Spacecraft Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: spacecraft
Spacecraft Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Spacecraft market covering insights on market size, growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033, industry trends, segmentation, and regional dynamics, along with profiles of key market players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
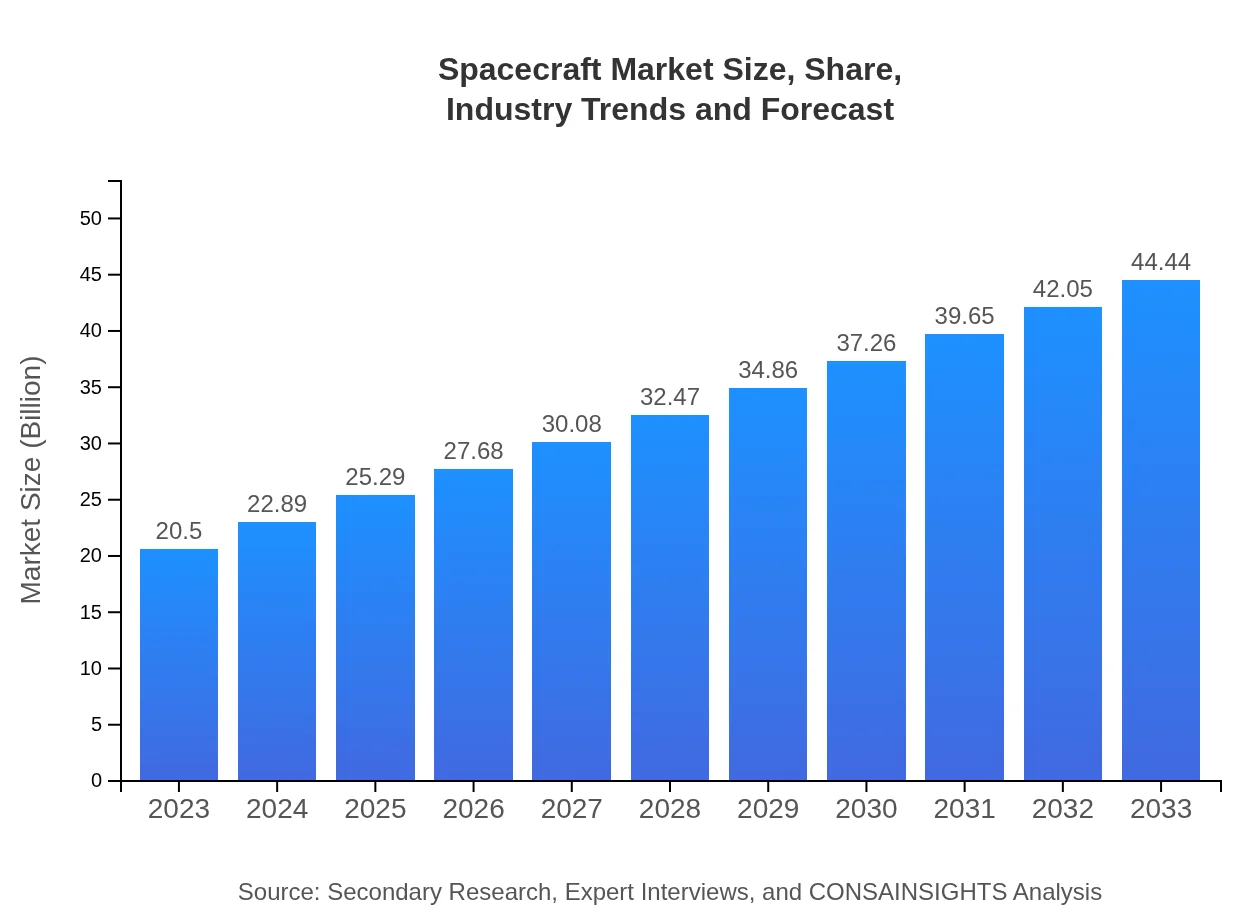
| 2023 Market Size | $20.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $44.44 Billion |
| Top Companies | NASA, SpaceX, Boeing , Lockheed Martin, European Space Agency (ESA) |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Spacecraft Market Overview
Customize Spacecraft Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Spacecraft market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Spacecraft's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Spacecraft
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Spacecraft market in 2023?
