Smart Thermostat Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-thermostat
Smart Thermostat Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report presents an in-depth analysis of the Smart Thermostat market, detailing insights on market size, trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It covers key facets such as regional performance, industry challenges, and competitive landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
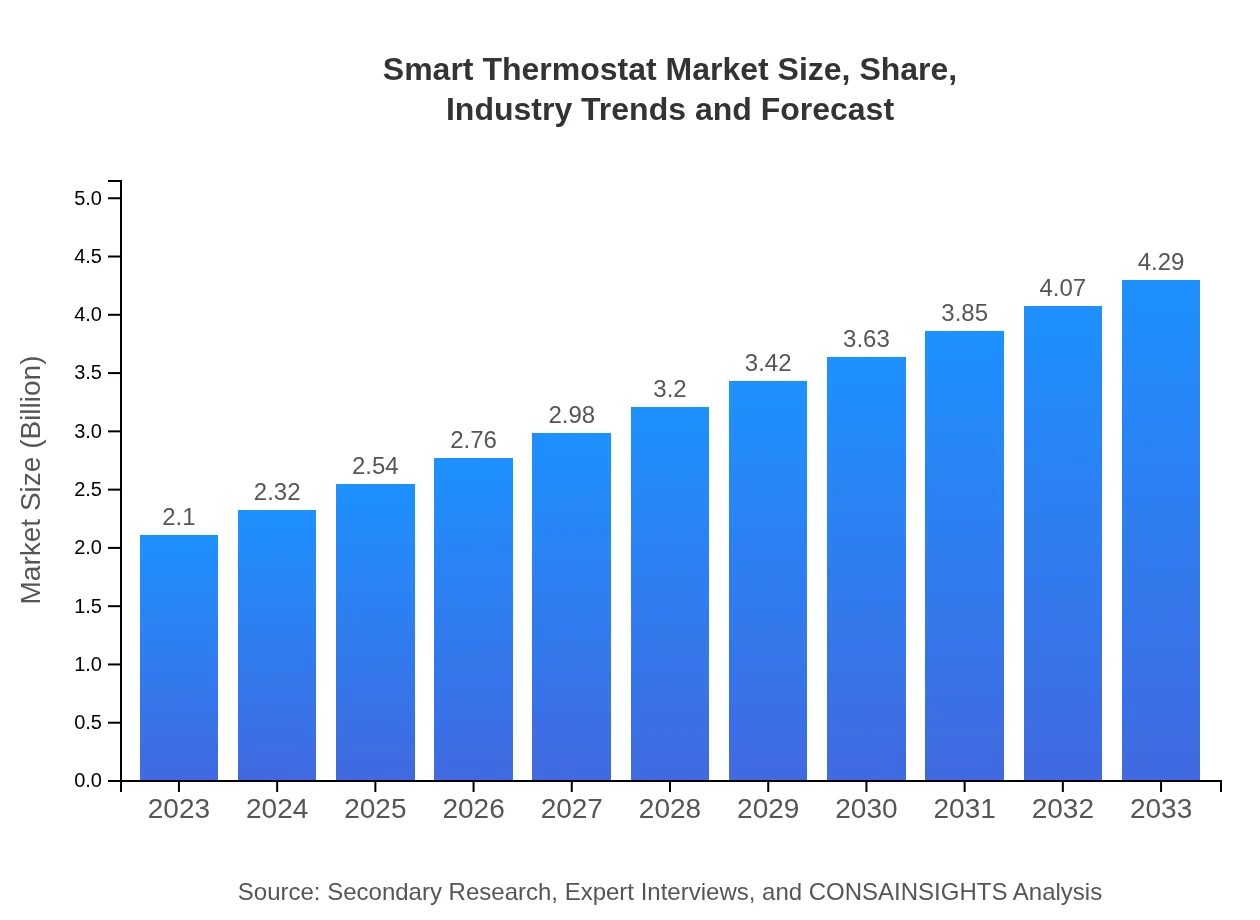
| 2023 Market Size | $2.10 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $4.29 Billion |
| Top Companies | Nest Labs, Ecobee, Honeywell , Tado° |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Smart Thermostat Market Overview
Customize Smart Thermostat Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Thermostat market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Thermostat's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Thermostat
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Thermostat market in 2023 and 2033?
