Starter Culture Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: starter-culture
Starter Culture Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Starter Culture market, covering trends, forecasts from 2023 to 2033, and insights into market dynamics, regional performances, and key players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
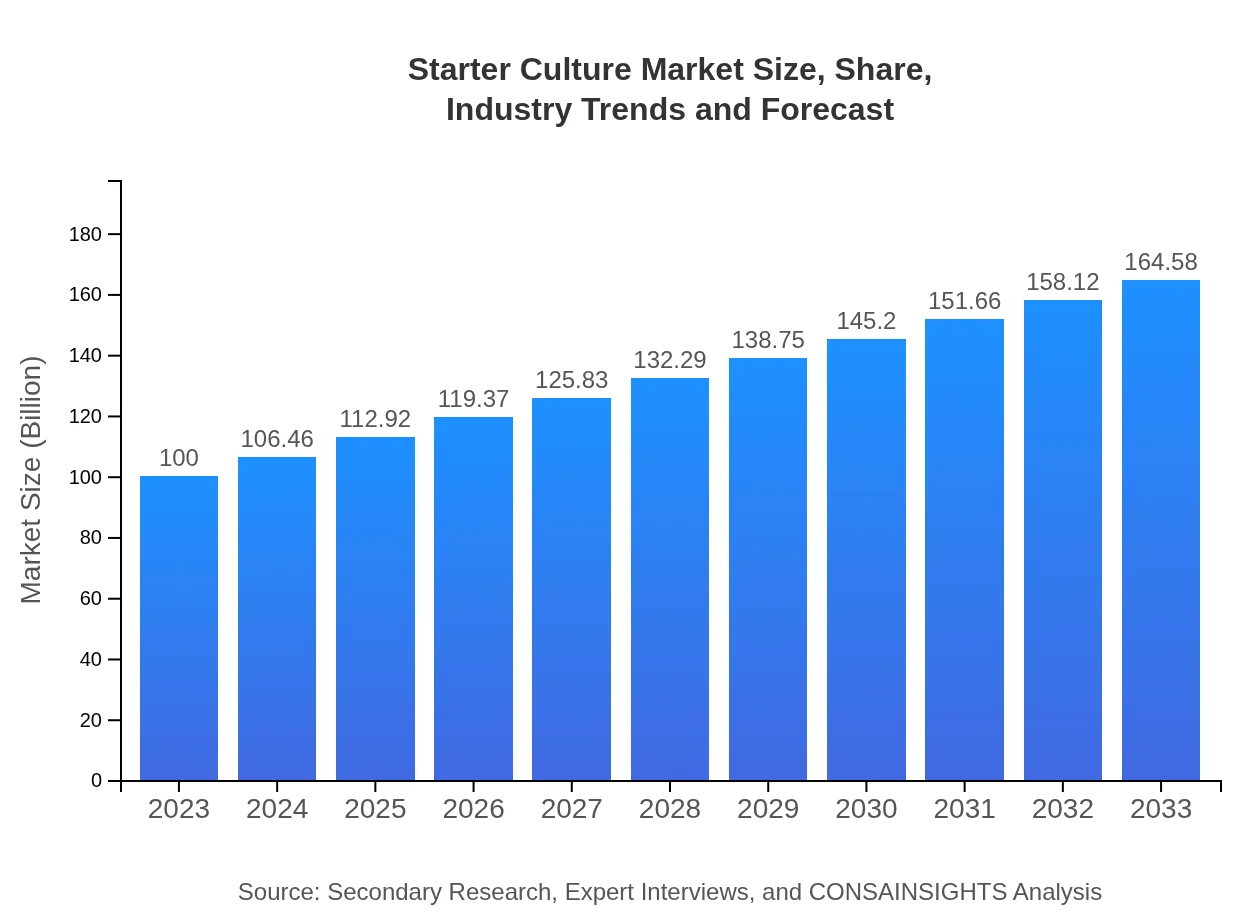
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Chr. Hansen A/S, Yqopia, Lallemand Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Starter Culture Market Overview
Customize Starter Culture Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Starter Culture market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Starter Culture's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Starter Culture
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Starter Culture market in 2023?
