Stem Cell Banking Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: stem-cell-banking
Stem Cell Banking Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Stem Cell Banking market from 2023 to 2033. It includes insights on market size, CAGR, industry trends, technological advancements, regional analysis, and forecasts to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
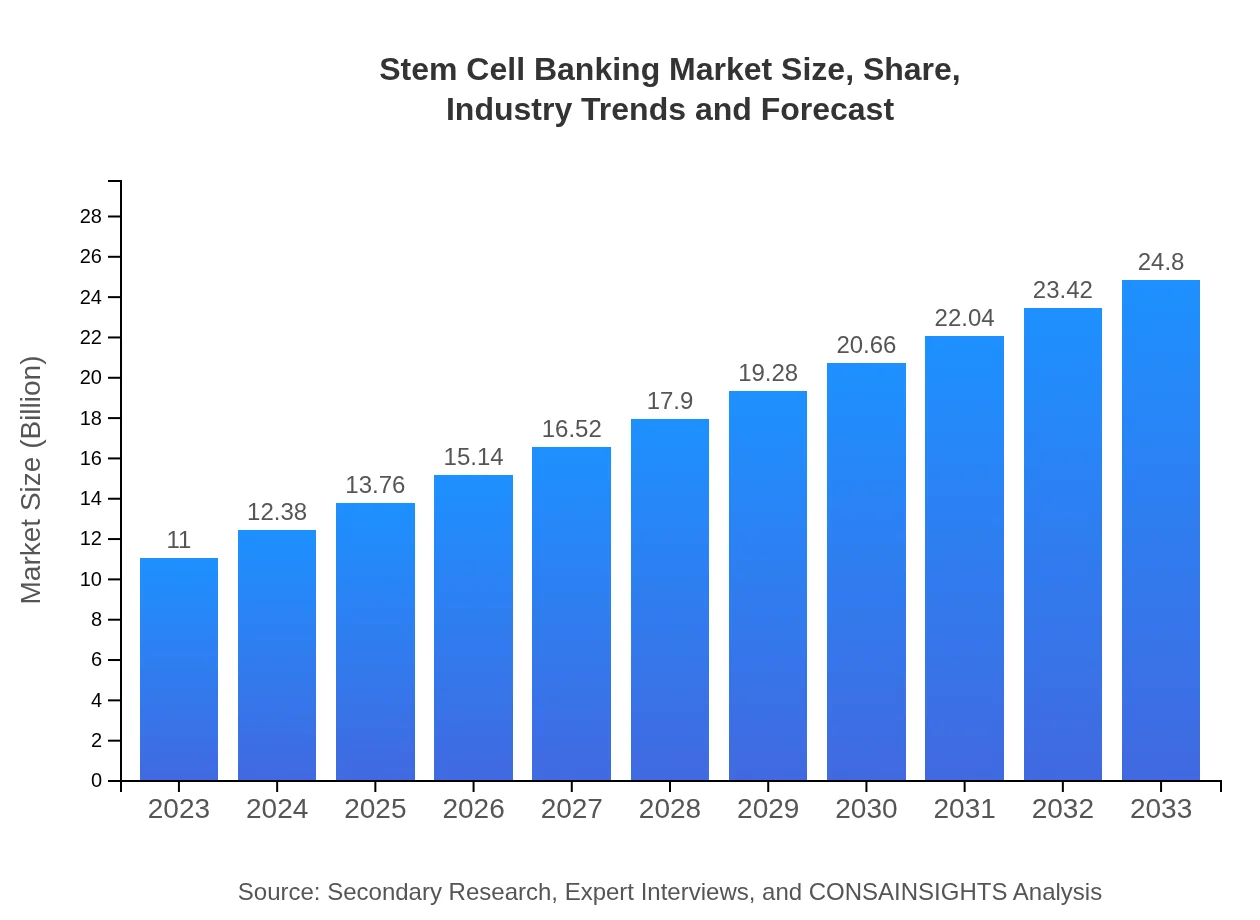
| 2023 Market Size | $11.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $24.80 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cord Blood Registry (CBR), Viacord, Cryo-Cell International, Inc., StemCyte Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Stem Cell Banking Market Overview
Customize Stem Cell Banking Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Stem Cell Banking market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Stem Cell Banking's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Stem Cell Banking
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Stem Cell Banking market in 2023?
