Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: spark-plasma-sintering
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the Spark Plasma Sintering market, analyzing its dynamics, trends, and growth potential from 2023 to 2033. It provides comprehensive insights into market size, industry analysis, segmentation, regional breakdown, key players, and future forecasts, equipping stakeholders with critical information for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
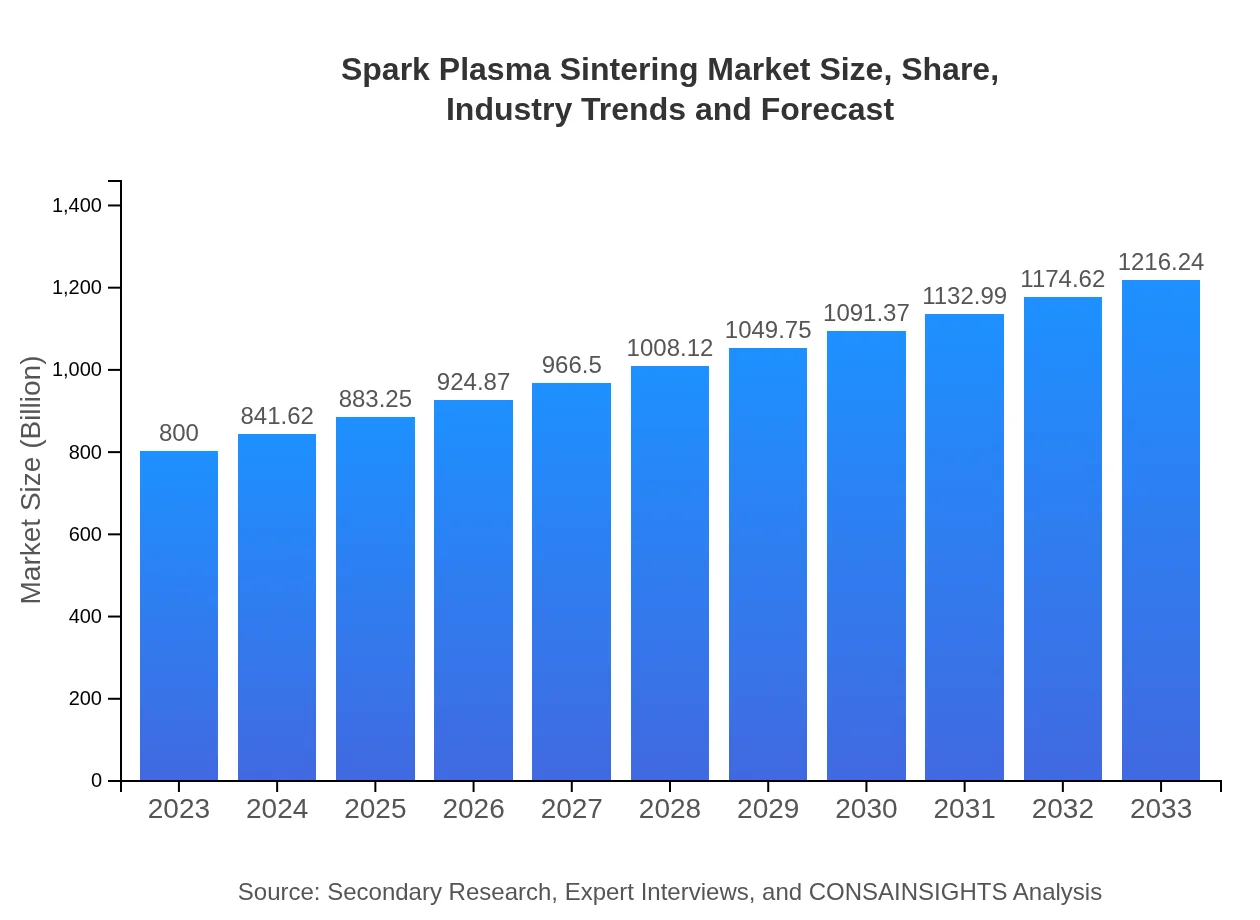
| 2023 Market Size | $800.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $1216.24 Million |
| Top Companies | FCT Systeme GmbH, Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Nihon Spindle Manufacturing, LGLS |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Overview
Customize Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Spark Plasma Sintering market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Spark Plasma Sintering's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Spark Plasma Sintering
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Spark Plasma Sintering market in 2023?