Starter Culture Industry Analysis
Starter Culture Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Starter Culture Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Starter Culture Market Report:
Europe represents the largest market, with growth projected from $30.99 billion in 2023 to $51.00 billion by 2033. The region enjoys a well-established dairy culture, complemented by a rising trend in probiotic products. Consumer awareness regarding gut health is driving innovations and expansion within the starter culture industry, further solidifying Europe's market dominance.Asia Pacific Starter Culture Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is poised for growth, with the market expected to grow from $19.15 billion in 2023 to $31.52 billion by 2033. Rising disposable income, changing consumer preferences towards health and wellness, and the growing popularity of traditional fermented foods contribute to this growth. Countries like China and India are leading contributors due to their rich culinary traditions involving fermentation.North America Starter Culture Market Report:
North America stands as a significant market, expected to rise from $34.53 billion in 2023 to $56.83 billion by 2033. The increase in health-conscious consumers and the trend towards organic food production bolster demand for starter cultures. The thriving dairy and meat processing industries further underscore North America's relevance in the global market.South America Starter Culture Market Report:
In South America, the Starter Culture market is anticipated to increase from $6.58 billion in 2023 to $10.83 billion by 2033. The demand for fermented beverages and dairy products is on the rise, driven by consumer interest in probiotics. Additionally, growing investments in food manufacturing infrastructure are likely to stimulate market growth.Middle East & Africa Starter Culture Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is on the rise, with the market expected to grow from $8.75 billion in 2023 to $14.40 billion by 2033. The growing demand for convenience foods and rapid urbanization are fostering market expansion. Moreover, increasing investments in food technology and production capabilities are likely to influence market dynamics positively.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
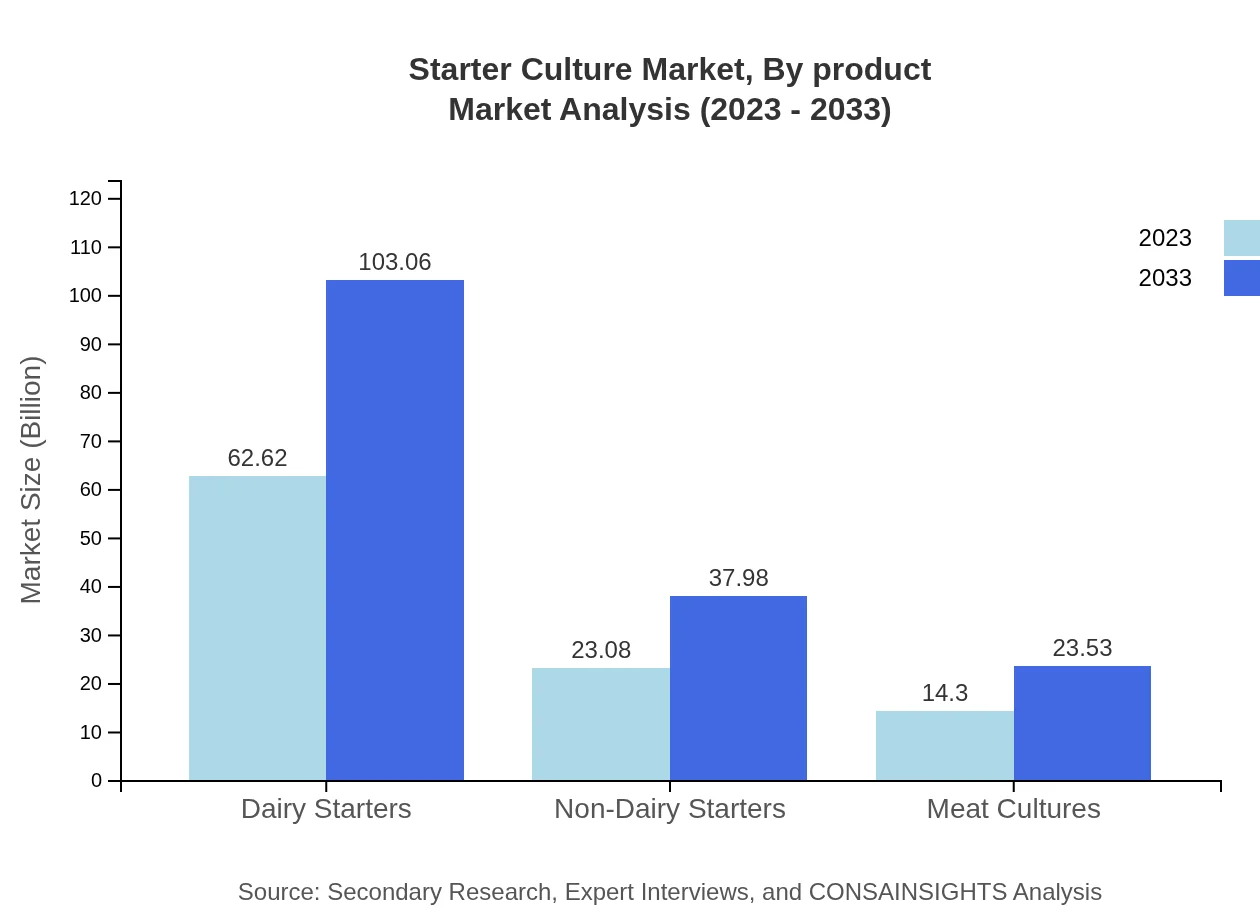
Starter Culture Market Analysis By Product