Smart Thermostat Industry Analysis
Smart Thermostat Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Thermostat Market Report:
The European market is predicted to grow from USD 0.61 billion in 2023 to USD 1.25 billion by 2033. With stringent energy efficiency regulations and a high level of consumer awareness, Europe is witnessing steady growth in smart thermostat adoption.Asia Pacific Smart Thermostat Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness significant growth, with the market projected to increase from USD 0.40 billion in 2023 to USD 0.82 billion by 2033. The growing middle class and urbanization are driving demand for smart home technologies in countries like China, Japan, and India.North America Smart Thermostat Market Report:
North America remains the largest market for smart thermostats, with an estimated growth from USD 0.77 billion in 2023 to USD 1.58 billion by 2033. The region's strong infrastructure for smart home technologies and early adoption trends support its market dominance.South America Smart Thermostat Market Report:
In South America, the smart thermostat market is expected to grow from USD 0.09 billion in 2023 to USD 0.19 billion by 2033. The increasing focus on energy savings and the introduction of government rebates for smart home products are fueling this growth.Middle East & Africa Smart Thermostat Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the smart thermostat market size is projected to increase from USD 0.23 billion in 2023 to USD 0.46 billion by 2033. Growth is driven by increasing residential construction and the rising adoption of smart technologies in urban areas.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
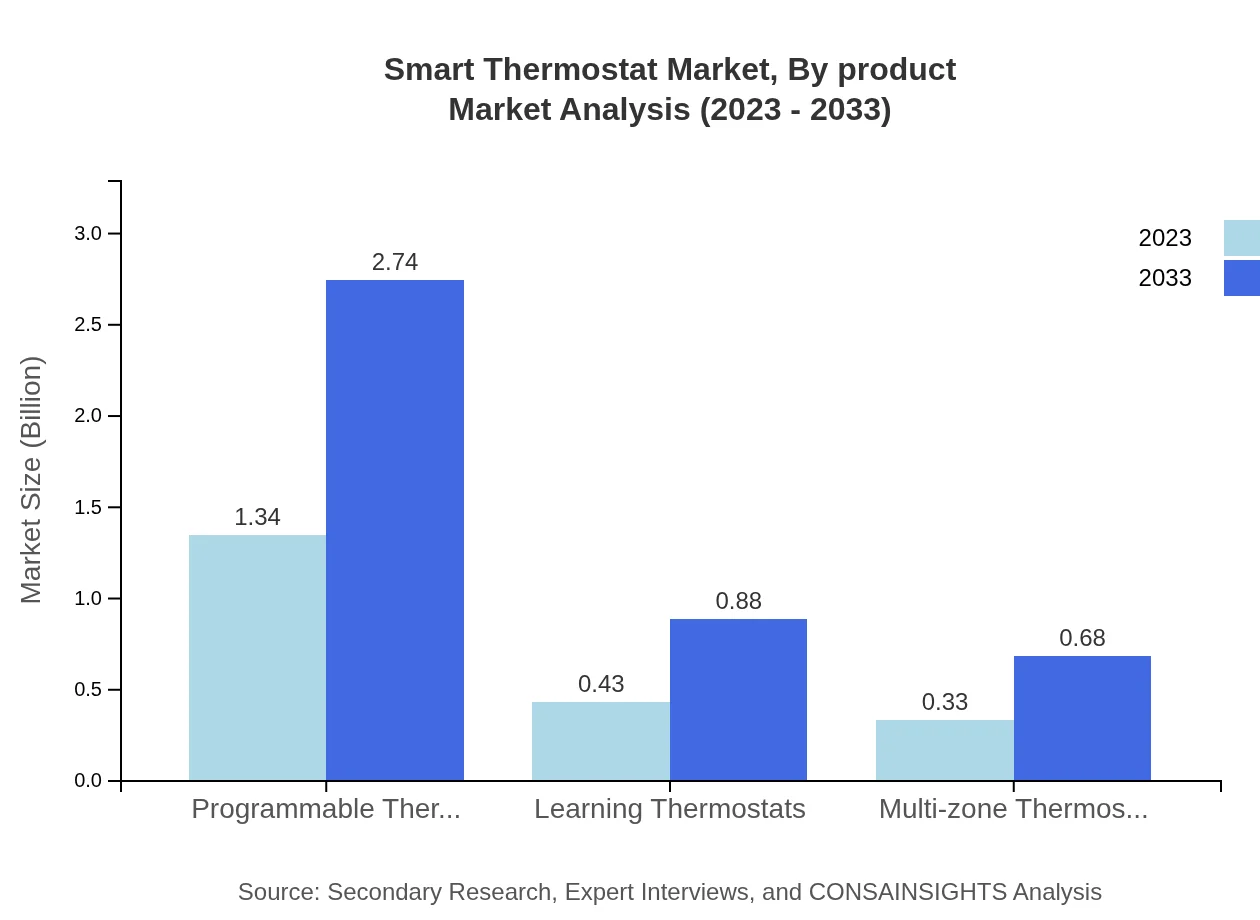
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis By Product
The market can be subdivided into three product categories: Programmable Thermostats, Learning Thermostats, and Multi-zone Thermostats. Programmable Thermostats dominate the market, expected to grow from USD 1.34 billion in 2023 to USD 2.74 billion by 2033. Learning Thermostats are gaining traction as they provide personalized climate control and efficient energy management, projected to increase from USD 0.43 billion to USD 0.88 billion.
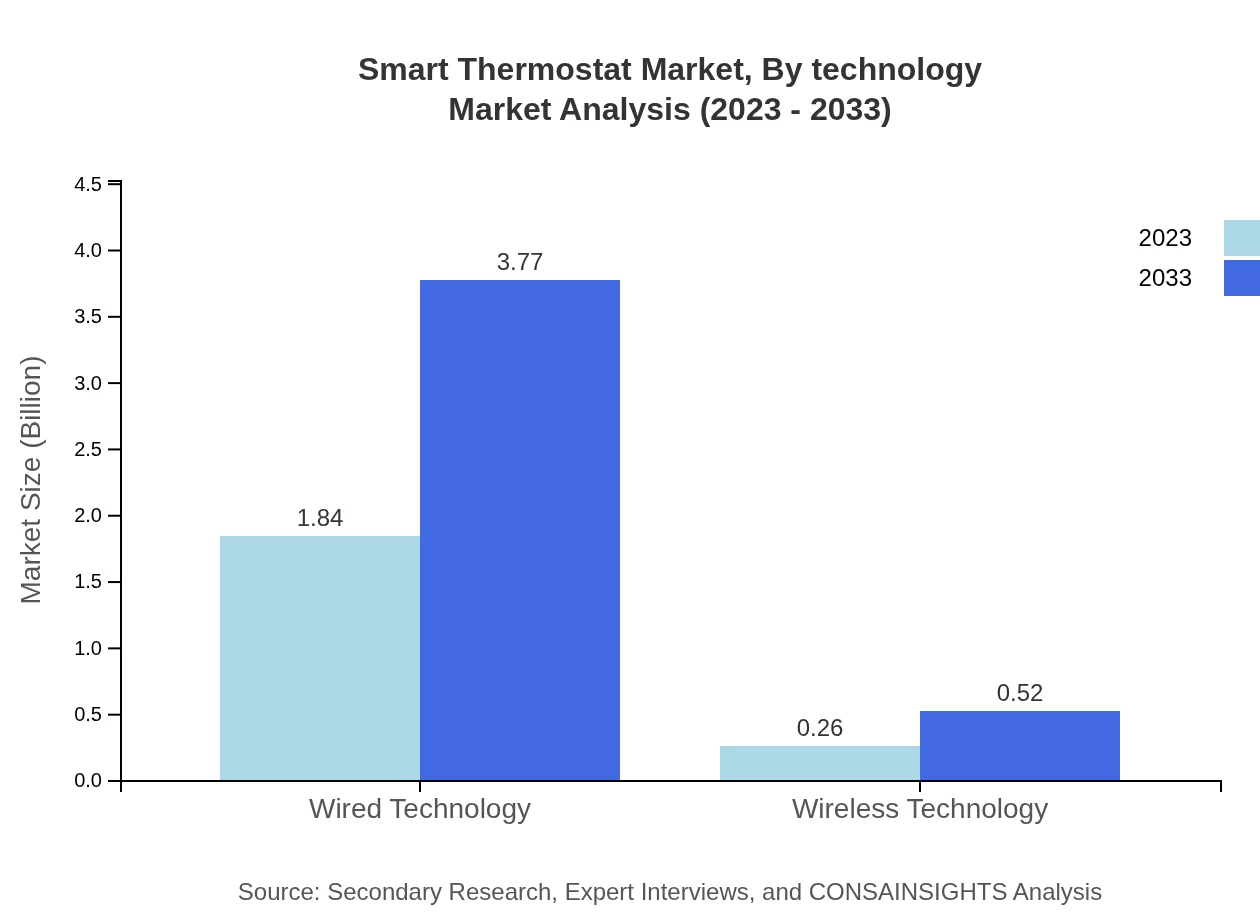
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis By Technology
