Space Propulsion Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: space-propulsion
Space Propulsion Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Space Propulsion market, encompassing market size, trends, technological advancements, regional insights, and a forecast from 2023 to 2033 aimed at aiding stakeholders in strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
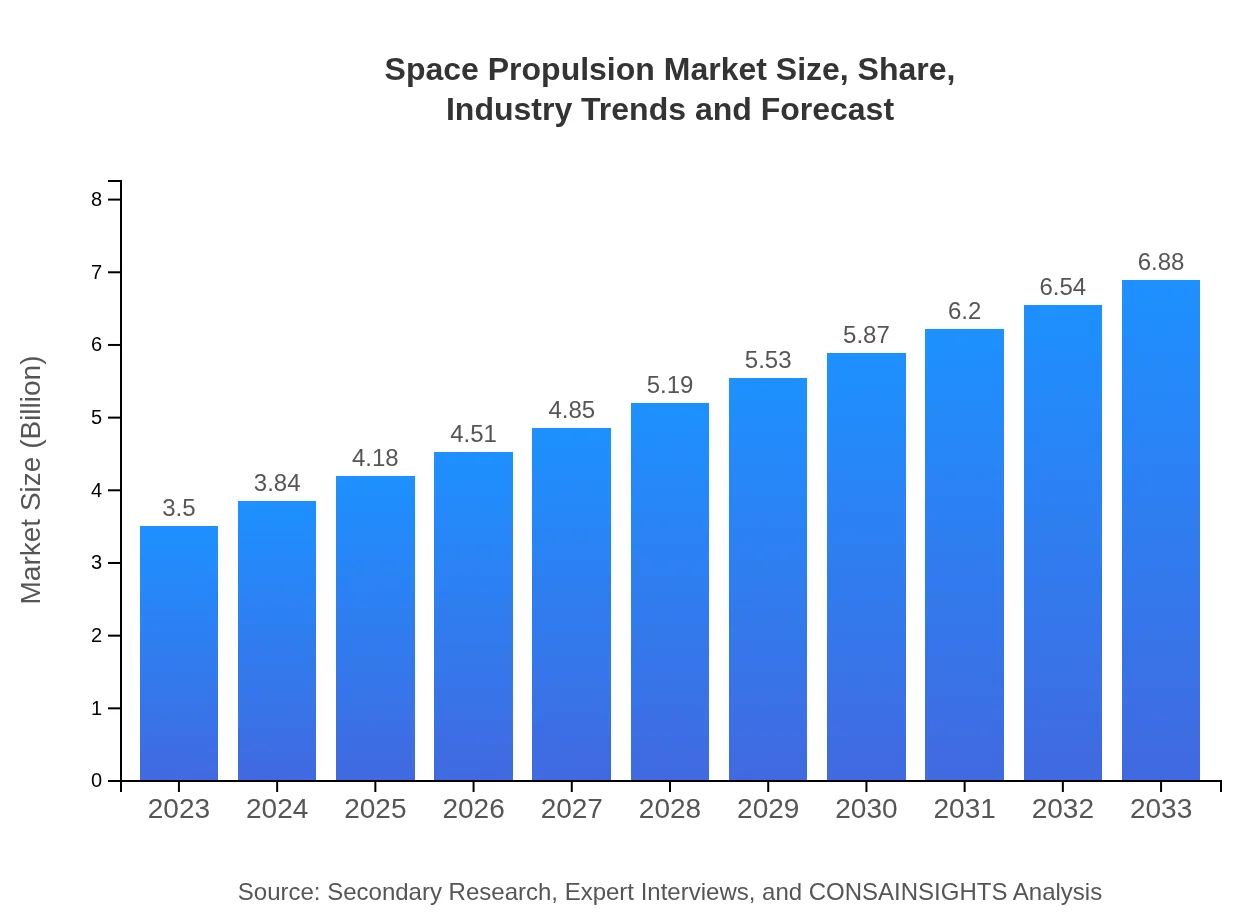
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $6.88 Billion |
| Top Companies | NASA, SpaceX, Blue Origin, Airbus Defence and Space, Arianespace |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Space Propulsion Market Overview
Customize Space Propulsion Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Space Propulsion market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Space Propulsion's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Space Propulsion
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Space Propulsion market in 2023 and 2033?
