Smart Greenhouse Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-greenhouse
Smart Greenhouse Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Smart Greenhouse market, showcasing key insights and data from 2023 to 2033. It covers market trends, size estimations, technological advancements, and regional dynamics, offering valuable forecasts for stakeholders and investors alike.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
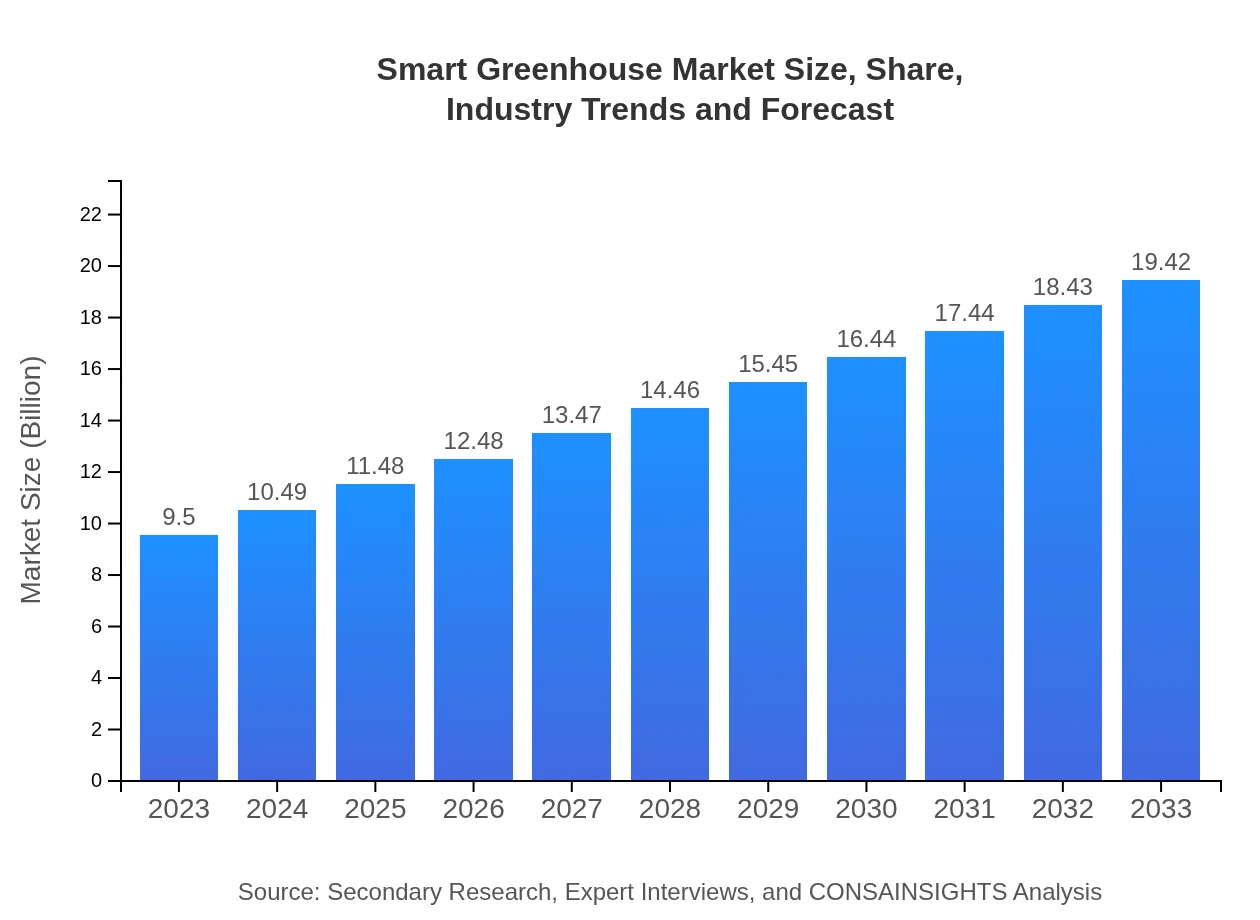
| 2023 Market Size | $9.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $19.42 Billion |
| Top Companies | Netafim, GreenTech Agro, Gotham Greens, Signify |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Greenhouse Market Overview
Customize Smart Greenhouse Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Greenhouse market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Greenhouse's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Greenhouse
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Greenhouse market in 2023?
