Soybean Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: soybean-seed
Soybean Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Soybean Seed industry, covering key insights, market trends, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It includes market size, growth rates, regional insights, and the performance of various segments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
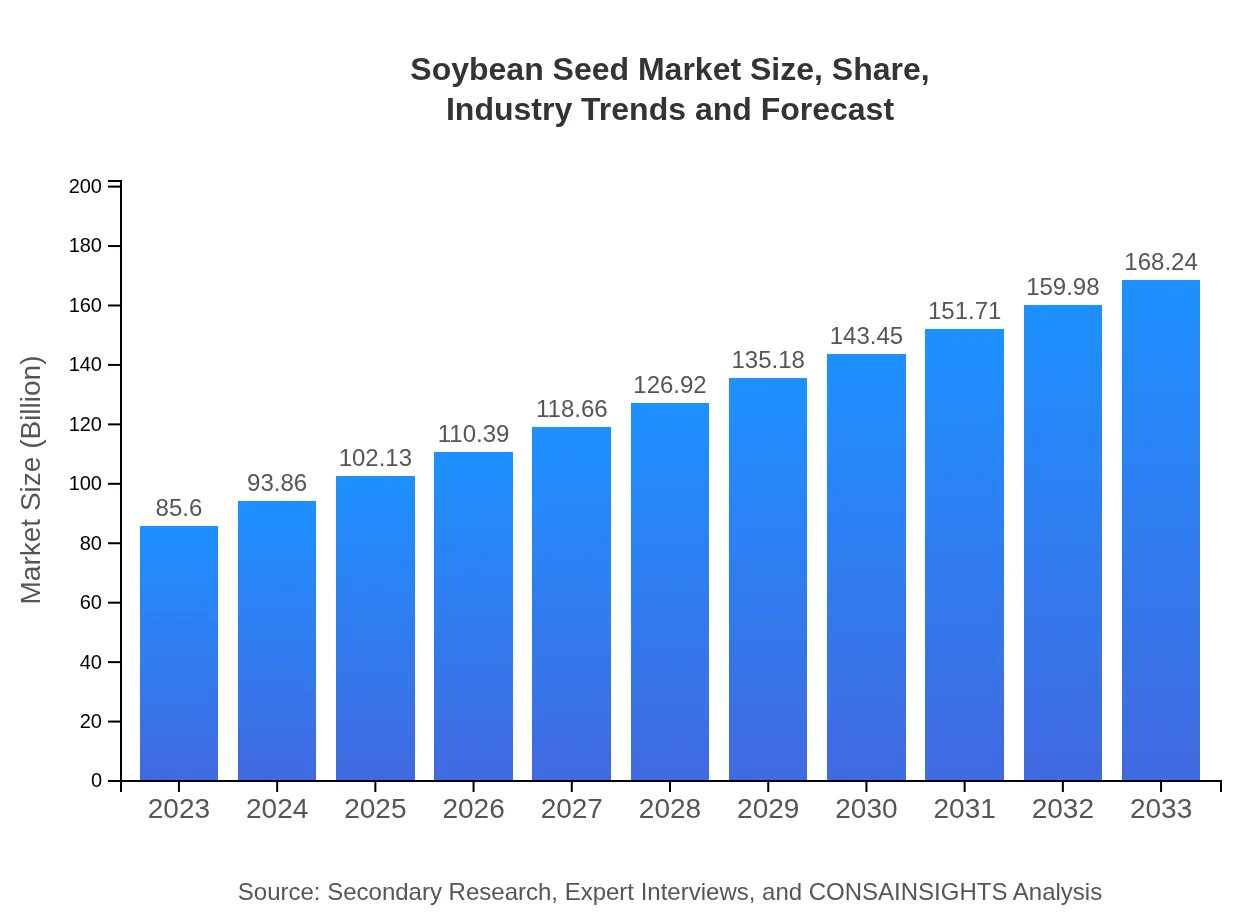
| 2023 Market Size | $85.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $168.24 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, DuPont Pioneer (Corteva Agriscience), Land O'Lakes Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Soybean Seed Market Overview
Customize Soybean Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Soybean Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Soybean Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Soybean Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Soybean Seed market in 2023?
