Structural Health Monitoring Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: structural-health-monitoring
Structural Health Monitoring Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report details the Structural Health Monitoring market, analyzing current trends, market size, and projections for the period between 2023 and 2033. Insights include segmentation by technology and application, regional performance, and competitive landscape analysis.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
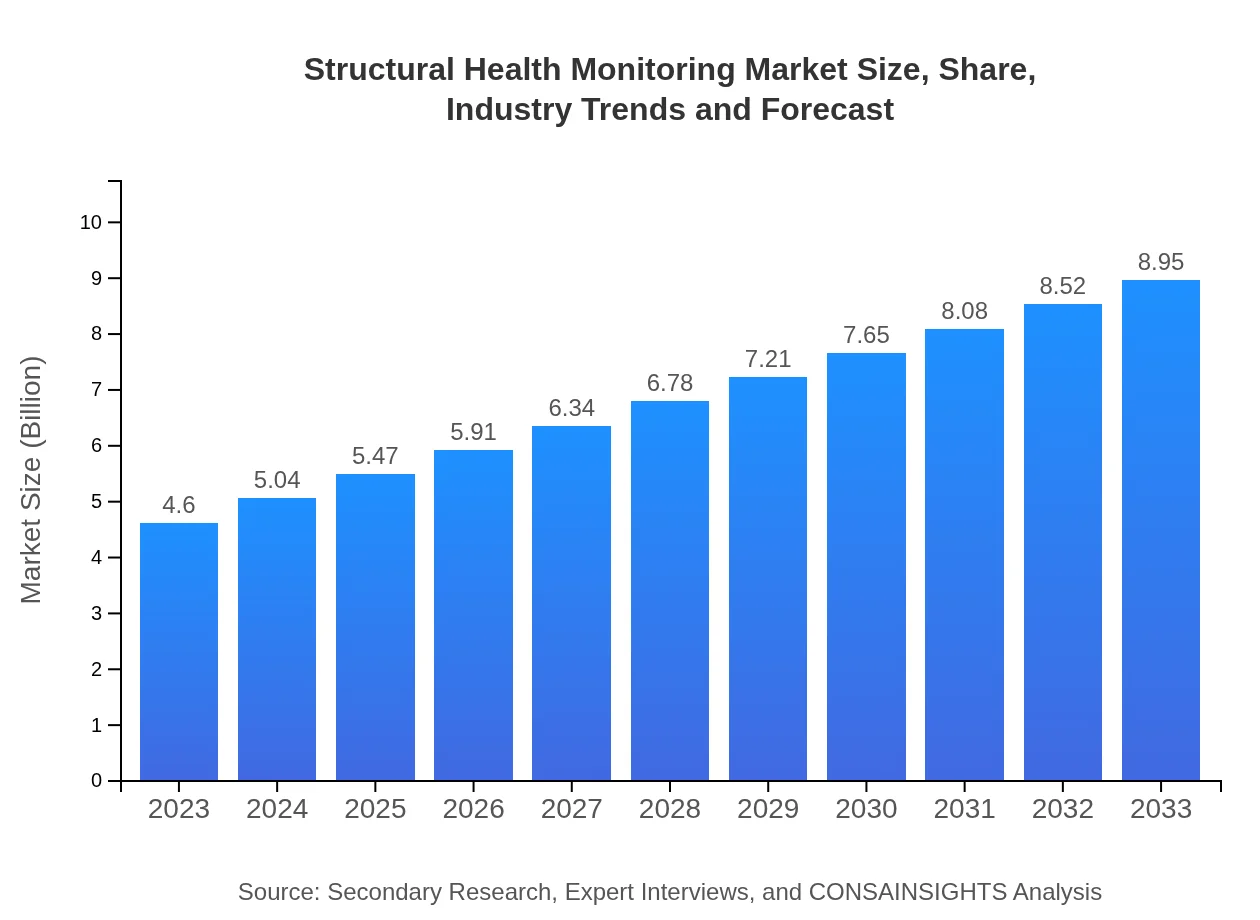
| 2023 Market Size | $4.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.7% |
| 2033 Market Size | $8.95 Billion |
| Top Companies | KCF Technologies, Fugro, Structural Monitoring Systems, GeoSIG, IFM Efector |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Structural Health Monitoring Market Overview
Customize Structural Health Monitoring Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Structural Health Monitoring market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Structural Health Monitoring's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Structural Health Monitoring
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Structural Health Monitoring market in 2023?