Stem Cell Banking Industry Analysis
Stem Cell Banking Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Stem Cell Banking Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Stem Cell Banking Market Report:
Europe's Stem Cell Banking market is set to expand from $3.11 billion in 2023 to $7.00 billion by 2033. Factors contributing to this growth include an aging population, increasing incidences of degenerative diseases, and supportive regulatory frameworks that promote stem cell research.Asia Pacific Stem Cell Banking Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Stem Cell Banking market is anticipated to grow from $2.27 billion in 2023 to $5.12 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increasing investments in healthcare, rising awareness of stem cell technologies, and a growing population suffering from chronic diseases, which necessitate regenerative therapies.North America Stem Cell Banking Market Report:
In North America, the market is projected to grow from $3.53 billion in 2023 to $7.96 billion by 2033. The dominance of this region can be attributed to robust healthcare infrastructure, high research investment, and a significant emphasis on innovative medical solutions and personalized medicine.South America Stem Cell Banking Market Report:
The South American market is expected to increase from $1.04 billion in 2023 to $2.34 billion in 2033. The primary drivers include improved healthcare access, rising medical tourism, and government initiatives to foster research in regenerative medicine as part of the broader healthcare agenda.Middle East & Africa Stem Cell Banking Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to rise from $1.06 billion in 2023 to $2.38 billion in 2033. Growth in this region is spurred by an increase in healthcare spending, emerging healthcare technologies, and the rising prevalence of lifestyle diseases.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
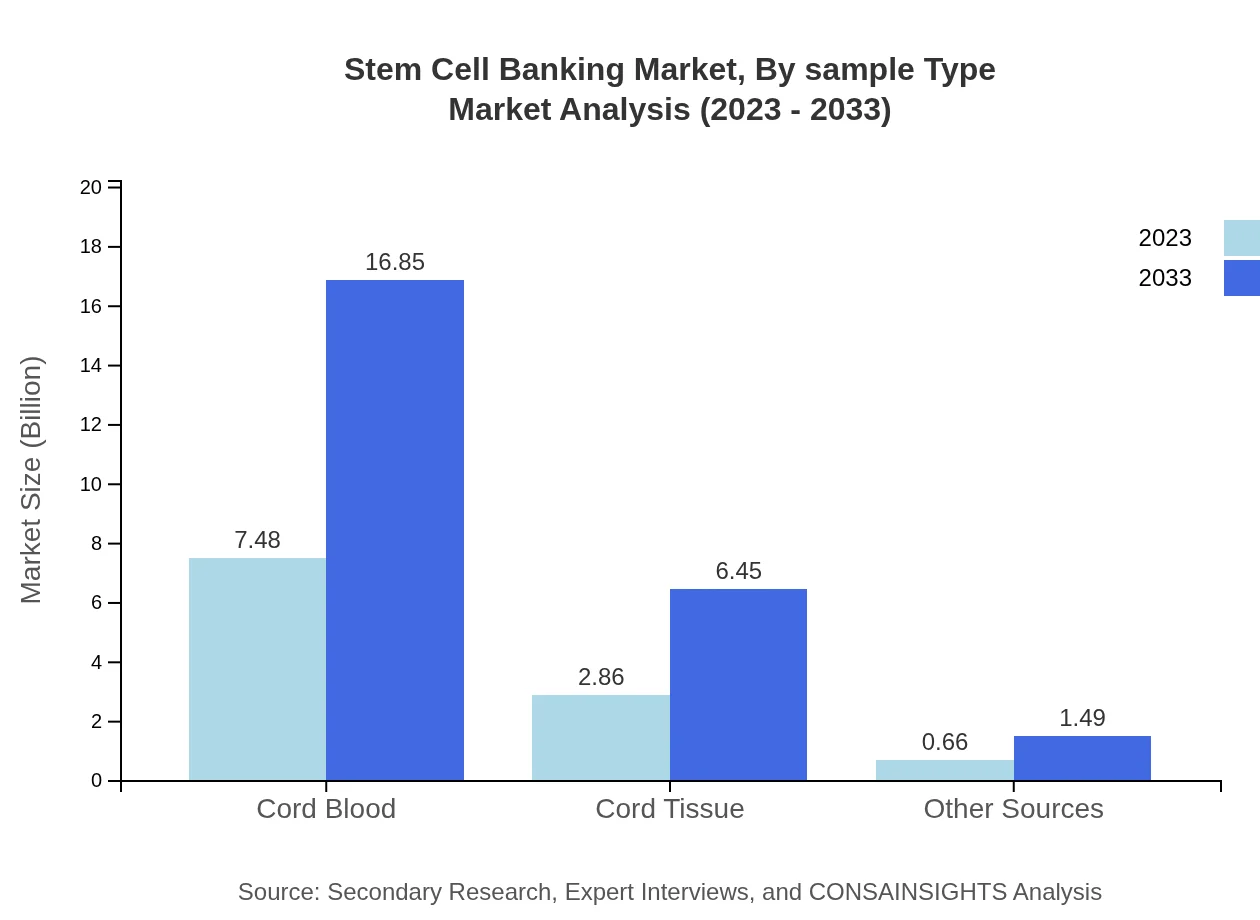
Stem Cell Banking Market Analysis By Sample Type
The market can be segmented by sample types, which include Cord Blood, Cord Tissue, and Other Sources. In 2023, the Cord Blood market is valued at $7.48 billion, maintaining a dominance of 67.97% share, expected to grow to $16.85 billion by 2033. Cord Tissue accounts for $2.86 billion with a 26.01% share, projected to rise to $6.45 billion. Other Sources make up $0.66 billion, with a 6.02% share growing to $1.49 billion.
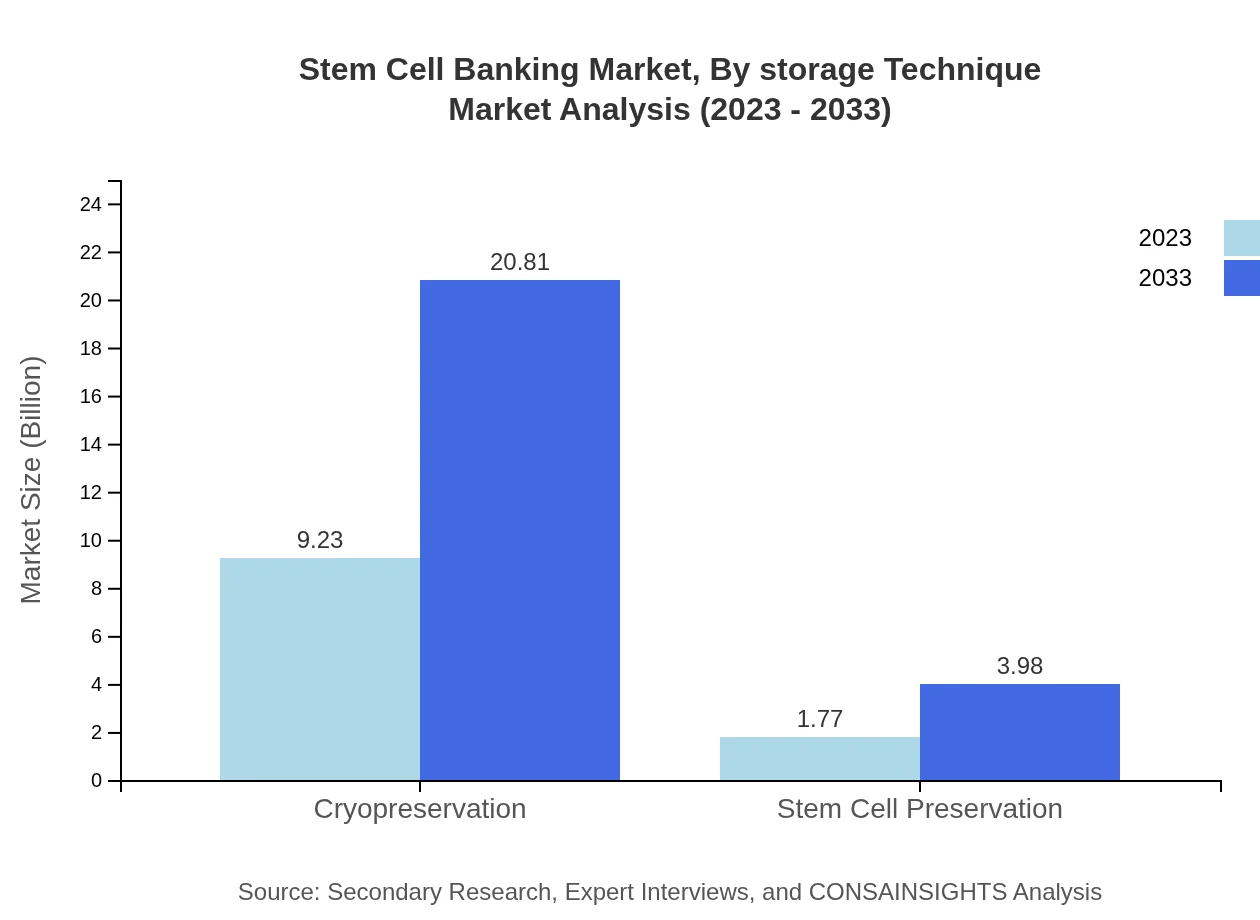
Stem Cell Banking Market Analysis By Storage Technique
Storage techniques primarily involve Cryopreservation, which constitutes $9.23 billion, representing 83.94% in 2023, and is expected to reach $20.81 billion by 2033. Stem Cell Preservation generates $1.77 billion with a 16.06% share, forecasting up to $3.98 billion by the end of 2033.