Spacecraft Industry Analysis
Spacecraft Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Spacecraft Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Spacecraft Market Report:
Europe's spacecraft market is set to grow significantly from $5.29 billion in 2023 to $11.47 billion by 2033. The European Space Agency (ESA) plays a pivotal role in spacecraft development, focusing on collaborative missions and expanding astronaut programs to enhance its competitive edge in global space initiatives.Asia Pacific Spacecraft Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region shows significant growth potential, projected to increase from $3.95 billion in 2023 to $8.55 billion by 2033. Key players are focusing on enhancing satellite capabilities for communication and remote sensing initiatives. India and China lead investments in space programs, focusing on both crewed and uncrewed missions.North America Spacecraft Market Report:
North America remains a dominant force in the global spacecraft market, with projections rising from $7.73 billion in 2023 to $16.76 billion by 2033. The US and Canada are heavily investing in both military and commercial spacecraft operations, including satellite launches and explorations by private enterprises like SpaceX.South America Spacecraft Market Report:
In South America, the spacecraft market is expected to grow from $1.82 billion in 2023 to $3.94 billion by 2033. Countries like Brazil are investing in satellite technology for weather forecasting and geolocation services, aiming for greater self-sufficiency in space capabilities.Middle East & Africa Spacecraft Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market is expected to rise from $1.71 billion in 2023 to $3.71 billion by 2033. Countries like the UAE are making headlines with their Mars missions, leading to increased investments in satellite technologies and space R&D.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Spacecraft Market Analysis By Type
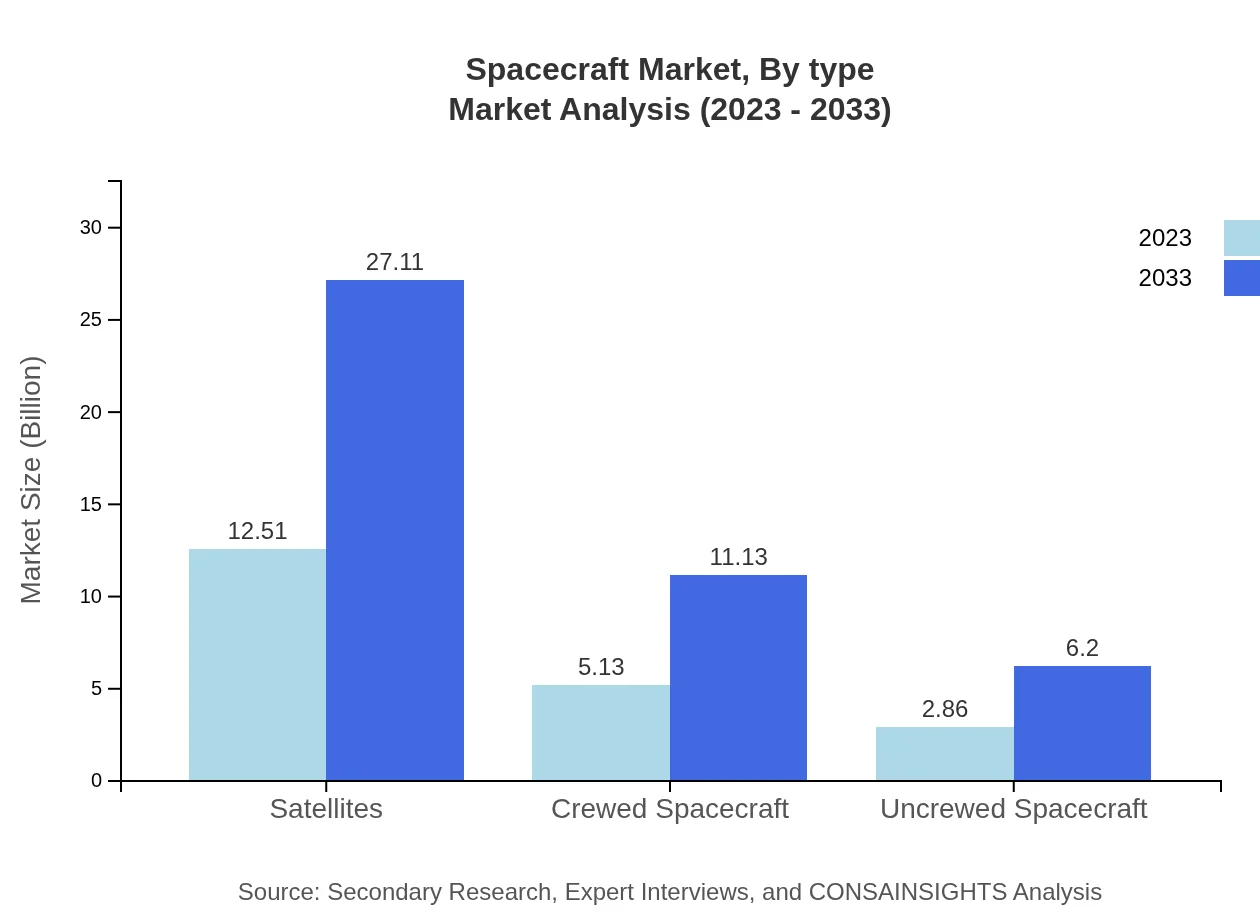
The Spacecraft market by type is segmented into: - **Satellites**: Dominating the market with approximately $12.51 billion in 2023, projected to reach $27.11 billion by 2033. - **Crewed Spacecraft**: Expected to grow from $5.13 billion in 2023 to $11.13 billion by 2033. - **Uncrewed Spacecraft**: With a market size of $2.86 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $6.20 billion by 2033.
