Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-microgrid-controller
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the Smart Microgrid Controller market, providing critical insights and data from 2023 to 2033, exploring market trends, regional performances, product analyses, and projections for future growth.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
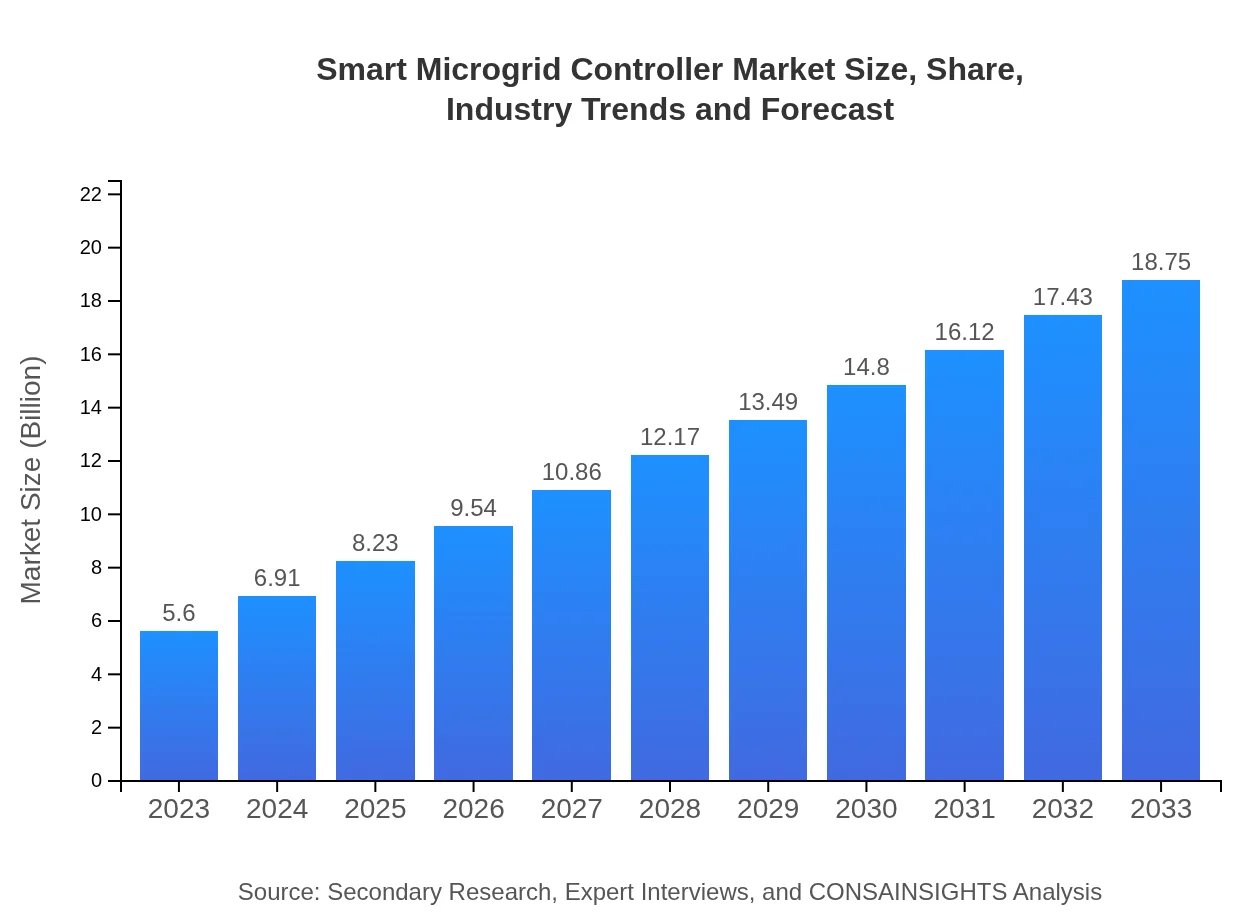
| 2023 Market Size | $5.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $18.75 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, General Electric (GE), Schneider Electric, ABB Group, Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Overview
Customize Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Microgrid Controller market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Microgrid Controller's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Microgrid Controller
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Microgrid Controller market in 2023?
