Smart Power Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-power
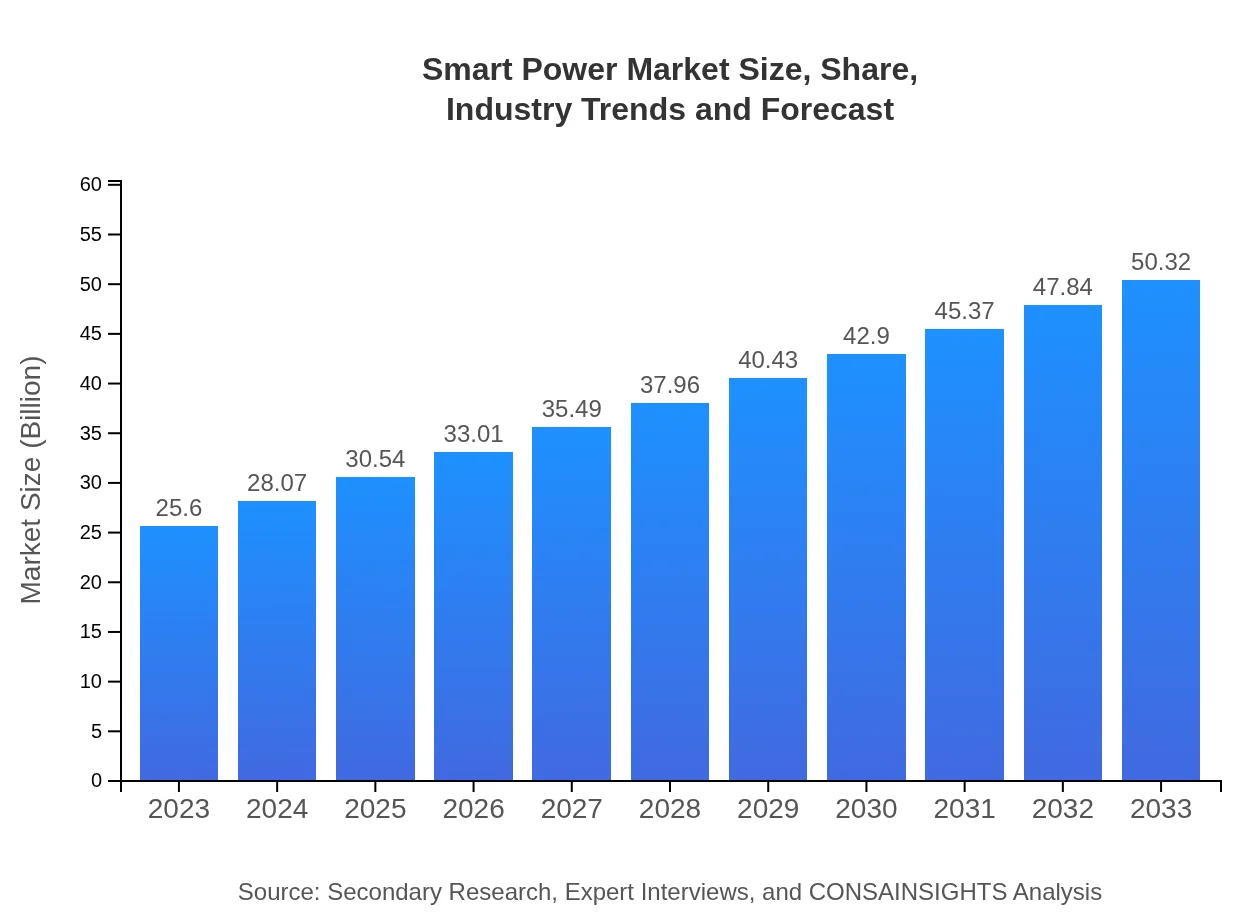
Smart Power Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Smart Power market, exploring its dynamics, segmentation, regional insights, and future trends from 2023 to 2033. Key data points and forecasts are included to support strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $25.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $50.32 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric, ABB Ltd., Honeywell International Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Smart Power Market Overview
Customize Smart Power Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Power market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Power's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Power
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Power market in 2023?