Spark Plasma Sintering Industry Analysis
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report:
The European Spark Plasma Sintering market recorded a value of USD 246.32 million in 2023, anticipated to reach USD 374.48 million by 2033. The presence of key players and research institutions dedicated to innovation in materials pushes the market forward, particularly in Germany, the UK, and France.Asia Pacific Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Spark Plasma Sintering market size stood at USD 149.60 million in 2023, projected to reach USD 227.44 million by 2033. The growth is driven by increased manufacturing in countries like China and Japan, alongside investments in R&D, focusing on sectors like electronics and automotive. Demand for advanced materials for high-tech applications is a significant driver.North America Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report:
North America's market, pegged at USD 284.72 million in 2023, is forecasted to reach USD 432.86 million by 2033. The region is witnessing significant advancements in SPS technology across the aerospace and automotive sectors, backed by established manufacturers and heightened R&D investment.South America Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report:
The South American market for Spark Plasma Sintering was valued at USD 61.12 million in 2023, with expectations to grow to USD 92.92 million by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are the leading contributors, supported by growing industrial applications and governmental initiatives promoting technological advancements in manufacturing.Middle East & Africa Spark Plasma Sintering Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's Spark Plasma Sintering market was valued at USD 58.24 million in 2023, projected to grow to USD 88.54 million by 2033. The region is gradually adopting SPS technology in local industries, supported by rising manufacturing and research activities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis By Material
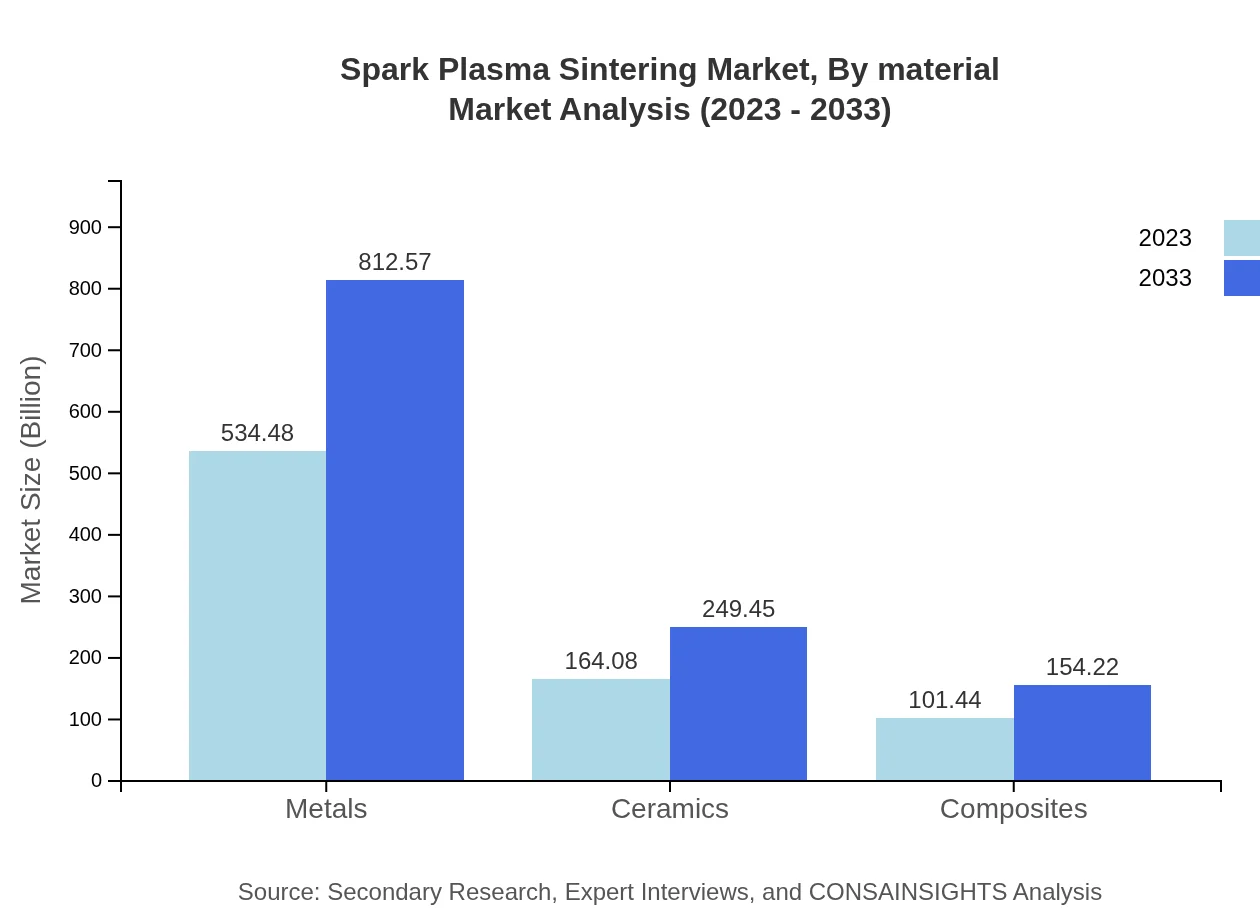
The Spark Plasma Sintering market is predominantly driven by the metals segment, which accounted for approximately USD 534.48 million in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 812.57 million by 2033. Ceramics and composites follow, with current values of USD 164.08 million and USD 101.44 million respectively, expected to reach USD 249.45 million and USD 154.22 million by 2033. These materials are being increasingly utilized for their superior properties across various applications.
