Smart Worker Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: smart-worker
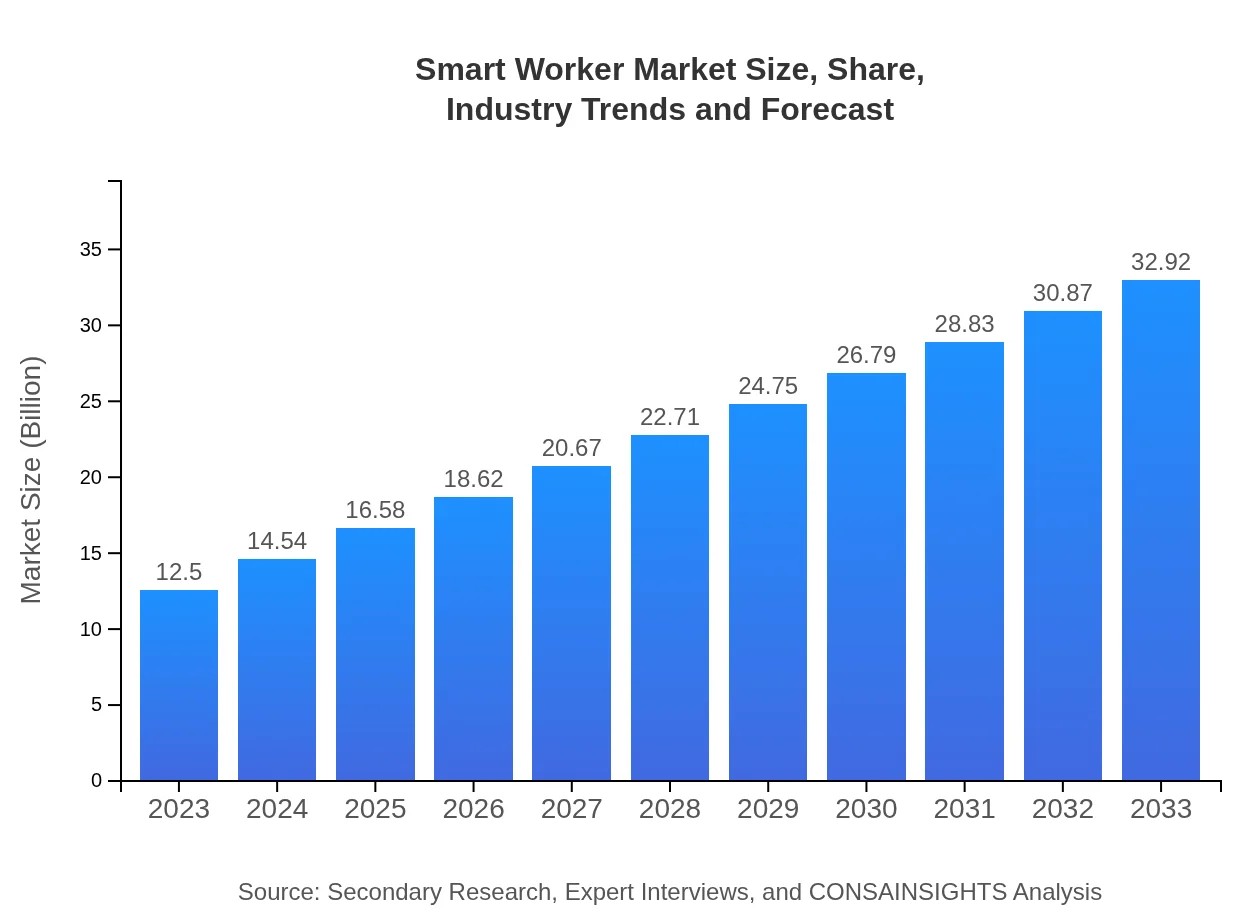
Smart Worker Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Smart Worker market, focusing on market trends, segments, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. Insights include regional distributions, technology impacts, and competitive landscape, facilitating informed strategic decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | Microsoft, IBM, Salesforce, Slack Technologies, SAP |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Smart Worker Market Overview
Customize Smart Worker Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Smart Worker market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Smart Worker's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Smart Worker
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Smart Worker market in 2023?