The Smart Thermostat market is bifurcated into Wired Technology and Wireless Technology. Wired Technology holds a significant share, currently valued at USD 1.84 billion with a growth forecast to USD 3.77 billion by 2033. Wireless Technology, though smaller at USD 0.26 billion, is projected to double over the same period, reflecting increasing consumer preference for ease of installation and connectivity.
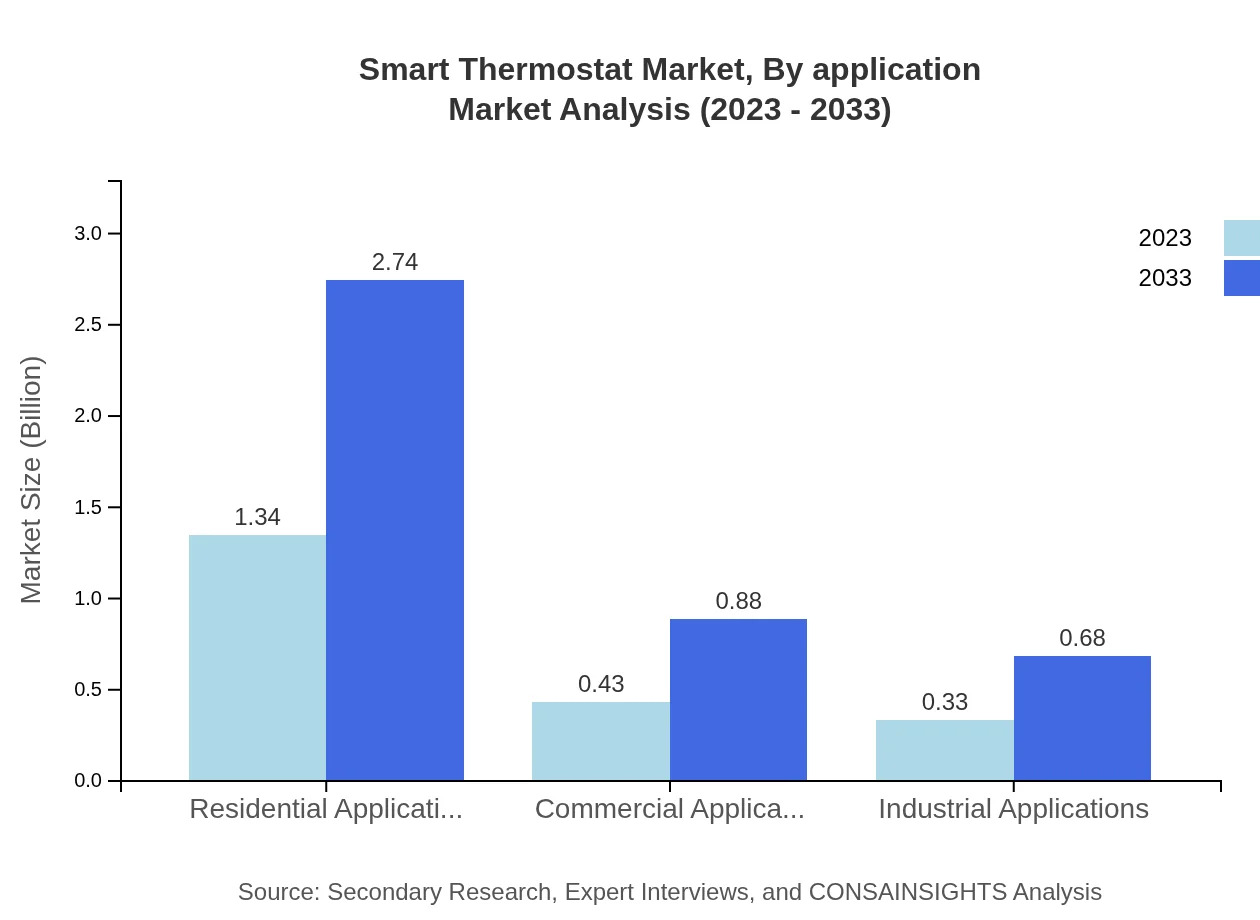
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis By Application
The Smart Thermostat market applications include Residential, Commercial, and Industrial sectors. Residential Applications constitute the largest segment, expected to grow from USD 1.34 billion in 2023 to USD 2.74 billion by 2033, driven by rising demand for home automation. Commercial Applications also show substantial growth due to increasing investments in smart office solutions.
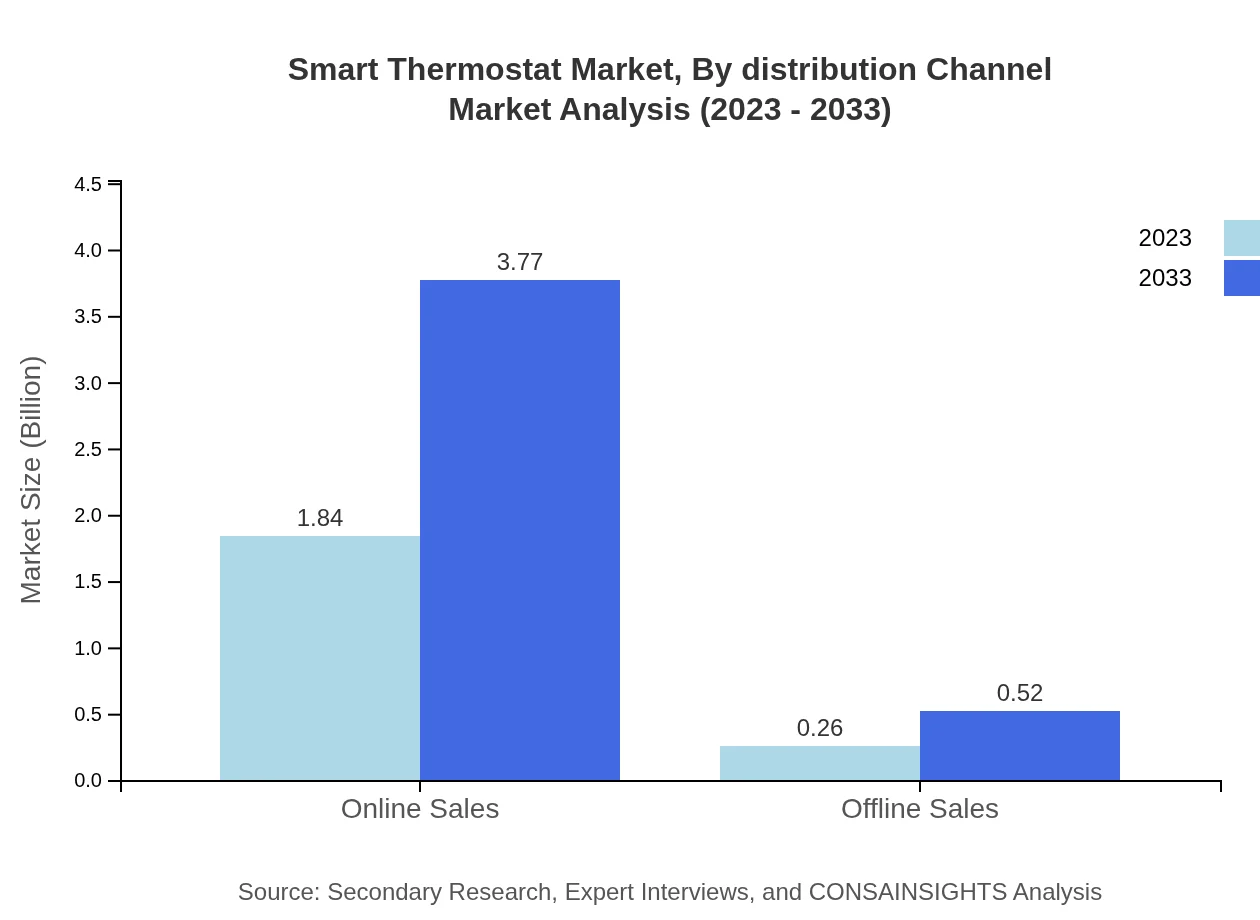
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels for Smart Thermostats include Online Sales and Offline Sales. Online Sales dominate the market with a share of approximately 87.79%, growing from USD 1.84 billion to USD 3.77 billion by 2033. Offline Sales, while smaller, are on the rise as more retailers incorporate smart home technologies into their offerings.