Spacecraft Market Analysis By Application
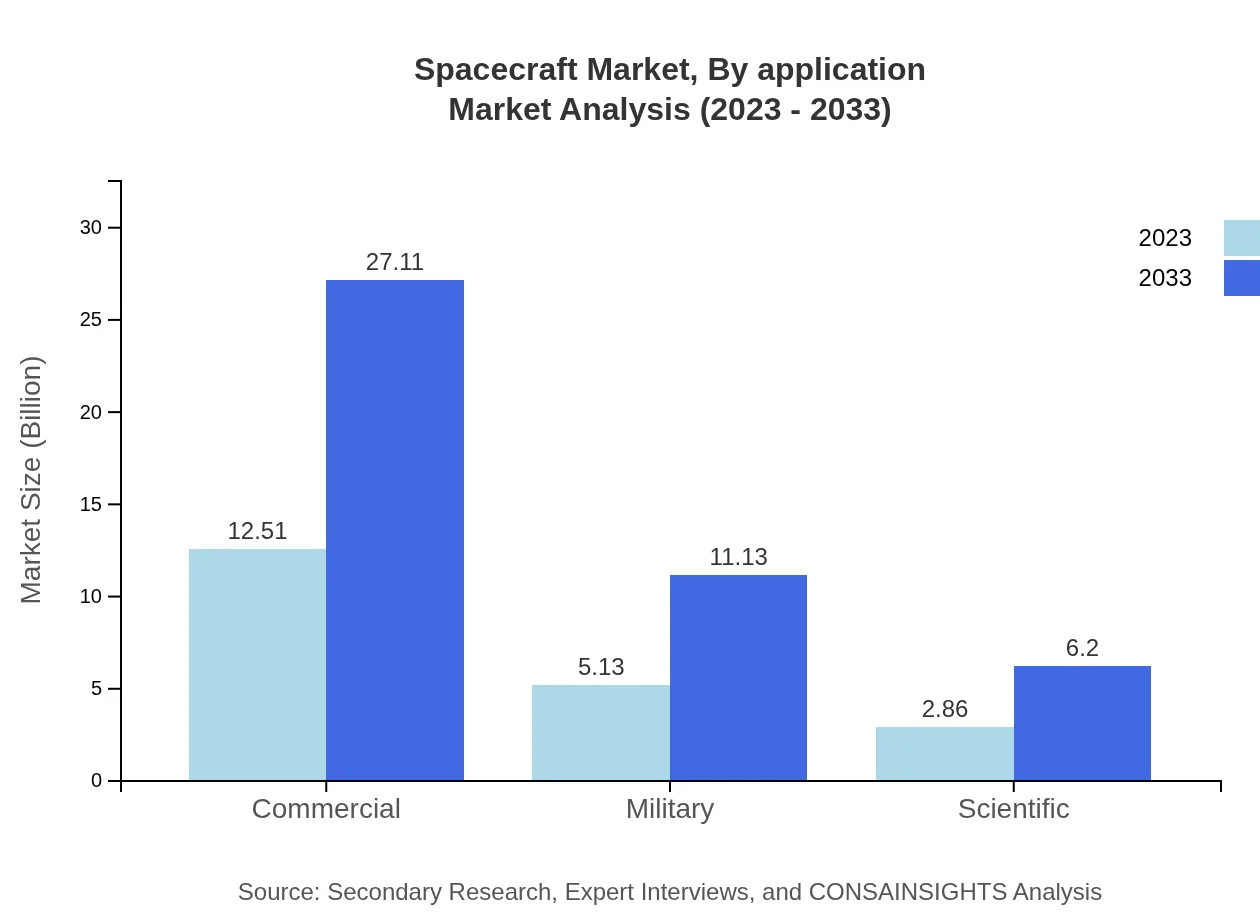
Applications of spacecraft are diverse and include: - **Government**: The largest segment, holding a share of 61.01%, with market size expanding from $12.51 billion to $27.11 billion by 2033. - **Commercial Companies**: Projected to increase from $5.13 billion to $11.13 billion, maintaining a 25.04% share. - **Research Institutions**: Expected growth from $2.86 billion to $6.20 billion, capturing a 13.95% market share.
Spacecraft Market Analysis By Launch System
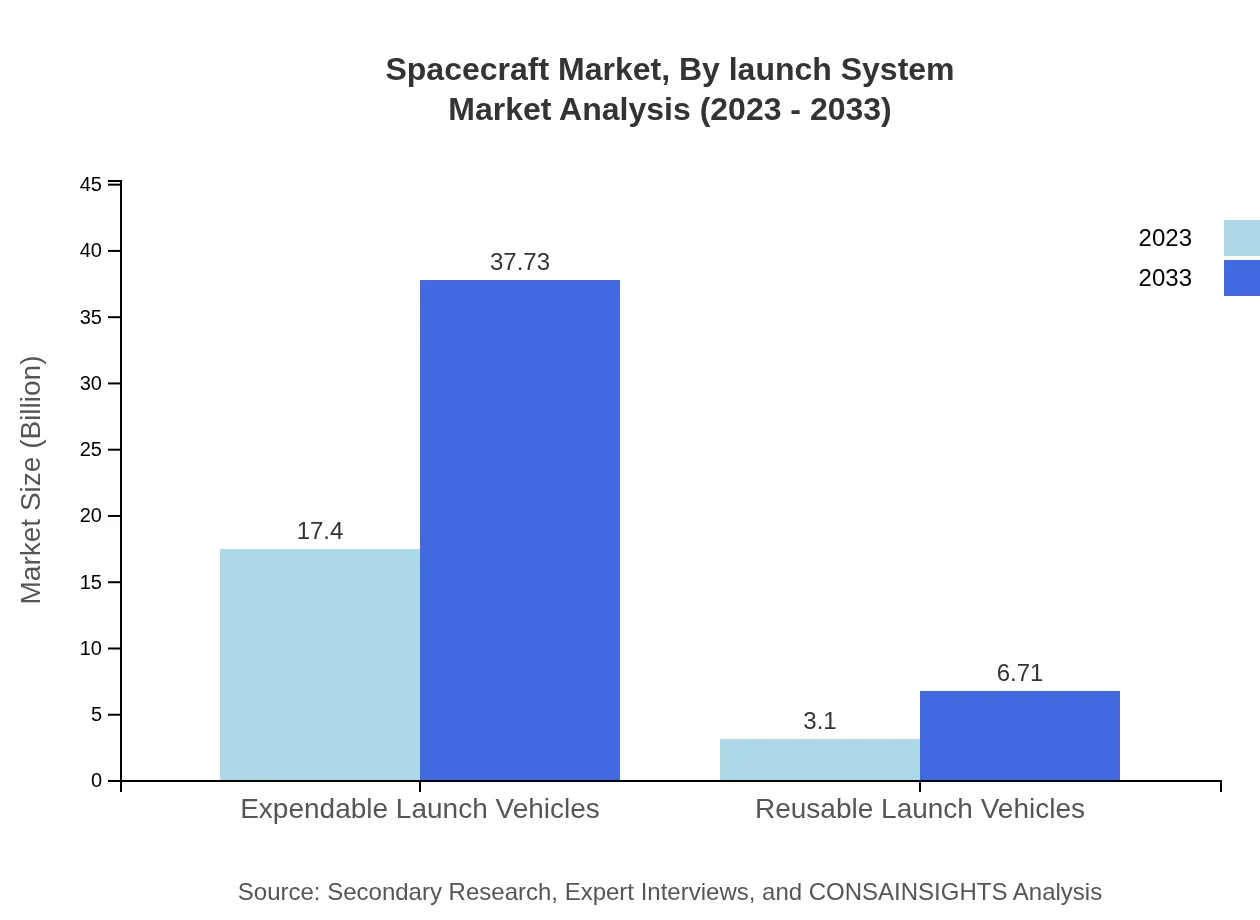
Launch systems are categorized into: - **Expendable Launch Vehicles**: Dominating the market with revenues increasing from $17.40 billion to $37.73 billion, maintaining a market share of 84.9%. - **Reusable Launch Vehicles**: Projected to grow from $3.10 billion to $6.71 billion by 2033, accounting for a 15.1% market share.
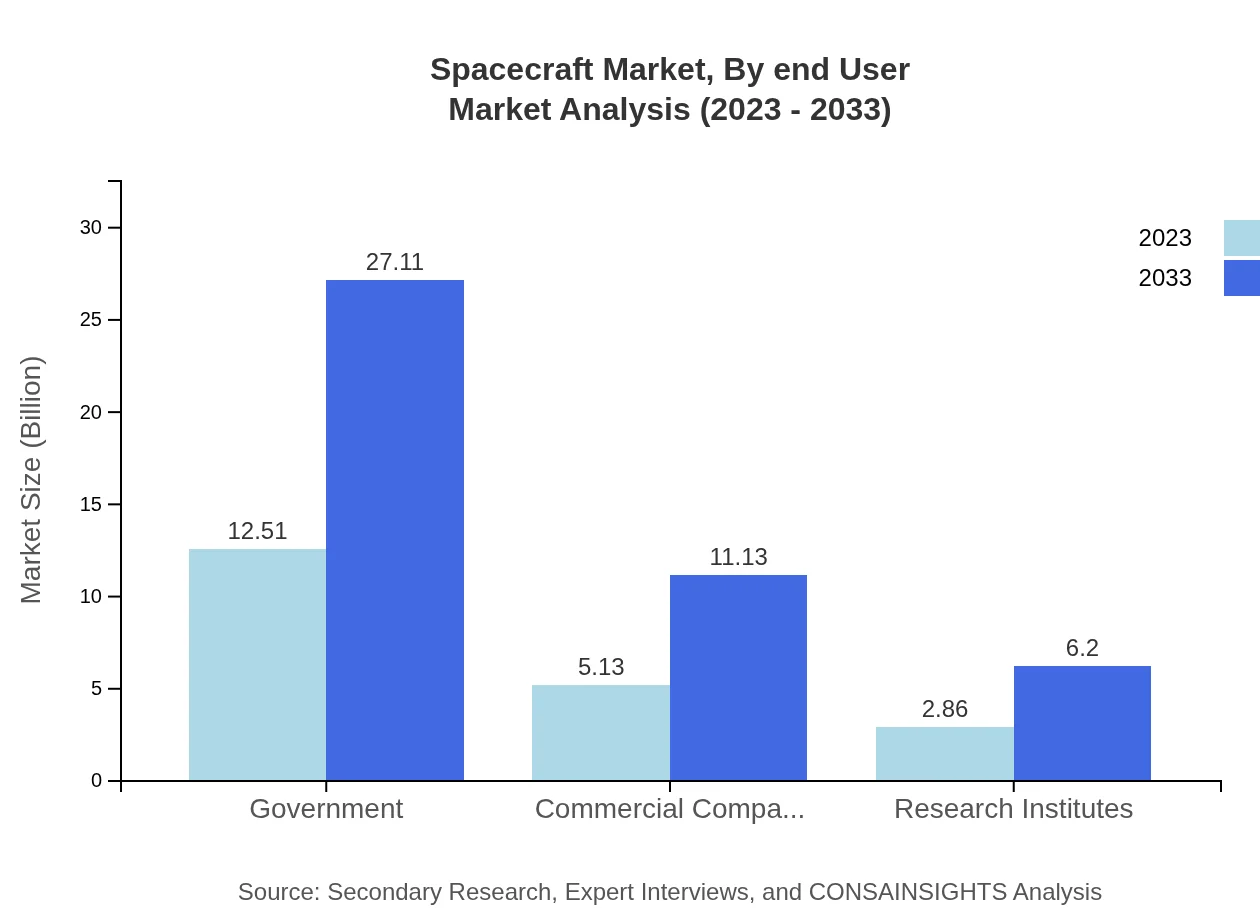
Spacecraft Market Analysis By End User