Smart Greenhouse Industry Analysis
Smart Greenhouse Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Greenhouse Market Report:
In Europe, the market was estimated at USD 2.80 billion in 2023, expected to rise to USD 5.73 billion by 2033. The region consistently leads in adopting smart agricultural technologies aimed at minimizing environmental impact.Asia Pacific Smart Greenhouse Market Report:
In 2023, the Smart Greenhouse market in Asia Pacific was valued at USD 1.96 billion, expected to grow to USD 4.01 billion by 2033. The increase is attributed to rapid urbanization and a growing focus on sustainable agriculture practices in countries like China and India.North America Smart Greenhouse Market Report:
North America, particularly the United States, had a Smart Greenhouse market size of USD 3.29 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to USD 6.73 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by an extensive agricultural framework that is increasingly adopting smart technologies.South America Smart Greenhouse Market Report:
The South American Smart Greenhouse market was valued at USD 0.38 billion in 2023 with projections to reach USD 0.78 billion by 2033. The region is witnessing a gradual shift towards advanced agricultural technologies, driven by the need to enhance food production.Middle East & Africa Smart Greenhouse Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region saw a market size of USD 1.06 billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 2.17 billion by 2033 as areas like the UAE emphasize technology-driven agriculture to address arid conditions.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
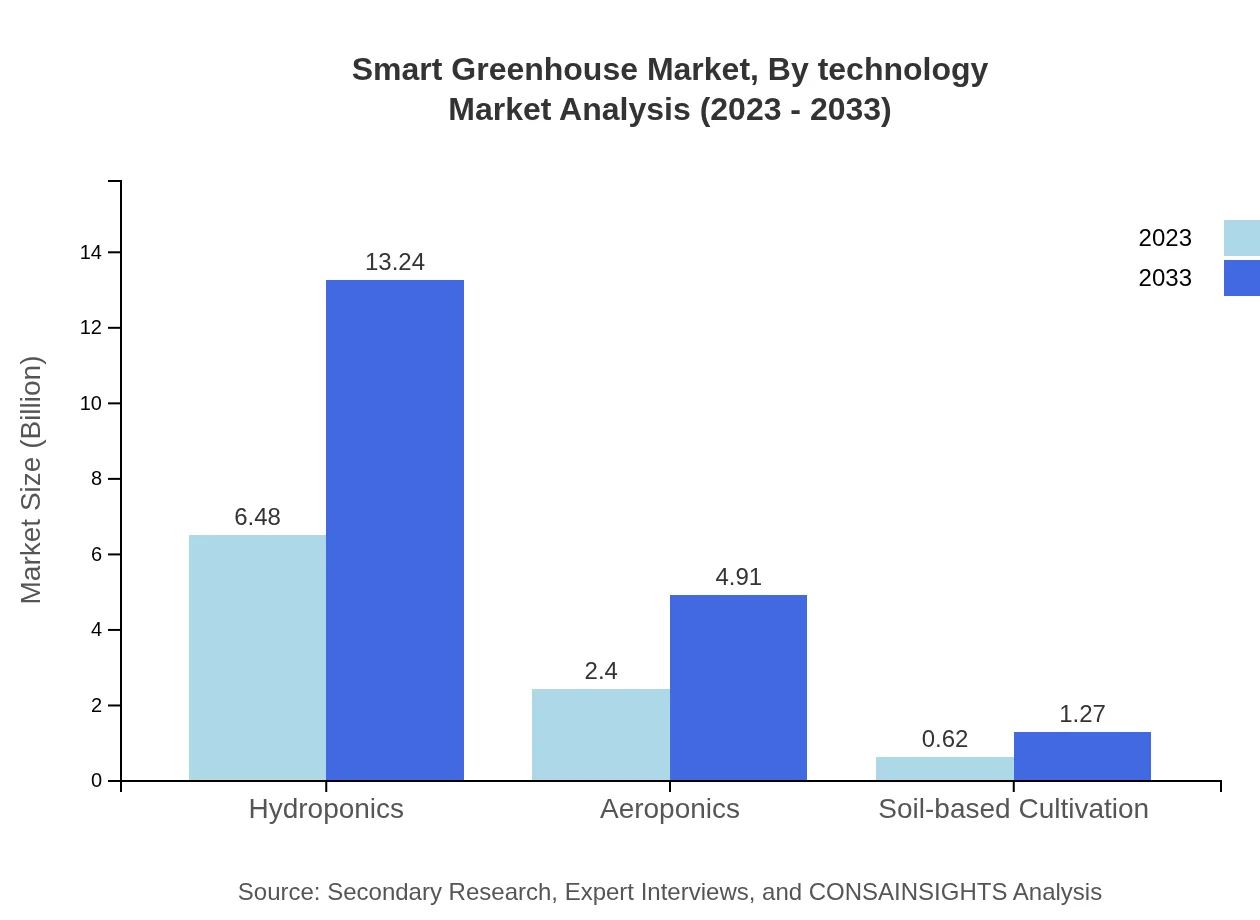
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis By Technology
The Smart Greenhouse market is largely driven by technology segments such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and soil-based cultivation, with hydroponics leading the way. In 2023, hydroponics accounted for approximately USD 6.48 billion, expected to maintain a significant share as it enhances water efficiency and soil-less cultivation methods.
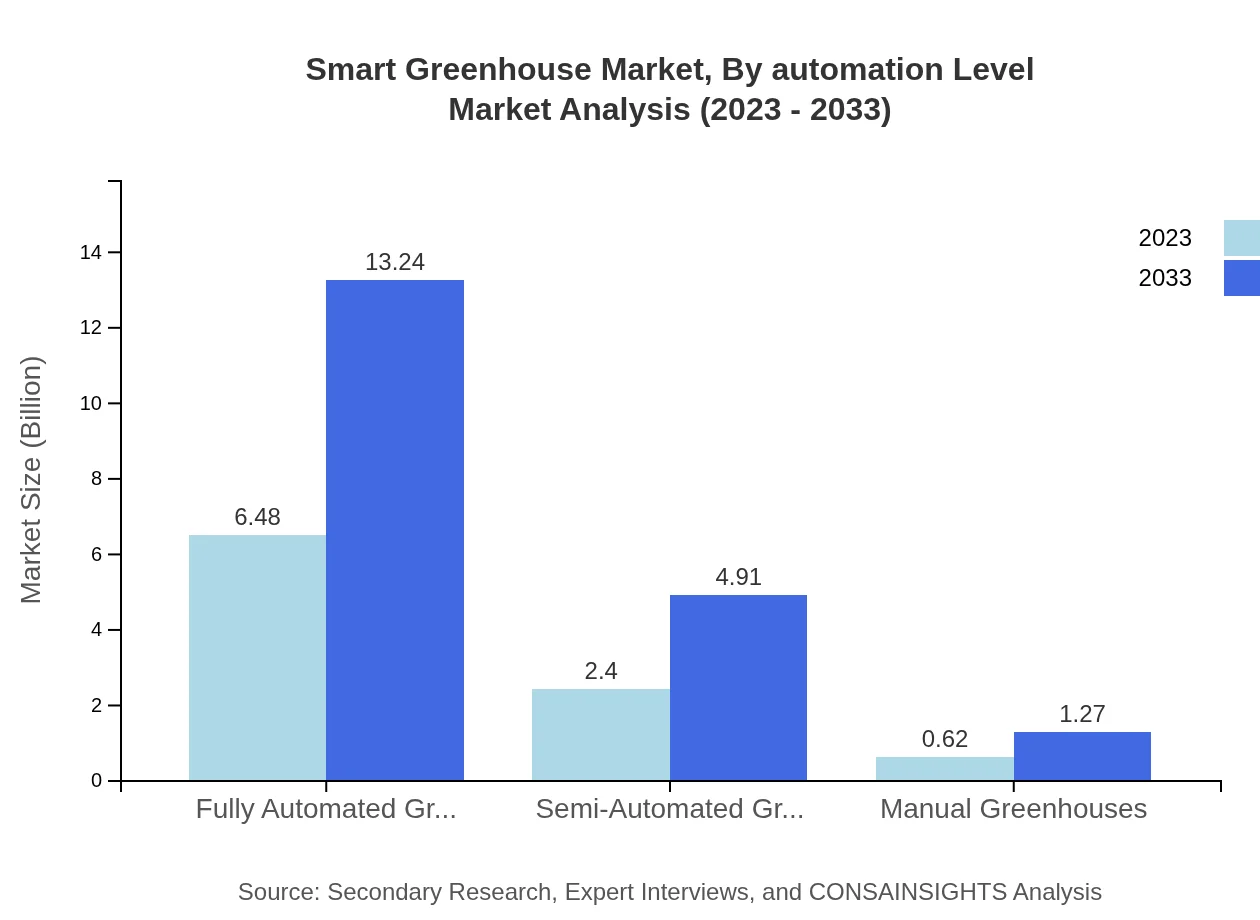
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis By Automation Level