Smart Worker Industry Analysis
Smart Worker Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Smart Worker Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Smart Worker Market Report:
Europe is projected to see its Smart Worker market size increase from $3.86 billion in 2023 to $10.16 billion by 2033. The push for sustainability and digital transformation in traditional industries has encouraged investment in smart technologies that improve worker productivity and employee satisfaction.Asia Pacific Smart Worker Market Report:
The Asia Pacific is a rapidly growing market for Smart Worker solutions, predicted to expand from $2.16 billion in 2023 to $5.69 billion by 2033. Factors such as a strong manufacturing base, increasing digitalization, and workforce mobility drive this market's growth. Countries like China and India are major contributors to this increase.North America Smart Worker Market Report:
North America leads the Smart Worker market, with a valuation of $4.67 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $12.30 billion by 2033. The region's dominance is attributed to high adoption rates of advanced technologies and innovation across industries, particularly in healthcare and finance.South America Smart Worker Market Report:
In South America, the Smart Worker market is expected to grow from $1.21 billion in 2023 to $3.18 billion by 2033. Economic developments and the push for digital transformation in sectors like agriculture, retail, and manufacturing drive this upward trend.Middle East & Africa Smart Worker Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa exhibit a nascent but promising Smart Worker market, projected to expand from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $1.58 billion by 2033. Growth in this region is fueled by increasing government initiatives in ICT, economic diversification, and a focus on enhancing operational efficiency across sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
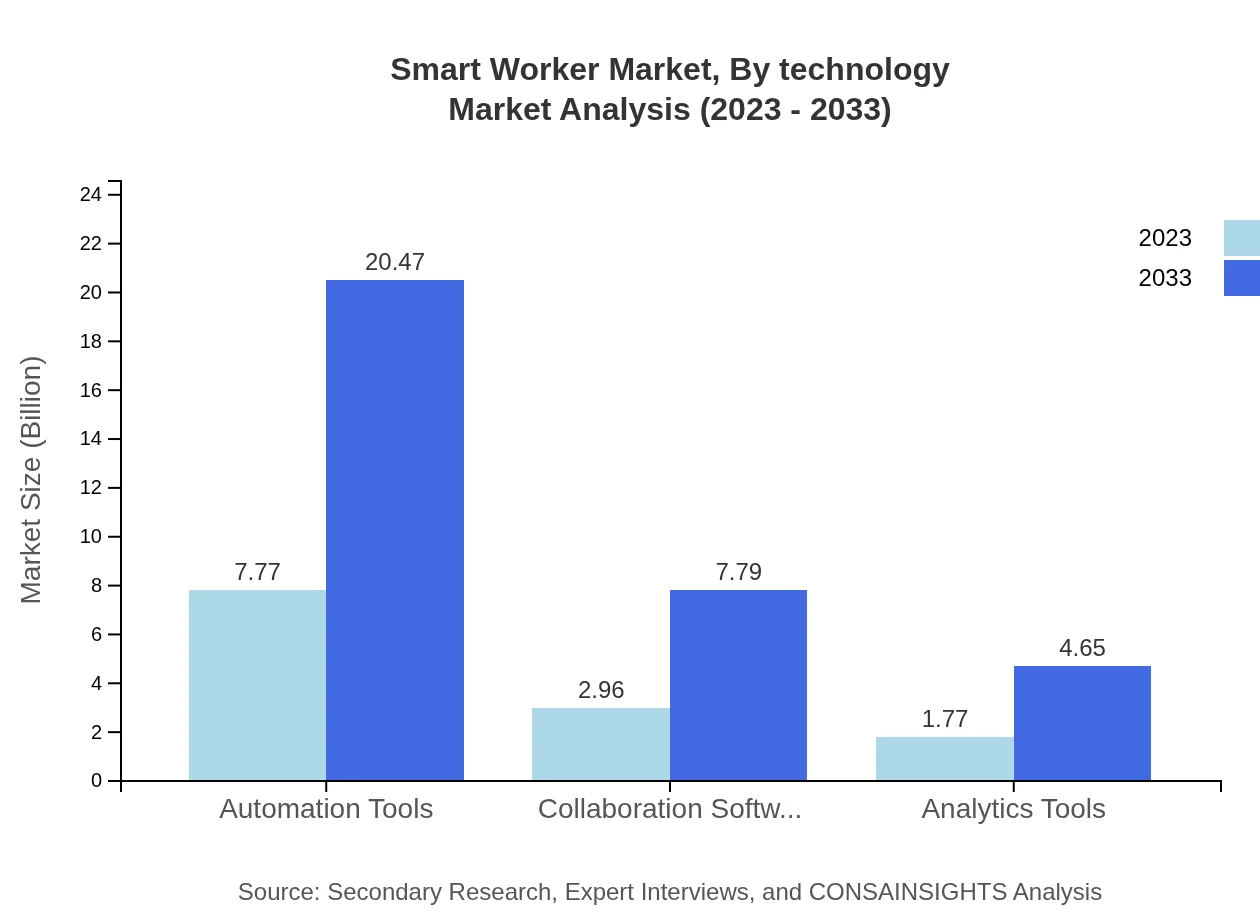
Smart Worker Market Analysis By Technology
Key technologies in the Smart Worker market include automation tools, collaboration software, and analytics tools. Automation tools are leading this segment, expected to reach $20.47 billion by 2033 from $7.77 billion in 2023, capturing 62.18% of the market share. Collaboration software and analytics tools also demonstrate significant growth potential, with market sizes projected to grow from $2.96 billion to $7.79 billion and $1.77 billion to $4.65 billion respectively during the same period.
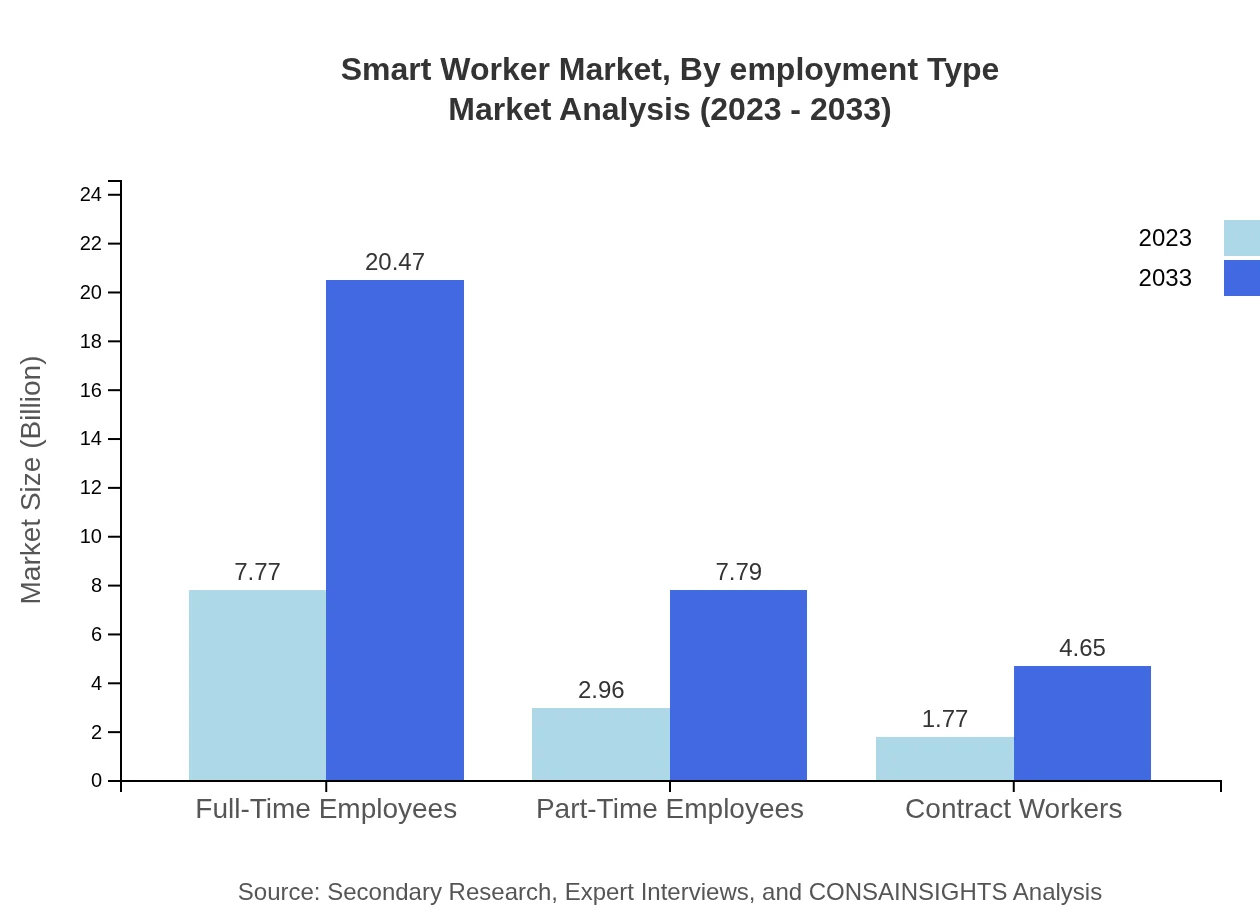
