Social Robots Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: social-robots
Social Robots Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Social Robots market from 2023 to 2033, highlighting the key trends, market segmentation, regional insights, and competitive landscape. It aims to deliver valuable insights to stakeholders looking to understand this rapidly evolving industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
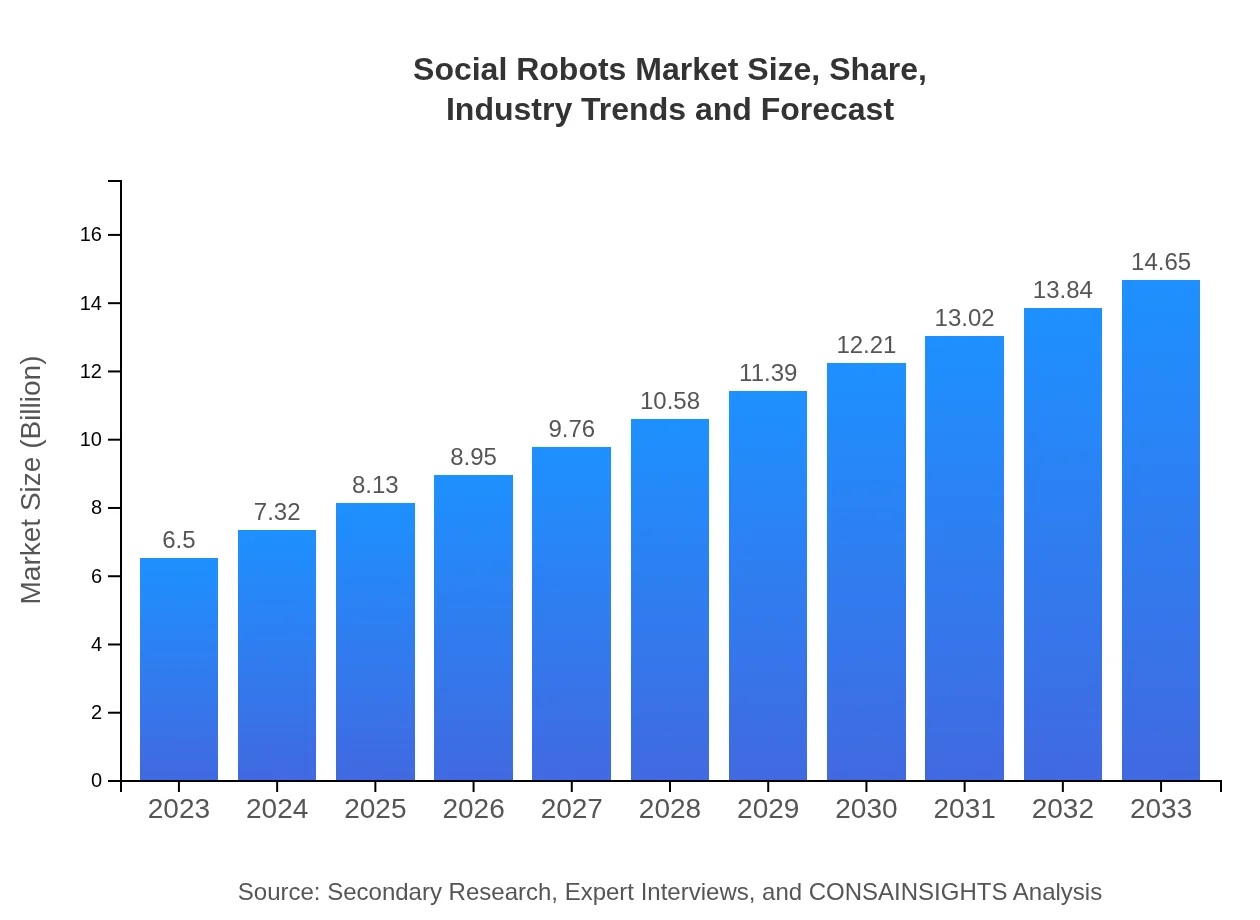
| 2023 Market Size | $6.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $14.65 Billion |
| Top Companies | SoftBank Robotics, Boston Dynamics, iRobot Corporation, Ubtech Robotics, Intuition Robotics |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Social Robots Market Overview
Customize Social Robots Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Social Robots market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Social Robots's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Social Robots
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Social Robots market in 2023?