The automation segment plays a crucial role in Smart Greenhouses, with fully automated structures capturing a large market share of 68.18% in 2023. This trend is supported by increasing labor costs and the need for precision agriculture, driving growth in technology integration.
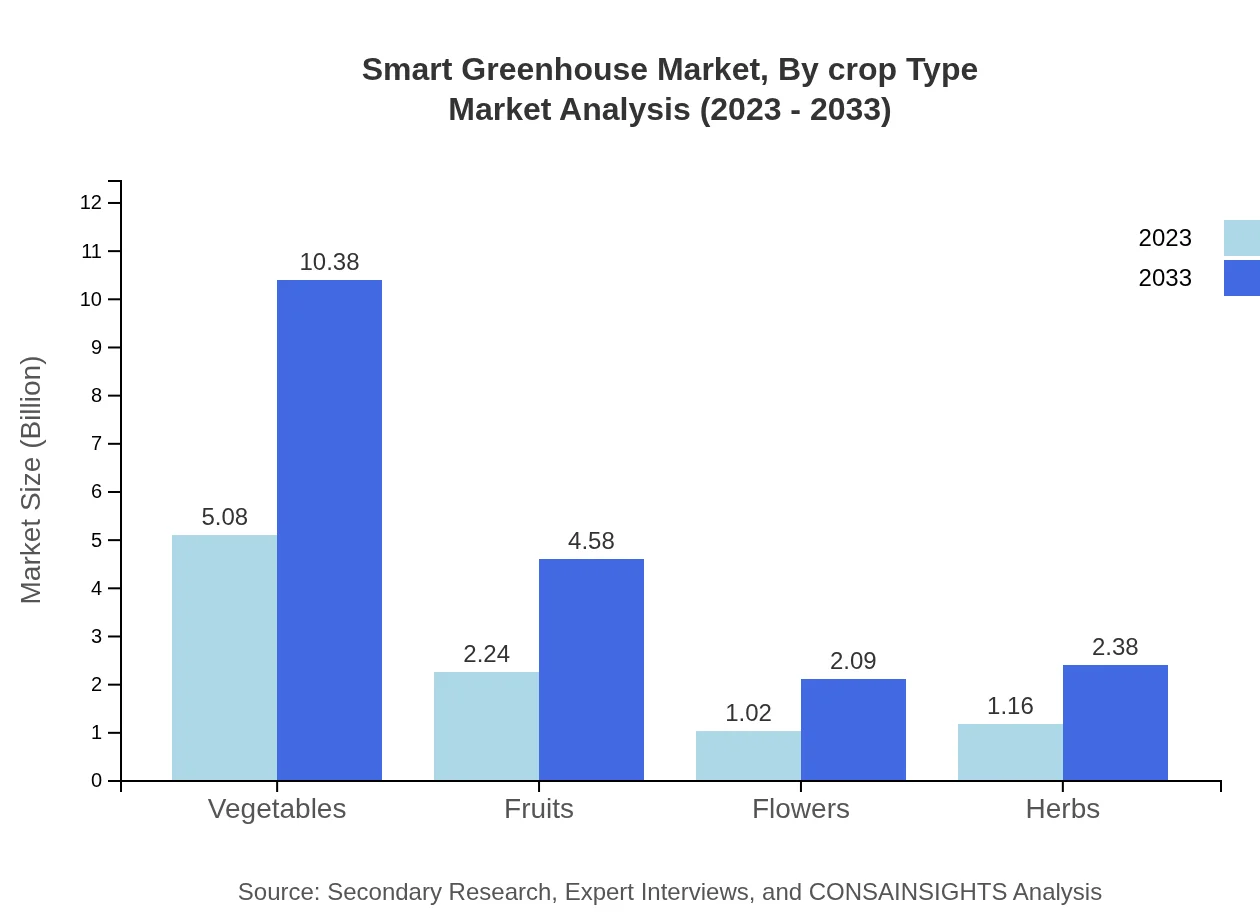
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis By Crop Type
The crop type segment is key to market dynamics, with vegetables holding the largest share of market revenue, approximately USD 5.08 billion in 2023. Fruits and flowers also contribute significantly, although additional investments in crop-specific technologies are expected to yield further growth.
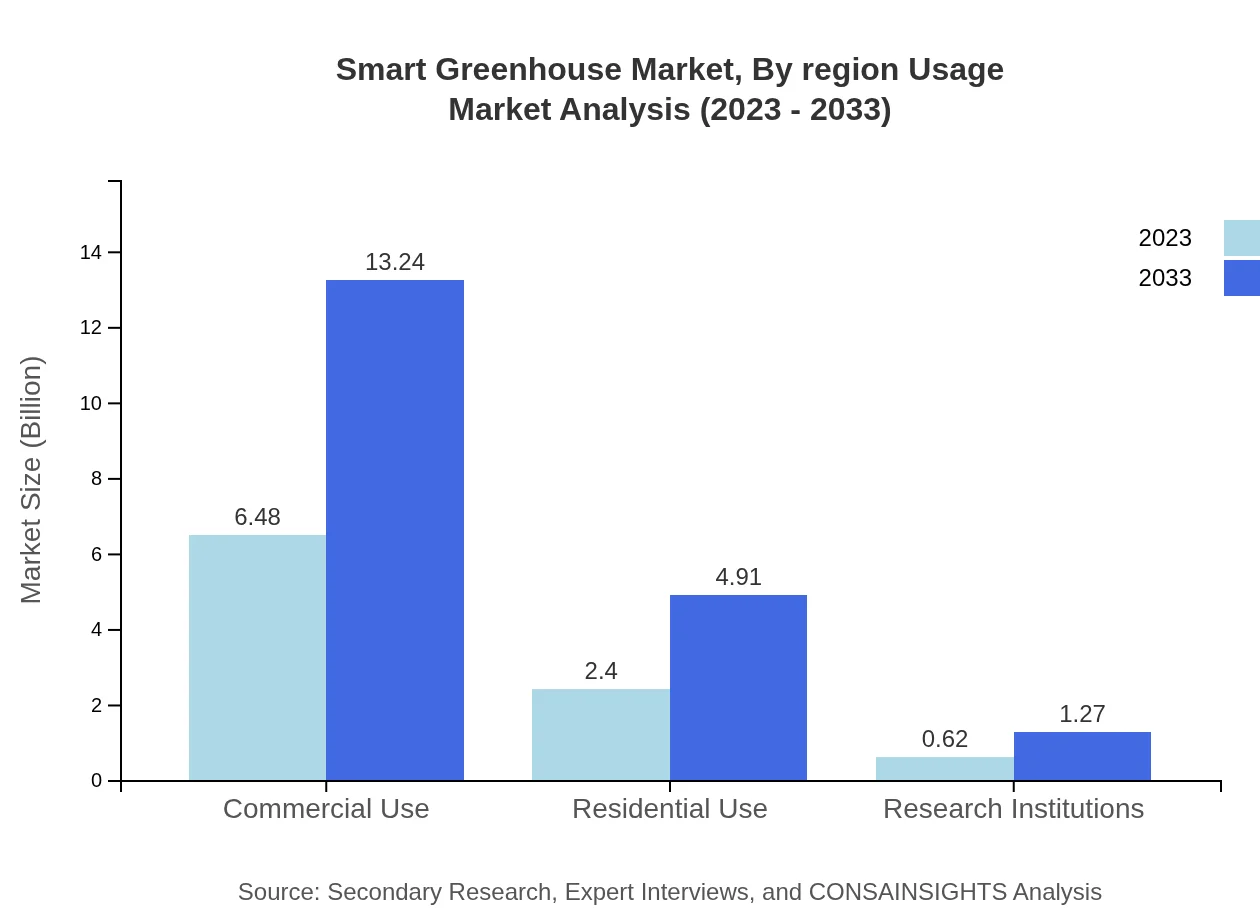
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis By Region Usage
Analyzing region-specific usage reveals that North America leads in applications of Smart Greenhouses due to advanced industrial practices, whereas Asia Pacific shows significant growth potential driven by rising urban farming initiatives.
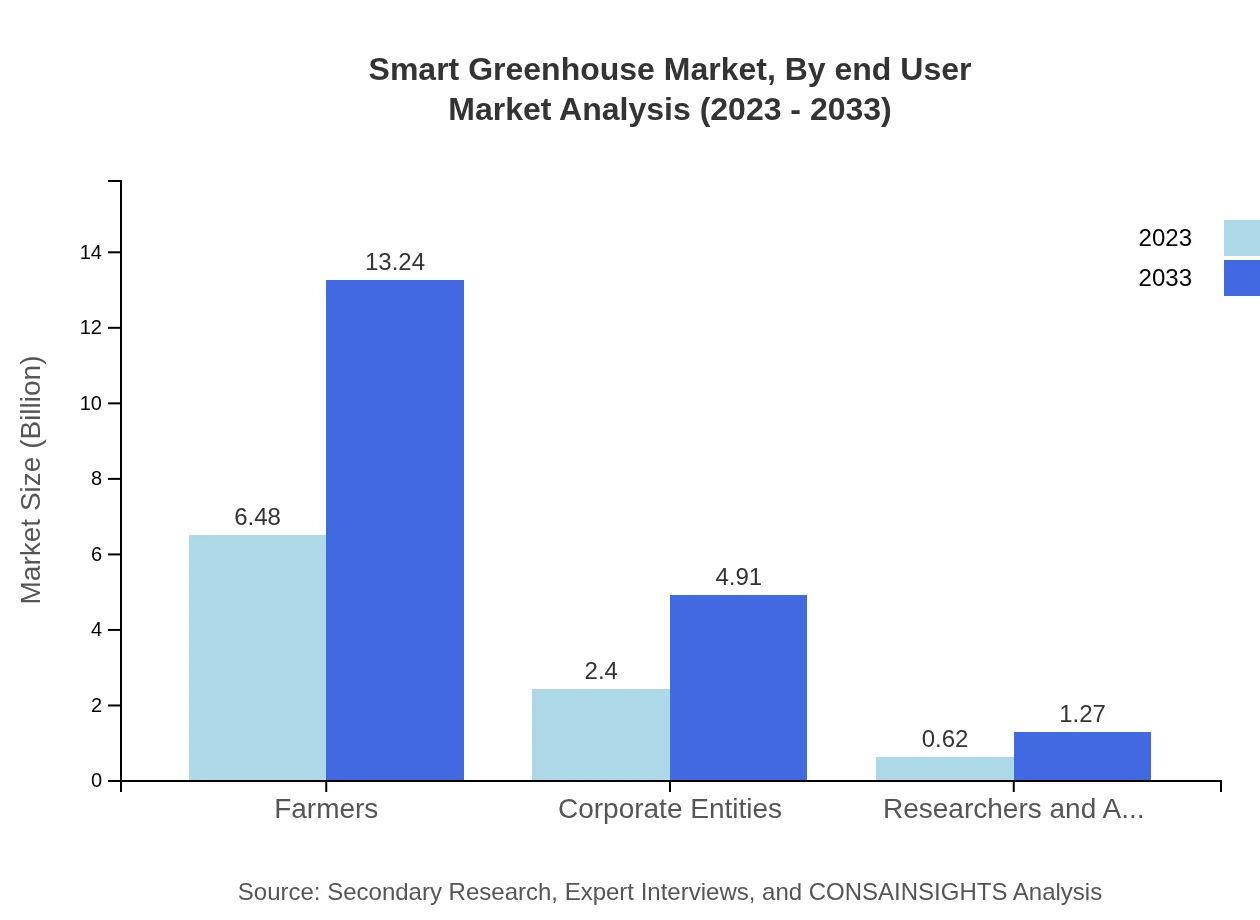
Smart Greenhouse Market Analysis By End User