Smart Worker Market Analysis By Employment Type
The Smart Worker market is segmented by employment type into full-time employees, part-time employees, and contract workers. Full-time employees represent a significant share of the market, expanding from $7.77 billion in 2023 to $20.47 billion by 2033. Part-time and contract workers are also essential segments, expected to grow from $2.96 billion to $7.79 billion and from $1.77 billion to $4.65 billion respectively, indicating a robust demand for smart tools across various employment arrangements.
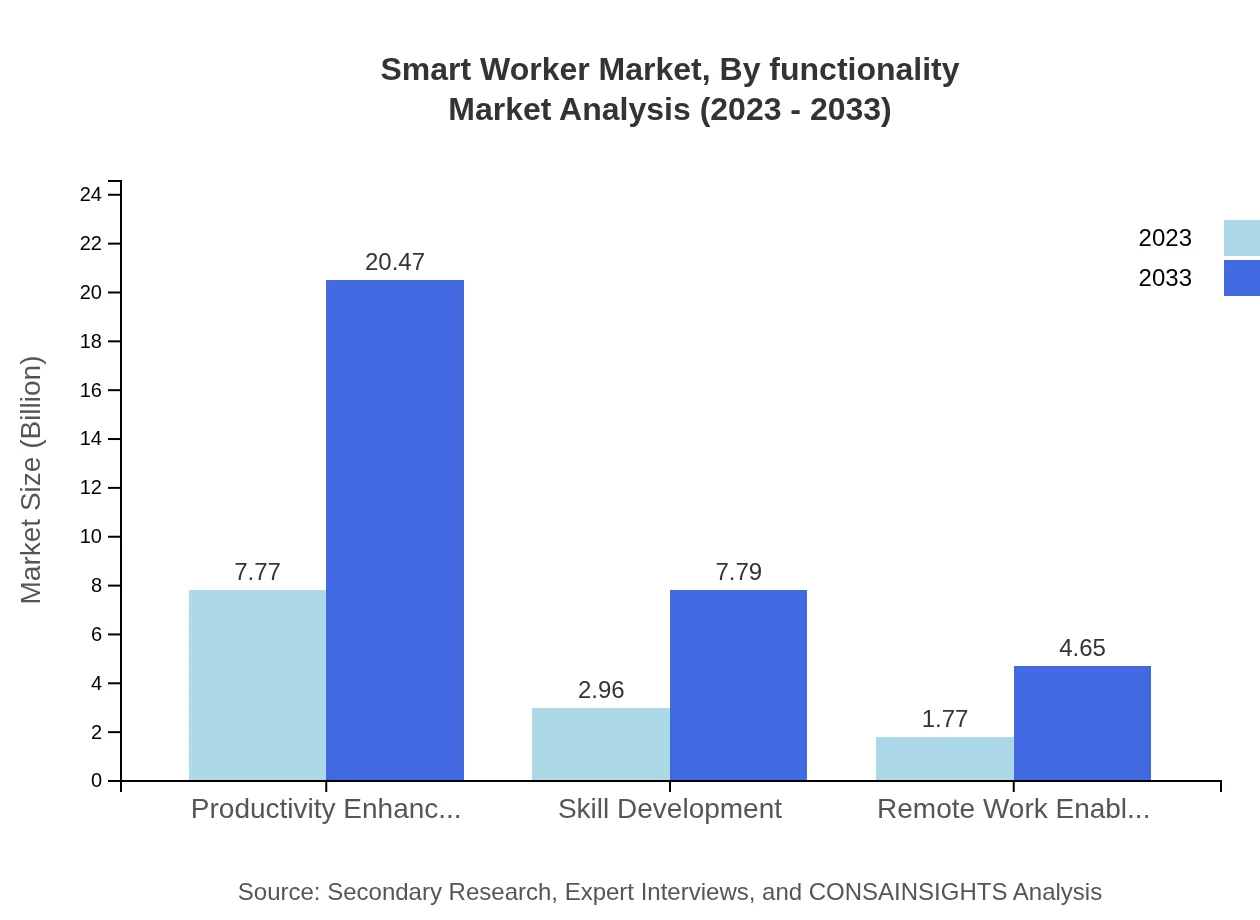
Smart Worker Market Analysis By Functionality
The market can also be categorized by functionality, highlighting areas such as cost-saving, employee satisfaction, and efficiency improvement. Cost-saving tools dominate the sector, projected to expand from $7.77 billion in 2023 to $20.47 billion by 2033, holding a 62.18% market share. Employee satisfaction tools are also critical, expected to increase from $2.96 billion to $7.79 billion, showcasing the growing investment in worker well-being.
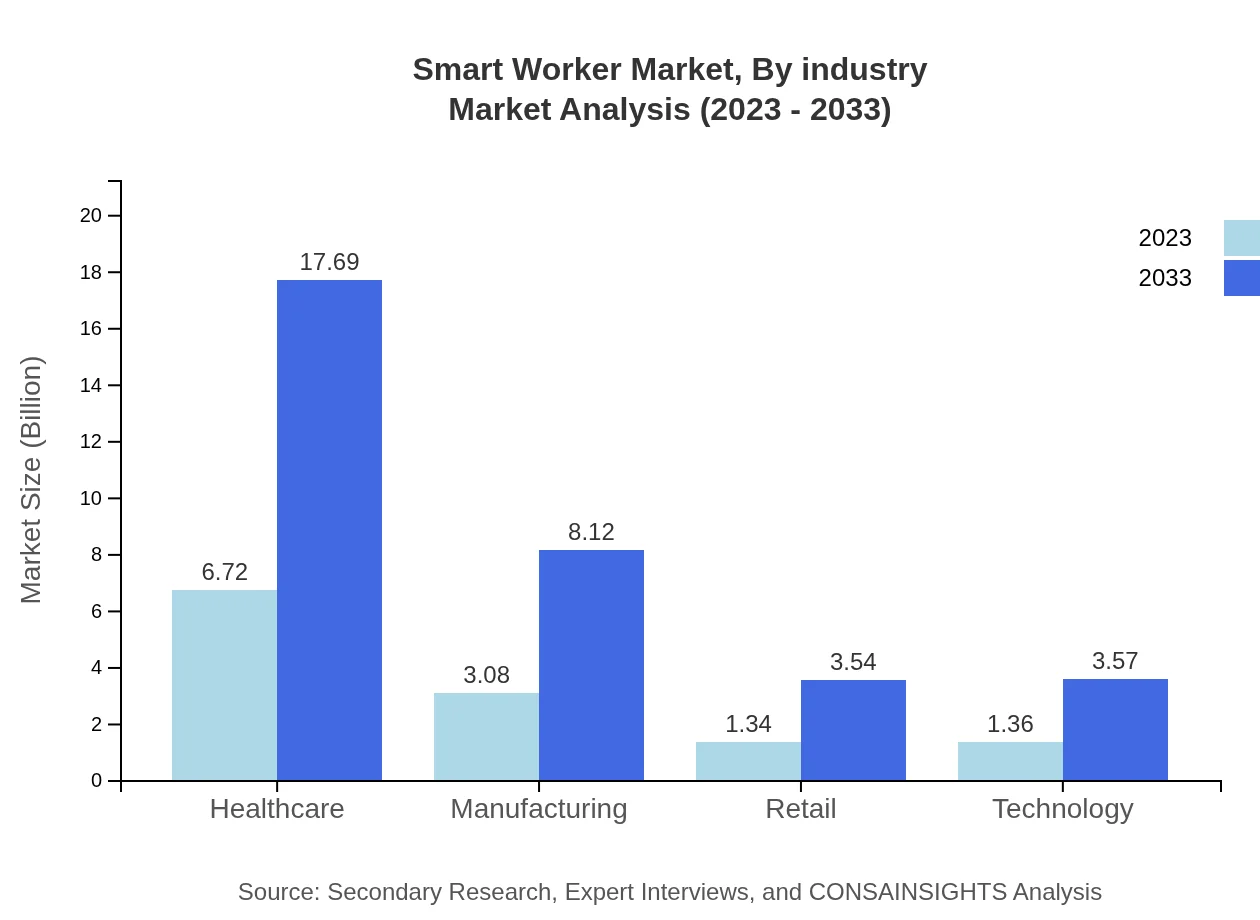
Smart Worker Market Analysis By Industry