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis By Application
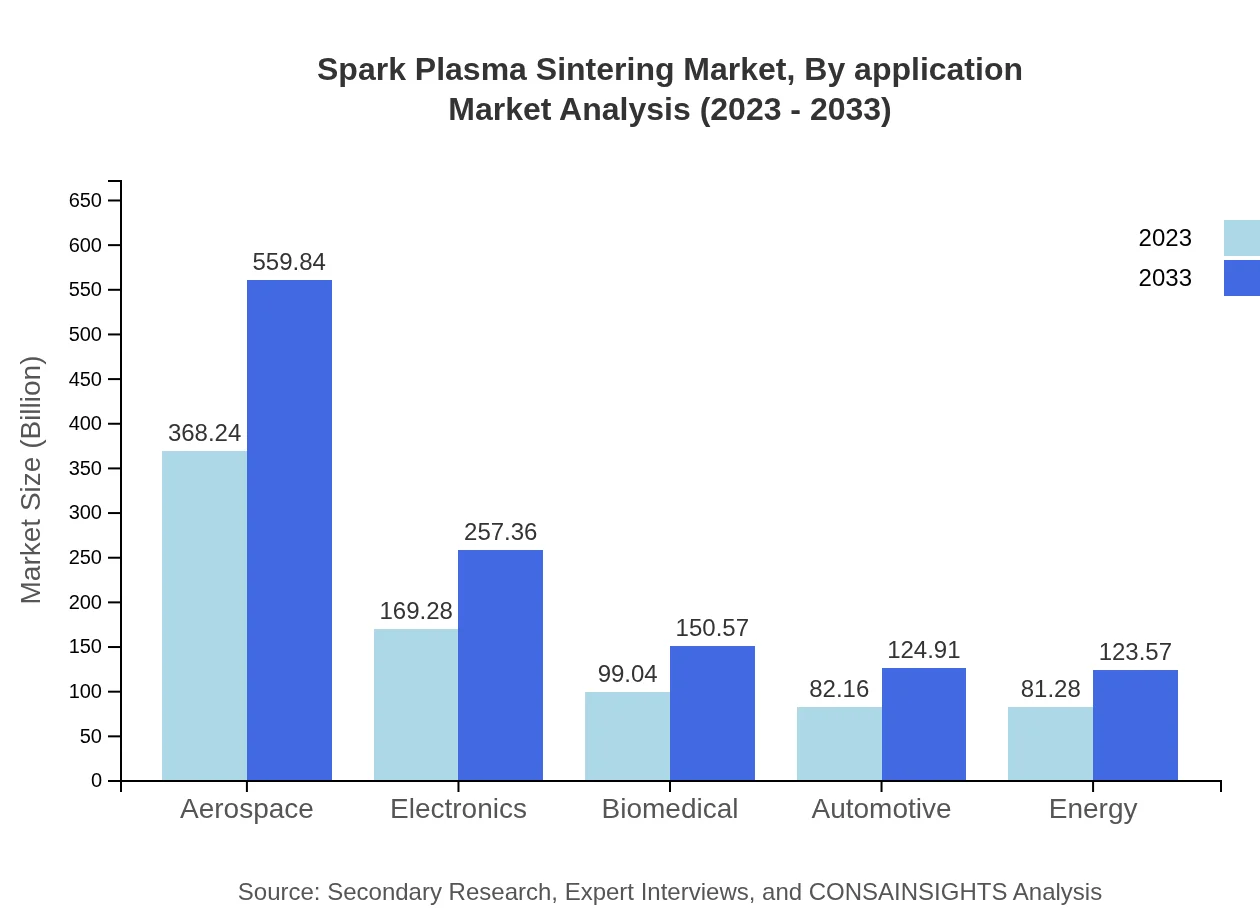
In 2023, the aerospace sector led the Spark Plasma Sintering market with a valuation of USD 368.24 million, expected to grow to USD 559.84 million by 2033, driven by the need for lightweight yet strong materials. Electronics and biomedical applications also represent significant markets, contributing USD 169.28 million and USD 99.04 million respectively, with forecasts indicating substantial growth as technology advances.
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis By Equipment Type
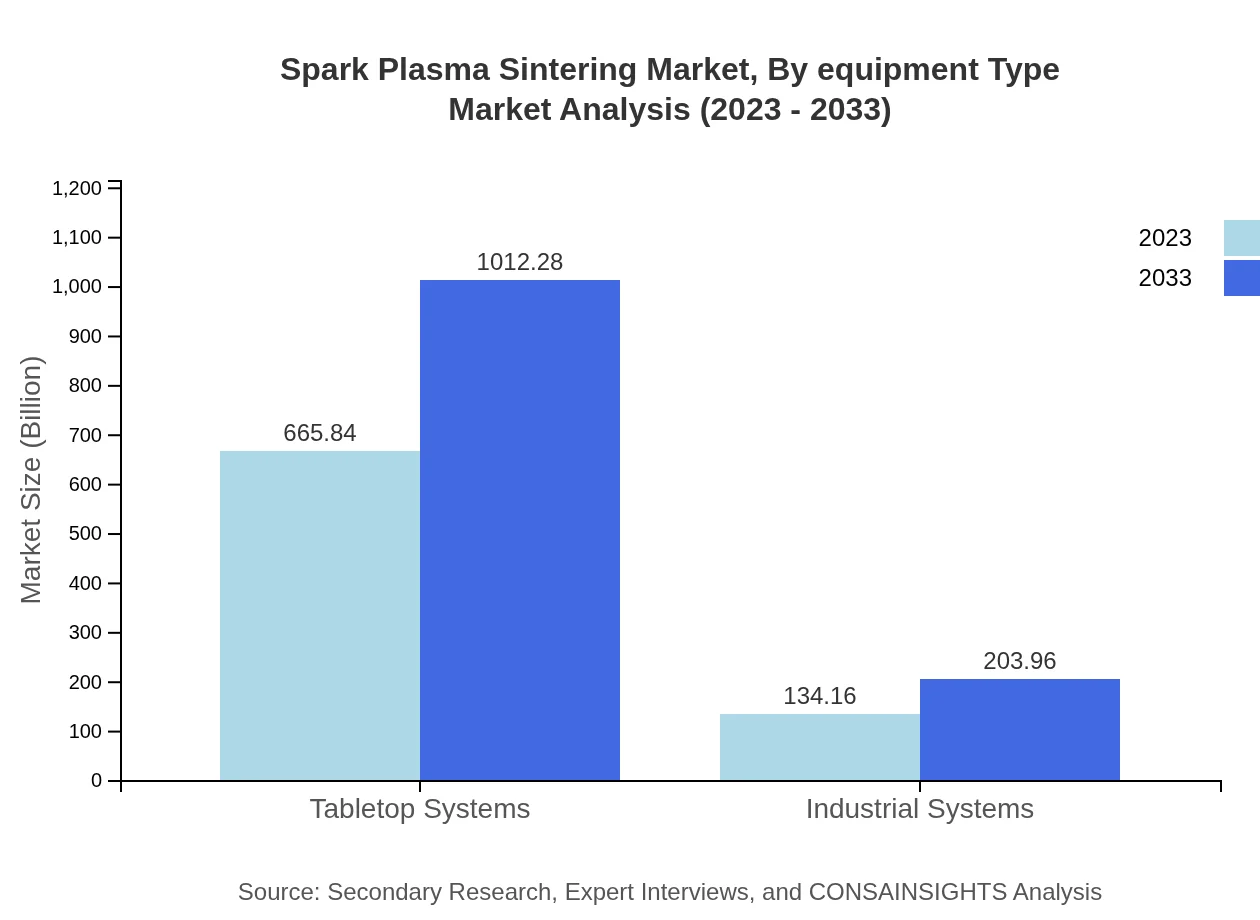
The Spark Plasma Sintering equipment market is segmented into tabletop systems and industrial systems. Tabletop systems dominate the market with revenue of USD 665.84 million in 2023, projected to reach USD 1.01 billion by 2033. The industrial systems segment, valued at USD 134.16 million currently, will grow to USD 203.96 million as industries scale up their production capabilities.
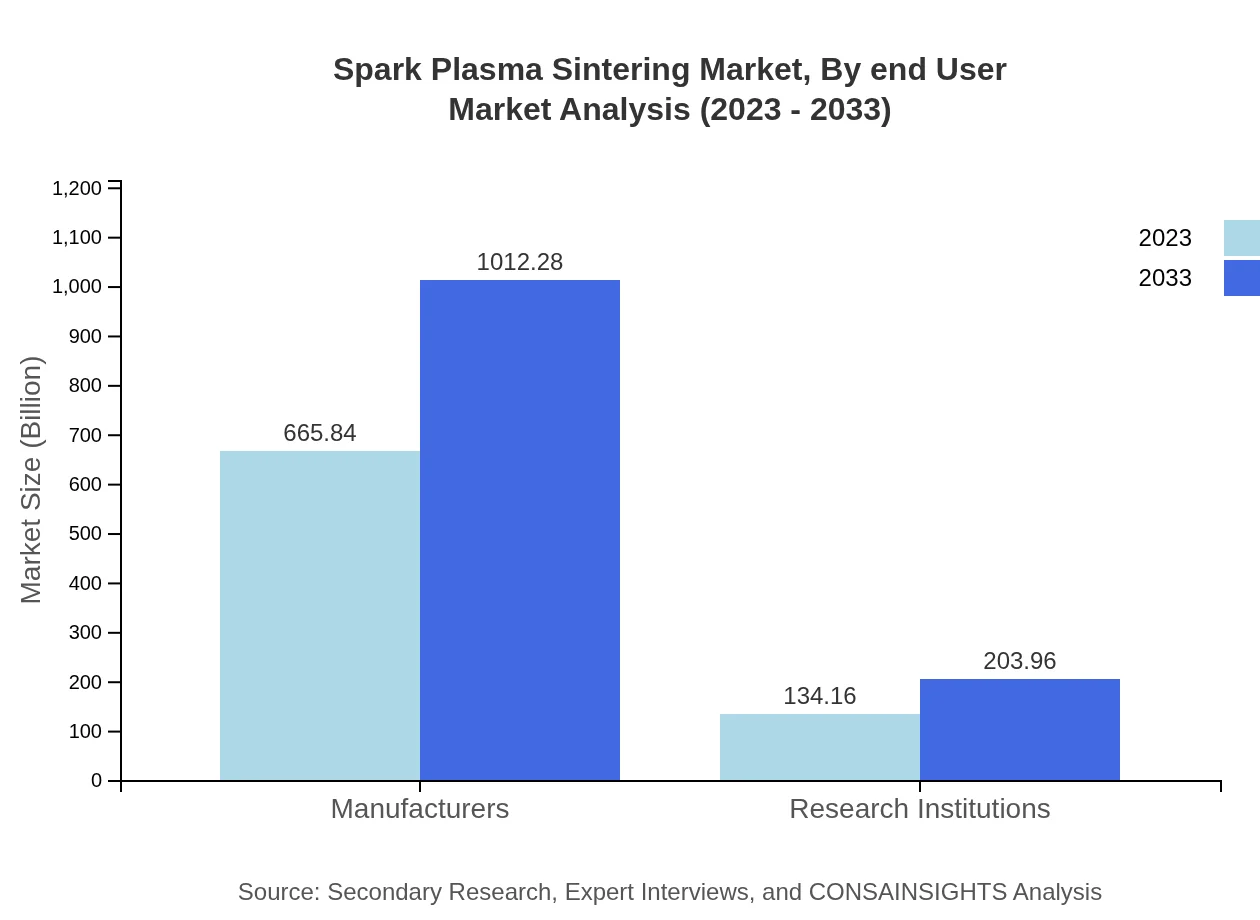
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis By End User