Social Robots Industry Analysis
Social Robots Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Social Robots Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Social Robots Market Report:
In Europe, the market is projected to grow from $1.78 billion in 2023 to approximately $4.01 billion by 2033. The region is focusing on integrating social robots in various sectors, such as healthcare and education, enhancing citizens' quality of life.Asia Pacific Social Robots Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is forecasted to witness substantial growth, with the market size expected to grow from $1.28 billion in 2023 to $2.88 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increased investments in robotics technology and rising consumer awareness of automation's benefits.North America Social Robots Market Report:
North America remains a significant market for social robots, with a size expected to increase from $2.44 billion in 2023 to $5.50 billion in 2033. High adoption rates of technology and a robust healthcare system are key drivers.South America Social Robots Market Report:
The South American market for social robots is anticipated to expand from $0.43 billion in 2023 to $0.98 billion by 2033. The growth is primarily due to the gradual adoption of robotics in education and healthcare.Middle East & Africa Social Robots Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is estimated to increase from $0.57 billion in 2023 to $1.29 billion by 2033. There is a rising interest in robotics for customer service in hospitality and healthcare sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
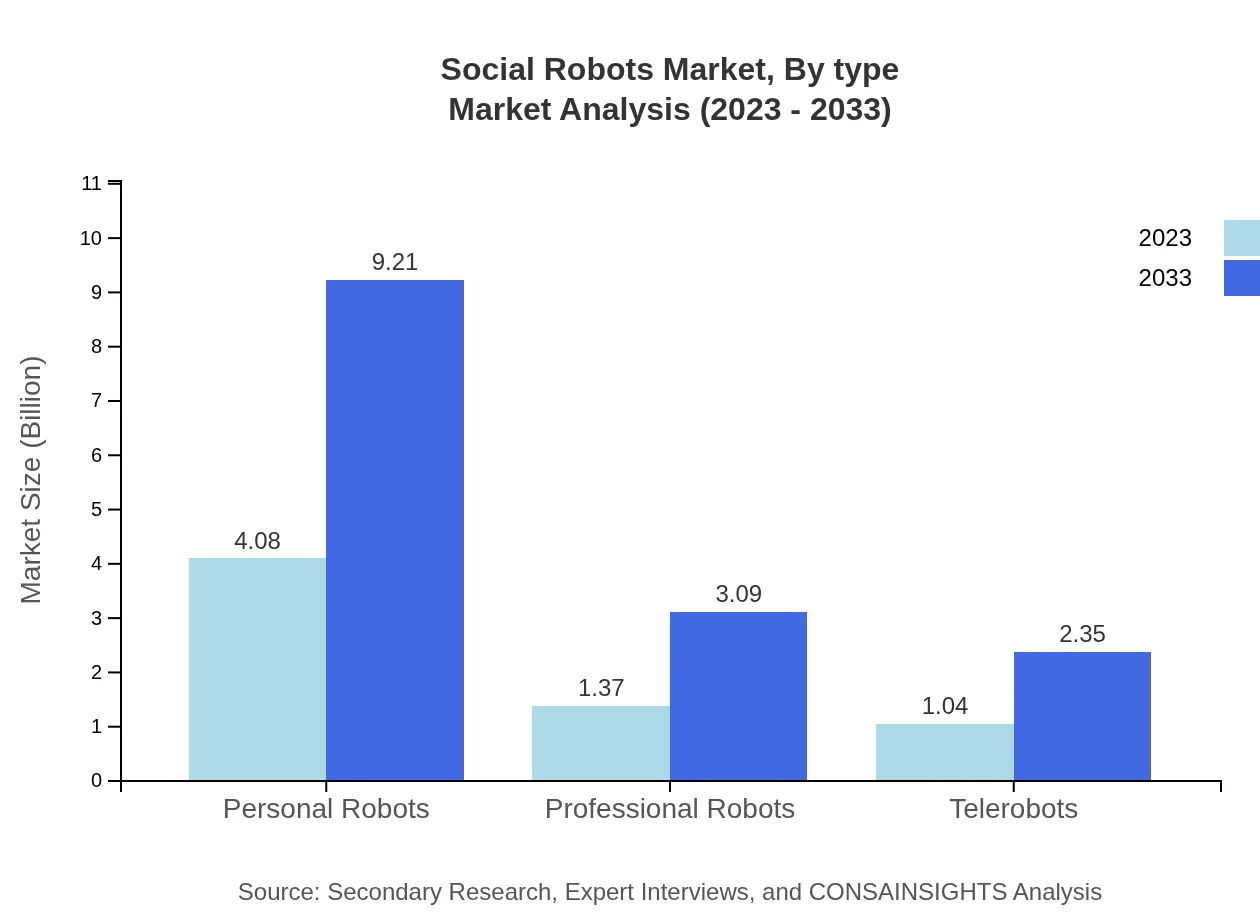
Social Robots Market Analysis By Type
The market is notably led by Personal Robots, which will see significant growth from $4.08 billion in 2023 to $9.21 billion by 2033, capturing 62.84% share. Professional Robots follow with growth from $1.37 billion to $3.09 billion (21.1% share). In addition, Telerobots are expected to grow from $1.04 billion to $2.35 billion (16.06% share).
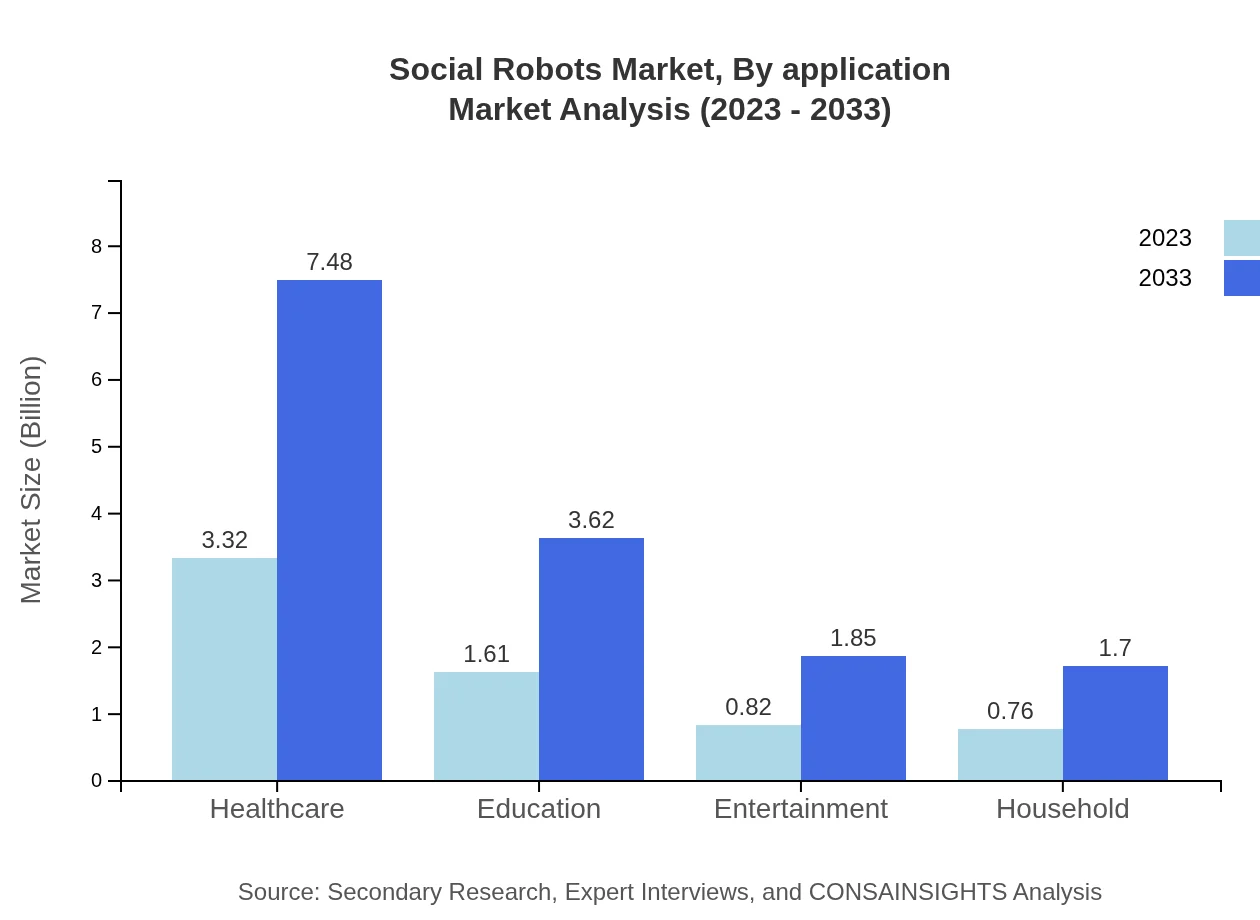
Social Robots Market Analysis By Application
The major applications include Healthcare, which accounts for 51.02% of the market with growth from $3.32 billion to $7.48 billion. Education represents 24.7% with an increase from $1.61 billion to $3.62 billion. Entertainment also plays a role, growing from $0.82 billion to $1.85 billion (12.66%).
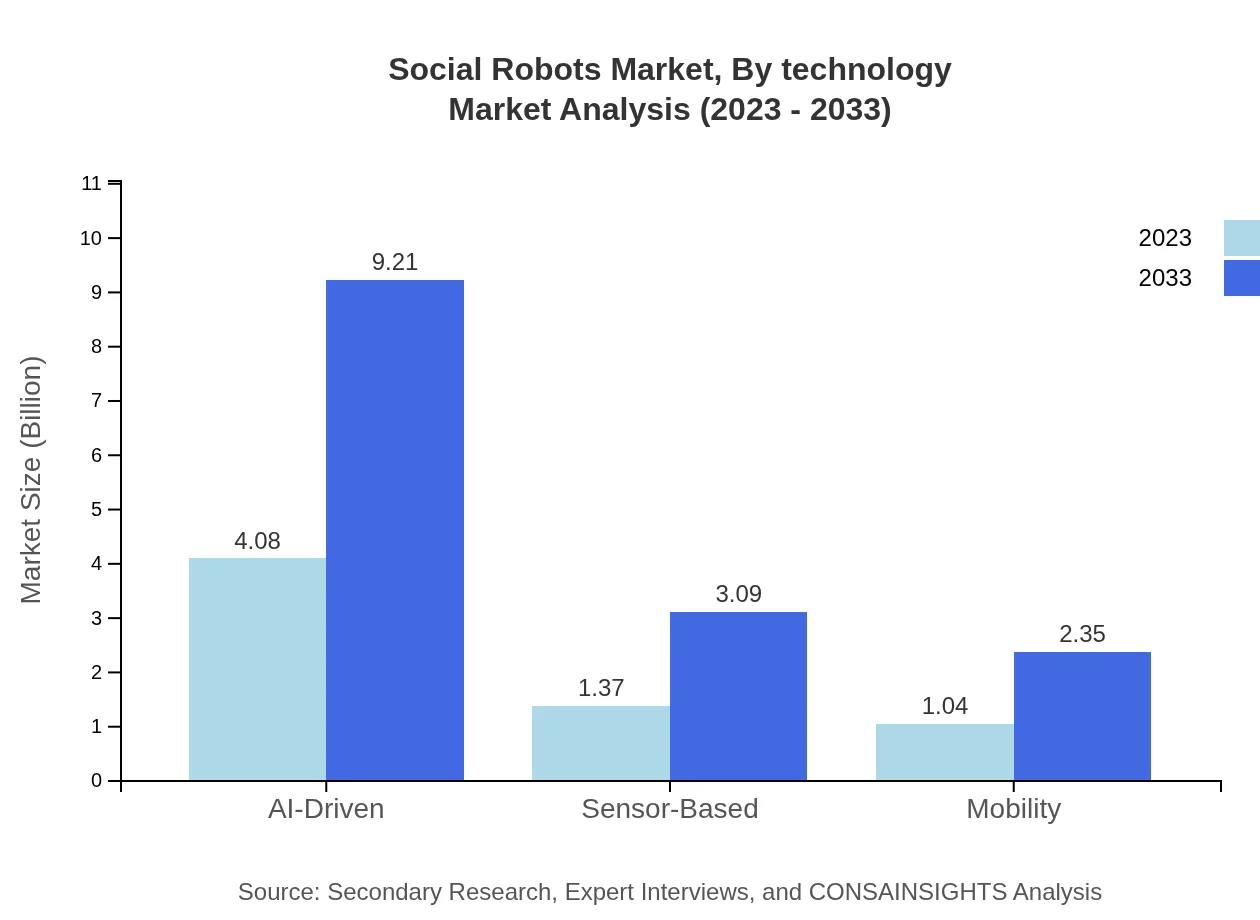