Space Propulsion Industry Analysis
Space Propulsion Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
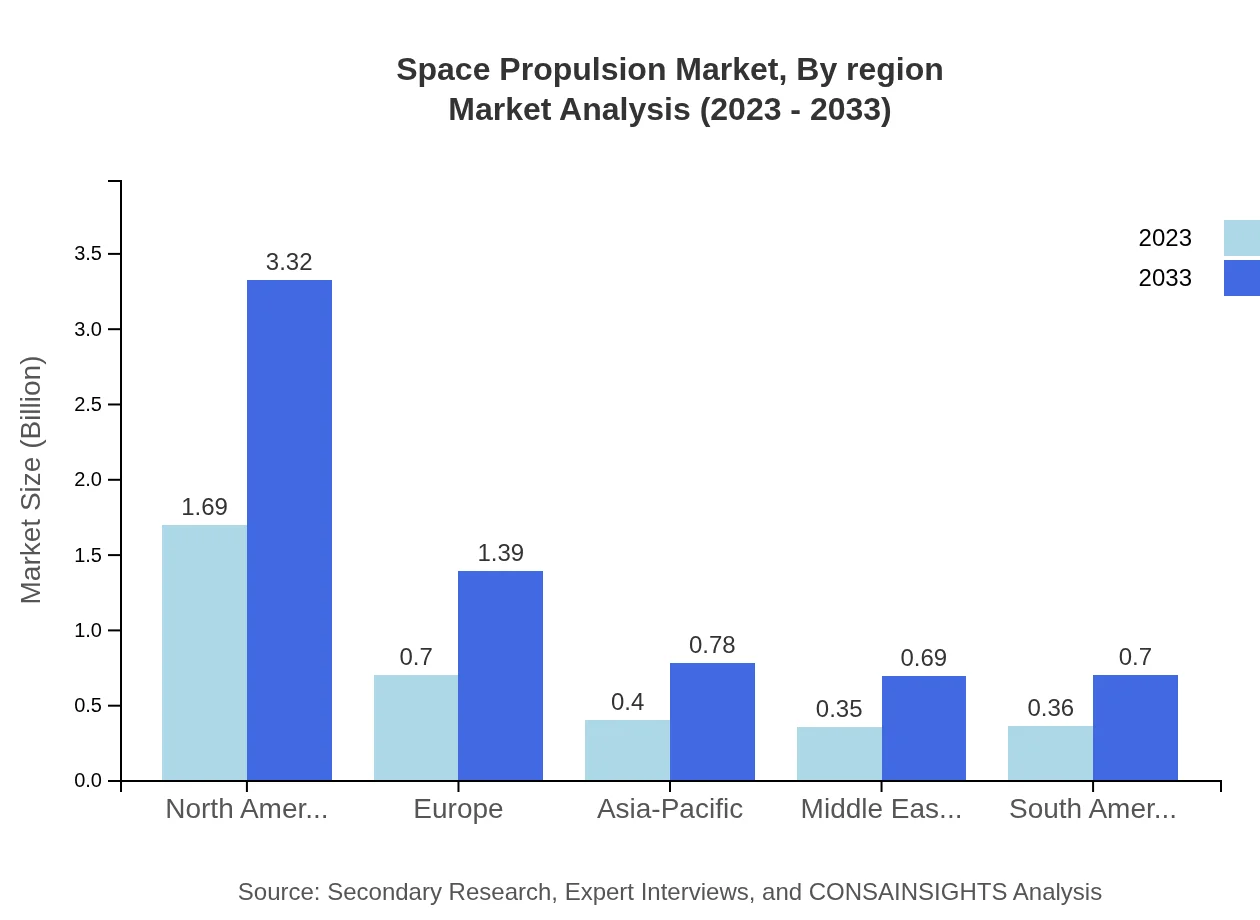
Space Propulsion Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Space Propulsion Market Report:
In Europe, the Space Propulsion market is anticipated to grow from $1.21 billion in 2023 to $2.38 billion by 2033. The European Space Agency's initiatives and the collaboration among nations have fostered a dynamic environment for propulsion system advancements.Asia Pacific Space Propulsion Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to grow significantly from $0.66 billion in 2023 to $1.29 billion in 2033, benefitting from increasing governmental funding in space exploration and commercial satellite launches. Countries like China and India are enhancing their space capabilities, making substantial investments in propulsion technologies.North America Space Propulsion Market Report:
North America dominates the Space Propulsion market, with a size of $1.13 billion in 2023 projected to surge to $2.22 billion by 2033. The region’s significant investment from NASA and private companies such as SpaceX is driving innovation in propulsion systems, focusing on reliability and efficiency.South America Space Propulsion Market Report:
South America’s Space Propulsion market is expected to increase from $0.19 billion in 2023 to $0.36 billion in 2033. Although currently smaller, the region is getting more attention as countries explore partnerships with larger space agencies and companies, especially for satellite deployments.Middle East & Africa Space Propulsion Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region’s market is expected to rise from $0.32 billion in 2023 to $0.63 billion by 2033. Increased interest in satellite technology and cooperation in research initiatives signify the region's potential for growth in space propulsion capabilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
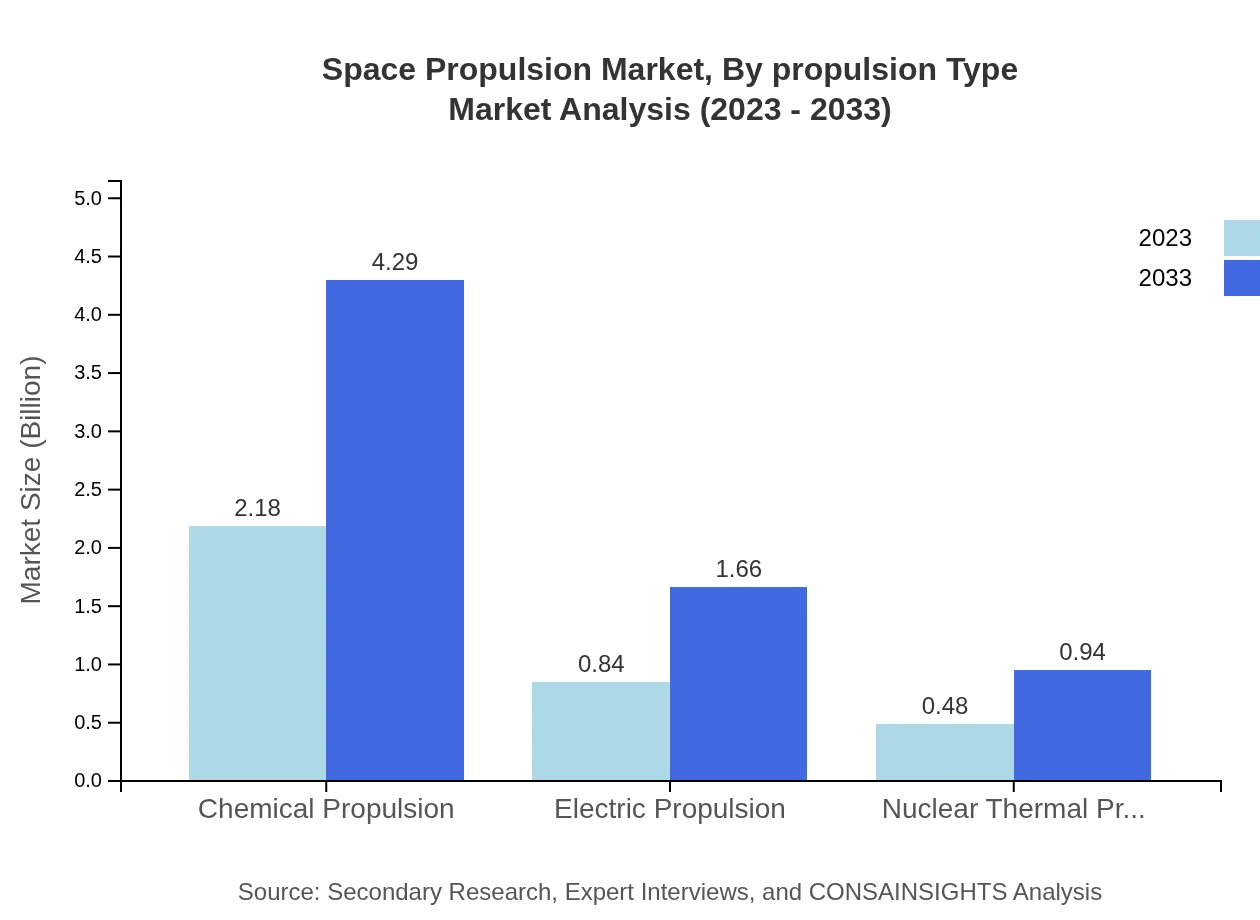
Space Propulsion Market Analysis By Propulsion Type
The propulsion type segment includes significant classifications such as chemical propulsion, which dominates with a market size of $2.18 billion in 2023 projected to grow to $4.29 billion by 2033. Electric propulsion has a growing share, with projections rising from $0.84 billion to $1.66 billion within the same period. Nuclear thermal propulsion will also see growth from $0.48 billion in 2023 to $0.94 billion in 2033 as advancements in nuclear technology become more accepted in space missions.