Soybean Seed Industry Analysis
Soybean Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Soybean Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Soybean Seed Market Report:
Europe's market is valued at about $22.61 billion currently and is predicted to reach $44.43 billion by 2033, driven by a growing trend towards sustainable farming and organic products. Regulations on food safety and environmental impact encourage the adoption of non-GMO and organic seed varieties in many European countries.Asia Pacific Soybean Seed Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Soybean Seed market is valued at approximately $16.57 billion in 2023, expecting to grow to $32.57 billion by 2033. The region benefits from high agricultural demands and increased production efficiency driven by modern farming technologies. Countries like China and India are crucial players, focusing on enhancing their agriculture sector.North America Soybean Seed Market Report:
North America is expected to establish itself as the largest market, with a size of $30.08 billion in 2023 expected to grow to $59.12 billion by 2033. The U.S. alone is the largest producer of soybeans globally, supported by advanced agricultural techniques and substantial investment in biotechnology. Increasing demand from livestock and consumer markets further bolsters this growth.South America Soybean Seed Market Report:
South America, a significant hub for soybean cultivation, has its market estimated at $7.07 billion in 2023 and projected to reach $13.90 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina lead in production, driven by favorable climatic conditions and large expanses of arable land. The growth of agricultural cooperatives has also contributed to market expansion in this region.Middle East & Africa Soybean Seed Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region shows potential growth, with a market valuation of $9.27 billion in 2023, expected to double to $18.22 billion by 2033. Nations in this region are increasingly focusing on agriculture to meet rising food demands and improve food security, with investments in seed quality and technology.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
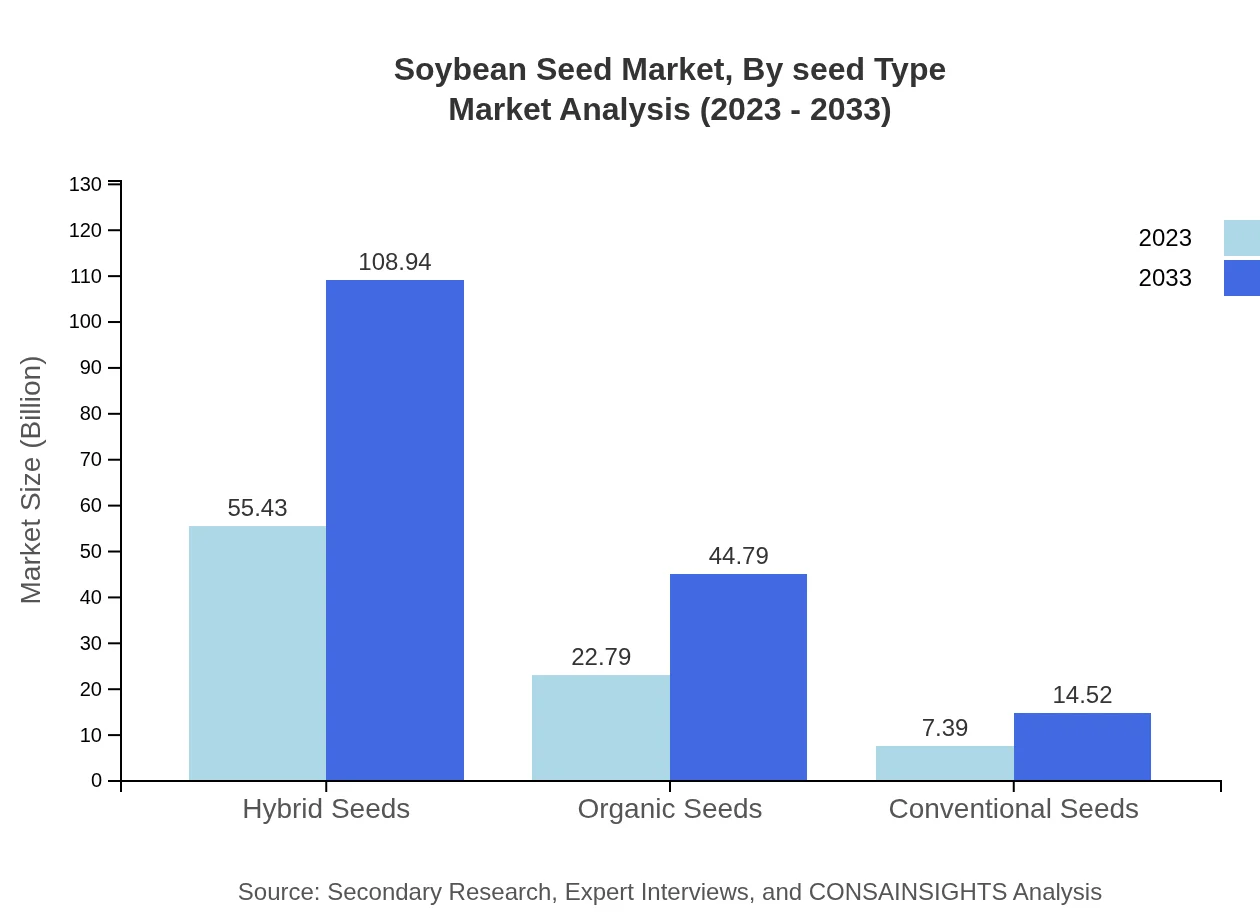
Soybean Seed Market Analysis By Seed Type
In the Soybean Seed market, hybrid seeds account for 64.75% market share in 2023, projected to continue dominating with a market size of $55.43 billion by 2033. Organic seeds are also gaining momentum, holding a 26.62% share and projected to grow from $22.79 billion in 2023 to $44.79 billion in 2033. Conventional seeds, while seeing modest growth, maintain a niche segment due to demand variations in regional markets.
