Smart Grid Communications Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-grid-communications
Smart Grid Communications Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Smart Grid Communications market, including insights on market size, growth trends, segmentation, regional analysis, technology innovations, and key players. The forecast period extends from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
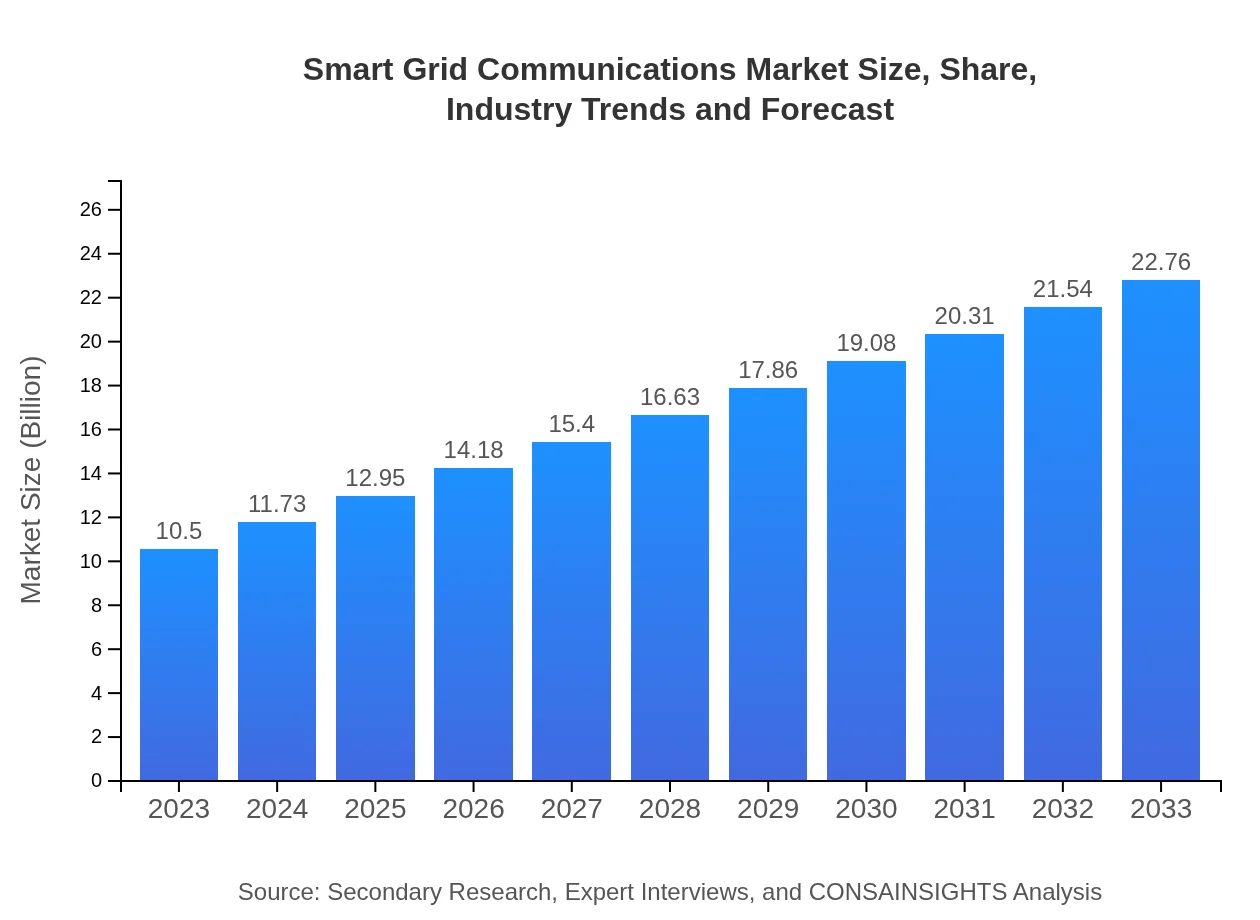
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $22.76 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, General Electric Company, ABB Ltd., Honeywell International Inc., Cisco Systems, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Smart Grid Communications Market Overview
Customize Smart Grid Communications Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Grid Communications market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Grid Communications's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Grid Communications
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Grid Communications market in 2023 and 2033?
