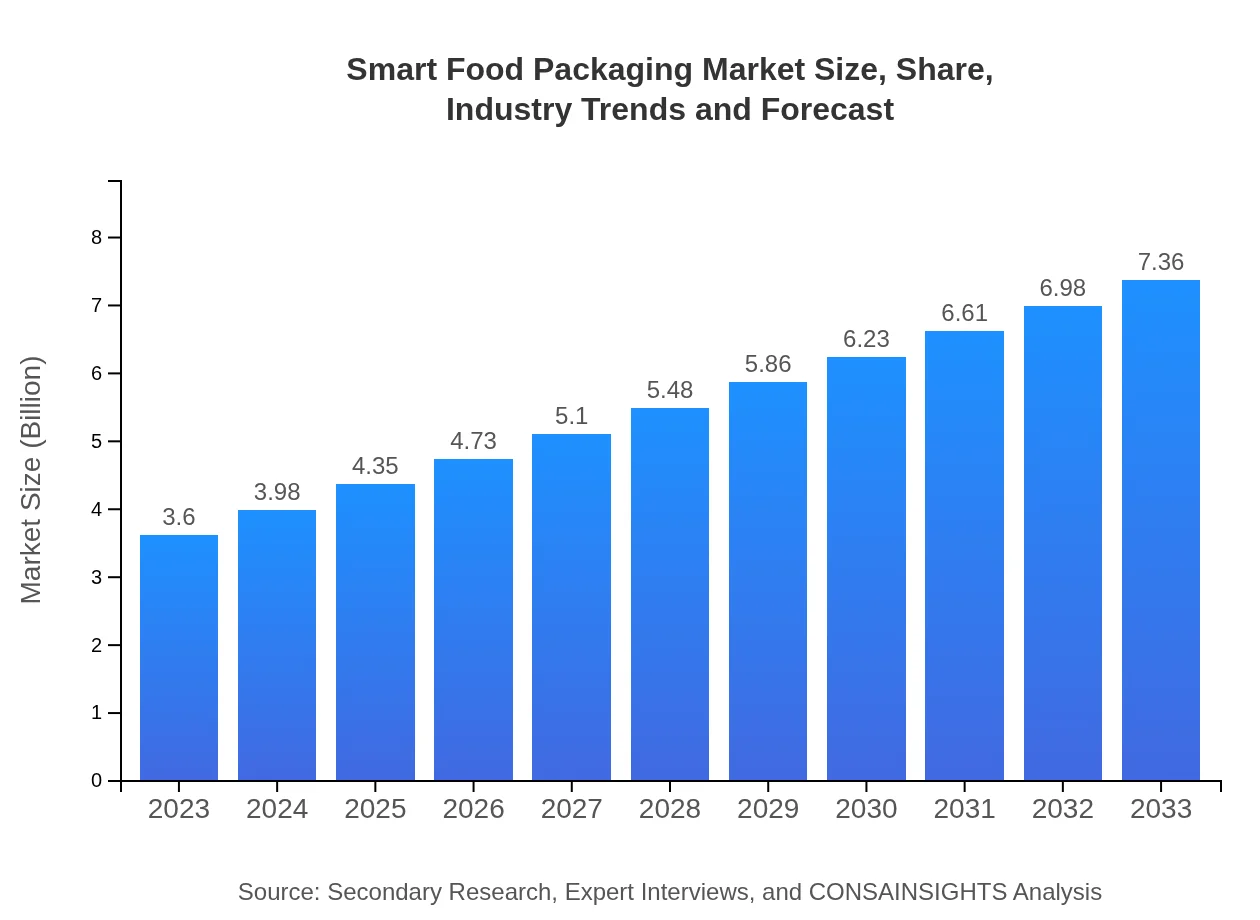
| 2023 Market Size | $3.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $7.36 Billion |
| Top Companies | Sealed Air Corporation, Tetra Pak International SA, Mondi Group, Amcor Plc, Bemis Company, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Smart Food Packaging Market Overview
Customize Smart Food Packaging Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Food Packaging market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Food Packaging's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Food Packaging
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Food Packaging market in 2023?