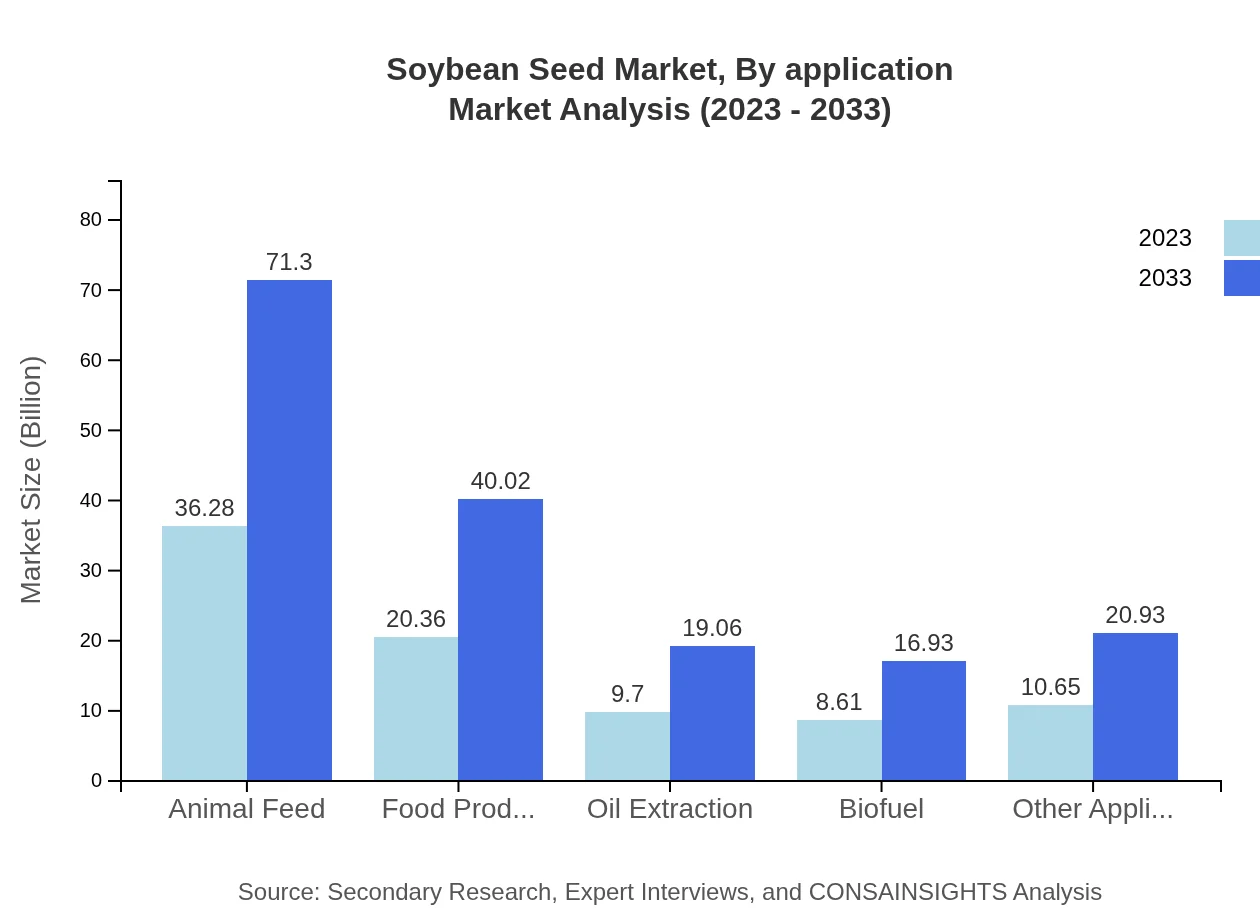
Soybean Seed Market Analysis By Application
Soybean seeds significantly contribute to various applications, with animal feed leading the market at $36.28 billion in 2023 and expected to rise to $71.30 billion by 2033. Food production follows, with a market size of $20.36 billion projected to reach $40.02 billion. Other applications, including biofuel and oil extraction, are emerging trends driven by renewable energy initiatives and sustainability practices.
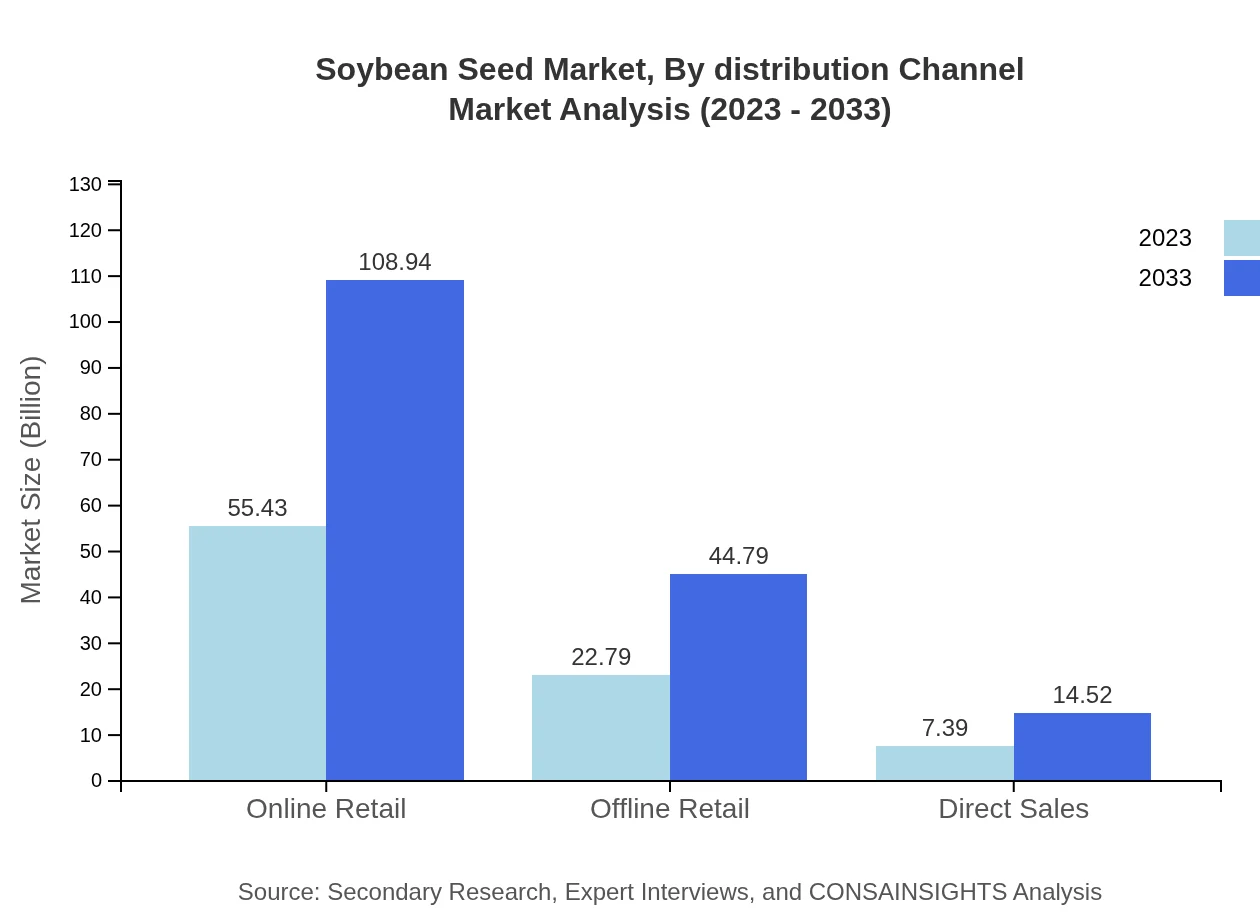
Soybean Seed Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channel analysis indicates that online retailing greatly influences the Soybean Seed market space, with a size of $55.43 billion in 2023 anticipated to double by 2033. Offline retail, while traditionally dominant, is expected to see slower growth rates, reinforcing the need for companies to enhance their online presence to capture emerging consumer demands.
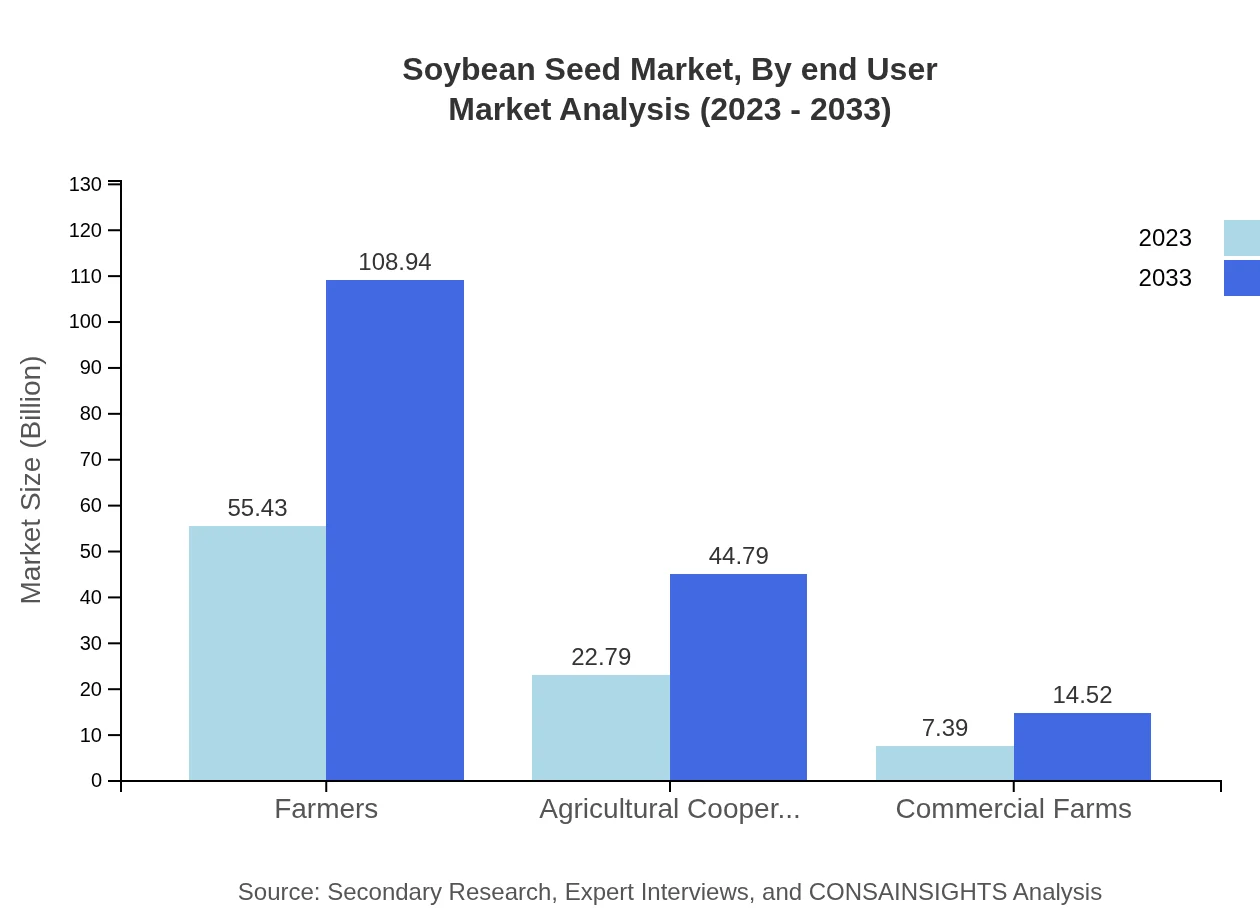
Soybean Seed Market Analysis By End User
Farmers constitute the largest end-user segment, with a significant market share of 64.75% in 2023 valued at $55.43 billion, projecting to grow substantially by 2033. Agricultural cooperatives show strong growth potential, moving from $22.79 billion to $44.79 billion, reflecting the trend of collective farming practices increasing in popularity across various regions.