Smart Power Industry Analysis
Smart Power Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Power Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Power Market Report:
The European Smart Power market is forecast to increase from $8.55 billion in 2023 to $16.81 billion by 2033. The European Union’s Green Deal and commitments toward a carbon-neutral economy are pushing advancements and investments in smart power technologies.Asia Pacific Smart Power Market Report:
In the Asia-Pacific region, the Smart Power market is projected to grow from $4.74 billion in 2023 to $9.32 billion by 2033. Increasing investments in smart grid technologies, coupled with government initiatives promoting renewable energy adoption, are driving growth. Countries like China and India are focusing on infrastructure upgrades to support smart energy solutions.North America Smart Power Market Report:
North America is a key player, with the market expected to expand from $8.78 billion in 2023 to $17.26 billion by 2033. The region's early adoption of smart technologies, coupled with stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing emissions, are significant growth drivers.South America Smart Power Market Report:
The South American Smart Power market, though smaller, is set to rise from $0.09 billion in 2023 to $0.18 billion by 2033. Economic development and urbanization in countries like Brazil and Argentina are pushing demand for smart energy solutions as they strive for efficient energy distribution.Middle East & Africa Smart Power Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is poised for growth, from $3.43 billion in 2023 to $6.74 billion by 2033. With escalating electricity demands and governmental initiatives to promote sustainable practices, regions are increasingly adopting smart technology to mitigate energy consumption.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
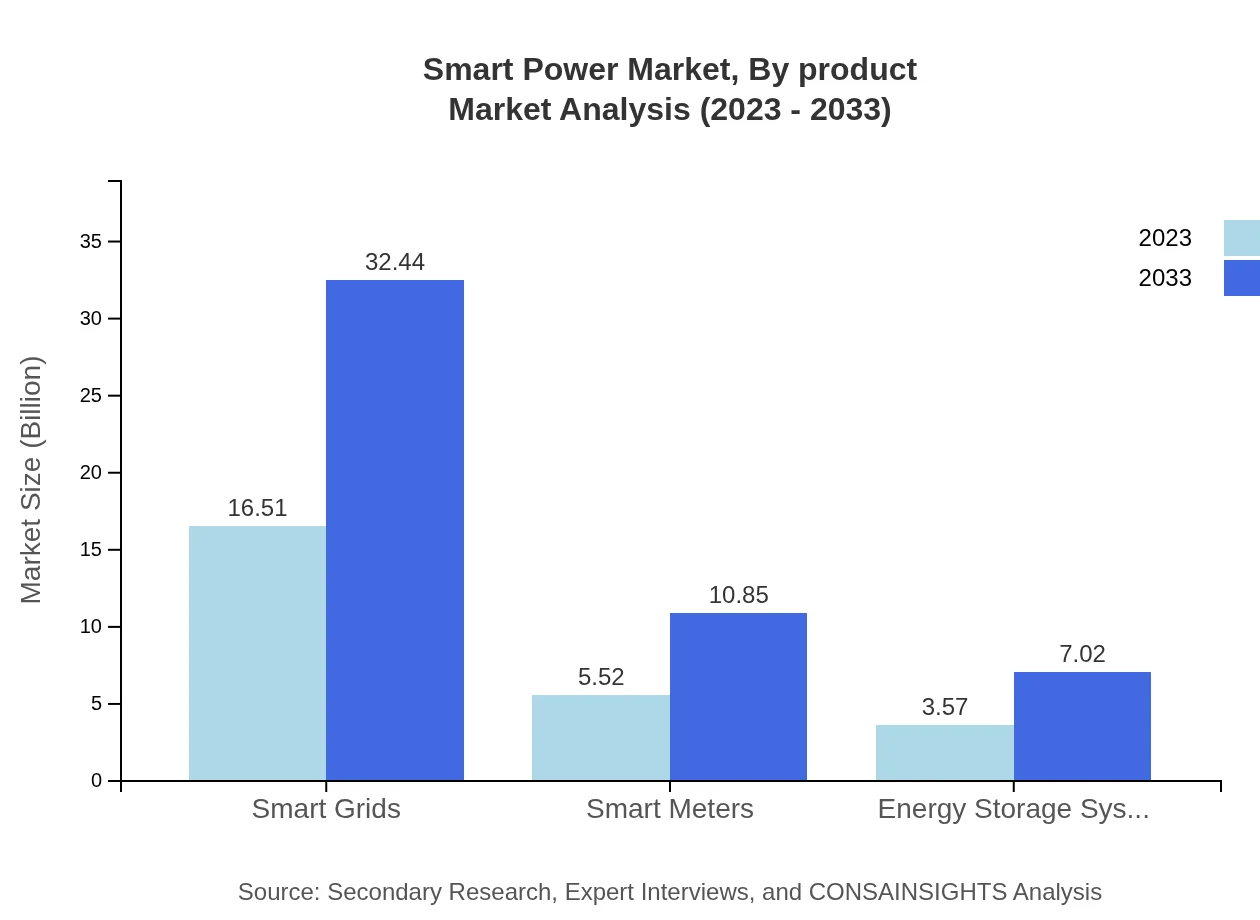
Smart Power Market Analysis By Product
Smart Grids dominate the Smart Power market, reflecting a market size of $16.51 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $32.44 billion by 2033. Smart Meters and Energy Storage Systems follow, addressing significant operational needs in energy management. This comprehensive range of products enables improved efficiency and consumer engagement.
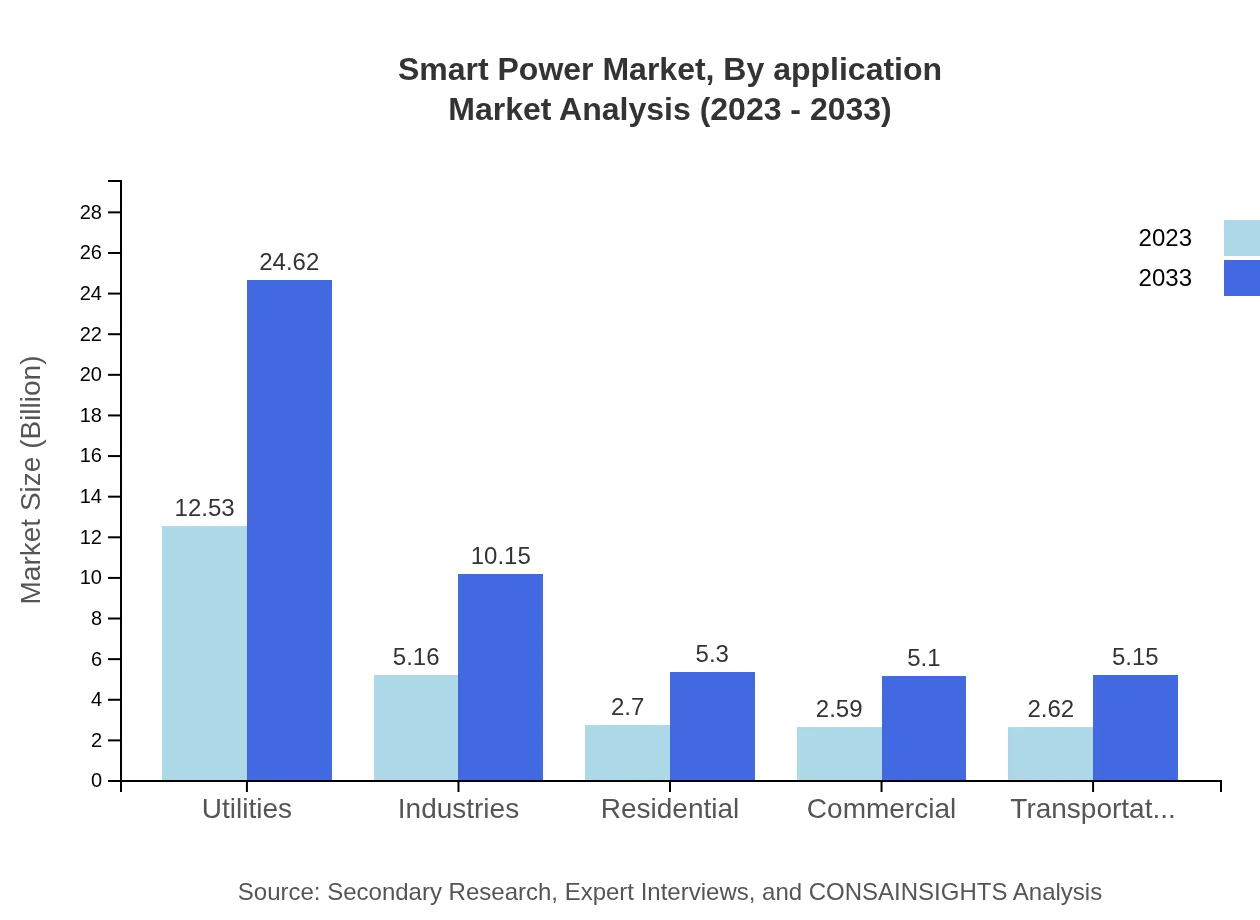
Smart Power Market Analysis By Application
The Smart Power market is increasingly catering to diverse applications across various sectors, including utilities, residential, commercial, industrial, and transportation. Utilities represent the largest market share, expected to hold approximately 48.93% by 2033, driven by the necessity for advanced grid management and integration of renewable energy sources.