Smart Food Packaging Industry Analysis
Smart Food Packaging Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Food Packaging Market Report:
Europe, valued at $1.22 billion in 2023, is anticipated to reach $2.49 billion by 2033. Stringent regulations on food safety and environmentally-conscious consumer behavior are accelerating the adoption of smart packaging innovations.Asia Pacific Smart Food Packaging Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region, valued at approximately $0.58 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to $1.19 billion by 2033. This surge is driven by rapid urbanization, increase in disposable income, and a growing emphasis on food safety practices in countries like China, Japan, and India.North America Smart Food Packaging Market Report:
North America leads the market, with a valuation of $1.30 billion in 2023 and a projected growth to $2.65 billion by 2033. The region's robust food and beverage industry and emphasis on advanced packaging technologies significantly contribute to market expansion.South America Smart Food Packaging Market Report:
In South America, the Smart Food Packaging market remains relatively small, with an estimated value of $0.02 billion in 2023, expected to reach $0.04 billion by 2033. The focus on sustainable packaging solutions is gradually growing within the retail and food service sectors.Middle East & Africa Smart Food Packaging Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region shows a notable rise from $0.48 billion in 2023 to $0.99 billion by 2033, led by increasing demand for packaged foods and beverages, alongside improvements in supply chain management.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
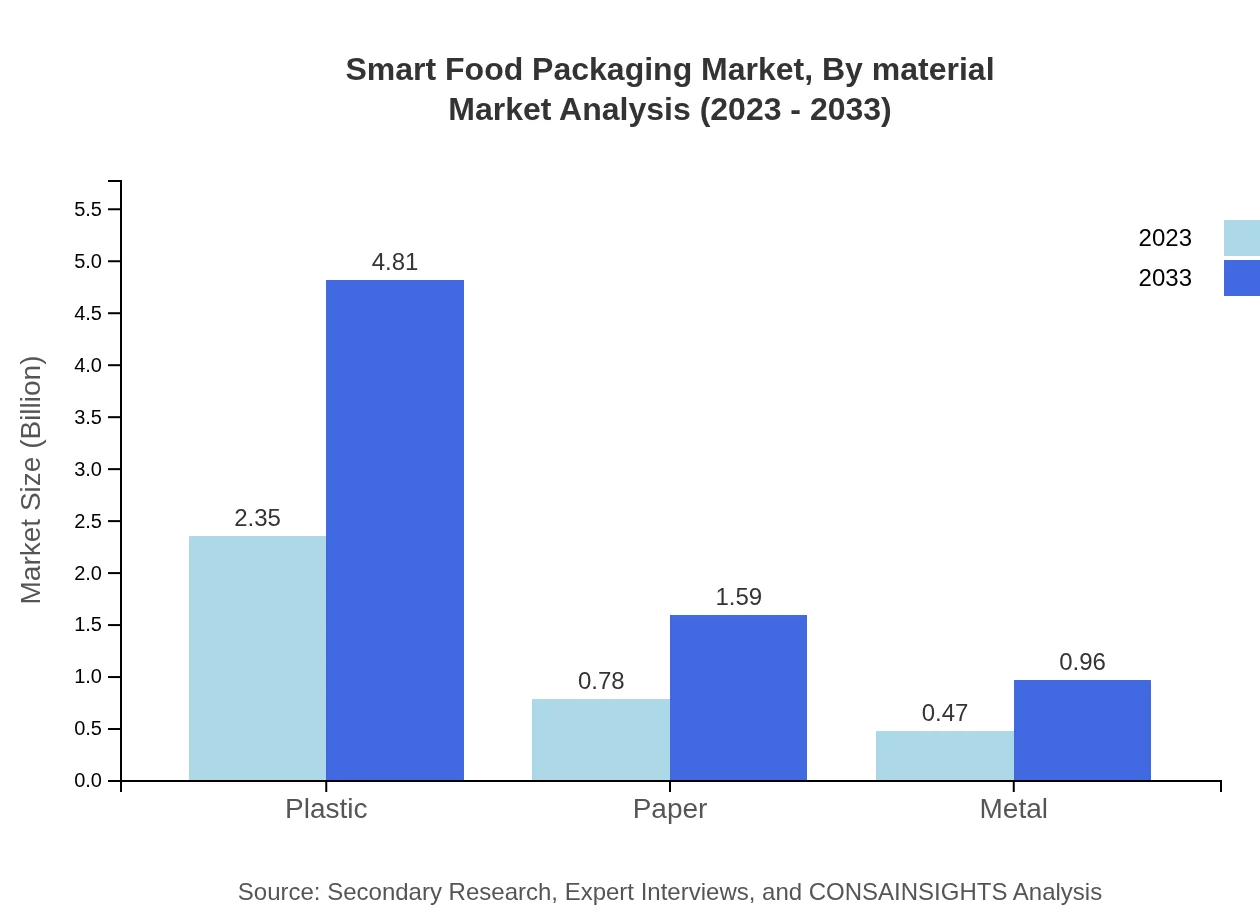
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis By Material
The materials used in Smart Food Packaging include plastic, paper, and metal. In 2023, plastic dominates the market at $2.35 billion, which is 65.34% of the market share, growing to $4.81 billion by 2033. Paper and biodegradable materials are gaining traction with a share of 21.59% and 13.07%, respectively, as sustainability becomes a priority for consumers.