Smart Grid Communications Industry Analysis
Smart Grid Communications Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Grid Communications Market Report:
Europe's Smart Grid Communications market size is projected to increase from $2.60 billion in 2023 to $5.64 billion by 2033. The EU's stringent environmental regulations and investment in digital infrastructure bolsters growth prospects across the region.Asia Pacific Smart Grid Communications Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness substantial growth in the Smart Grid Communications market, with a projected market size of $4.93 billion by 2033, up from $2.27 billion in 2023. This growth is fueled by rising urbanization, government initiatives for modernization, and the increasing incorporation of renewable energy sources in energy portfolios.North America Smart Grid Communications Market Report:
North America leads the Smart Grid Communications market with a valuation of $3.78 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $8.19 billion by 2033. The U.S. government’s commitment to renewable energy and infrastructure upgrades is a crucial driver for this market segment.South America Smart Grid Communications Market Report:
In South America, the market is anticipated to grow from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.90 billion by 2033. Key initiatives to develop smart grids and enhance energy efficiency present numerous opportunities for market players in this region.Middle East & Africa Smart Grid Communications Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa are also emerging markets for Smart Grid Communications, with an increase in market size from $0.97 billion in 2023 to $2.11 billion by 2033. Regional governments are driving initiatives to improve power management and distribution efficiency.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
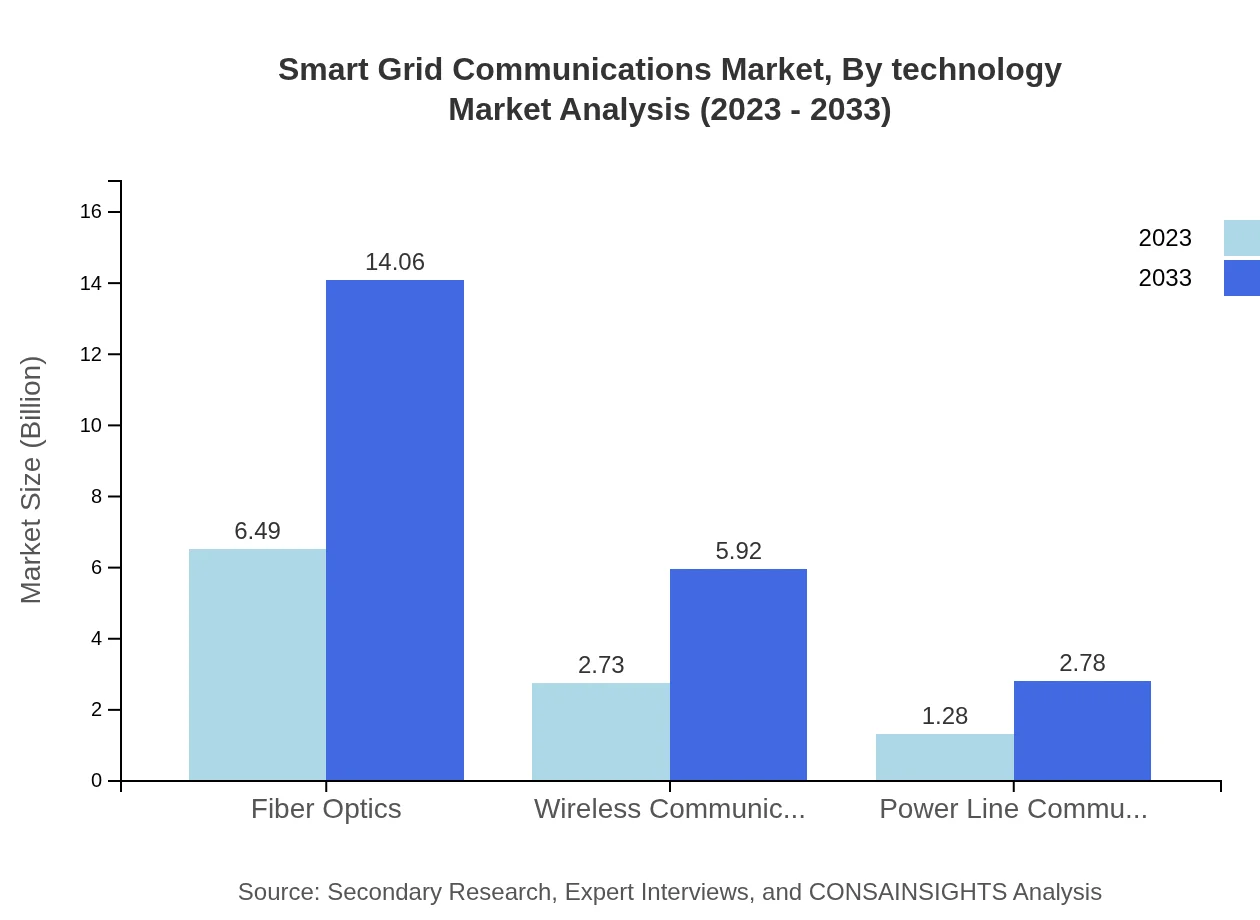
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis By Technology
The technology segment of the Smart Grid Communications market focuses on infrastructure such as fiber optics, wireless communications, and power line communications. Fiber optics leads the market, accounting for 61.78% of the total market share in 2023, estimated to grow to 61.78% by 2033. Wireless communications, with a share of 26% in 2023, are expected to maintain similar trends through 2033.
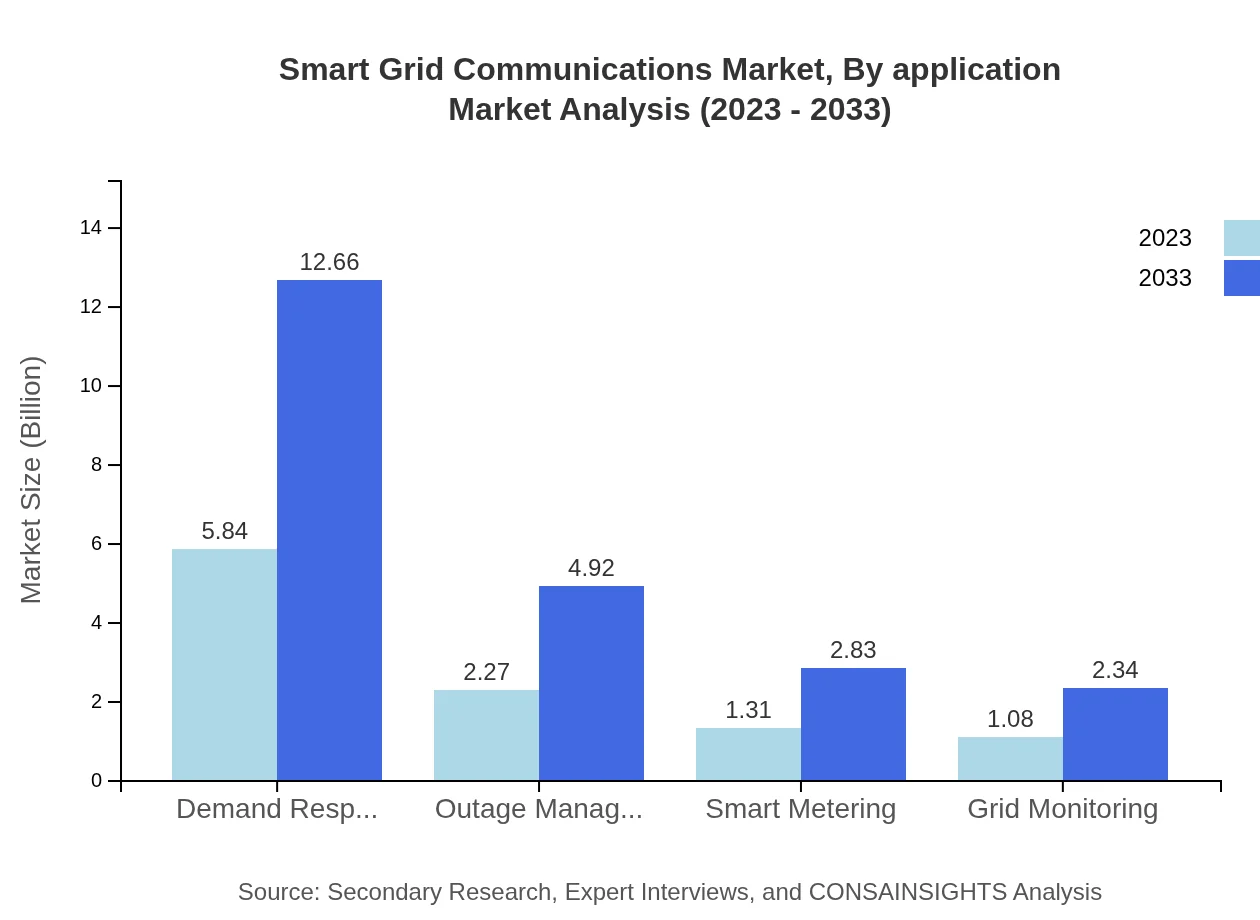
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis By Application
Demand response and outage management constitute vital applications of the Smart Grid Communications system. Demand response control will hold a 55.62% market share in 2023, expected to persist through 2033, while outage management will maintain its share at 21.63%. These applications are critical to improving grid resiliency and customer satisfaction.
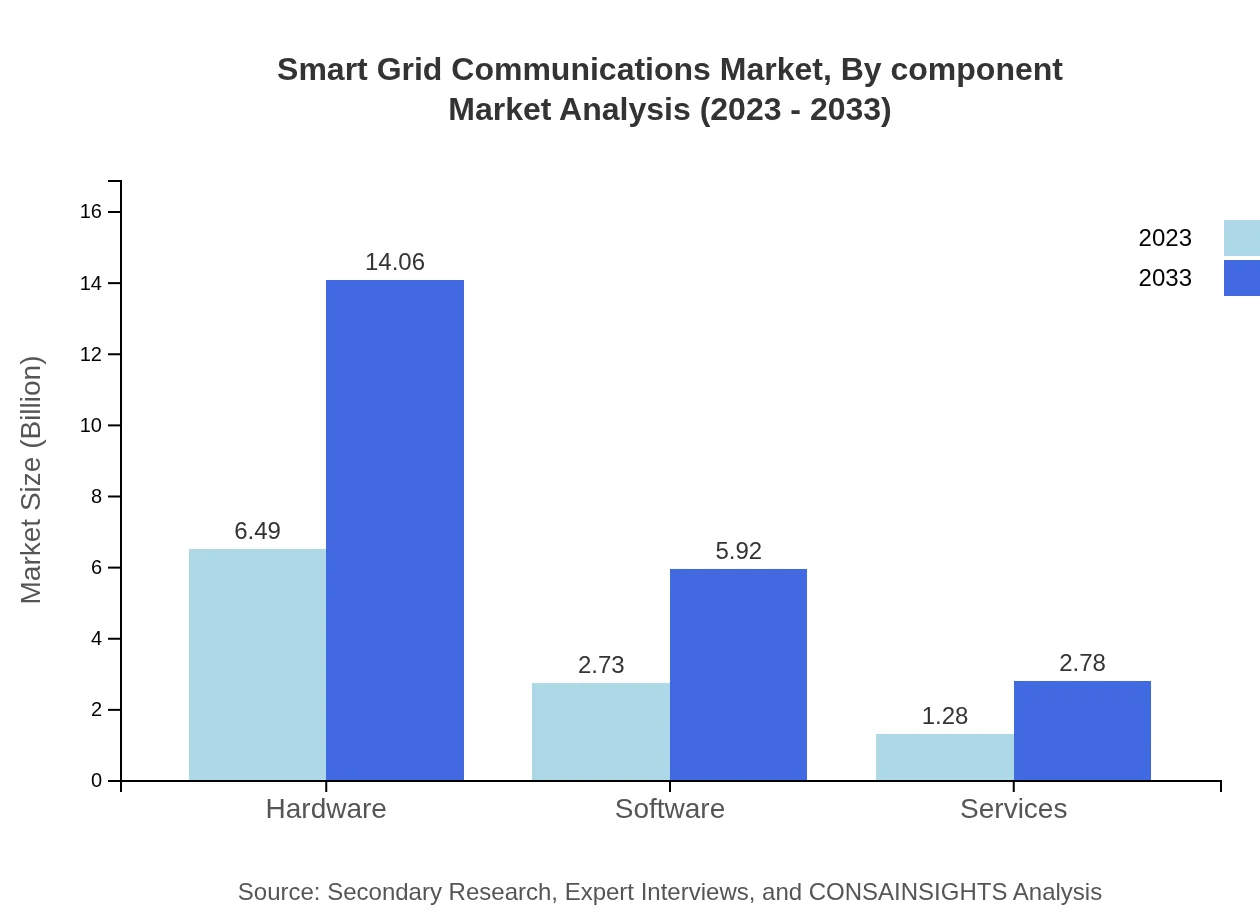
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis By Component