The Dairy Starters segment dominates the Starter Culture market with an anticipated growth from $62.62 billion in 2023 to $103.06 billion by 2033. Non-Dairy Starters are also showing promise, expected to rise from $23.08 billion in 2023 to $37.98 billion by 2033, catering to the growing vegan population. Meat Cultures hold an essential market share as well, foreseen to increase from $14.30 billion in 2023 to $23.53 billion by 2033.
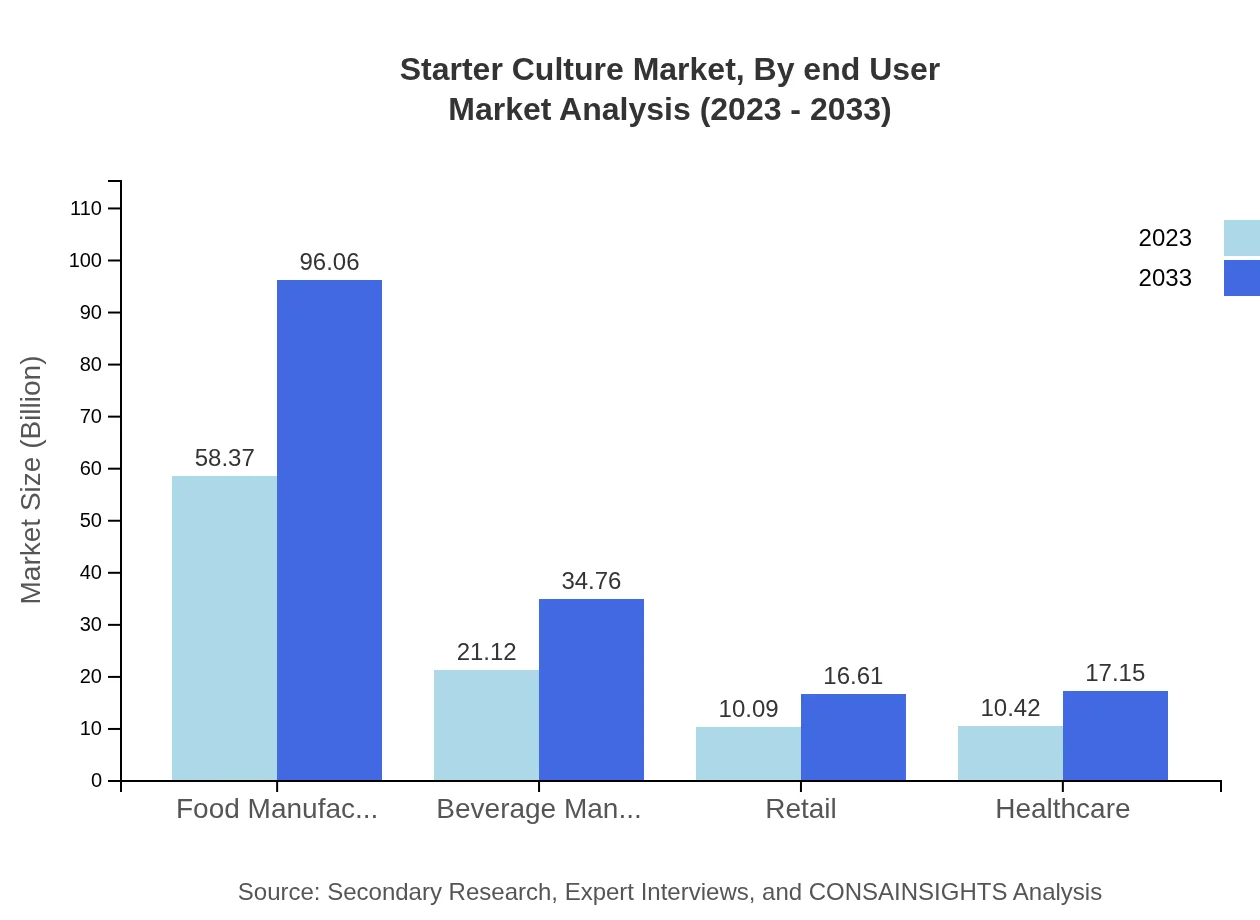
Starter Culture Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, Food Manufacturers lead the market with a size of $58.37 billion in 2023, projected to reach $96.06 billion by 2033. Beverage Manufacturers follow with a significant share of $21.12 billion, expected to reach $34.76 billion. The growth in demand for probiotics underpins increasing applications across various food sectors.
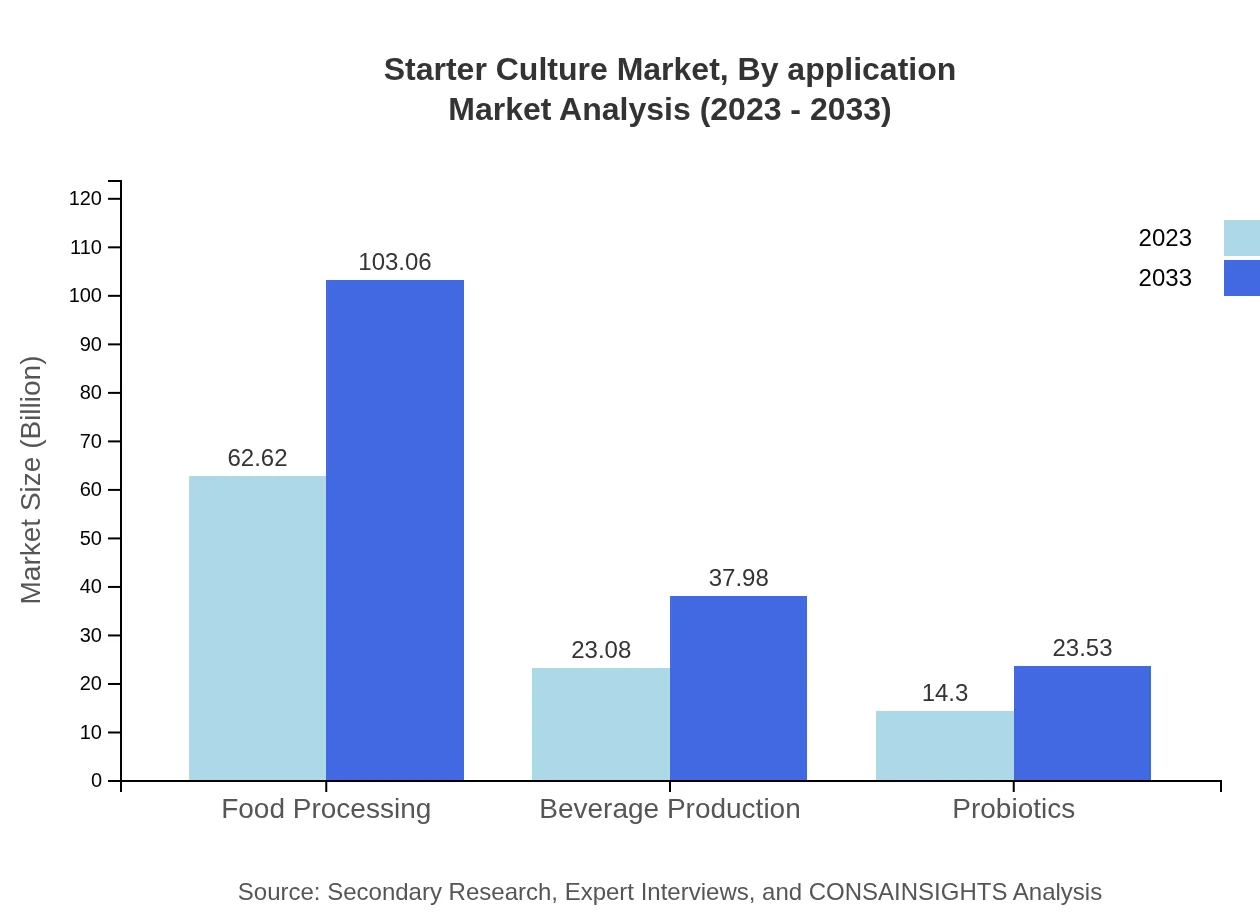
Starter Culture Market Analysis By End User
Food Processing is the largest segment among end-users, valued at $62.62 billion with a forecast to grow to $103.06 billion by 2033. Beverage Production also holds a substantial market share, estimated at $23.08 billion in 2023, slated to reach $37.98 billion. The healthcare sector is witnessing a notable surge due to the rising interest in dietary supplements containing probiotic cultures.