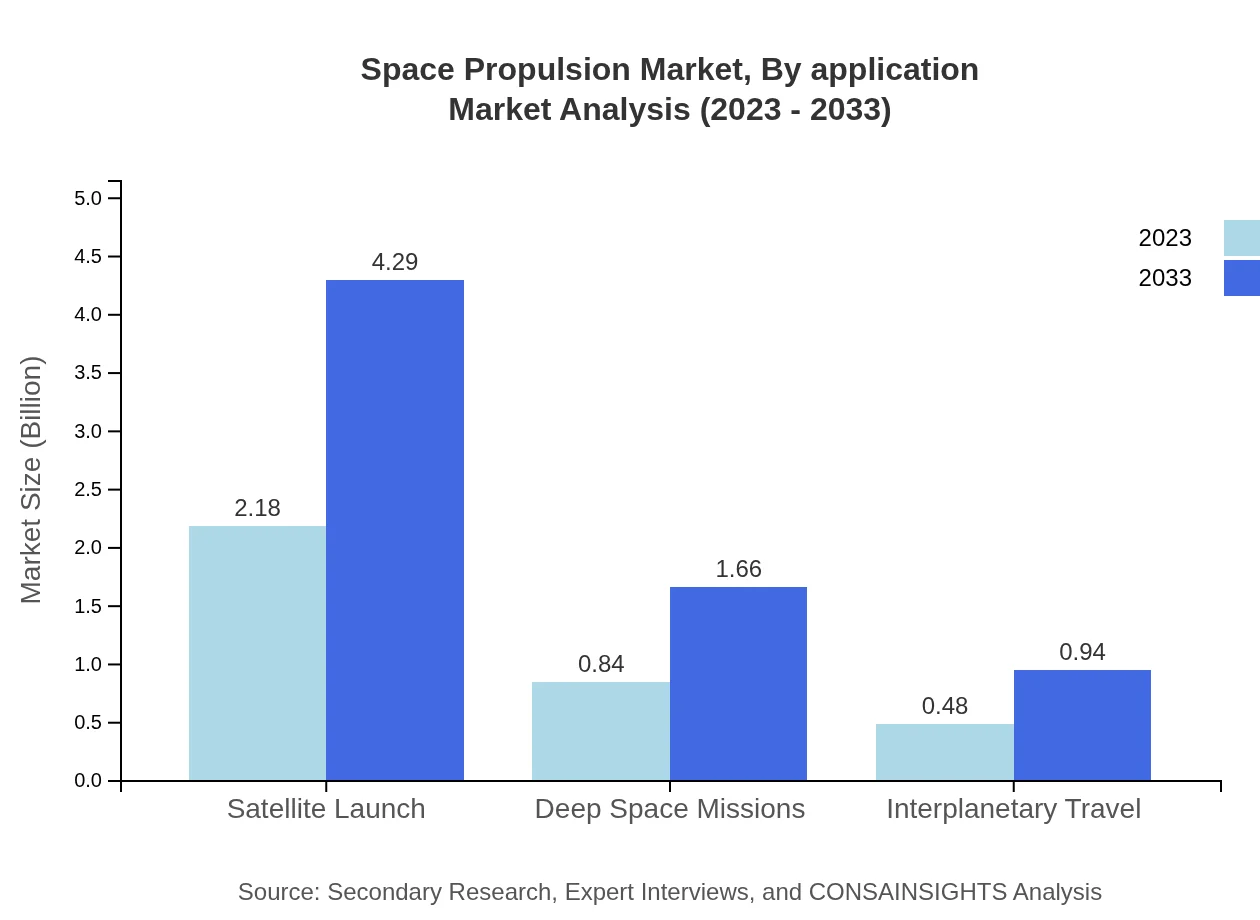
Space Propulsion Market Analysis By Application
The application segment captures satellite launch, deep space missions, and interplanetary travel. Satellite launches hold the largest market share at 62.3% in 2023 with an anticipated increase to $4.29 billion by 2033. Meanwhile, deep space missions, currently at $0.84 billion, are projected to reach $1.66 billion with growing interest in lunar and Martian exploration.
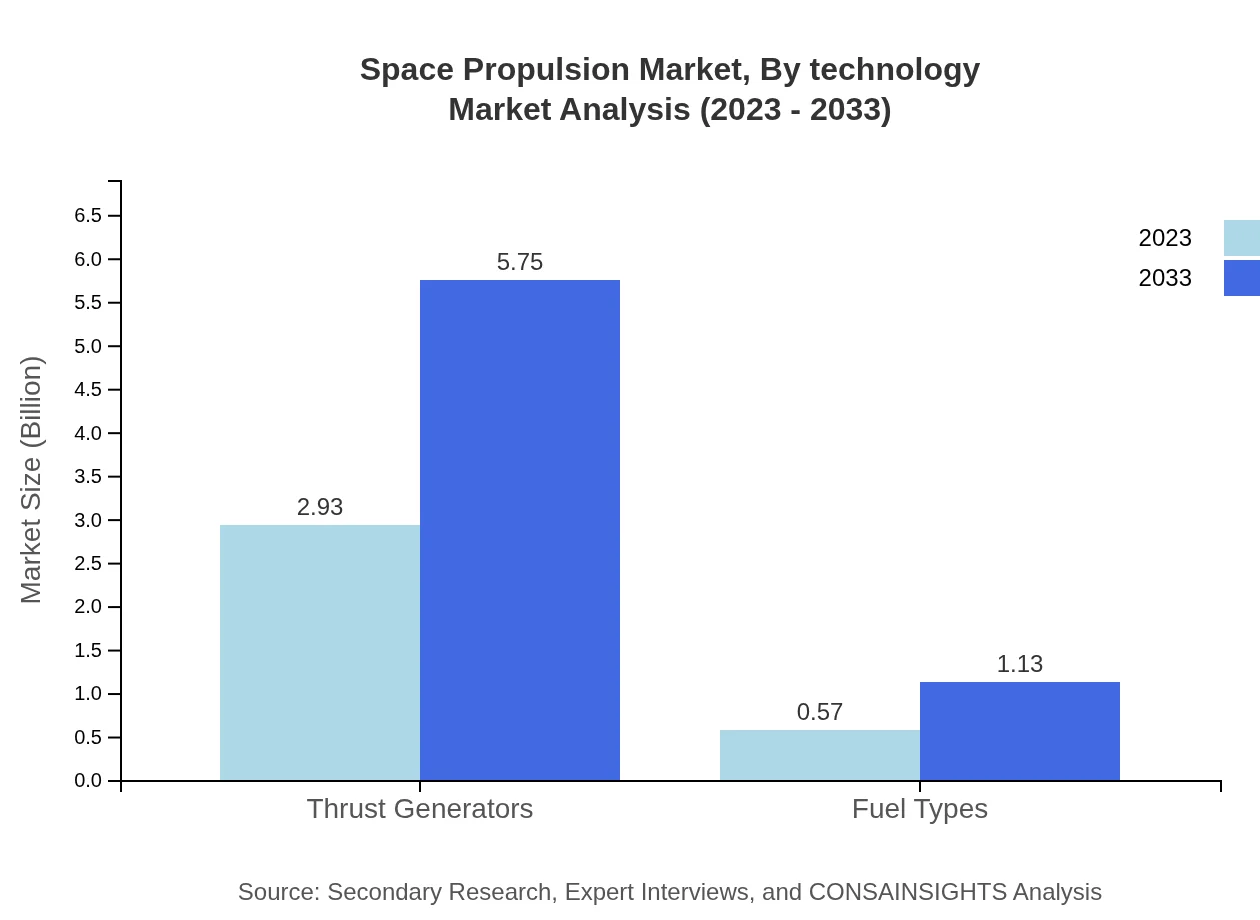
Space Propulsion Market Analysis By Technology
Technology advancement remains pivotal in shaping the Space Propulsion market. Innovations in thrust generators and hybrid propulsion technologies are gaining traction. The propulsion segment, particularly thrust generators, captured an impressive 83.62% share of the market in 2023 and is expected to remain a key focal point as efficiencies improve.
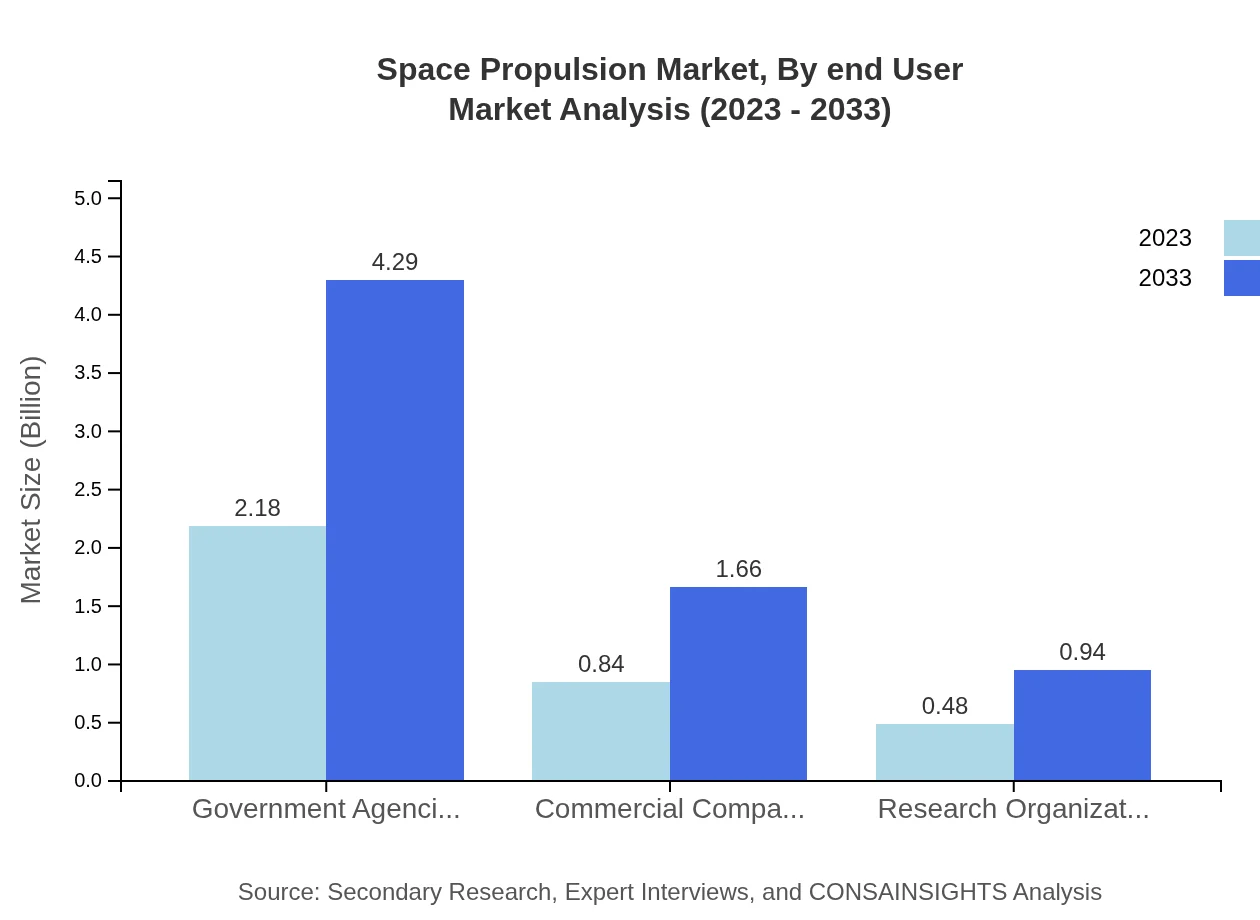