Smart Microgrid Controller Industry Analysis
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report:
Europe's market for Smart Microgrid Controllers is projected to grow from $1.36 billion in 2023 to $4.57 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by stringent regulations regarding carbon emissions and commitments to renewable energy targets. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are leading the push towards smart energy systems, implementing policies that encourage the adoption of microgrid technologies.Asia Pacific Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is poised for significant growth, with the market expected to expand from $1.19 billion in 2023 to $3.98 billion by 2033. The growth is underpinned by rapid urbanization, a shift towards renewable energy, and supportive government policies. Countries like China and India are leading the adoption of smart microgrid technologies to ensure energy security and resilience amidst increasing energy demands.North America Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report:
North America is expected to see substantial growth, with the market rising from $2.09 billion in 2023 to $7.00 billion by 2033. The region has been a pioneer in adopting smart grid technologies, driven by the need for energy efficiency, improved grid resilience, and strong government initiatives. The United States, in particular, is at the forefront of deploying smart microgrid solutions.South America Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report:
In South America, the market is projected to grow from $0.32 billion in 2023 to $1.07 billion by 2033. The region's focus on improving energy infrastructure and promoting renewable energy integration is a major driving factor. Brazil and Argentina are key players, investing in smart grid solutions to modernize their energy systems and enhance grid reliability.Middle East & Africa Smart Microgrid Controller Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is expected to grow from $0.64 billion in 2023 to $2.13 billion by 2033. Energy diversification and renewable energy projects are key priorities for many countries in this region. Investment in smart microgrid solutions is increasing as nations aim to enhance energy security and sustainability.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
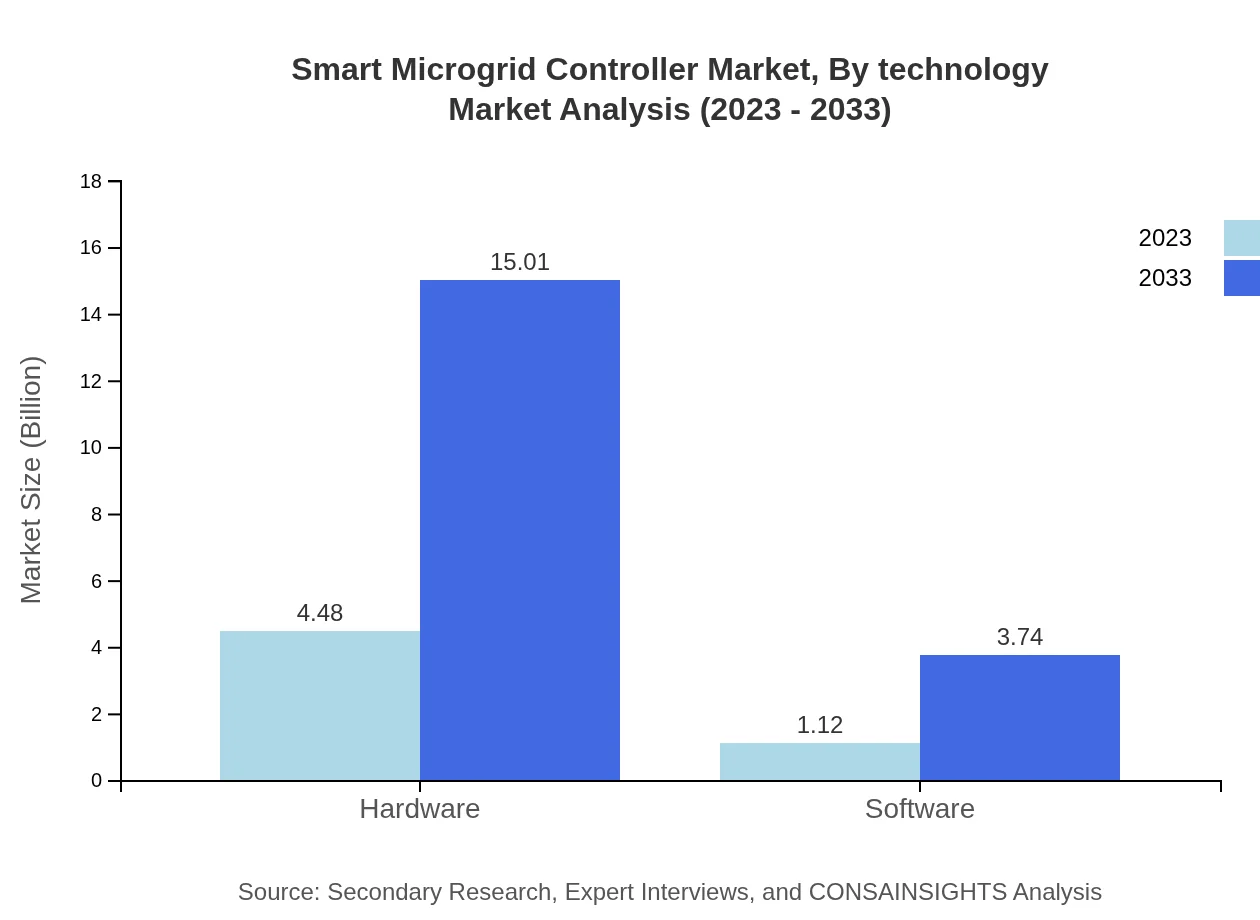
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Analysis By Technology
The Smart Microgrid Controller Market is bifurcated into hardware and software. Currently, hardware dominates the market due to its foundational role in enabling microgrid functionalities. By 2033, the hardware segment is expected to maintain its lead, driven by advancements in sensor technologies and control systems. The software segment, encompassing energy management systems and analytics, is projected to grow significantly as businesses recognize the value of data-driven decision-making.
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the Government and Public Sector segment is the largest, valued at $3.73 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $12.50 billion by 2033. This is followed by the Commercial and Industry sector, which is expected to grow from $1.31 billion to $4.40 billion. Residential users and Off-Grid systems are also significant, with a notable shift towards optimizing energy consumption and sustainability.