Industries leveraging Smart Worker solutions include healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and technology. The healthcare segment is particularly robust, growing from $6.72 billion in 2023 to $17.69 billion by 2033 and maintaining a 53.74% market share. Manufacturing and retail are also significant, predicted to see growth from $3.08 billion to $8.12 billion and from $1.34 billion to $3.54 billion respectively.
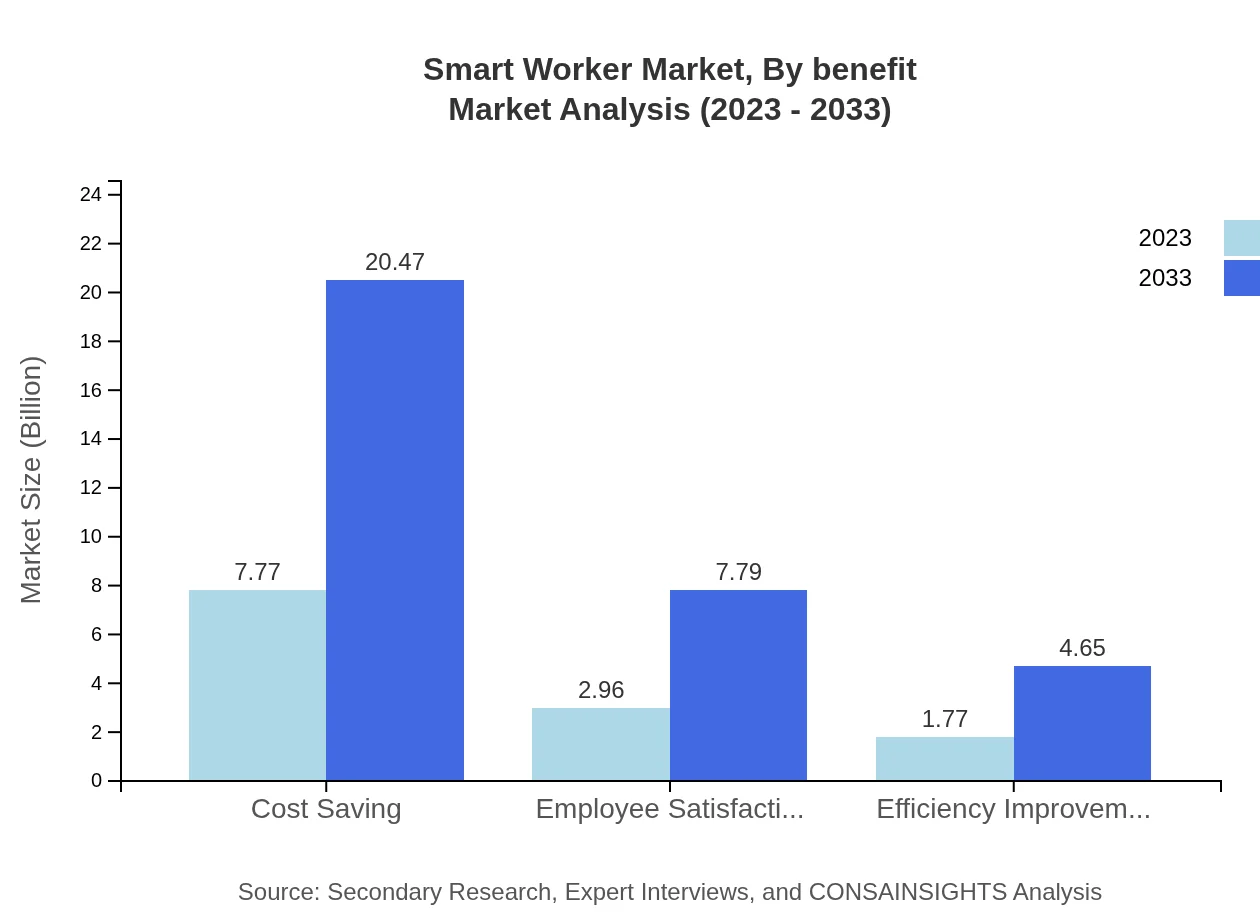
Smart Worker Market Analysis By Benefit
The benefits derived from Smart Worker tools encompass cost savings, productivity enhancement, and skill development. Cost-saving solutions lead the market with anticipated growth from $7.77 billion to $20.47 billion, representing a significant scale of investment. Productivity enhancement is also substantial, with a projection to rise from $7.77 billion to $20.47 billion, reflecting the priority placed on operational efficiency.
Smart Worker Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Smart Worker Industry
Microsoft:
Microsoft leads in developing smart collaboration and productivity tools, such as Microsoft Teams and Office 365, enhancing workplace communication and teamwork.IBM:
IBM fosters innovation in employee engagement and automation with its AI-driven platforms, focusing on enhancing workforce capabilities and operational efficiency.Salesforce:
As a leader in CRM software, Salesforce leverages smart tools to improve customer interactions and employee productivity across service sectors.Slack Technologies:
Slack specializes in collaboration software that integrates various tools for better team communication and project management in diverse industries.SAP:
SAP provides enterprise resource planning solutions and analytics tools designed to streamline operations and promote workforce efficiency in large enterprises.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Smart Worker?
The Smart Worker market is projected to reach a size of $12.5 billion by 2033, growing significantly from its current valuation. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is estimated at 9.8%, indicating robust expansion opportunities in this sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the Smart Worker industry?
Key players in the Smart Worker industry include major companies that specialize in automation tools, collaboration software, and productivity enhancement solutions. These organizations lead the market by developing cutting-edge technologies aimed at improving workforce efficiency.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Smart Worker industry?
Key drivers of growth in the Smart Worker industry include the rising need for automation, increased focus on employee satisfaction, and enhanced productivity measures. Companies are investing in smart technologies to streamline operations and reduce costs.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Smart Worker?
The fastest-growing region for the Smart Worker market is North America, with a market size projected to grow from $4.67 billion in 2023 to $12.30 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by an increasing adoption of advanced technologies in workplaces.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Smart Worker industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs in the Smart Worker industry. This includes data insights, market trends, and forecasts that help businesses navigate this sector effectively.
What deliverables can I expect from this Smart Worker market research project?
Deliverables from the Smart Worker market research project typically include detailed reports, market analysis, segment data, forecasts, and actionable insights tailored to help businesses make informed decisions within the industry.
What are the market trends of Smart Worker?
Current trends in the Smart Worker market showcase a strong emphasis on automation, employee engagement, and the integration of advanced analytics tools. Companies are prioritizing cost savings and efficiency improvements to stay competitive.