Space Propulsion Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segment is dominated by government agencies holding a market share of 62.3% in 2023, growing from $2.18 billion to $4.29 billion by 2033, indicating their critical role in mission funding. Commercial companies and research organizations are also emerging, focusing on private satellite launches and innovations within the industry.
Space Propulsion Market Analysis By Region
Regional dynamics reveal distinct growth patterns. North America is anticipated to maintain the largest share, followed by Europe and the Asia Pacific. Each region's investment climate and technological capabilities influence market trajectories.
Space Propulsion Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Space Propulsion Industry
NASA:
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is a key player in developing and innovating propulsion technologies for space exploration.SpaceX:
A commercial aerospace manufacturer and space transportation company known for its breakthroughs in rocket technology and reusable launch systems.Blue Origin:
Founded by Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin specializes in developing technologies to enable private human access to space.Airbus Defence and Space:
This division of Airbus Group is heavily involved in space and defense technologies, including propulsion systems.Arianespace:
The world’s first commercial launch service provider, Arianespace is renowned for its satellite launch services utilizing advanced propulsion systems.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of space propulsion?
The global space propulsion market is currently valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023. It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8%, reaching significant valuation by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the space propulsion industry?
Key players in the space propulsion market include major aerospace manufacturers and propulsion technology specialists. Notable entities include SpaceX, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman, playing crucial roles in advancing propulsion technologies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the space propulsion industry?
Growth in the space propulsion market is driven by increasing launches of satellites, advancements in propulsion technologies, and rising investments from government agencies and private companies in space exploration initiatives.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the space propulsion market?
The fastest-growing regions in the space propulsion market include North America and Europe, with respective market sizes projected to reach $2.22 billion and $2.38 billion by 2033, highlighting robust growth in these areas.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the space propulsion industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to individual needs, providing in-depth analysis specific to different segments of the space propulsion industry to support informed decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this space propulsion market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables, including market size analysis, growth forecasts, competitive landscape evaluations, regional assessments, and detailed insights into market segments and key players.
What are the market trends of space propulsion?
Current market trends in space propulsion include increased reliance on innovative propulsion systems, heightened collaboration between government and private sectors, and a significant shift towards electric and nuclear thermal propulsion technologies.