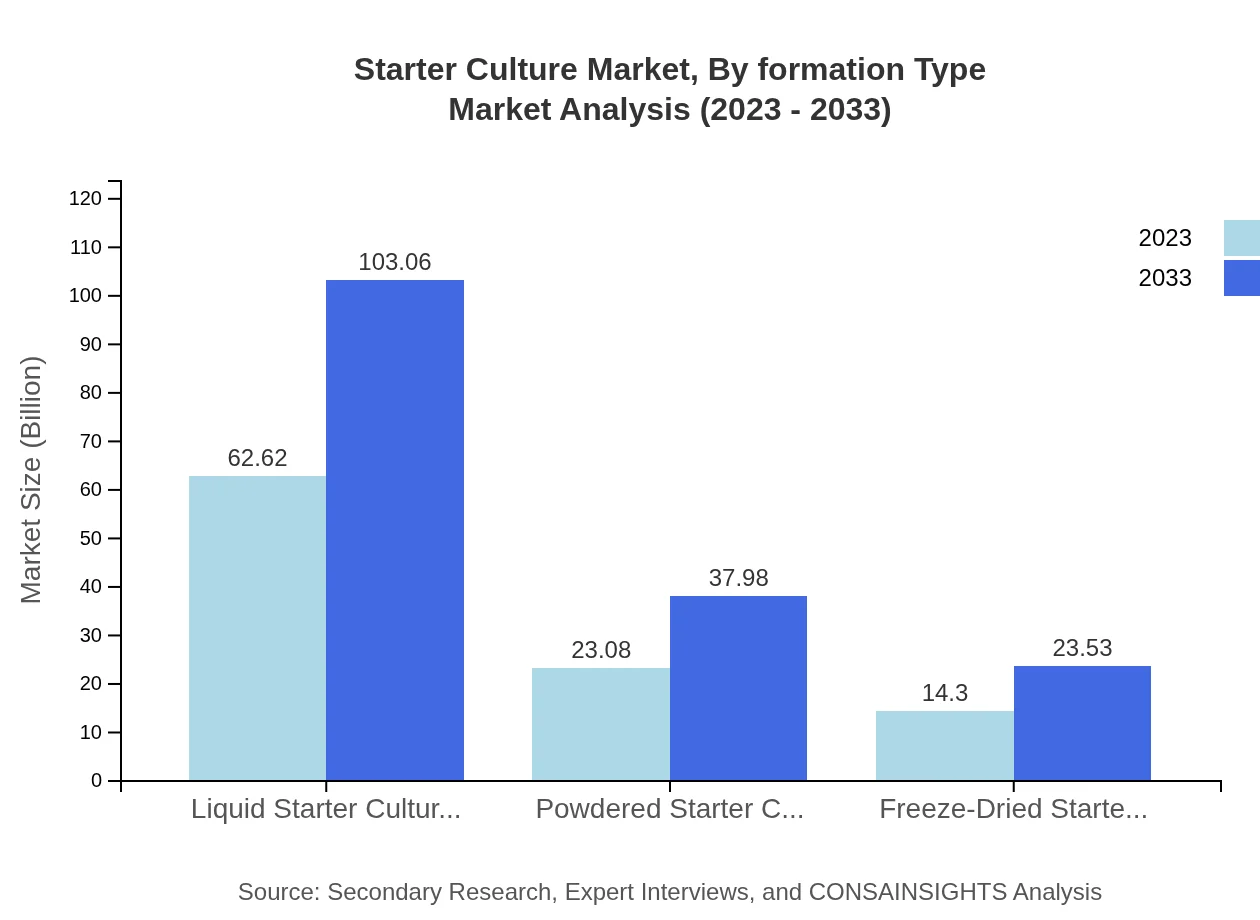
Starter Culture Market Analysis By Formation Type
Liquid Starter Cultures account for a prominent share, valued at $62.62 billion in 2023 and expected to reach $103.06 billion by 2033. Powdered Starter Cultures represent a significant segment with a growth forecast from $23.08 billion to $37.98 billion. Freeze-Dried Starter Cultures are also gaining traction, increasing from $14.30 billion to $23.53 billion, due to their convenience and extended shelf life.
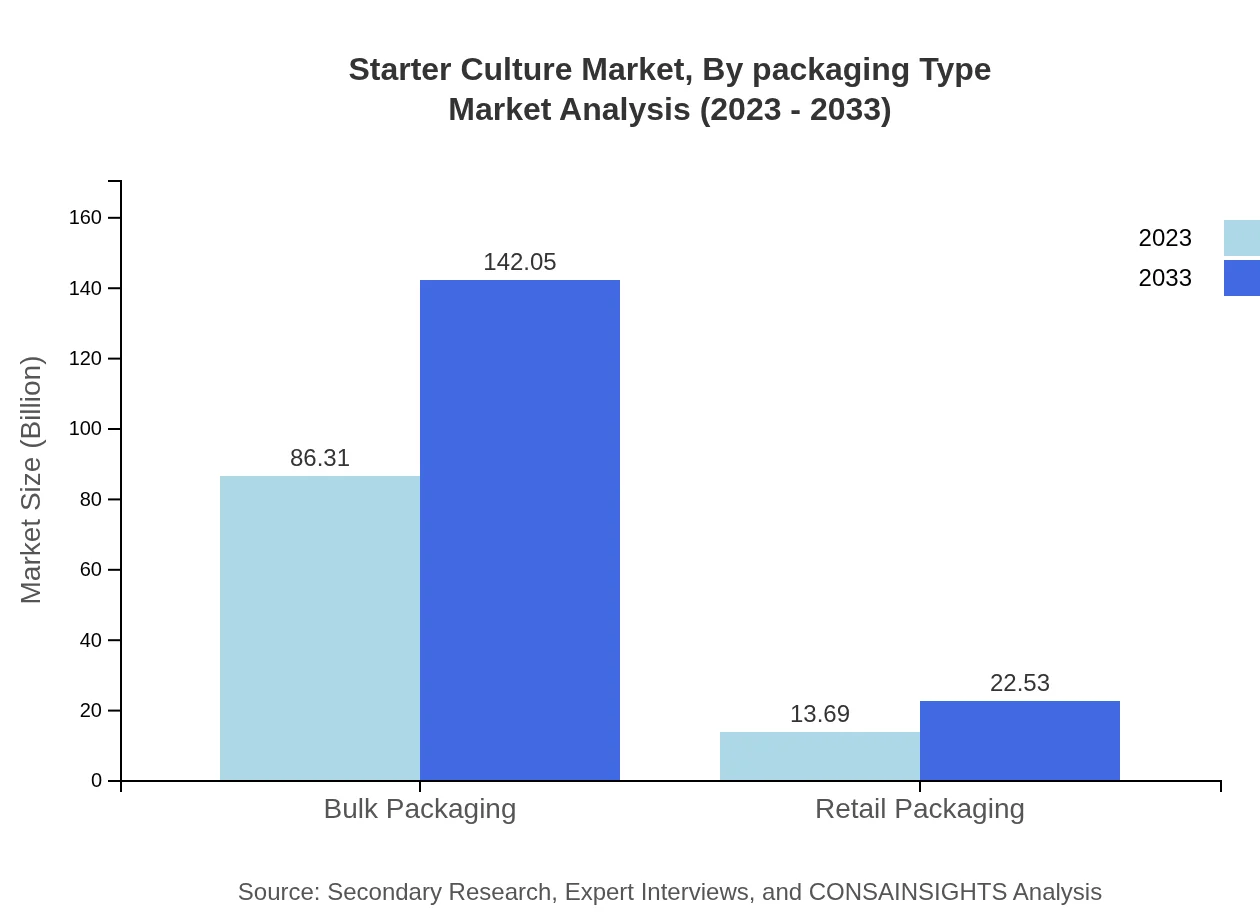
Starter Culture Market Analysis By Packaging Type
Bulk Packaging dominates the market, estimated at $86.31 billion in 2023 and expected to grow to $142.05 billion by 2033. Retail Packaging shows promising growth, anticipated to rise from $13.69 billion to $22.53 billion. As convenience becomes paramount, both packaging types are adapting to consumer demands for sustainable and efficient solutions.
Starter Culture Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Starter Culture Industry
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
A global leader in science and technology, DuPont offers a wide range of starter cultures for dairy and meat products, focusing on innovation and sustainability.Chr. Hansen A/S:
Danisco, a subsidiary of DuPont, develops biosolutions including starter cultures designed to enhance food quality and longevity, holding significant market share.Yqopia:
Specialized in yeast-based starter cultures, Yqopia aims to leverage fermentation technology to create healthier food products.Lallemand Inc.:
This Canadian company provides a range of starter cultures and is committed to research-driven development, specializing in the microbiology domain.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Starter Culture?
The global starter culture market is estimated to be valued at approximately $100 million in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 5% through 2033, indicating consistent growth and expansion in the industry.
What are the key market players or companies in the Starter Culture industry?
Key players in the starter culture market include global leaders such as DuPont, Chr. Hansen, and DSM, known for their innovative starter culture solutions catering to various segments like dairy, beverages, and meat products.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Starter Culture industry?
Growth is driven by increasing consumer demand for fermented products, innovations in microbial technology, and rising awareness of health benefits associated with probiotics and fermented foods, fostering significant industry expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Starter Culture market?
North America is identified as the fastest-growing region in the starter culture market, projected to grow from $34.53 million in 2023 to $56.83 million by 2033, reflecting a strong demand for diverse food applications.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the Starter Culture industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers tailored market research reports, allowing customers to gain specific insights into the starter culture market that cater to niche segments or particular geographies.
What deliverables can I expect from this Starter Culture market research project?
Deliverables typically include comprehensive reports, executive summaries, market forecasts, competitive analysis, and insights into consumer trends and market dynamics in the starter culture sector.
What are the market trends of Starter Culture?
Trends include a growing focus on health and wellness, increased demand for organic starter cultures, and innovations in product offerings, including lactose-free and plant-based solutions to cater to diverse consumer preferences.