Soybean Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: soybean
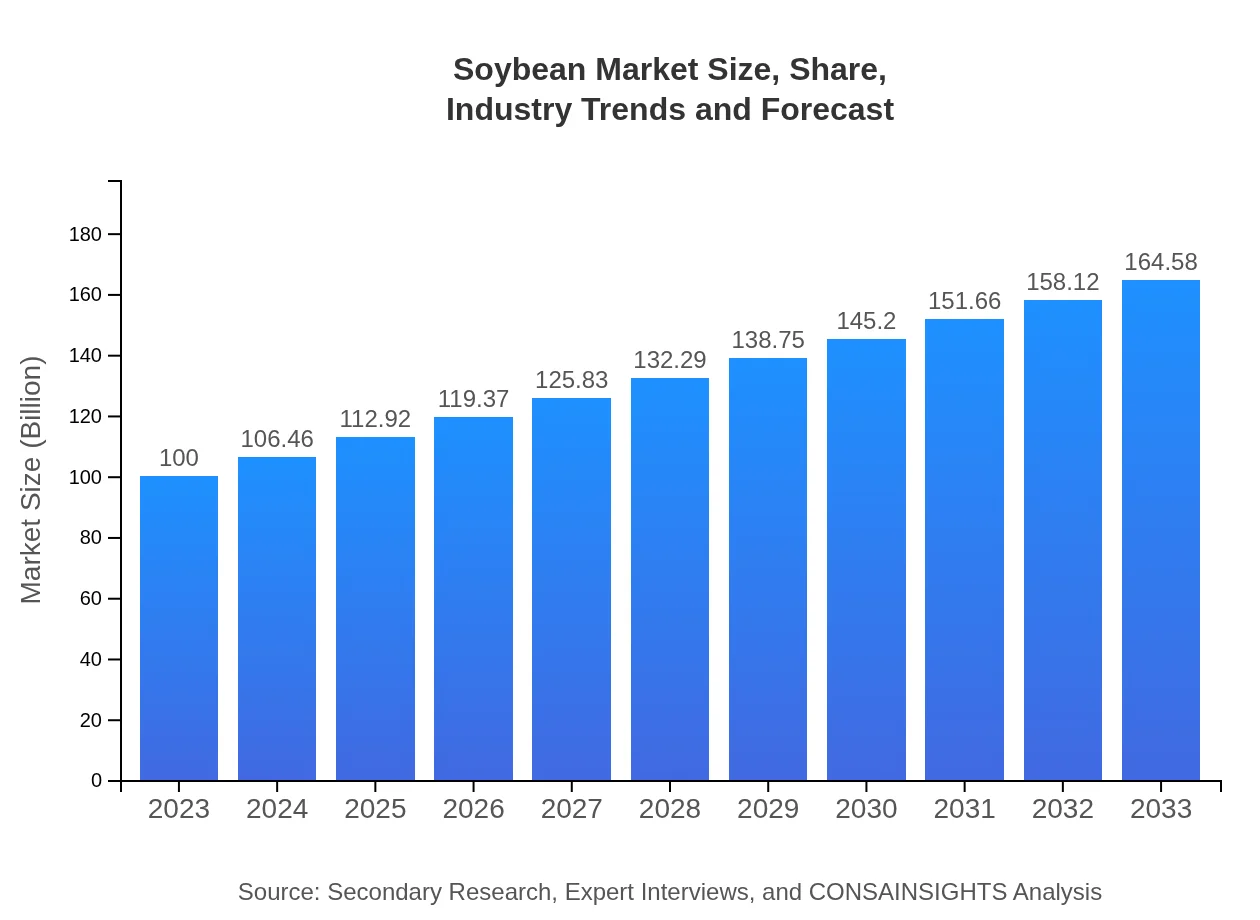
Soybean Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global soybean market from 2023 to 2033. It covers market dynamics, regional insights, technological advancements, key players, and future trends to aid stakeholders in making informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cargill, Inc., Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM), Bunge Limited, Louis Dreyfus Company, Wilmar International Limited |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Soybean Market Overview
Customize Soybean Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Soybean market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Soybean's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Soybean
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Soybean market in 2023?