Social Robots Market Analysis By Technology
AI-Driven technology dominates the market, holding a 62.84% share, with growth from $4.08 billion to $9.21 billion. Sensor-Based technology follows with a 21.1% share, increasing from $1.37 billion to $3.09 billion, indicating a trend towards smarter and more interactive robots.
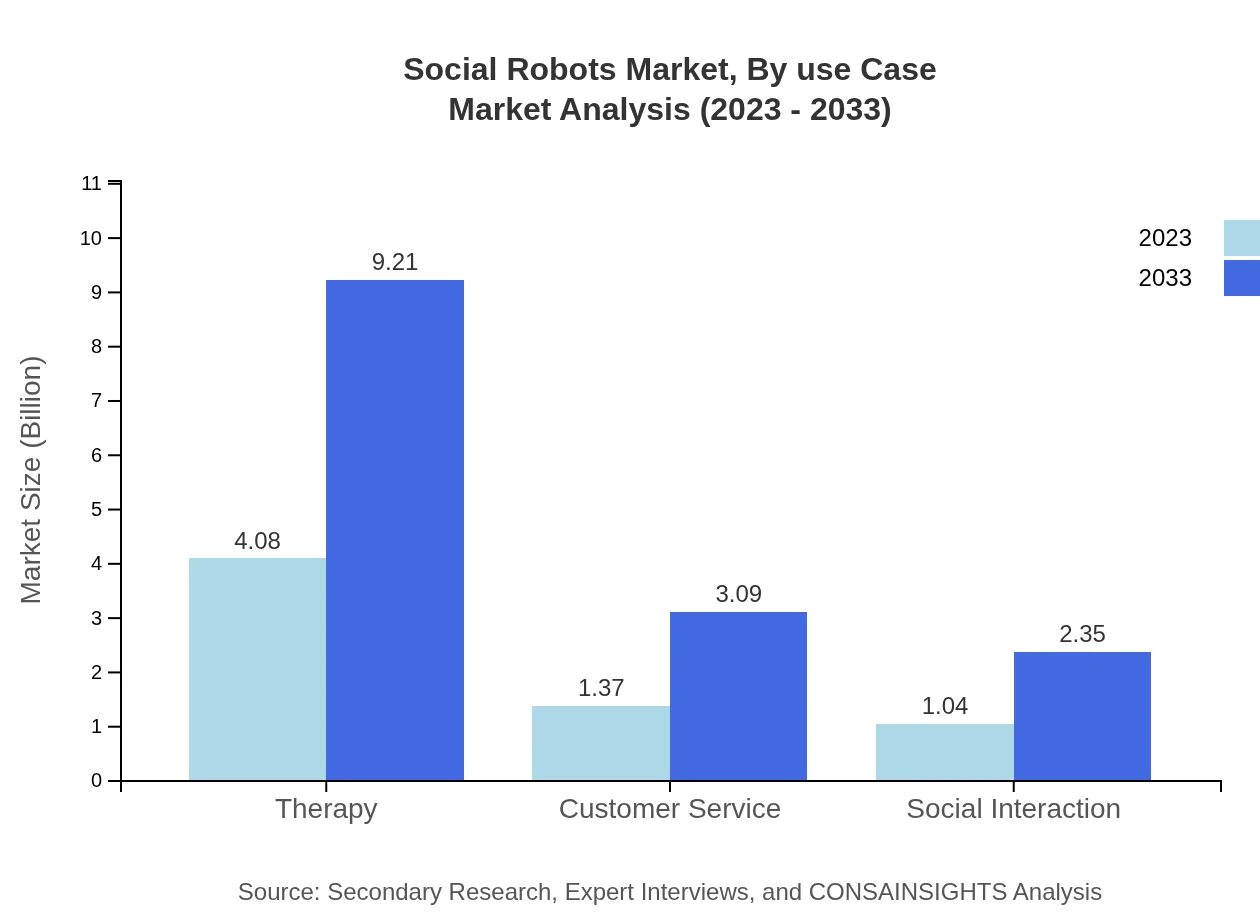
Social Robots Market Analysis By Use Case
Healthcare will significantly benefit from social robots, driven by an increasing focus on patient engagement. The customer service sector is also thriving, expected to rise from $1.37 billion to $3.09 billion over the forecast period, indicating a growing reliance on robots in service industries.
Social Robots Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Social Robots Industry
SoftBank Robotics:
Known for its humanoid robot Pepper, SoftBank Robotics focuses on social interaction and has a diverse portfolio targeting education, healthcare, and entertainment.Boston Dynamics:
A leader in robotics known for its innovative models like Spot. They focus on advanced robotics applications across various industries.iRobot Corporation:
Famous for its Roomba line, iRobot is a pioneer in home robotics, with a focus on automation and smart home integration.Ubtech Robotics:
Specializes in humanoid and interactive robots for education and customer service, driving innovation in robotics accessibility.Intuition Robotics:
Focused on developing social companions for senior care, enhancing emotional well-being through robotics.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of social Robots?
The global market size for social robots in 2023 is approximately $6.5 billion, with a projected CAGR of 8.2% leading to significant growth through 2033. This market encompasses personal, professional, and therapy robots among others.
What are the key market players or companies in this social robots industry?
Key players in the social robots industry include established technology leaders and innovative startups focusing on AI, interactive designs, and applications across various sectors like healthcare and education, contributing to ongoing market expansion.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the social robots industry?
Growth in the social robots industry is primarily driven by advancements in AI technology, increasing demand for automation in various sectors, and the growing acceptance of robots for social interaction and customer service applications.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the social robots market?
The fastest-growing region in the social robots market is Europe, projected to grow from $1.78 billion in 2023 to $4.01 billion by 2033, showing a robust expansion that reflects increasing investment in robotics and automation across industries.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the social robots industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of clients, allowing for detailed insights into the social robots industry including regional trends, competitive landscape, and segment analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this social robots market research project?
From this market research project, you can expect comprehensive insights including detailed market analysis, trend forecasts, segment data, competitive landscape reports, and actionable recommendations designed to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of social robots?
Current trends in the social robots market include increased integration of AI and machine learning for enhanced interactivity, rising consumer interest in home automation solutions, and expanding applications in sectors such as healthcare, education, and customer service.