The end-user segments for the Spacecraft market are: - **Commercial**: Projected to grow with revenues from $12.51 billion to $27.11 billion, maintaining a 61.01% market share. - **Military**: Expected to grow from $5.13 billion to $11.13 billion, capturing 25.04% of the market. - **Scientific Applications**: Projected to grow modestly from $2.86 billion to $6.20 billion, holding a 13.95% market share.
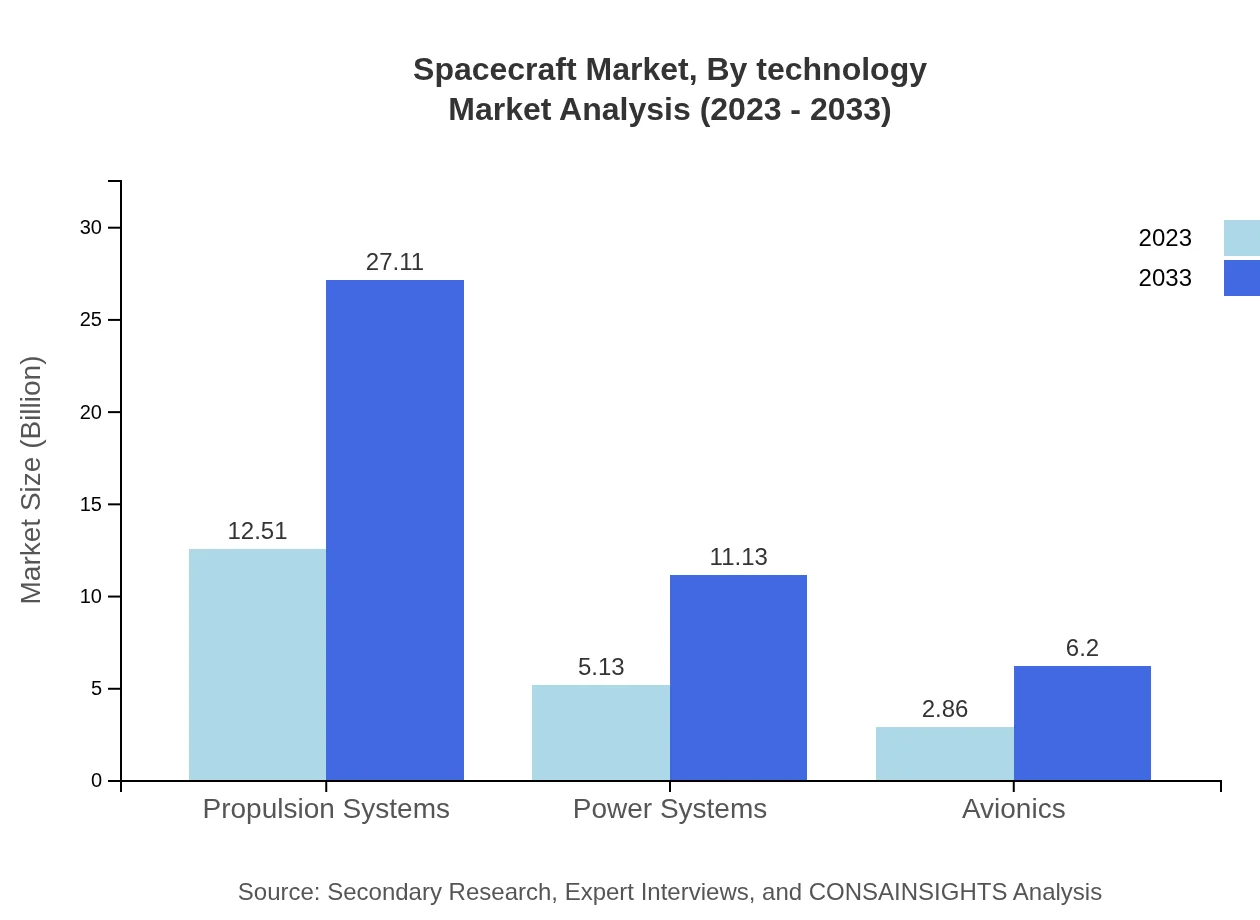
Spacecraft Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are key in the Spacecraft market, divided into: - **Propulsion Systems**: Market size growing from $12.51 billion to $27.11 billion, with a share of 61.01%. - **Power Systems**: Expected growth from $5.13 billion to $11.13 billion, with 25.04% market share. - **Avionics**: Anticipated to grow from $2.86 billion to $6.20 billion, maintaining a 13.95% share.
Spacecraft Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Spacecraft Industry
NASA:
The United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration, leading in space research, exploration, and technology development, significantly influencing crewed and uncrewed missions.SpaceX:
An aerospace manufacturer and space transport services company, pioneering advancements in reusable rocket technology and commercial space travels.Boeing :