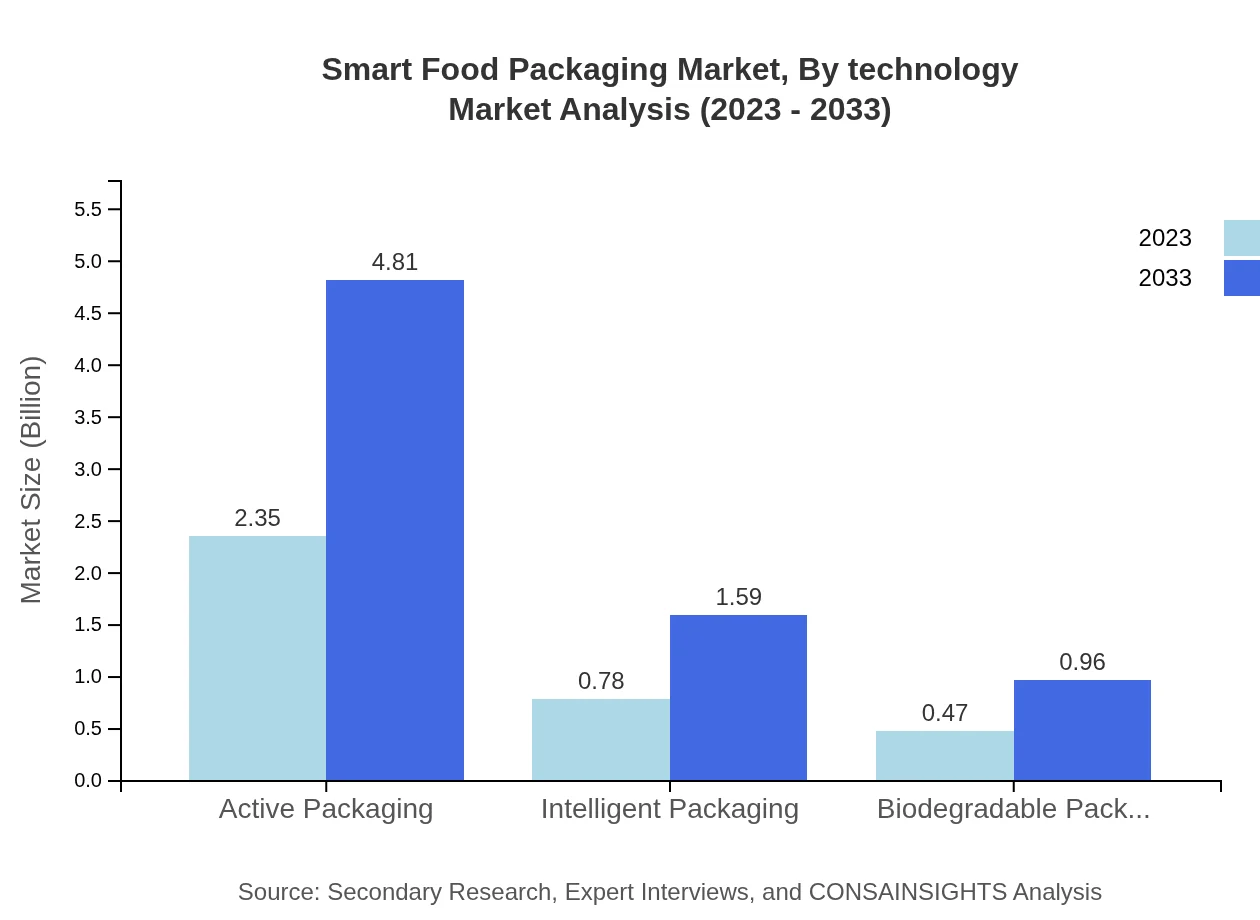
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis By Technology
Technology segmentation includes active packaging ($2.35 billion, 65.34% share) and intelligent packaging ($0.78 billion, 21.59% share), with both set to experience substantial growth as demand for enhanced shelf life and consumer safety increases.
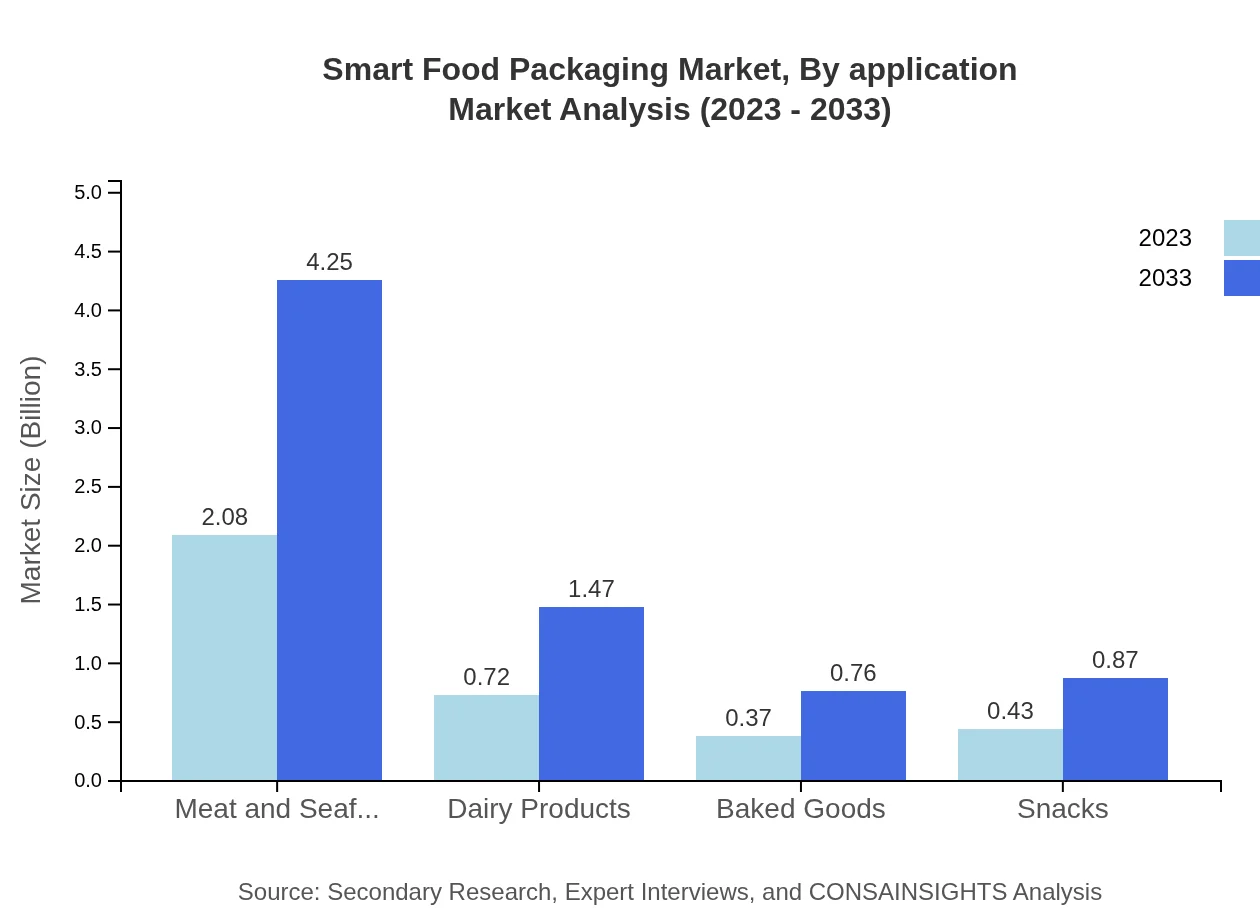
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis By Application
Application segments cover meat and seafood, dairy, baked goods, and snacks. Meat and seafood packaging leads with $2.08 billion (57.79% market share), expected to grow to $4.25 billion by 2033, driven by innovations focused on protein preservation.
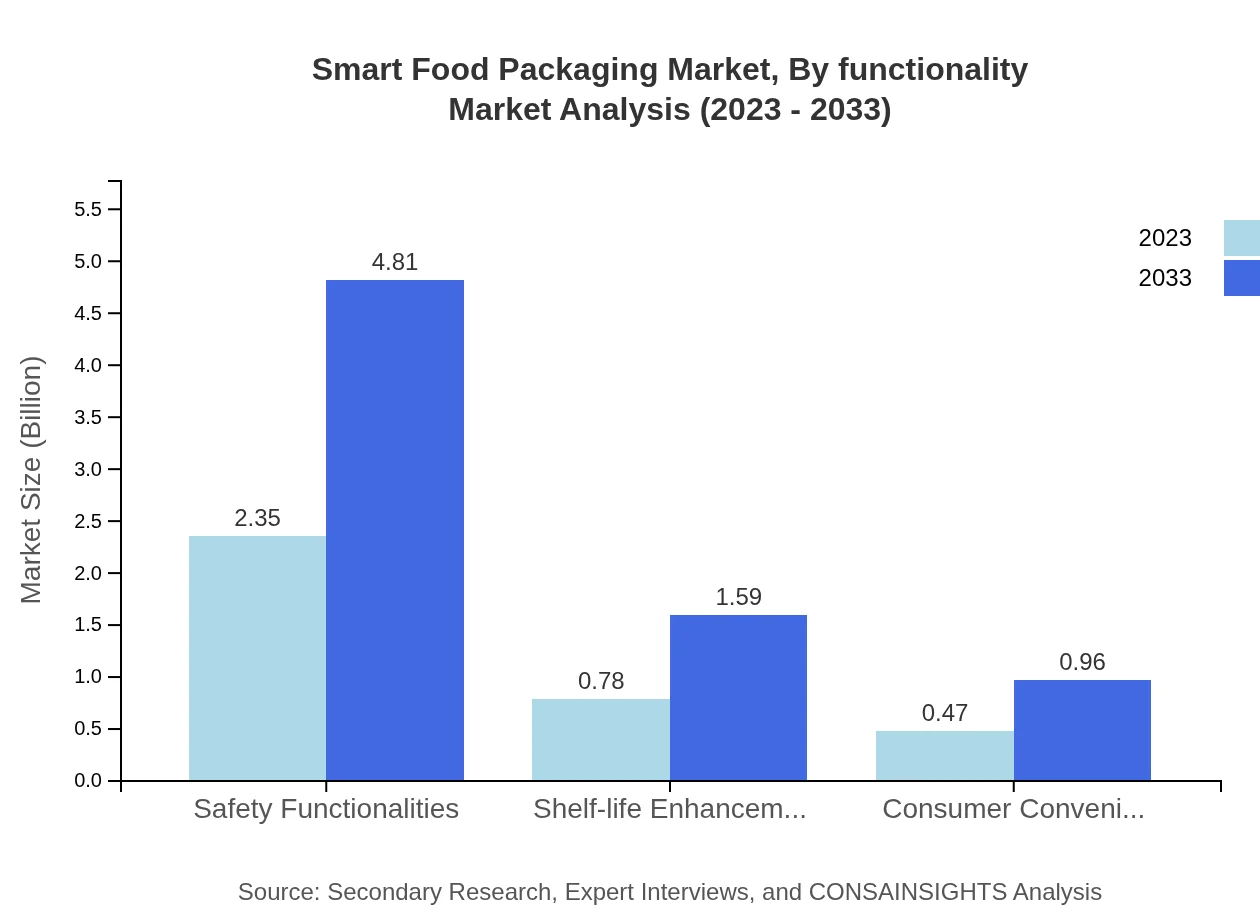
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis By Functionality
Functionality includes safety functionalities (65.34% market share) and shelf-life enhancement (21.59%). These features ensure food safety and quality, responding to consumer demands for transparency and reliability in food products.
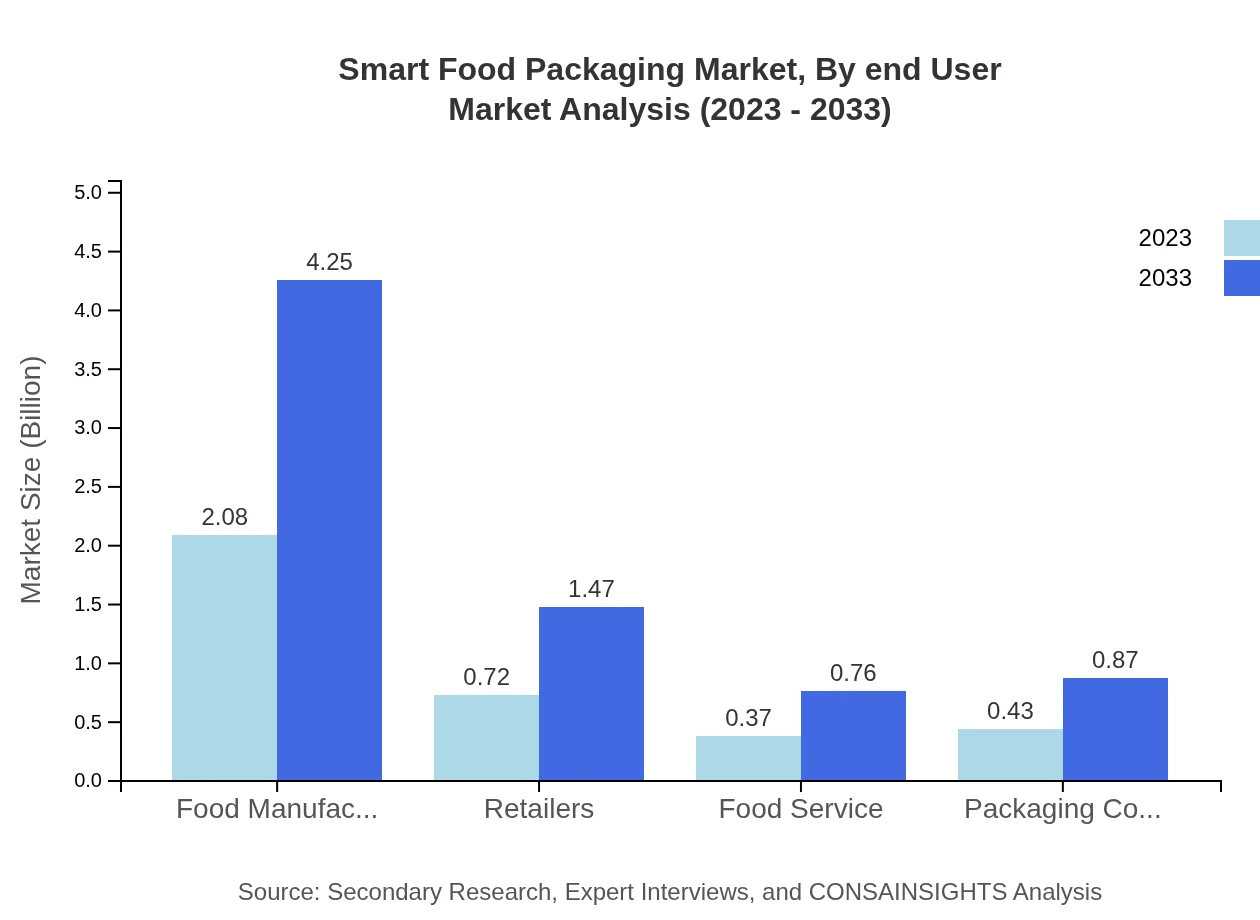