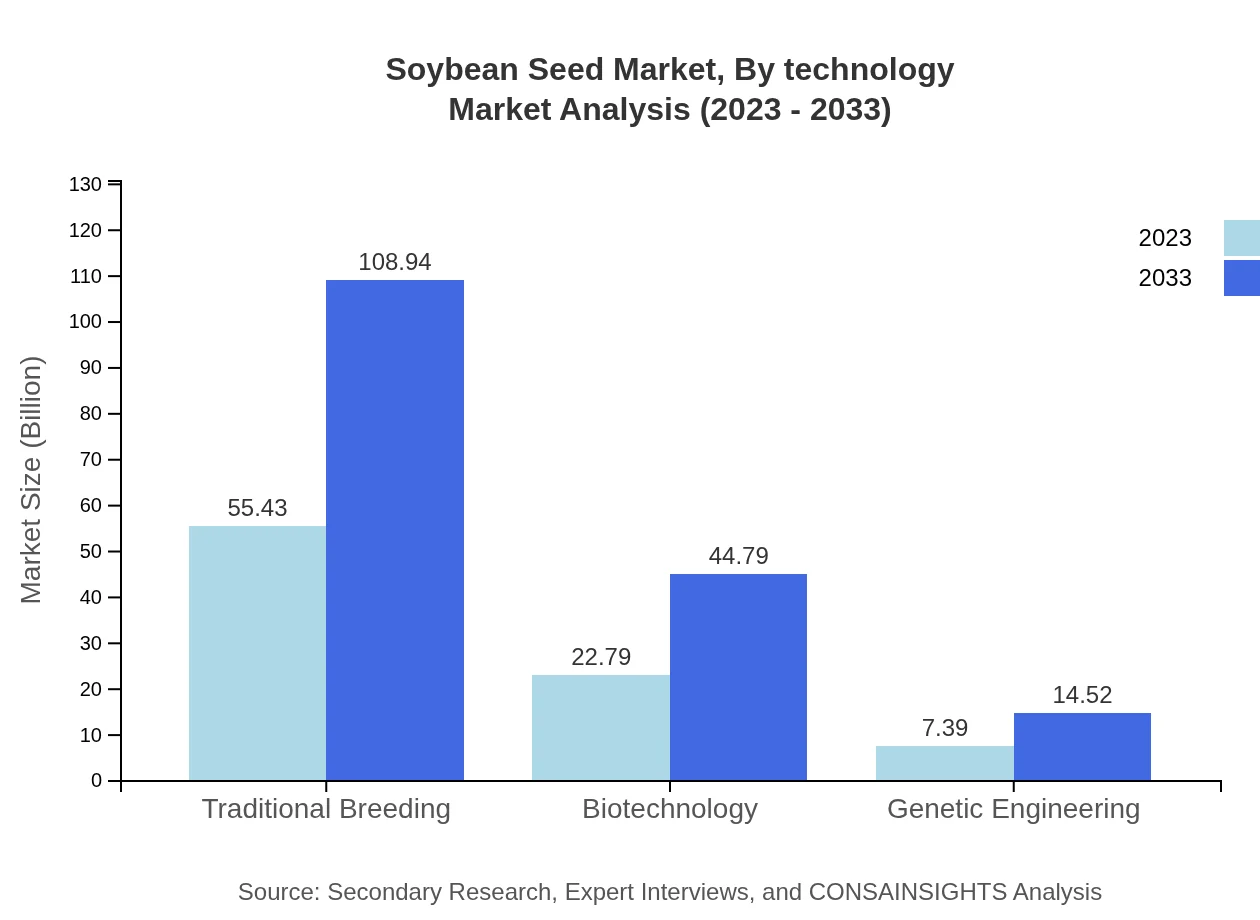
Soybean Seed Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements play a critical role in shaping the Soybean Seed market. By 2033, traditional breeding methods are expected to maintain a strong market position, while biotechnology and genetic engineering are anticipated to grow steadily, driven by the increasing need for higher yields and disease resistance. Consumer preferences for organic and naturally bred seeds are further influencing this segment.
Soybean Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Soybean Seed Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leader in agricultural products, Monsanto is known for its biotechnology advancements in soybean seeds, particularly its genetically modified varieties that enhance yield and pest resistance.Bayer AG:
Bayer is a significant player in the soybean seed market, focused on innovating integrated solutions that combine crop protection and high-performance seeds.Syngenta AG:
Syngenta specializes in high-quality seeds and crop protection products, offering a wide range of soybean varieties tailored to address the needs of different regions and farming practices.DuPont Pioneer (Corteva Agriscience):