A major aerospace player, involved in crewed space missions and satellite systems, contributing to numerous space program advancements.Lockheed Martin:
Dominating the defense and aerospace sectors, with extensive involvement in spacecraft and satellite technology development.European Space Agency (ESA):
An intergovernmental organization dedicated to the exploration of space, focusing on international collaboration for space missions and research.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of spacecraft?
The spacecraft market is projected to reach approximately $20.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.8%. This growth indicates a robust expansion from its current valuation, highlighting increased investment across various segments.
What are the key market players or companies in the spacecraft industry?
Key players in the spacecraft industry include major aerospace firms like SpaceX, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin, alongside emerging companies focusing on space exploration technologies that are shaping the market's future.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the spacecraft industry?
Growth factors for the spacecraft industry include technological advancements, increasing government investments in space exploration, and the proliferation of satellite applications supporting telecommunications and earth observation.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the spacecraft?
The North America region is the fastest-growing in the spacecraft market, projected to expand from $7.73 billion in 2023 to $16.76 billion by 2033, driven by dynamic advancements in aerospace technology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the spacecraft industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific aspects of the spacecraft industry, ensuring clients receive insights that meet their unique research needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this spacecraft market research project?
Expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, trend forecasting, competitive landscape assessment, and actionable insights to inform strategic decisions in the spacecraft market.
What are the market trends of spacecraft?
Key trends in the spacecraft market include increased collaboration between government and private sectors, advancements in reusable launch technologies, and a surge in satellite deployment for various applications.