Submarine Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: submarine
Submarine Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the submarine market, covering market size, trends, segmentation, regional analysis, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It aims to deliver valuable insights for stakeholders looking to navigate this evolving industry landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
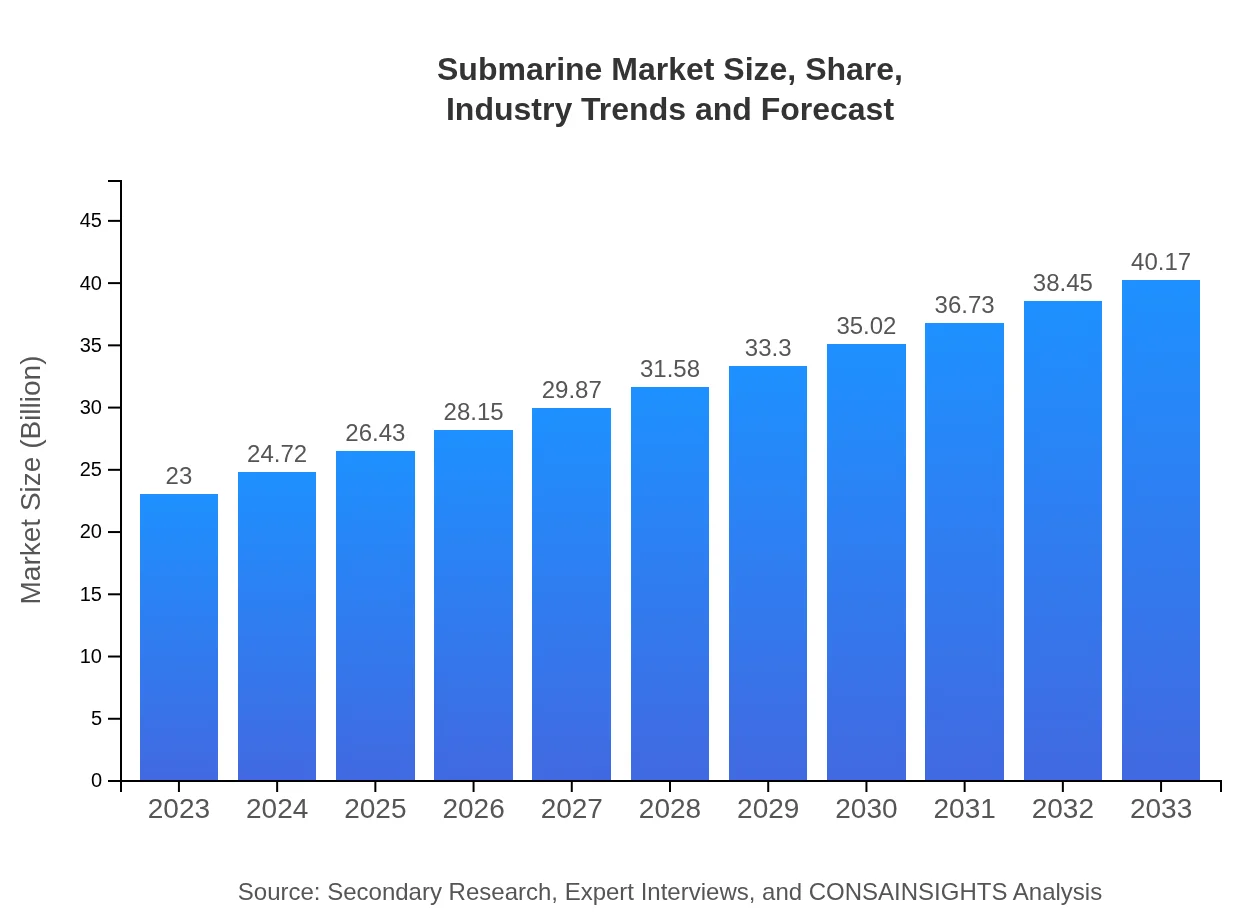
| 2023 Market Size | $23.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.6% |
| 2033 Market Size | $40.17 Billion |
| Top Companies | General Dynamics, BAE Systems, Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems, Huntington Ingalls Industries |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Submarine Market Overview
Customize Submarine Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Submarine market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Submarine's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Submarine
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Submarine market in 2023?