In terms of end-users, the commercial sector accounts for the majority share, particularly among farmers. In 2023, farmers utilized smart greenhouse technology extensively, representing a market size of USD 6.48 billion.
Smart Greenhouse Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Greenhouse Industry
Netafim:
Netafim is a global leader in smart irrigation solutions, offering drip irrigation systems tailored for greenhouse adaptations to enhance water usage efficiency.GreenTech Agro:
Known for its next-generation greenhouse solutions, GreenTech Agro provides automated systems that optimize plant growth while minimizing resource use.Gotham Greens:
As a pioneer in urban agriculture, Gotham Greens operates commercial greenhouses utilizing advanced technologies, contributing towards local food supplies.Signify:
A leader in horticultural lighting, Signify specializes in solutions that enhance greenhouse productivity through tailored lighting solutions increasing yield.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Greenhouse?
The global smart greenhouse market is projected to reach approximately $9.5 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 7.2% from its current valuation. This growth reflects increasing technological integration in agriculture and rising demand for sustainable crop production.
What are the key market players or companies in the smart Greenhouse industry?
In the smart greenhouse market, prominent players include companies specializing in agricultural technology, automation, and environmental monitoring systems. These manufacturers focus on innovations in control systems, IoT technologies, and sustainable farming practices to maintain competitive advantage.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart greenhouse industry?
Key drivers of growth in the smart greenhouse industry include the rise in the adoption of IoT-based technologies, increasing demand for food security, sustainability practices, and the efficiency gains associated with automated solutions that optimize resource usage and crop yield.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart greenhouse?
The fastest-growing region in the smart greenhouse market is expected to be North America, projected to grow from $3.29 billion in 2023 to $6.73 billion by 2033. Europe and the Asia Pacific regions also show significant growth potential due to increasing agricultural innovations.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart greenhouse industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to meet specific client needs within the smart greenhouse industry. This includes in-depth analysis, market forecasts, and competitive landscape assessments based on unique parameters and market segments.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart greenhouse market research project?
From the smart greenhouse market research project, you can expect comprehensive reports including market size forecasts, competitive analysis, regional insights, consumer trends, and strategic recommendations. Detailed segment analysis will also provide actionable insights for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of smart greenhouse?
Market trends in the smart greenhouse sector include increasing reliance on automation technologies, advancements in hydroponics and aeroponics, and an emphasis on sustainable agriculture practices. Additionally, integration of data analytics and AI is reshaping greenhouse management.