Soybean Industry Analysis
Soybean Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Soybean Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Soybean Market Report:
Europe's soybean market is anticipated to grow from USD 32.49 billion in 2023 to USD 53.47 billion by 2033. This growth is supported by increasing health-conscious consumers and a shift towards plant-based diets, driving demand for soy-based products.Asia Pacific Soybean Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region holds significant promise for the soybean market, with a market size projected to grow from USD 18.92 billion in 2023 to USD 31.14 billion by 2033. The demand is driven primarily by countries like China and India, where soybean consumption for oil and animal feed is increasing robustly due to rising affluence and population growth.North America Soybean Market Report:
North America, particularly the United States, is one of the largest soybean producers globally. The market is expected to expand from USD 35.87 billion in 2023 to USD 59.03 billion by 2033, primarily fueled by robust domestic demand and export activities.South America Soybean Market Report:
In South America, especially Brazil and Argentina, the market is progressing from USD 1.21 billion in 2023 to USD 1.99 billion by 2033. The region remains a leading exporter of soybeans, capitalizing on its agricultural landscape suited for high-yield production.Middle East & Africa Soybean Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the soybean market is projected to increase from USD 11.51 billion in 2023 to USD 18.94 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by rising meat consumption and related feed requirements, alongside efforts to improve agricultural methods in various countries.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
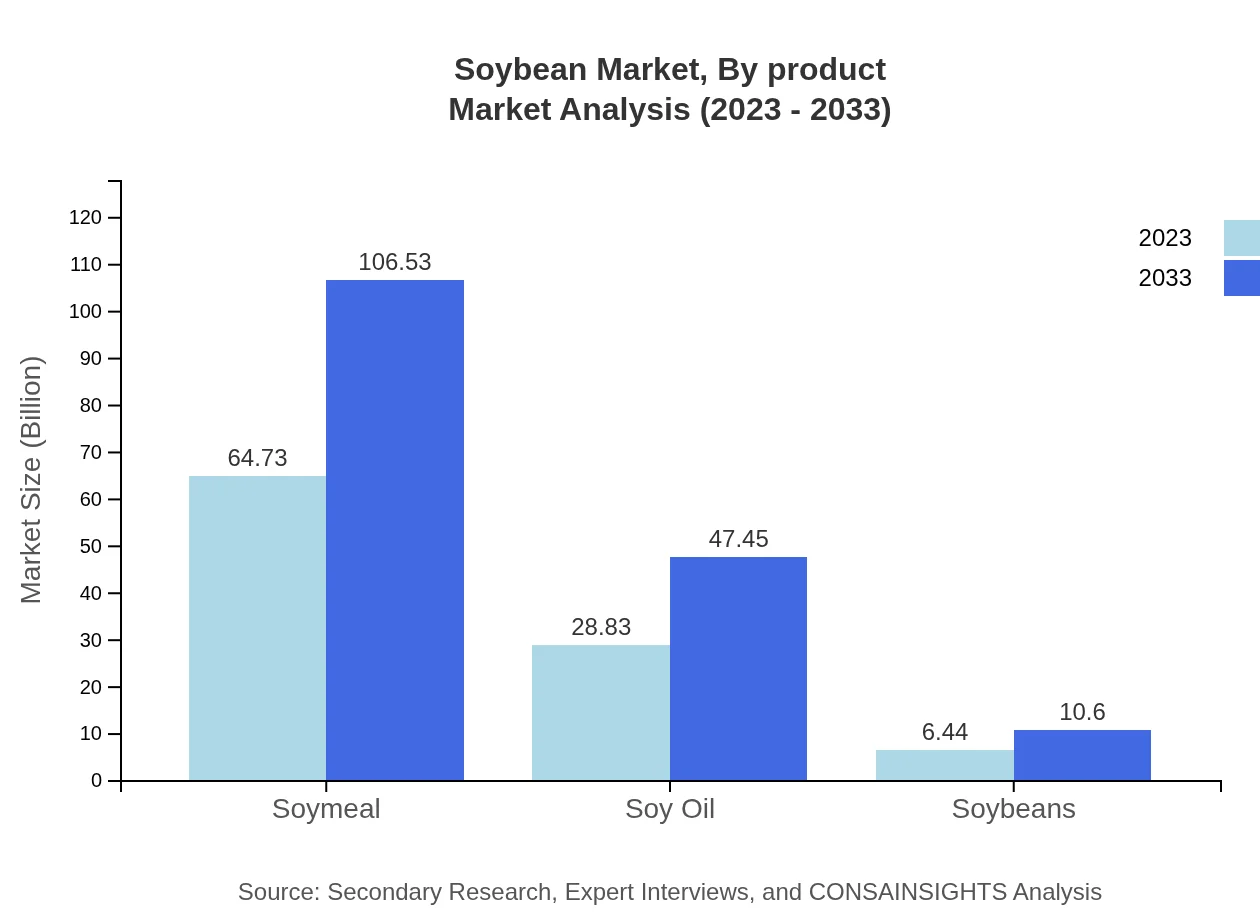
Soybean Market Analysis By Product
The whole soybean market is substantial, projected to rise from USD 84.01 billion in 2023 to USD 138.26 billion by 2033. Other product segments include soybean meal, which is vital for animal feed, and soybean oil, both essential for food production and industrial applications.
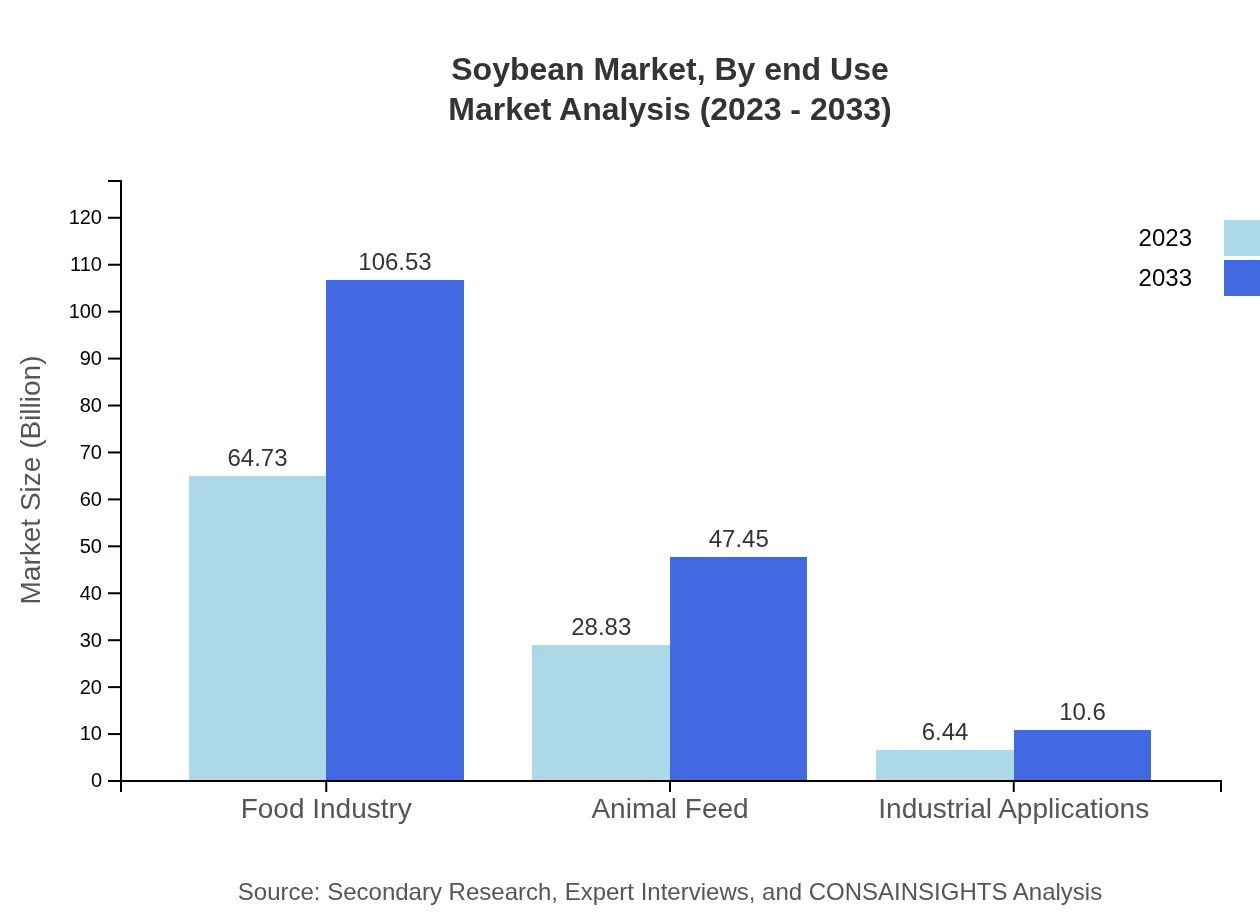
Soybean Market Analysis By End Use
The food industry holds the largest share of the soybean market, with expected growth from USD 64.73 billion in 2023 to USD 106.53 billion by 2033. Additionally, the animal feed segment is projected to see significant growth, expanding from USD 28.83 billion to USD 47.45 billion due to increasing livestock farming.
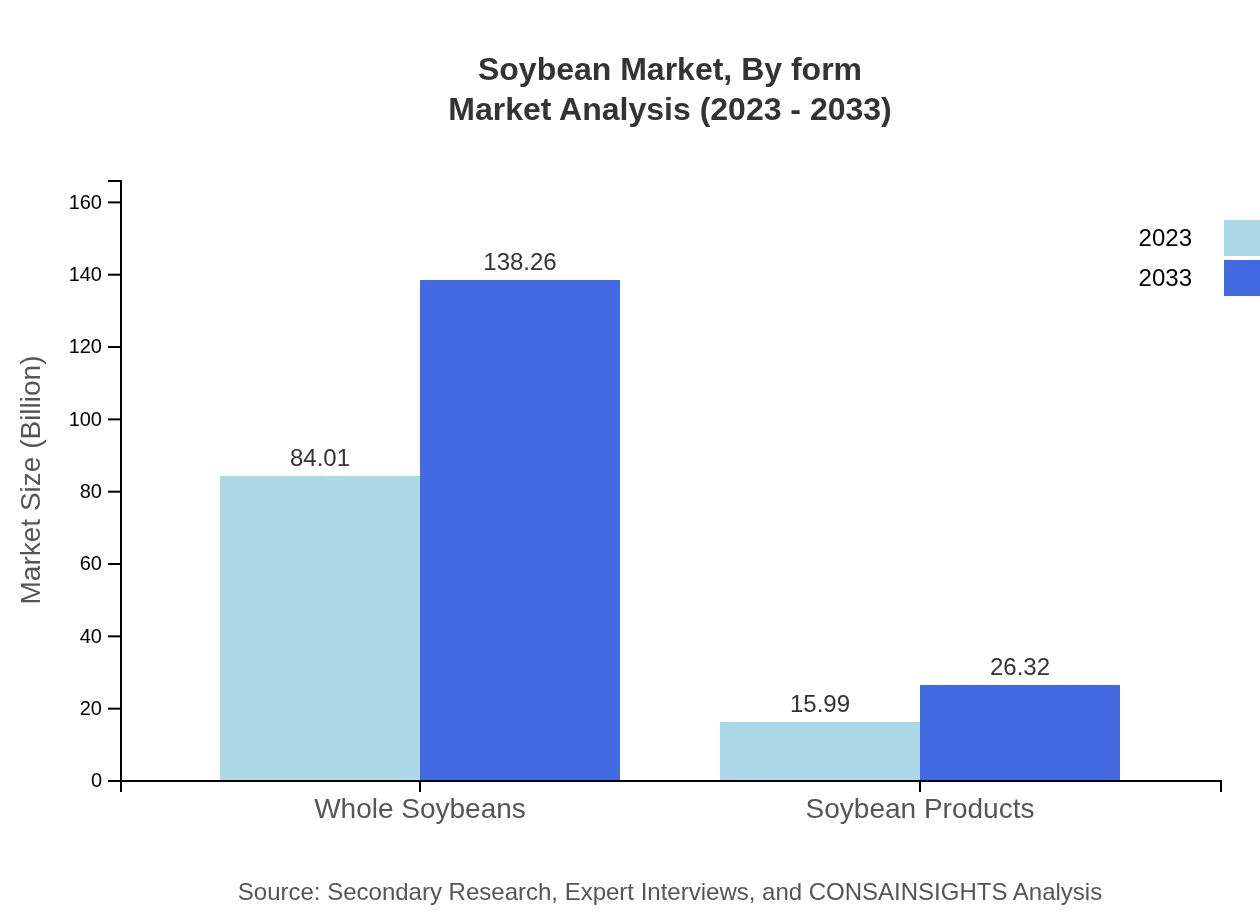