The market is delineated into hardware, software, and services. Hardware remains the dominant component, expected to grow from a market size of $6.49 billion in 2023 to $14.06 billion by 2033. Software, with a current market share of 26%, is projected for consistent growth alongside services, particularly in consulting and system integration.
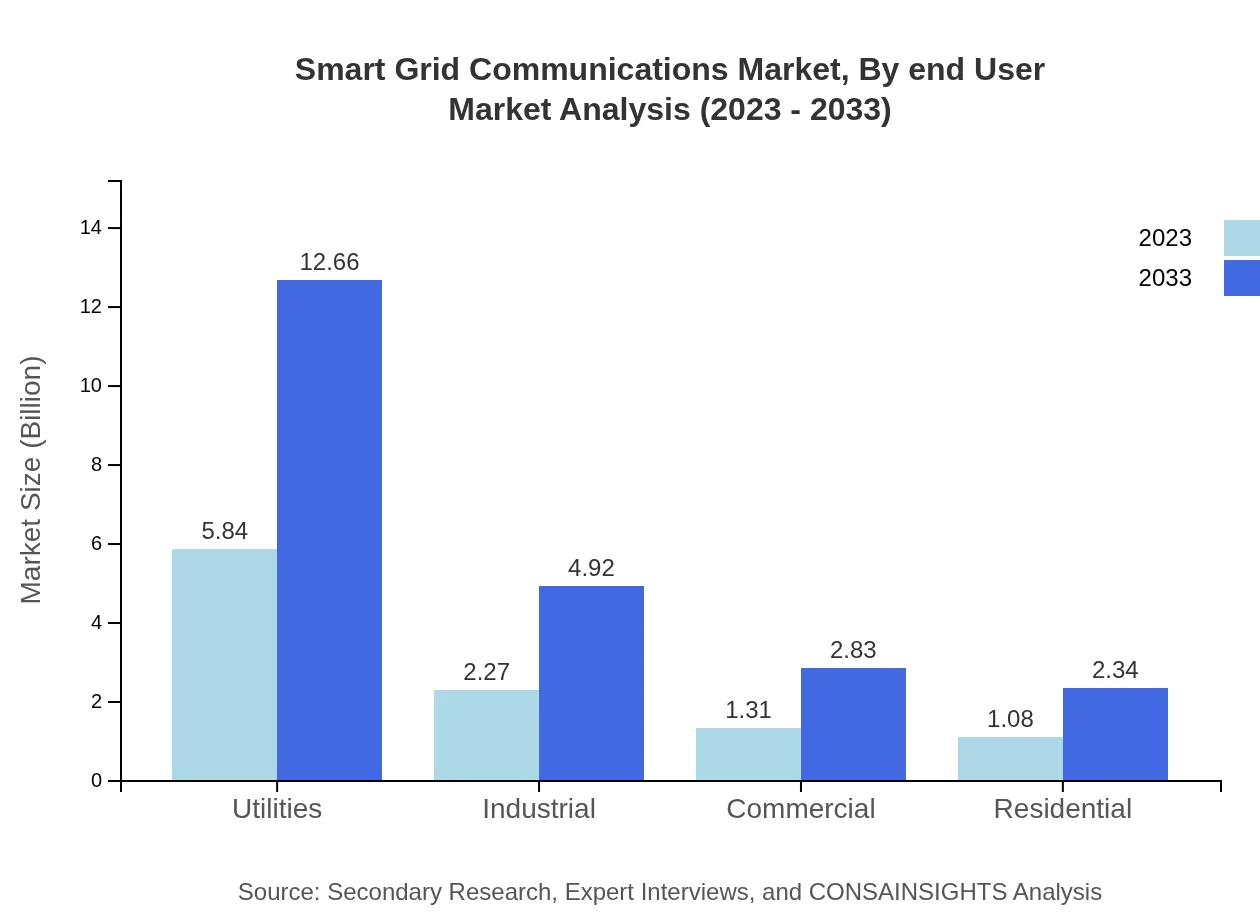
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis By End User
Utilities represent the primary end-user in the Smart Grid Communications market, expected to grow from $5.84 billion in 2023 to $12.66 billion by 2033, maintaining a 55.62% market share. Other end-users include industrial, commercial, and residential sectors, with corresponding growth as smart grid technology adoption rises.
Smart Grid Communications Market Analysis By Region
Global Smart Grid Communications Market, By Region Market Analysis (2023 - 2033)
Regional analysis reveals North America leading the market, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific. Each region shows unique growth drivers, from governmental incentives in North America to rapid urbanization in Asia Pacific, signifying differentiated opportunities for market players globally.
Smart Grid Communications Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Grid Communications Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a renowned leader in smart grid solutions, providing advanced automation and digitalization technologies to enhance grid efficiency and reliability.General Electric Company:
General Electric Company is a global innovator in energy solutions, specializing in smart grid technologies that improve energy management and customer engagement.ABB Ltd.:
ABB Ltd. delivers comprehensive smart grid technologies, focusing on enhancing the electrical grid with innovative control and automation solutions.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell International has been at the forefront of smart consumer metering and energy management solutions, thus advancing smart grid communications.Cisco Systems, Inc.:
Cisco Systems offers networking technologies that enhance communication capabilities within smart grid systems, crucial for real-time data management.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Smart Grid Communications?
The Smart Grid Communications market is projected to reach a size of $10.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.8%. The market growth reflects a rising demand for efficient energy management systems globally.
What are the key market players or companies in the Smart Grid Communications industry?
Some key players in the Smart Grid Communications industry include major utilities, technology providers, and communication equipment manufacturers. These companies focus on developing smart meter technologies, grid management systems, and communication networks enhancing grid reliability.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Smart Grid Communications industry?
The growth in Smart Grid Communications is driven by increasing energy demand, technological advancements in grid management, government policies promoting renewable energy, and the need for enhanced operational efficiency and reliability in electricity distribution networks.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Smart Grid Communications?
The North America region is the fastest-growing market for Smart Grid Communications, projected to expand from $3.78 billion in 2023 to $8.19 billion by 2033. The growth is attributed to significant investments in smart grid technologies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Smart Grid Communications industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the Smart Grid Communications industry. Clients can request detailed analyses reflecting unique market conditions and trends.
What deliverables can I expect from this Smart Grid Communications market research project?
Deliverables from the market research project on Smart Grid Communications include comprehensive reports, market size statistics, competitive analyses, regional trends, and segmented data that aid in strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of Smart Grid Communications?
Current market trends in Smart Grid Communications include the integration of IoT technologies, increased focus on renewable energy sources, enhanced security measures for grid infrastructure, and growing demand for real-time data analytics.