Known for its extensive research and development, DuPont Pioneer provides advanced soybean seed solutions aimed at improving productivity and sustainability.Land O'Lakes Inc.:
An agricultural cooperative that plays a key role in the soybean seed market by providing farmers with quality seeds and effective agronomic support services.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of soybean Seed?
The global soybean seed market is currently valued at approximately $85.6 billion, with a projected CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2033. This growth reflects the increasing demand for soybeans due to their versatile applications in food, feed, and biofuel.
What are the key market players or companies in this soybean Seed industry?
Key players in the soybean seed market include major firms like Bayer, Corteva Agriscience, and Syngenta. These companies are recognized for their advanced research, development activities, and commitment to sustainable agricultural practices and high-quality seed production.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the soybean Seed industry?
The growth in the soybean seed industry is primarily driven by the rising global population, increasing demand for animal feed, and growing awareness of the health benefits of soybean products. Additionally, advancements in biotechnology further enhance crop yields and resistance to pests.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the soybean Seed market?
North America is projected to be the fastest-growing region in the soybean seed market, with a market size expected to grow from $30.08 billion in 2023 to $59.12 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to the significant agricultural output and adoption of advanced farming technologies.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the soybean Seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the soybean seed industry. Clients can request tailored insights that focus on specific regions, market segments, or trends that meet their strategic business needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this soybean Seed market research project?
Deliverables from the soybean seed market research project include detailed market analysis, trend reports, competitive landscape summaries, and regional forecasts. Additionally, clients receive segment-specific insights and strategic recommendations to guide decision-making.
What are the market trends of soybean Seed?
Current market trends in the soybean seed industry include the rising adoption of hybrid seeds, increasing investment in biotechnology, and an emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices. Additionally, there is a notable shift towards organic farming methods in response to consumer preferences.