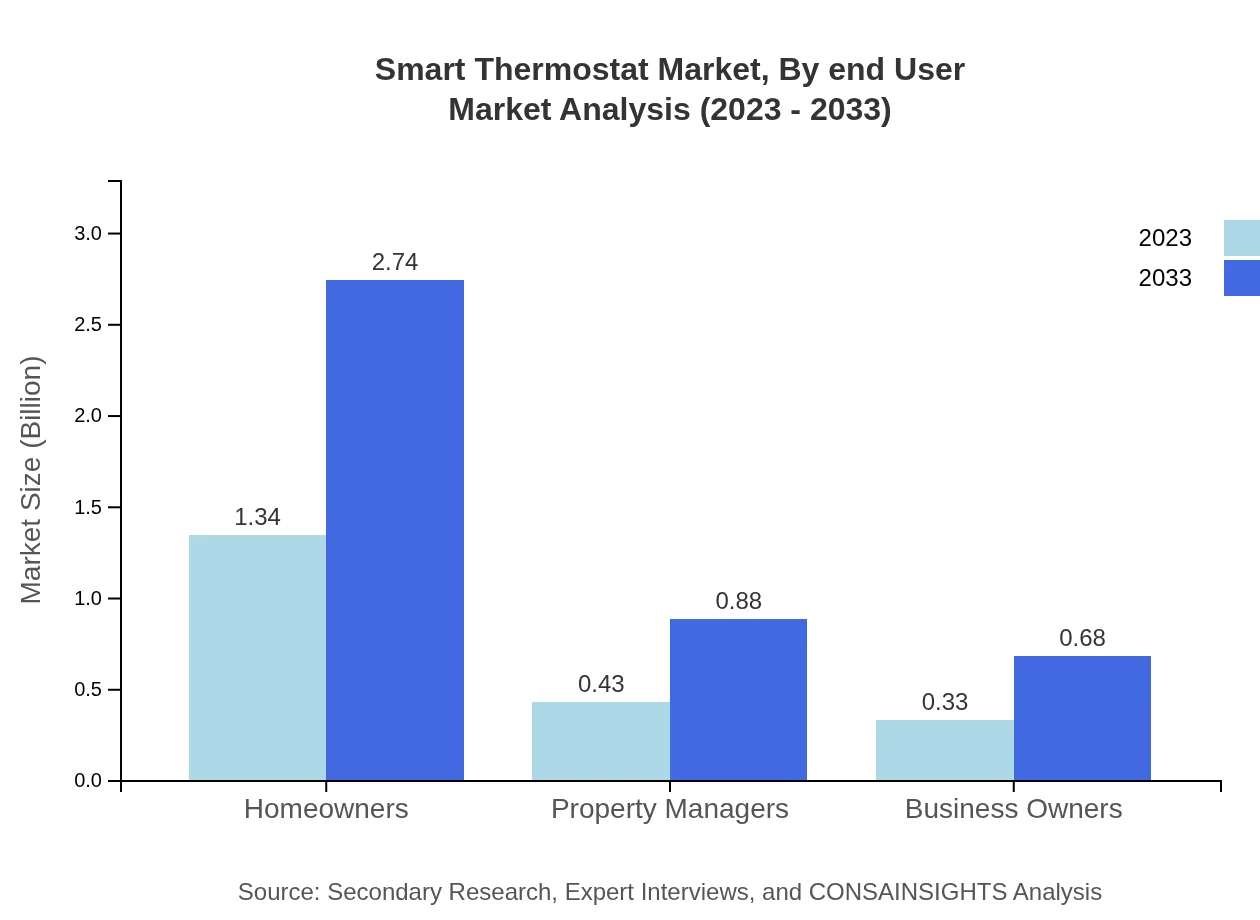
Smart Thermostat Market Analysis By End User
The Smart Thermostat market segments based on end-users include Homeowners, Property Managers, and Business Owners. Homeowners represent the largest percentage of the market with a stable share expected to maintain at 63.75%. Property Managers and Business Owners also show considerable participation, highlighting the increasing use of smart energy solutions in property management.
Smart Thermostat Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Thermostat Industry
Nest Labs:
A pioneer in the smart thermostat sector, Nest Labs introduced innovative features like remote monitoring and learning algorithms for efficient energy management.Ecobee:
Ecobee is known for its user-friendly smart thermostats that integrate with various home systems, providing advanced energy-saving capabilities.Honeywell :
A well-established company in the HVAC industry, Honeywell offers a range of smart thermostats equipped with features to enhance energy efficiency.Tado°:
Tado° specializes in smart climate control systems and emphasizes energy use transparency to achieve significant savings.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of smart Thermostat?
The smart thermostat market is projected to reach approximately $2.1 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%. By 2033, it is expected to experience significant growth as technology adoption increases.
What are the key market players or companies in the smart Thermostat industry?
Key players in the smart thermostat market include Nest Labs, Ecobee, Honeywell, and Emerson. These companies drive innovation and market growth through advanced features and smart technology solutions, catering to residential and commercial applications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the smart thermostat industry?
Growth in the smart thermostat industry is driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) technology, and the growing trend of smart home automation, which enhances consumer convenience and reduces energy costs.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the smart thermostat market?
The fastest-growing region for smart thermostats is North America, expected to grow from $0.77 billion in 2023 to $1.58 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also show rapid growth, driven by intensified technological adoption and increased consumer awareness.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the smart thermostat industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the needs of clients in the smart thermostat industry, ensuring that insights align with specific business objectives and market segments for optimized strategic planning.
What deliverables can I expect from this smart thermostat market research project?
Clients can expect comprehensive deliverables including market analysis, competitive landscape, segmentation insights, consumer trends, and growth forecasts for the smart thermostat market, providing valuable data for informed decision-making.
What are the market trends of smart thermostat?
Current market trends in the smart thermostat sector include a shift towards energy-saving technologies, increased integration with smart home systems, and the adoption of learning thermostats that adapt to user behavior to optimize heating and cooling efficiency.