Soybean Market Analysis By Form
In terms of form, soybeans are marketed as whole beans, soybean oil, and soybean meal. Whole soybeans have a leading market size, whereas processed products like soy oil are increasingly gaining importance due to their diverse applications in cooking and food manufacturing.
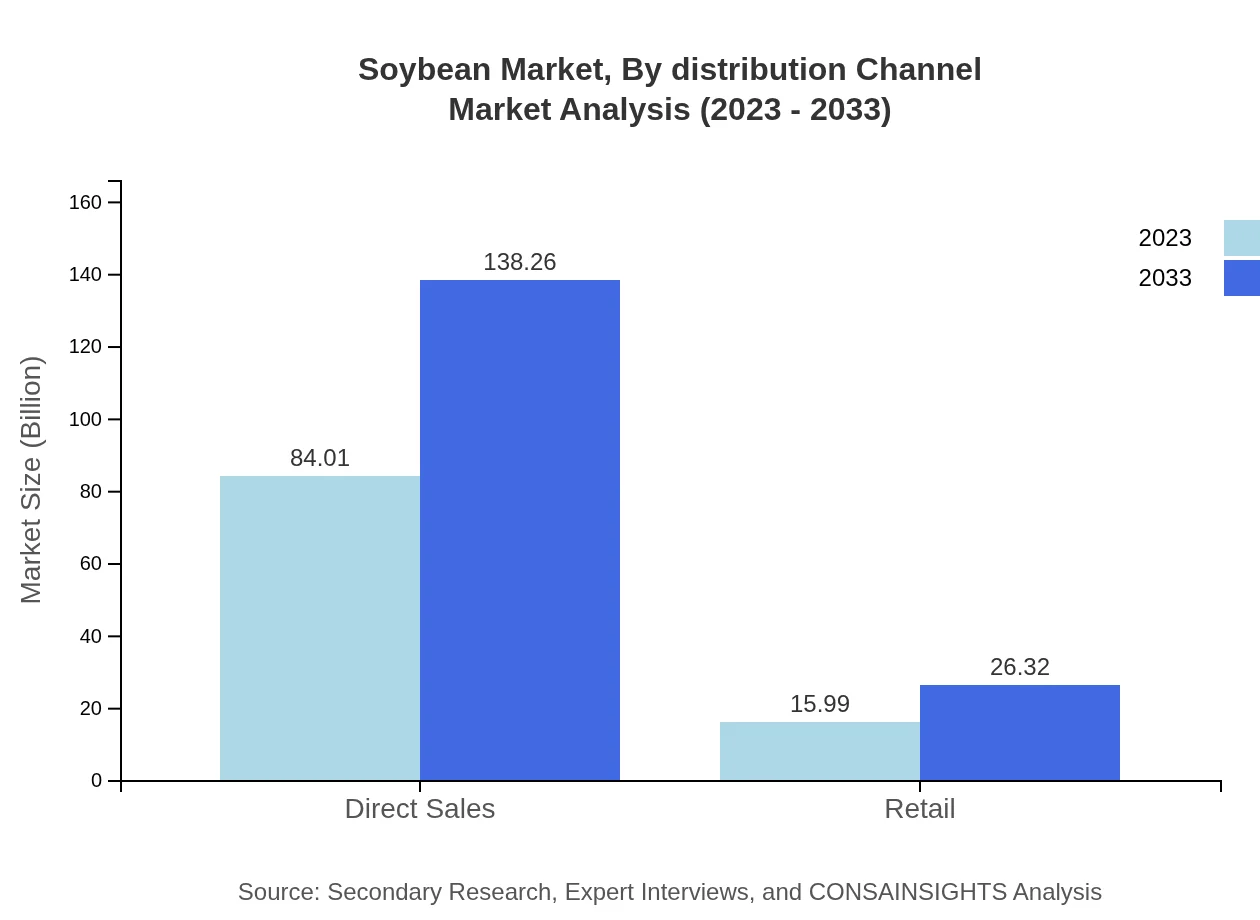
Soybean Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The direct sales segment dominates the distribution channels, with a market expansion from USD 84.01 billion to USD 138.26 billion. Retail channels, including supermarkets and online platforms, also play a crucial role in reaching consumers, growing from USD 15.99 billion to USD 26.32 billion during the forecast period.
Soybean Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Soybean Industry
Cargill, Inc.:
Cargill is a major player in the global soybean market, involved in the production, processing, and distribution of soybean-based products, playing a critical role in supply chain dynamics.Archer Daniels Midland Company (ADM):
ADM is an American multinational food processing and trading corporation that is a leading producer of soybean oil and meal, with significant investments in sustainable agriculture.Bunge Limited:
Bunge is a well-established agribusiness and food company that processes soybeans into oil and meal while focusing on viable agriculture practices to promote growth.Louis Dreyfus Company:
Louis Dreyfus Company is a global merchant and processor of agricultural goods, including soybeans, known for its commitment to sustainable sourcing and market leadership.Wilmar International Limited:
Wilmar is one of Asia's leading agribusiness groups, integrating oil palm and soybean farming, processing, and trading to maximize value and sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of soybean?
The soybean market is projected to reach a size of approximately $100 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5% during the forecast period. This growth signifies expanding global demand and consumption.
What are the key market players or companies in this soybean industry?
The soybean industry is characterized by several key players, including agricultural giants, food processing companies, and biotechnology firms. These companies are integral in driving innovation and meeting global demand for soybean products.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the soybean industry?
Growth in the soybean industry is primarily driven by increased demand for plant-based protein, expansion of biofuel production, and rising utilization of soy products in livestock feed. Additionally, consumer trends favoring sustainable food sources contribute significantly.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the soybean market?
The fastest-growing region in the soybean market is North America, projected to expand from $35.87 billion in 2023 to $59.03 billion by 2033. Other notable growth can be observed in Asia Pacific and Europe, reflecting rising demand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the soybean industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the soybean industry. Clients can receive tailored analysis based on specific needs, geographical focus, and product segmentation to drive strategic decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this soybean market research project?
Deliverables from this soybean market research project typically include detailed market size reports, growth forecasts, competitive analysis, regional breakdowns, and insights into industry trends and consumer behaviors.
What are the market trends of soybean?
Key market trends in soybean include increased consumer preference for bio-based products, growth in organic soy farming, and advancements in genetic modification aimed at improving yields. The market is also witnessing innovation in soybean processing techniques.