Submarine Industry Analysis
Submarine Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Submarine Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Submarine Market Report:
In Europe, the submarine market was valued at USD 6.61 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 11.55 billion by 2033. European nations are enhancing their defensive postures amid geopolitical tensions and are investing in advanced submarine technologies with collaborative defense projects.Asia Pacific Submarine Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the submarine market size was valued at USD 4.60 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 8.03 billion by 2033. Increasing territorial disputes and maritime challenges drive defense spending, leading to a rapid modernization of naval technologies among countries like China and India.North America Submarine Market Report:
North America accounted for USD 7.91 billion in 2023, with forecasts to escalate to USD 13.82 billion by 2033. The U.S. Navy continues to expand its submarine fleet, emphasizing stealth and advanced combat systems to maintain dominance.South America Submarine Market Report:
The South American submarine market was valued at USD 2.22 billion in 2023, expected to grow to USD 3.88 billion by 2033. Countries are exploring enhanced naval capabilities despite budget constraints, focusing on strategic partnerships for technology acquisition.Middle East & Africa Submarine Market Report:
The submarine market in the Middle East and Africa was valued at USD 1.66 billion in 2023, projected to expand to USD 2.89 billion by 2033. Growing regional conflicts and the need for maritime security are driving countries to invest in submarine capabilities.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
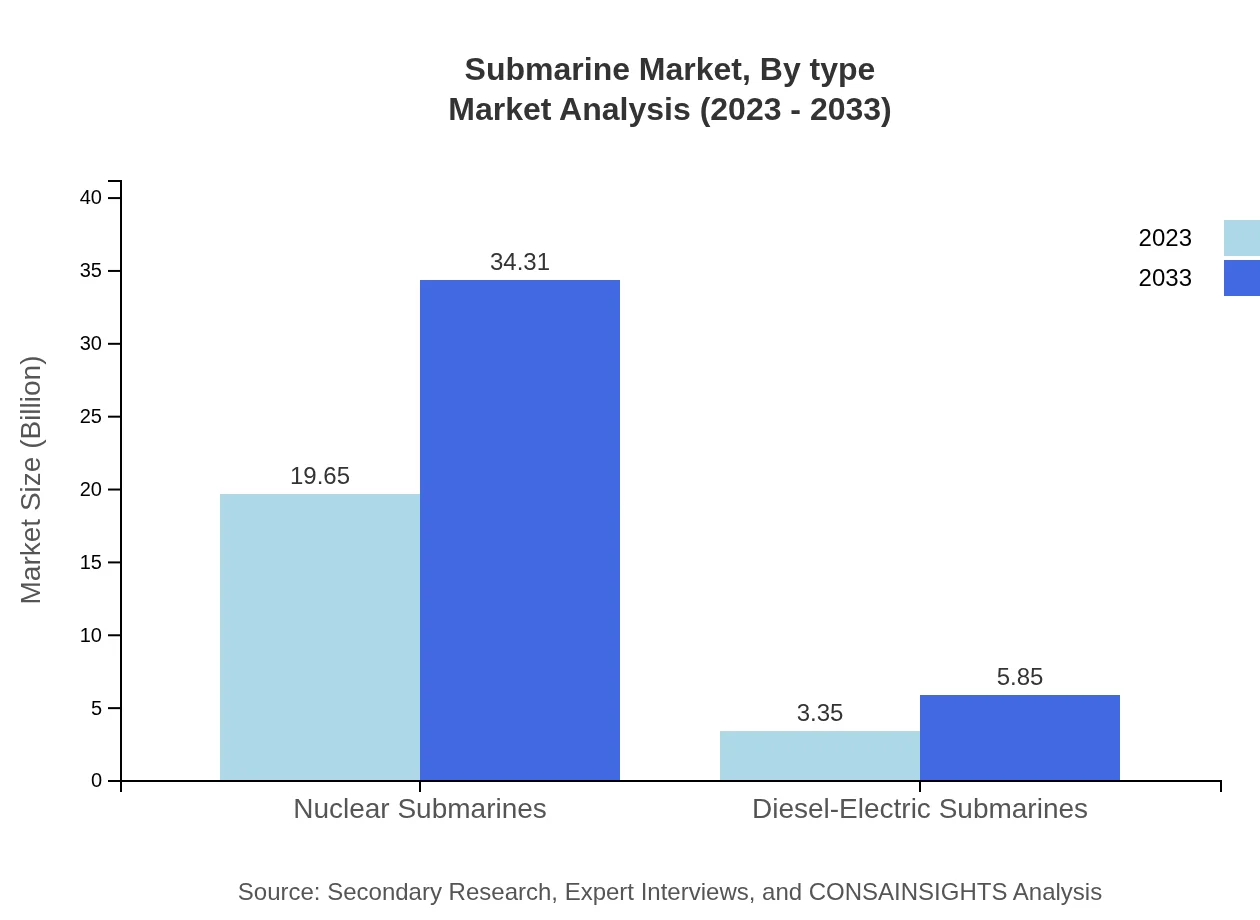
Submarine Market Analysis By Type
The market is predominantly segmented into nuclear and diesel-electric submarines. In 2023, nuclear submarines were valued at USD 19.65 billion and are expected to reach USD 34.31 billion by 2033, owning an 85.43% market share. Diesel-electric submarines, valued at USD 3.35 billion in 2023, are expected to grow to USD 5.85 billion, holding a 14.57% market share throughout the forecast period.