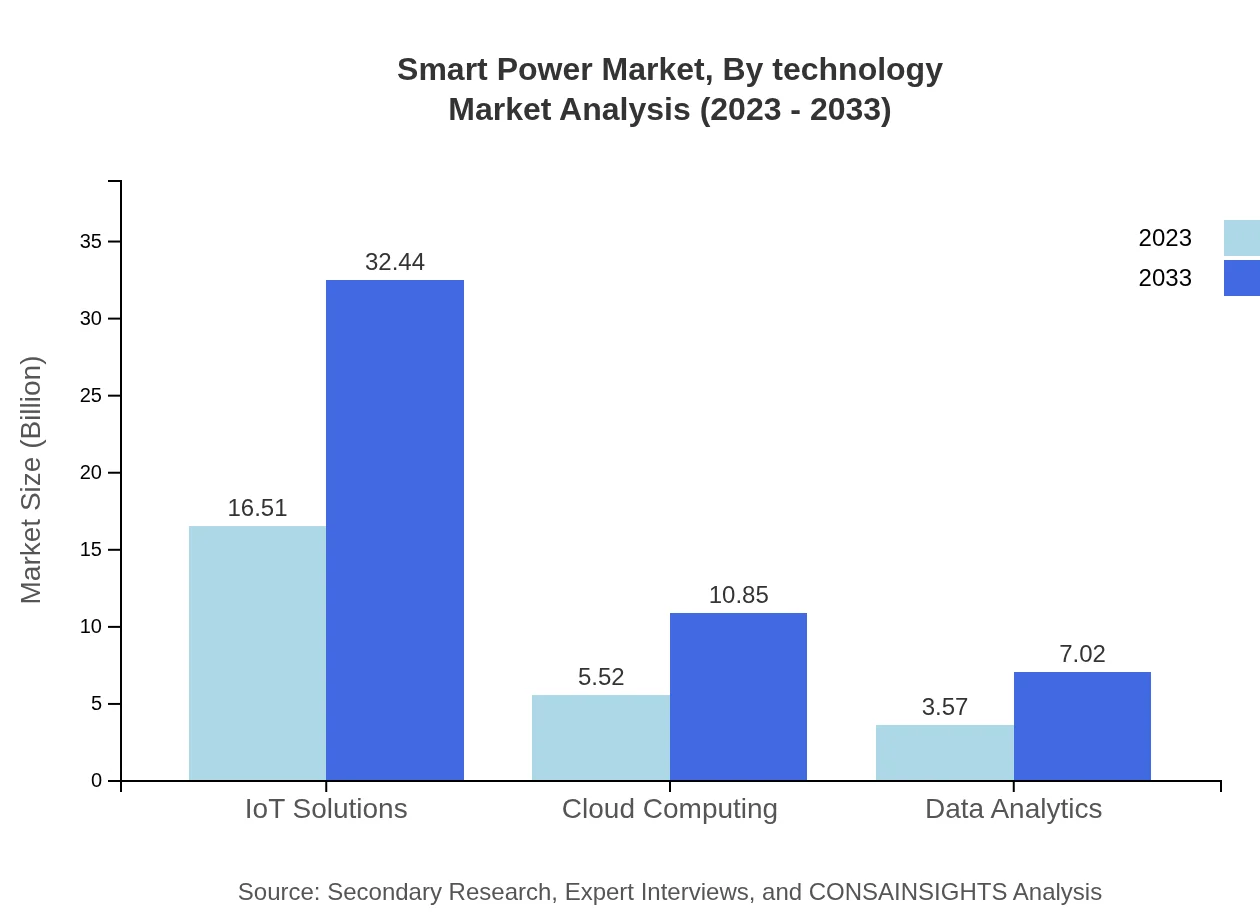
Smart Power Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements lead the Smart Power market's evolution, particularly in IoT solutions and data analytics. The adoption of IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance is vital, while data analytics support strategic decision-making, optimizing energy usage and minimizing waste.
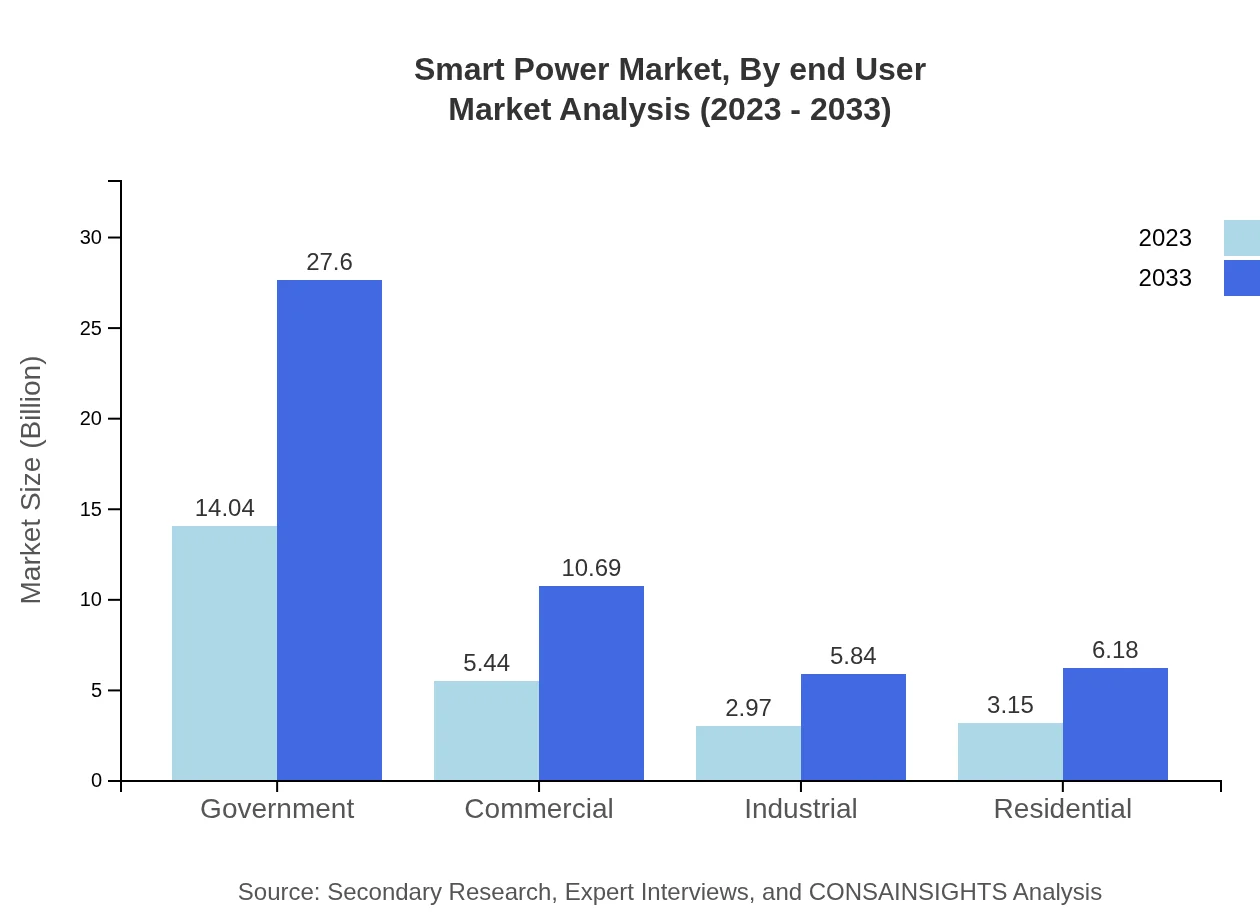
Smart Power Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries driving demand for Smart Power solutions include utilities, industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. Utilities maintain a commanding presence, necessitating innovation for improved efficiency. Commercial applications aim for cost-saving measures through energy management technologies, while residential consumers seek enhancements in energy efficiency and sustainability.
Smart Power Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Power Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG provides smart grid solutions and is a key player in automation and digitalization of energy systems, focusing on sustainability and operational efficiency.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric is a global leader in energy management, providing solutions across various industries to optimize energy usage and drive smart technology innovation.General Electric:
General Electric plays a pivotal role in the Smart Power market with its extensive portfolio in energy generation, grid modernization, and renewable energy integration.ABB Ltd.:
ABB offers a wide range of smart power solutions that enable utilities to meet real-time energy demands while enhancing grid reliability and efficiency.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell is notable in the Smart Power market with its IoT-based energy management solutions that cater to industrial and commercial sectors, maximizing energy efficiency.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Smart Power?
The global smart power market is valued at approximately $25.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8%, reaching significant growth by 2033, highlighting the increasing reliance on smarter technologies in energy management.
What are the key market players or companies in the Smart Power industry?
Key market players in the smart power industry include prominent technology firms and energy solutions providers that specialize in innovative solutions for smart grids, energy management systems, and advanced metering infrastructures.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Smart Power industry?
Factors driving market growth include increasing energy demand, the need for efficient energy distribution, advancements in renewable energy technologies, and government initiatives promoting smart grid applications and sustainable energy solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Smart Power?
Among global regions, Europe is the fastest-growing market for smart power, projected to expand from $8.55 billion in 2023 to $16.81 billion by 2033, closely followed by North America, which will grow from $8.78 billion to $17.26 billion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Smart Power industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific business needs within the smart power industry, allowing organizations to obtain targeted insights and strategic intelligence based on unique market parameters.
What deliverables can I expect from this Smart Power market research project?
The deliverables from the smart power market research project typically include comprehensive reports detailing market size, trends, competitor analysis, regional growth projections, and actionable insights tailored to assist in strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of Smart Power?
Current trends in the smart power market include the adoption of IoT solutions, growth in energy storage technologies, integration of renewable energy sources, and the increasing focus on sustainability and smarter grid infrastructure.