Manufacturers and research institutions are the key end-users of Spark Plasma Sintering. The manufacturers' segment leads with USD 665.84 million in 2023 and is projected to grow to USD 1.01 billion by 2033. Research institutions, while currently representing a smaller revenue segment at 134.16 million, are expected to significantly increase their contributions as they spearhead R&D in advanced materials.
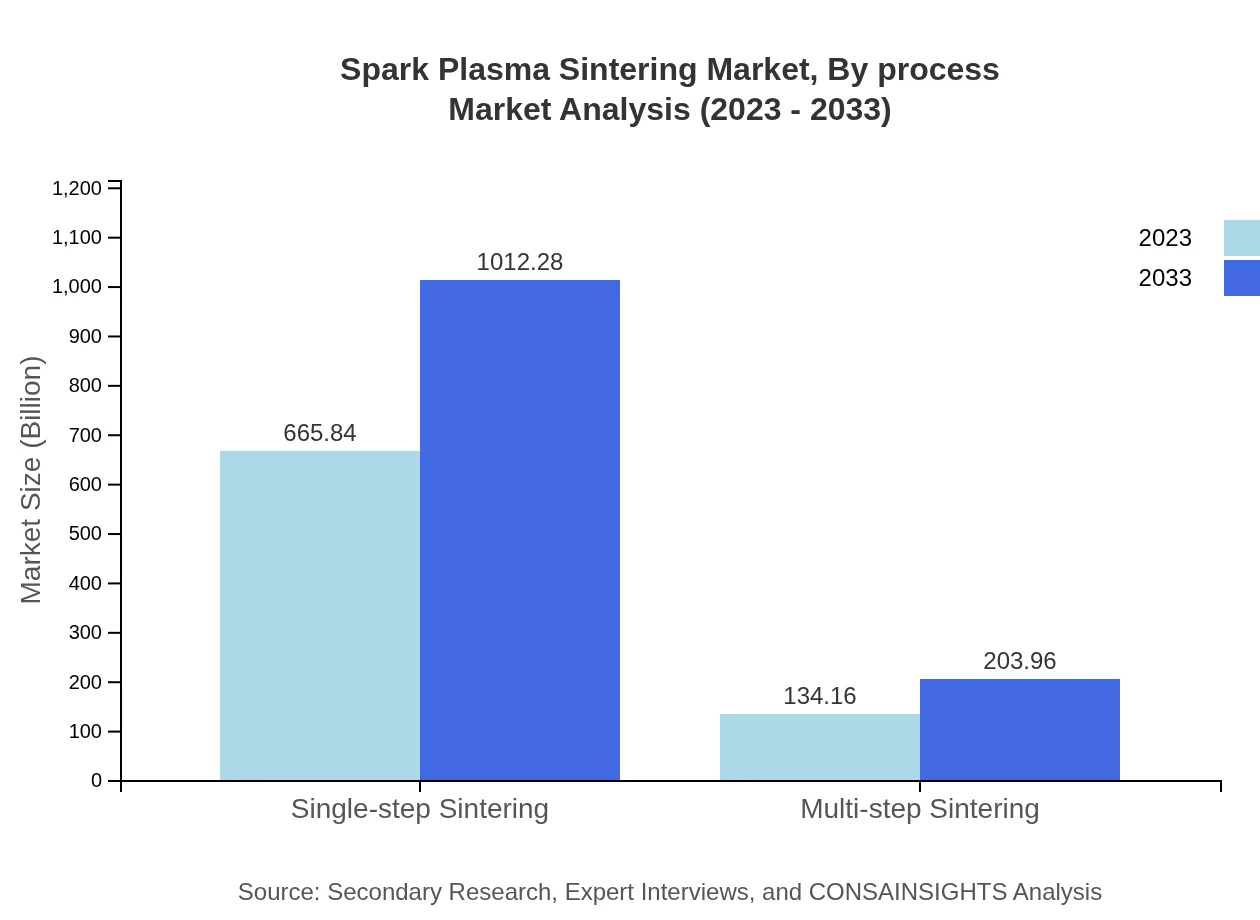
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Analysis By Process
The single-step sintering process commands the market size with USD 665.84 million in 2023 and anticipated growth to USD 1.01 billion by 2033. The two-step (multi-step) process, valued at USD 134.16 million, is also expected to grow significantly, driven by its application in specific materials and configurations.
Spark Plasma Sintering Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Spark Plasma Sintering Industry
FCT Systeme GmbH:
FCT Systeme GmbH is a leading manufacturer of SPS equipment, offering advanced sintering solutions with a wide range of applications in material science and engineering. Their innovative technologies have set benchmarks in the industry.Sumitomo Heavy Industries:
Sumitomo Heavy Industries produces high-end Spark Plasma Sintering machines known for their precision and performance, catering to the aerospace and automotive industries among others.Nihon Spindle Manufacturing:
Nihon Spindle Manufacturing is recognized for its cutting-edge SPS equipment, focusing on the development of more efficient and sustainable sintering processes across various material applications.LGLS:
LGLS specializes in innovative sintering technologies and manufactures equipment catered towards precision and advanced materials, contributing heavily to R&D in the SPS domain.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of spark Plasma Sintering?
The spark-plasma-sintering market is valued at approximately $800 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2033. This growth reflects the increasing demand for advanced materials in various industries.
What are the key market players or companies in the spark Plasma Sintering industry?
Key market players in spark-plasma-sintering include prominent manufacturers and research institutions that specialize in advanced manufacturing technologies and materials innovation, contributing significantly to the market's developmental landscape.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the spark Plasma Sintering industry?
The growth of the spark-plasma-sintering industry is driven by advancements in material science, increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials, and applications across aerospace, electronics, biomedical, and automotive sectors.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the spark Plasma Sintering?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the spark-plasma-sintering market, projected to grow from $284.72 million in 2023 to $432.86 million by 2033, reflecting a surge in technological innovations and investment.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the spark Plasma Sintering industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the spark-plasma-sintering industry. Clients can receive tailored insights that align with their specific needs and interests, enhancing strategic decision-making.
What deliverables can I expect from this spark Plasma Sintering market research project?
Deliverables from this market research project include detailed market analysis reports, segment data insights, growth projections, competitive landscape evaluations, and regional market dynamics tailored to client specifications.
What are the market trends of spark Plasma Sintering?
Current market trends in spark-plasma-sintering include increased adoption of metals and ceramics in advanced applications, a focus on sustainable manufacturing processes, and the growing prominence of tabletop systems in production environments.