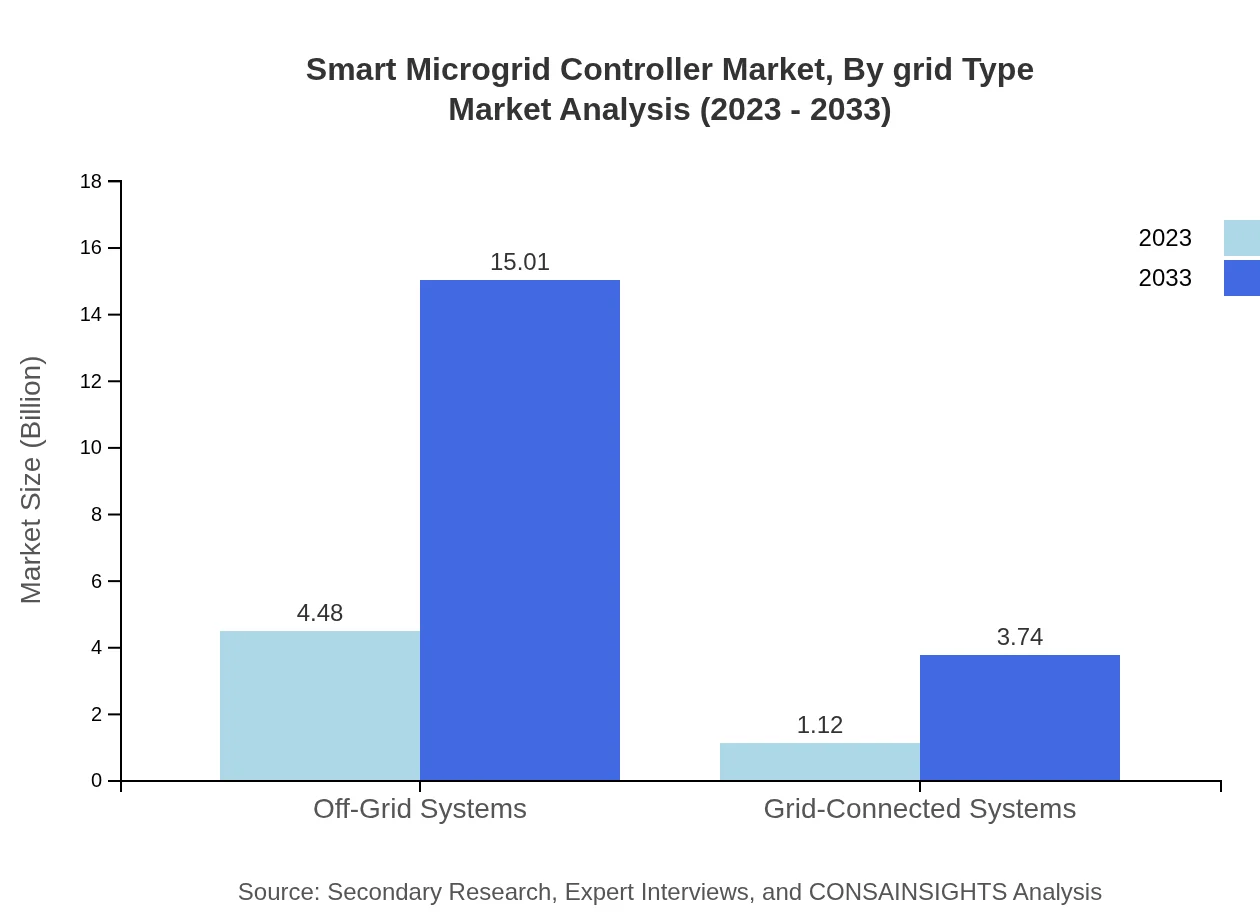
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Analysis By Grid Type
The market is segmented into Off-Grid and Grid-Connected systems. Off-Grid systems are currently leading, notably encompassing a large share at 80.07% in 2023, which demonstrates a preference for independent energy solutions in remote areas. Similarly, Grid-Connected systems are expected to grow significantly as cities seek to enhance their grid stability and efficiency through smart technology.
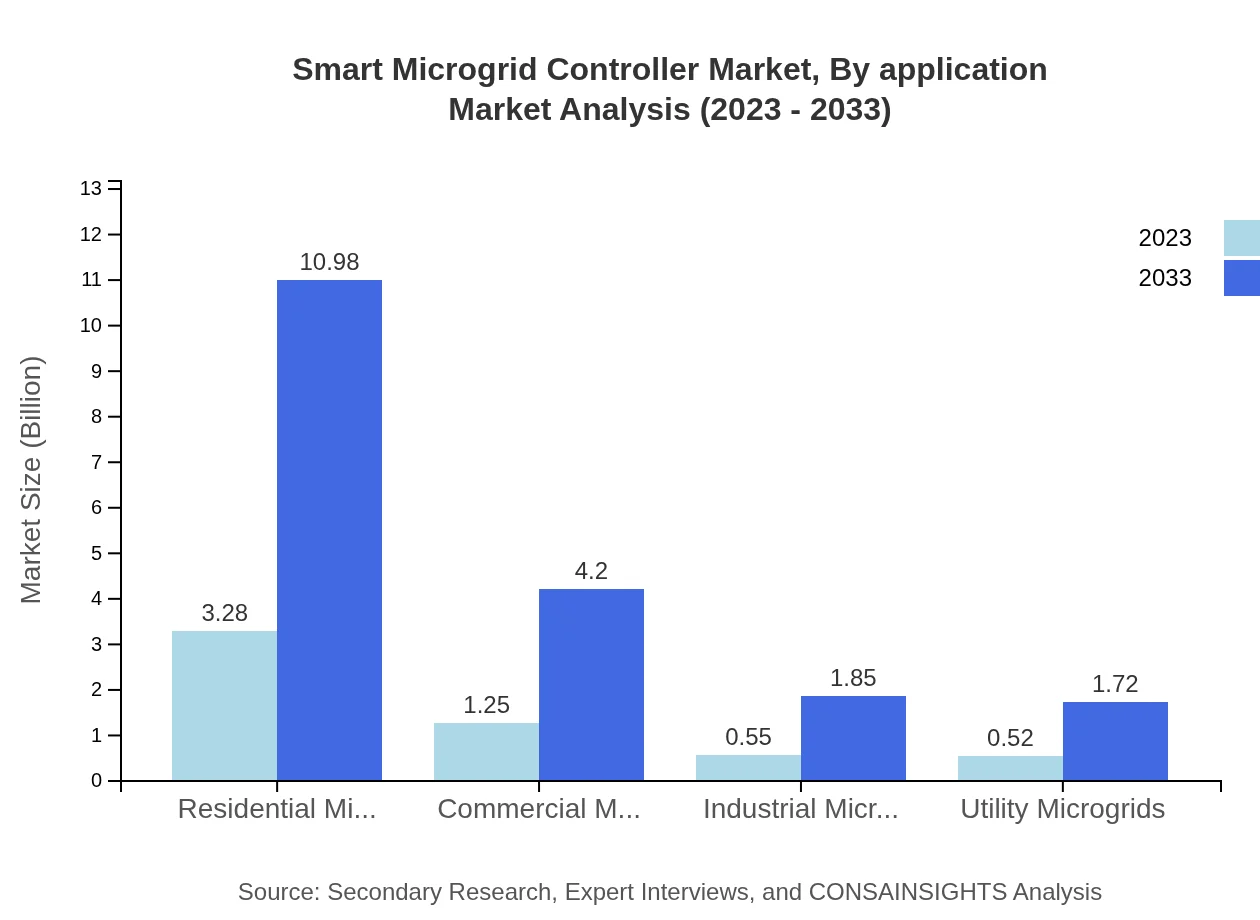
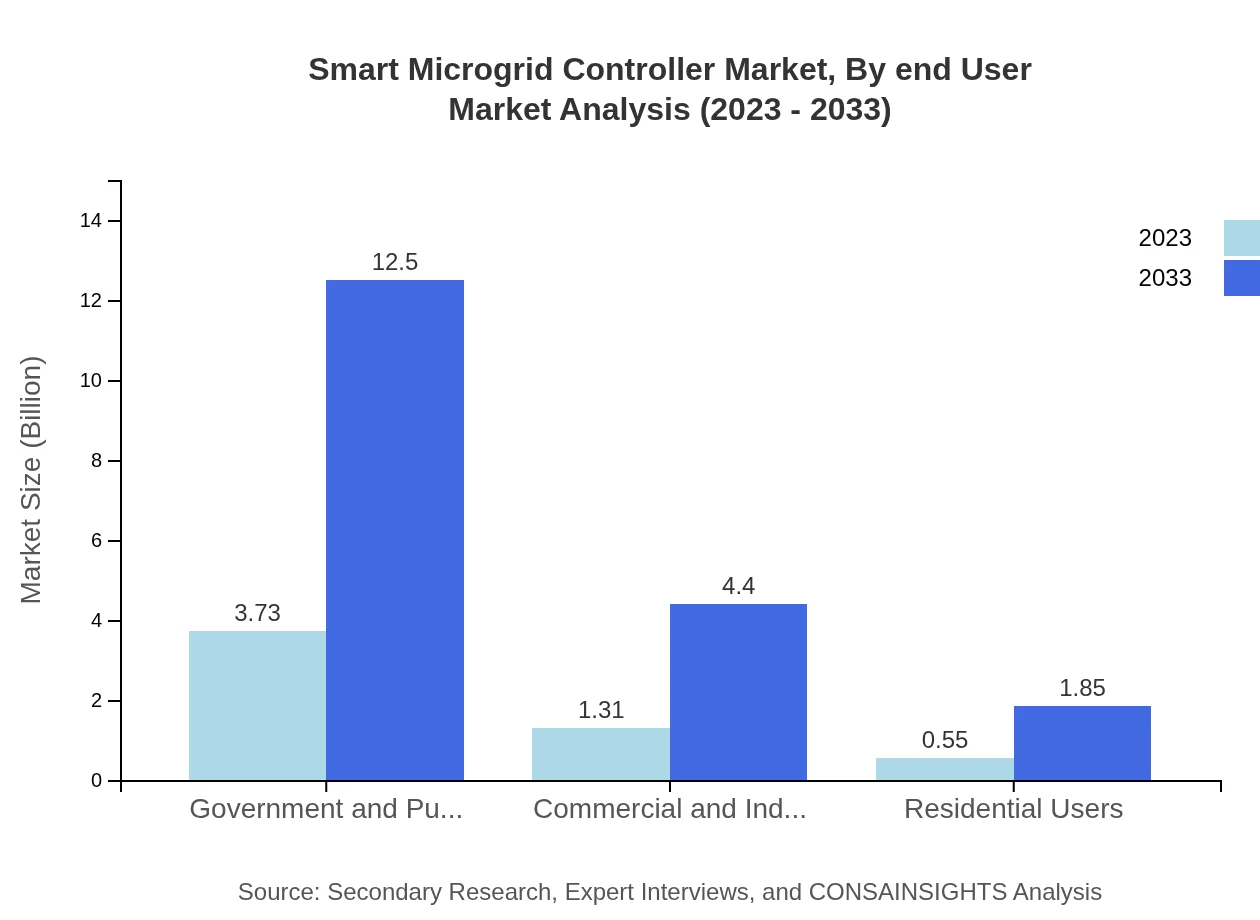
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Analysis By End User
The Smart Microgrid Controller market also segments by end-users, including Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Utility microgrids. Each segment shows steady growth, with utility microgrids being critical for integrating renewable energy sources. For instance, Residential microgrids are projected to expand from $3.28 billion to $10.98 billion, reflecting increasing energy autonomy among households.
Smart Microgrid Controller Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Microgrid Controller Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens is a global technology company known for its innovative microgrid solutions that enhance energy efficiency and resilience. Their focus on smart infrastructure and sustainable energy systems places them at the forefront of the industry.General Electric (GE):