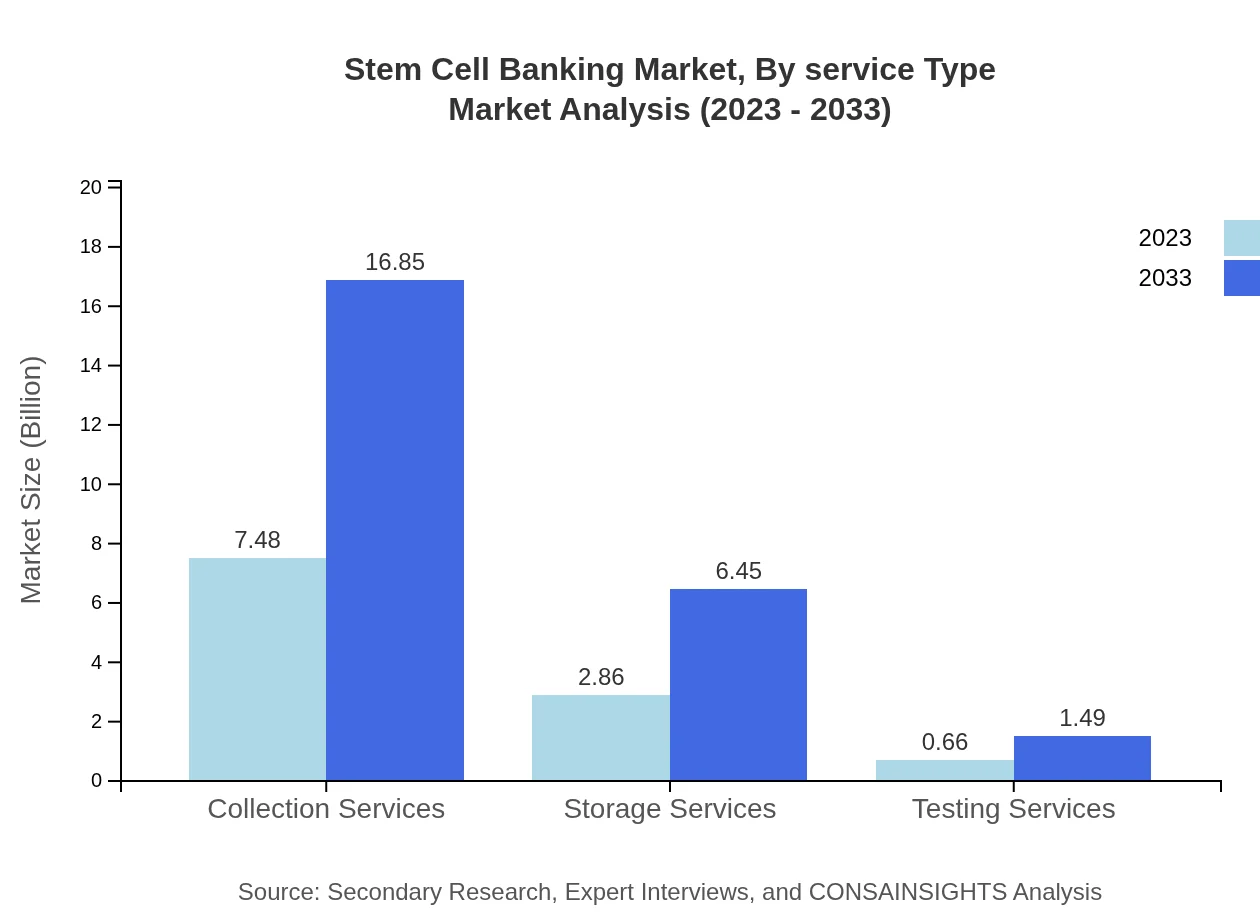
Stem Cell Banking Market Analysis By Service Type
The market for service types includes Collection Services, Storage Services, and Testing Services. Collection Services lead at $7.48 billion with a 67.97% share, with projections of $16.85 billion by 2033. Storage Services are at $2.86 billion, making up 26.01% share expected to grow to $6.45 billion. Testing Services account for $0.66 billion in 2023 and will rise to $1.49 billion.
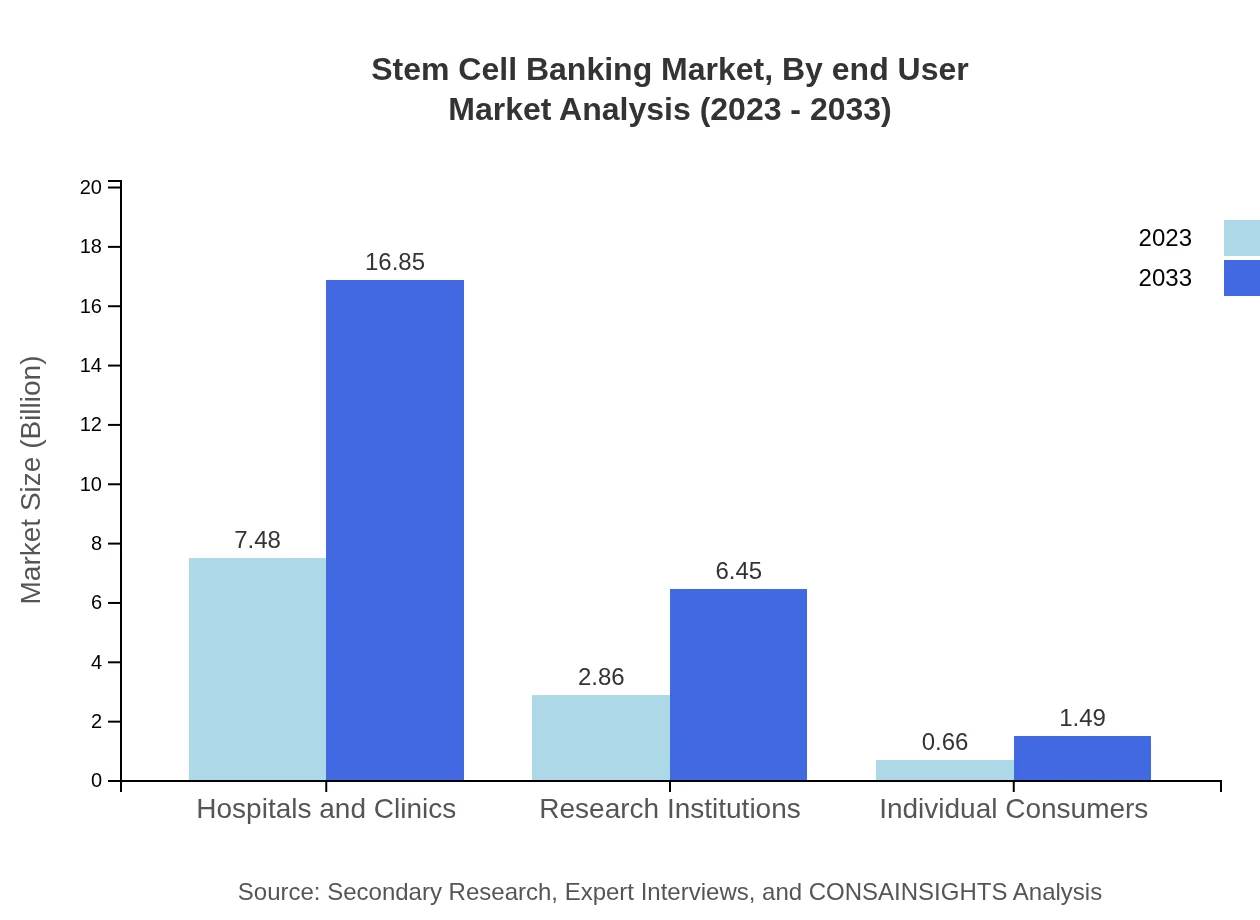
Stem Cell Banking Market Analysis By End User
Hospitals & Clinics dominate the market, achieving a size of $7.48 billion and a 67.97% share in 2023, anticipated to increase to $16.85 billion. Research Institutions account for $2.86 billion at 26.01%, projected to reach $6.45 billion, while Individual Consumers represent $0.66 billion growing to $1.49 billion.
Stem Cell Banking Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Stem Cell Banking Industry
Cord Blood Registry (CBR):
As a market leader in cord blood banking, CBR offers comprehensive cord blood and cord tissue collection and storage services, contributing significantly to advancements in regenerative medicine.Viacord:
A prominent player in the industry, Viacord provides innovative cord blood and tissue banking services, focusing on quality and security for families seeking stem cell storage.Cryo-Cell International, Inc.:
Pioneering in the field of cord blood banking, Cryo-Cell International has introduced various technologies to improve storage practices and promote the use of stem cells in therapies.StemCyte Inc.:
Recognized for its role in expanding stem cell therapy options, StemCyte focuses on cord blood banking, emphasizing on providing quality stem cells for transplantations.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of stem Cell Banking?
The stem cell banking market is projected to reach $11 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2%. This growth is driven by increasing awareness and advancements in regenerative medicine, along with expanding applications in treatments.
What are the key market players or companies in the stem Cell Banking industry?
Key players in the stem cell banking industry include major biobanks and research institutions, but specific companies were not detailed in the data provided. These entities are influential due to their roles in collection, storage, and research.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the stem Cell Banking industry?
The growth in the stem cell banking industry is driven by advancements in medical technology, increasing demand for personalized medicine, awareness about the therapeutic potential of stem cells, and favorable regulatory frameworks supporting cell therapy.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the stem Cell Banking market?
Asia Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region in the stem cell banking market, with its market size expected to grow from $2.27 billion in 2023 to $5.12 billion by 2033, reflecting increasing adoption and investment in healthcare.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the stem Cell Banking industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the stem cell banking industry, including detailed insights on market size, trends, and forecasts across various segments and regions.
What deliverables can I expect from this stem Cell Banking market research project?
Deliverables from the stem cell banking market research project typically include comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth forecasts, competitive landscape analysis, segmentation insights, and actionable recommendations for stakeholders.
What are the market trends of stem Cell Banking?
Current trends in the stem cell banking market include an increase in cord blood storage, trends towards home collection services, growing consumer awareness, and technological advancements in storage and preservation methods.