Structural Health Monitoring Industry Analysis
Structural Health Monitoring Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Structural Health Monitoring Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Structural Health Monitoring Market Report:
Europe's SHM market, anticipated to grow from $1.21 billion in 2023 to $2.36 billion by 2033, is influenced by stringent regulatory mandates and a substantial focus on sustainable development practices among EU member states.Asia Pacific Structural Health Monitoring Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region, valued at $0.94 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to $1.82 billion by 2033, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. Government initiatives promoting infrastructure safety are expected to bolster SHM adoption in the region.North America Structural Health Monitoring Market Report:
North America holds a significant share of the global SHM market, with a valuation of $1.59 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $3.09 billion by 2033. The primary drivers include aging infrastructure, government funding for improvements, and rising safety regulations.South America Structural Health Monitoring Market Report:
In South America, the SHM market is expected to expand from $0.24 billion in 2023 to $0.47 billion by 2033. The growth is supported by increasing investments in critical infrastructure projects and heightened awareness of the benefits of monitoring systems.Middle East & Africa Structural Health Monitoring Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa SHM market is expected to evolve from $0.62 billion in 2023 to $1.21 billion by 2033, spurred by investments in mega-projects and a growing need for effective monitoring solutions to ensure safety.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
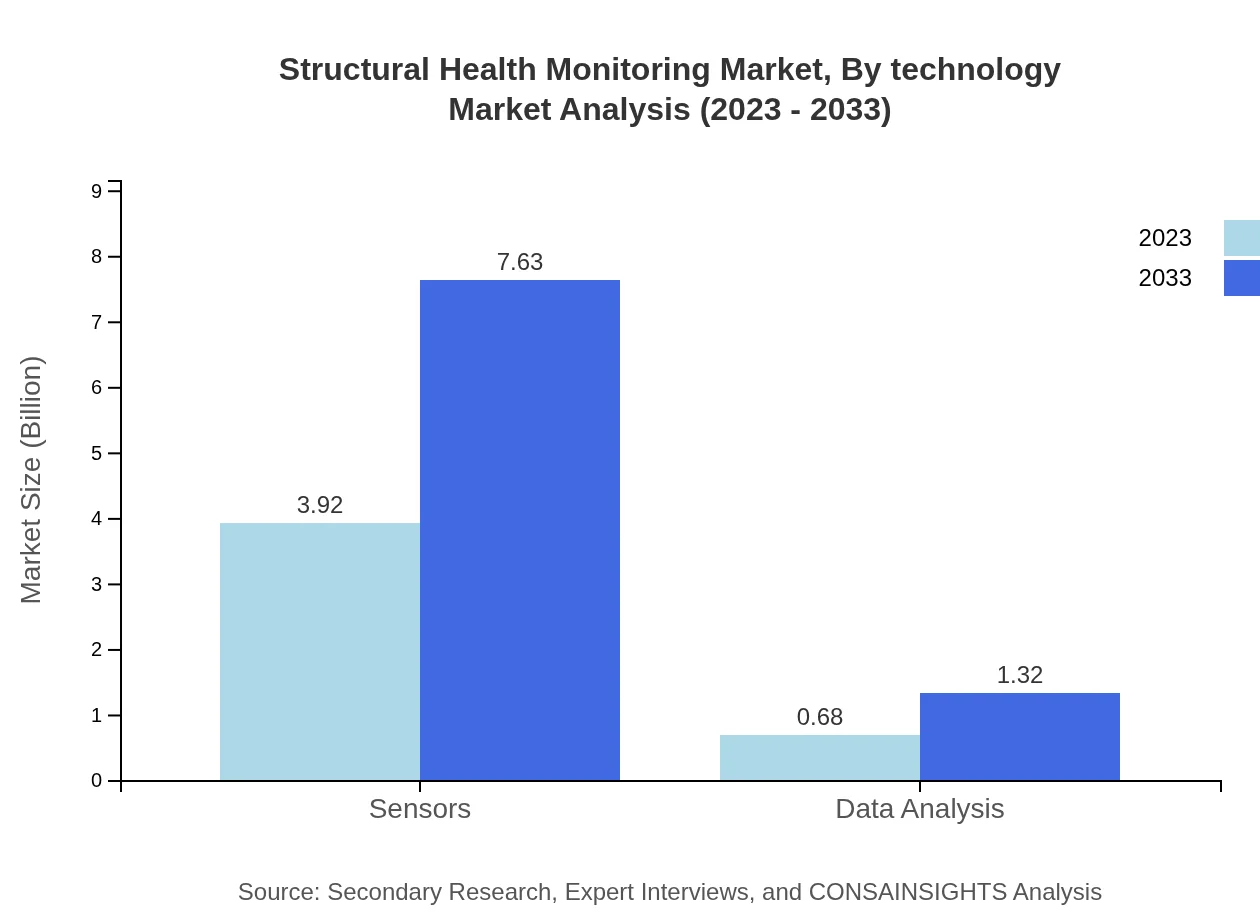
Structural Health Monitoring Market Analysis By Technology
Key technologies in SHM include Sensors (85.23% market share in 2023), Data Analysis (14.77% market share), allowing organizations to monitor equipment condition and performance. The Sensors segment, growing from $3.92 billion to $7.63 billion by 2033, underscores the dominance of real-time monitoring systems in ensuring infrastructure reliability.
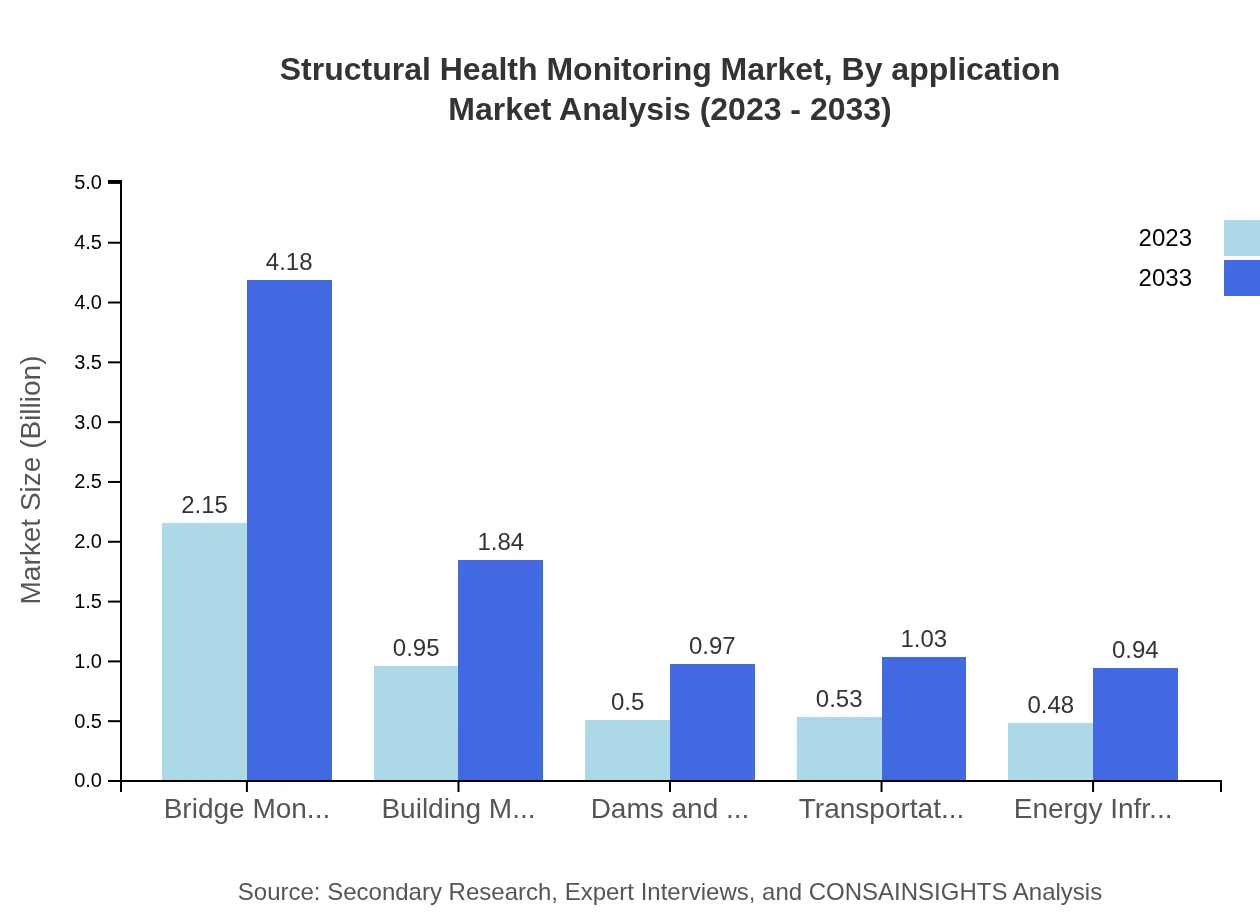
Structural Health Monitoring Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the Construction sector leads with a market size growing from $2.15 billion in 2023 to $4.18 billion in 2033, illustrating its critical role in ensuring building integrity. The Transportation segment, also significant, is growing from $0.95 billion to $1.84 billion during the same period.