Smart Food Packaging Market Analysis By End User
End-user segmentation identifies food manufacturers (57.79% share), retailers (20.02% share), food service providers (10.38% share), and packaging companies (11.81% share). The food manufacturing sector is the most significant player, driven by efficiency and quality needs.
Smart Food Packaging Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Food Packaging Industry
Sealed Air Corporation:
A leader in food packaging solutions, products include Cryovac brand packaging that enhances food safety and extends shelf life.Tetra Pak International SA:
Specializes in food processing and packaging, particularly known for its technology that helps ensure the quality and safety of food products.Mondi Group:
An international packaging and paper group that develops and manufactures innovative and sustainable packaging solutions for food products.Amcor Plc:
A global leader in packaging, focusing on sustainability and working closely with customers to deliver packaging solutions that enhance food safety.Bemis Company, Inc.:
Acquired by Amcor, Bemis specializes in flexible and rigid packaging, especially for the food industry, emphasizing safety and innovation.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Food Packaging?
The global smart food packaging market is sized at approximately $3.6 billion in 2023, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.2% over the next decade, highlighting significant growth potential.
What are the key market players or companies in the smart Food Packaging industry?
Key players in the smart food packaging industry include major food manufacturers, innovative packaging companies, and technology firms specializing in intelligent packaging solutions, contributing to advancements in food safety and convenience.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart Food Packaging industry?
The growth in the smart food packaging industry is driven by increasing demand for food safety, enhanced shelf-life solutions, consumer convenience, and advancements in packaging technologies that support sustainable practices.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart Food Packaging?
The fastest-growing region in the smart food packaging market is North America, projected to increase from $1.30 billion in 2023 to $2.65 billion by 2033, indicating a robust demand for innovative packaging solutions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart Food Packaging industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the smart food packaging industry, providing in-depth insights and analysis to facilitate informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart Food Packaging market research project?
From the smart food packaging market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size data, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, and regional insights, tailored to your specific business objectives.
What are the market trends of smart Food Packaging?
Current trends in the smart food packaging market include the rise of active and intelligent packaging technologies, increased focus on sustainability with biodegradable options, and growing consumer preferences for enhanced product safety and convenience.