General Electric is a leading player in the energy sector, providing cutting-edge microgrid technologies and services. GE's initiatives in renewable energy integration and digital grid management drive the growth of smart microgrid solutions.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric specializes in automation and energy management solutions, offering comprehensive microgrid controller systems that focus on sustainability and energy efficiency.ABB Group:
ABB is a global leader in power and automation technologies, providing innovative microgrid solutions that enhance grid connectivity and operational efficiency across various sectors.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell offers integrated solutions for smart microgrids designed to optimize energy use and enhance reliability. Their focus on advanced software solutions complements their hardware offerings in the market.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Microgrid Controller?
The smart microgrid controller market is currently valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3% through to 2033. This growth signifies the increasing demand for more efficient energy management solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in this smart Microgrid Controller industry?
Key players in the smart microgrid controller market include Schneider Electric, Siemens, and General Electric. These companies lead in technology development and deployment, significantly impacting market dynamics and driving innovation within the industry.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart Microgrid Controller industry?
The growth in the smart microgrid controller industry is primarily driven by increasing energy demands, the need for renewable energy integration, advancements in technology, and governmental policies promoting energy efficiency and sustainability in urban planning.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart Microgrid Controller?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the smart microgrid controller market. Estimated at $2.09 billion in 2023, it is expected to expand to $7.00 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong push towards decentralized energy solutions.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart Microgrid Controller industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific client needs within the smart microgrid controller industry, allowing for deeper insights and targeted strategies based on unique market dynamics.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart Microgrid Controller market research project?
Deliverables from the smart microgrid controller market research project include comprehensive reports, market trend analyses, regional breakdowns, competitive landscapes, and segmented data that help stakeholders make informed decisions.
What are the market trends of smart Microgrid Controller?
Current trends in the smart microgrid controller market include increased adoption of renewable energy sources, advancements in IoT technologies, growth of electric vehicle infrastructure, and rising consumer awareness of energy efficiency solutions.