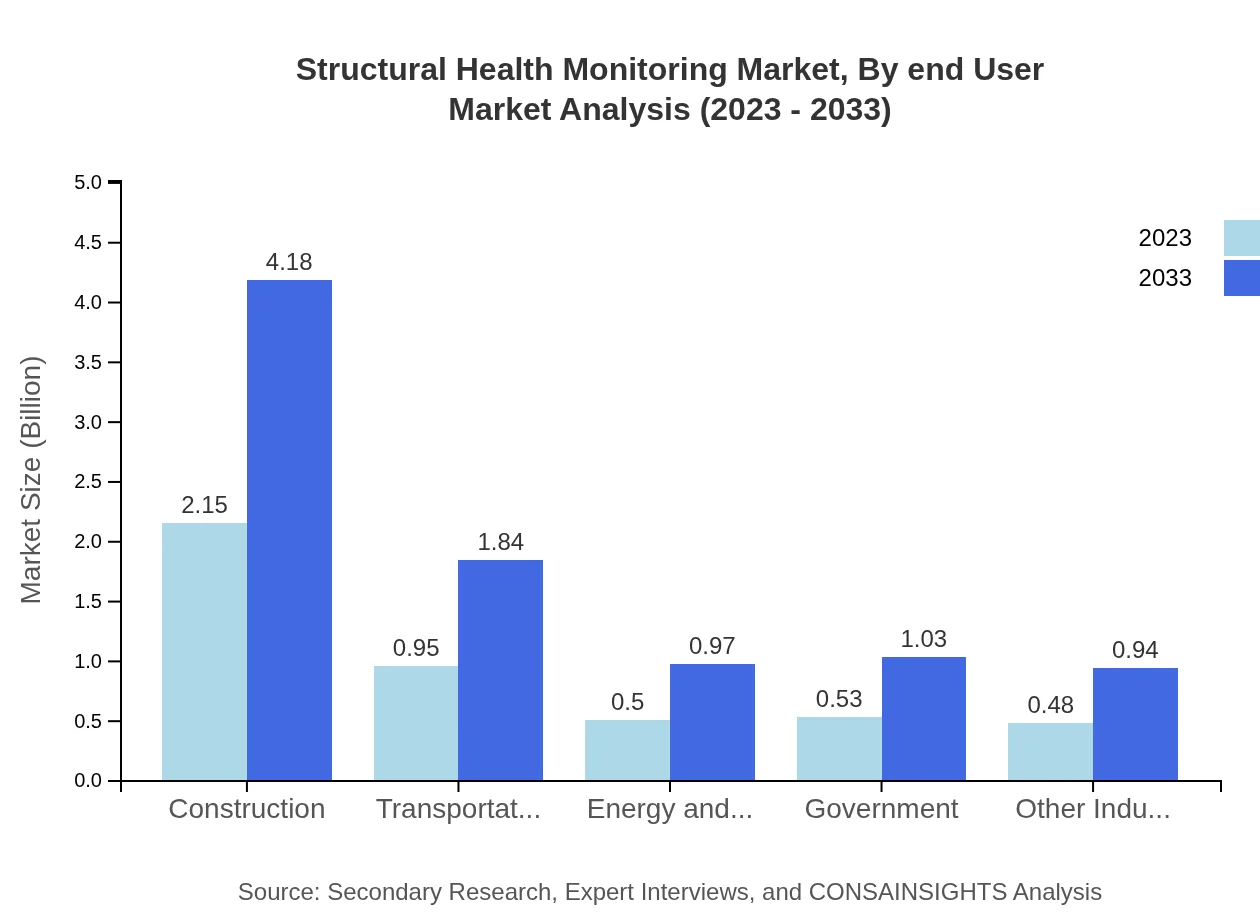
Structural Health Monitoring Market Analysis By End User
The Public Sector remains a major contributor across applications like transportation and government infrastructure, achieving a growth from $0.53 billion in 2023 to $1.03 billion by 2033. Similarly, the Private Sector is engaged in investments due to increasing infrastructures and transportation requirements.
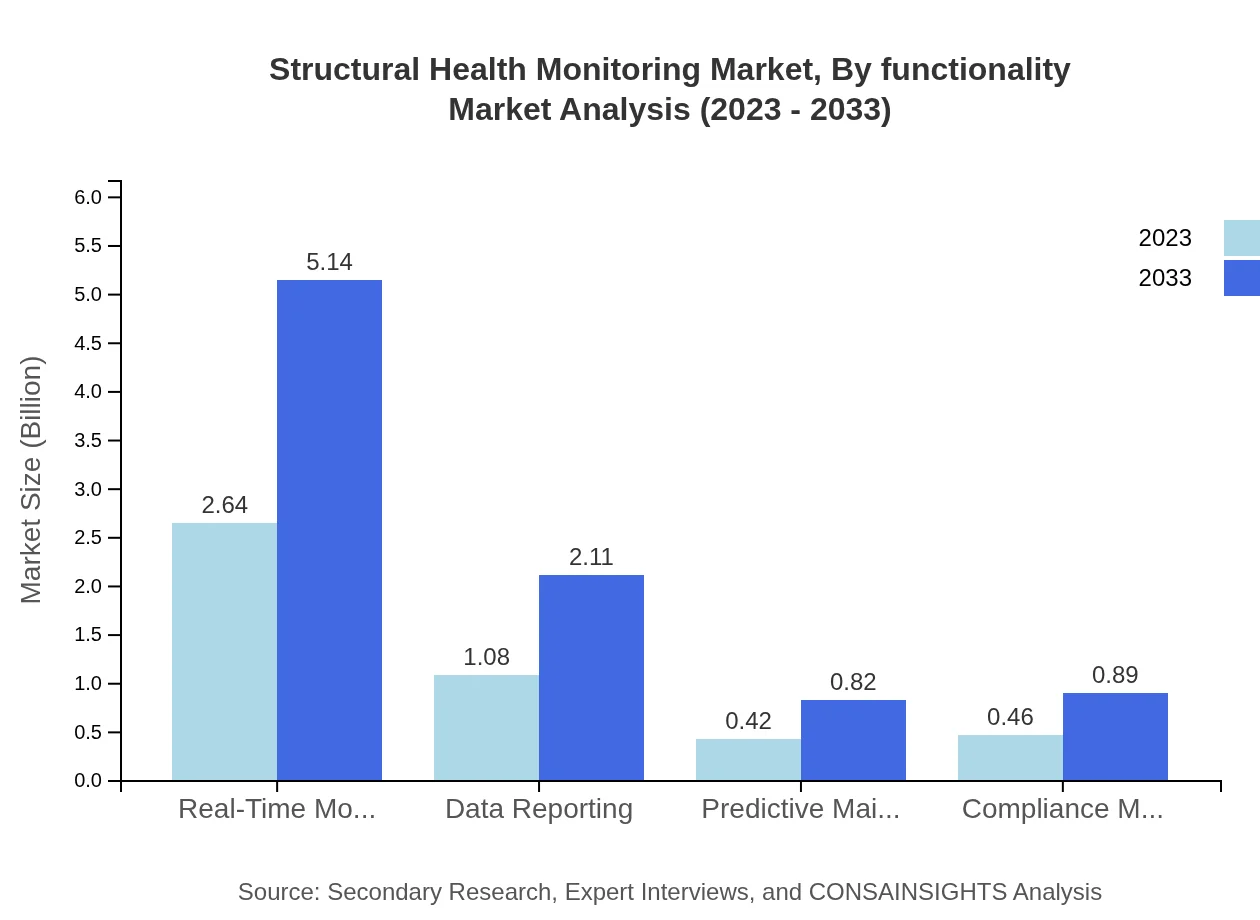
Structural Health Monitoring Market Analysis By Functionality
Functionality-wise, Real-Time Monitoring constitutes the largest segment, expanding from $2.64 billion in 2023 to $5.14 billion in 2033. Data Reporting and Predictive Maintenance are also critical, focusing on condition monitoring and planned maintenance.
Structural Health Monitoring Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Structural Health Monitoring Industry
KCF Technologies:
A leader in SHM solutions, KCF Technologies specializes in real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance systems tailored for industrial applications.Fugro:
A global geotechnical consultancy known for its innovative monitoring technology that enhances structural integrity assessments.Structural Monitoring Systems:
An expert in developing novel monitoring equipment that provides insights into structural health across various industries.GeoSIG:
Specializes in developing instrumentation for the monitoring of seismic activity and structural health evaluation.IFM Efector:
Provides a broad range of sensors and monitoring solutions focused on industrial automation and infrastructure health.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of structural health monitoring?
The global structural health monitoring market size is projected to reach $4.6 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% from its current value. This growth is driven by increasing infrastructure projects and the need for safety measures.
What are the key market players or companies in this structural health monitoring industry?
Key players in the structural health monitoring industry include major companies like Acellent Technologies, Geo-Systems, and Kinsley Construction. These companies are recognized for their innovative solutions in monitoring infrastructure health and safety.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the structural health monitoring industry?
Key growth factors in the structural health monitoring industry include an increasing number of infrastructure projects globally, rising safety regulations, and advancements in sensor technologies that enhance data collection and analysis capabilities.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the structural health monitoring?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the structural health monitoring market, with projected growth from $1.59 billion in 2023 to $3.09 billion by 2033, driven by significant investments in infrastructure and technology.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the structural health monitoring industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the structural health monitoring industry. This includes detailed insights that cater to unique market segments or geographical areas.
What deliverables can I expect from this structural health monitoring market research project?
Deliverables from the structural health monitoring market research project include comprehensive market analysis, competitive landscape assessments, segment growth forecasts, and actionable insights to inform strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of structural health monitoring?
Current market trends in structural health monitoring include a shift towards real-time monitoring systems and predictive maintenance strategies. Additionally, increased focus on smart city initiatives is driving demand for advanced monitoring solutions.