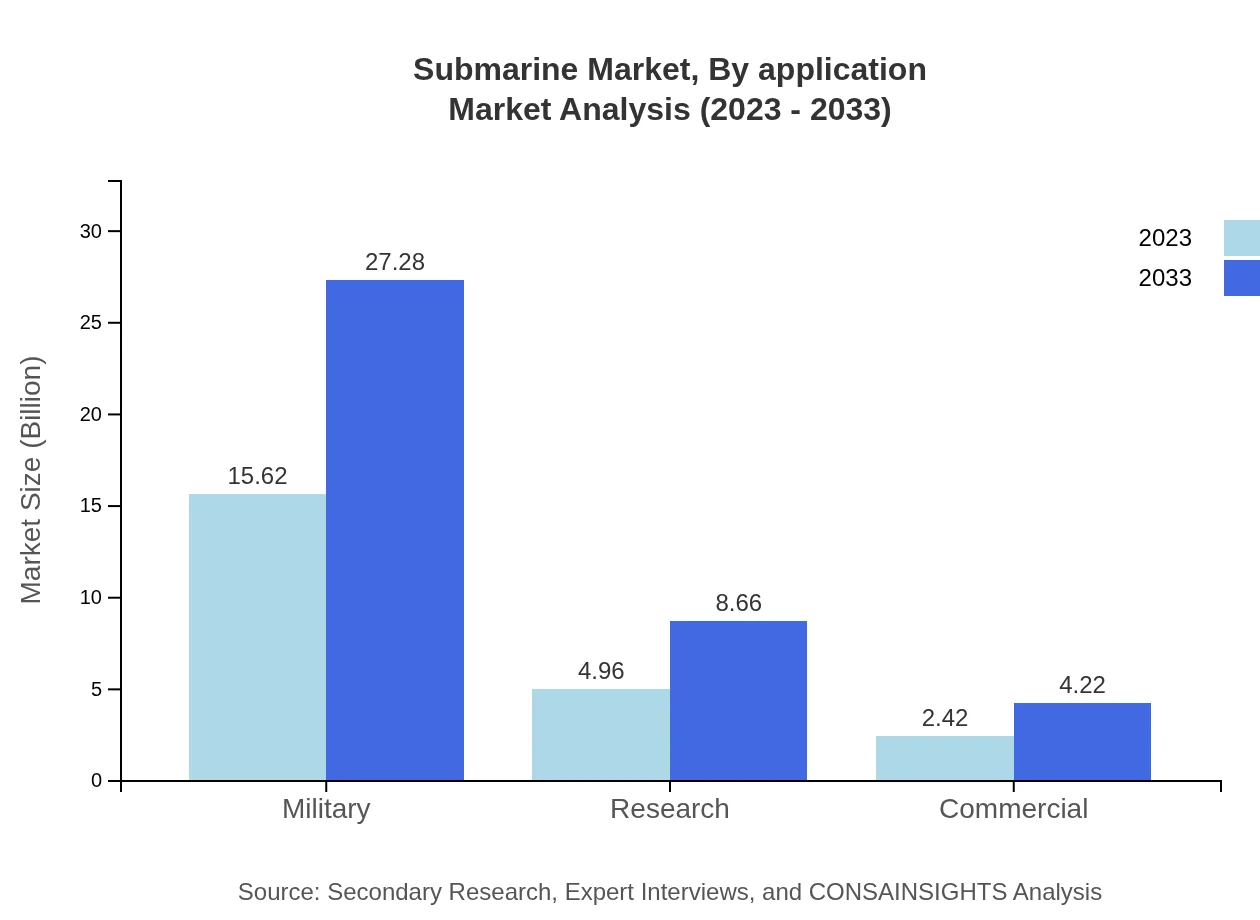
Submarine Market Analysis By Application
By application, military usage dominates the submarine market with a valuation of USD 15.62 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to USD 27.28 billion in 2033, equating to a 67.92% share. Research institutes and commercial applications comprise 21.57% and 10.51%, respectively, highlighting their importance in technology advancements and marine research applications.
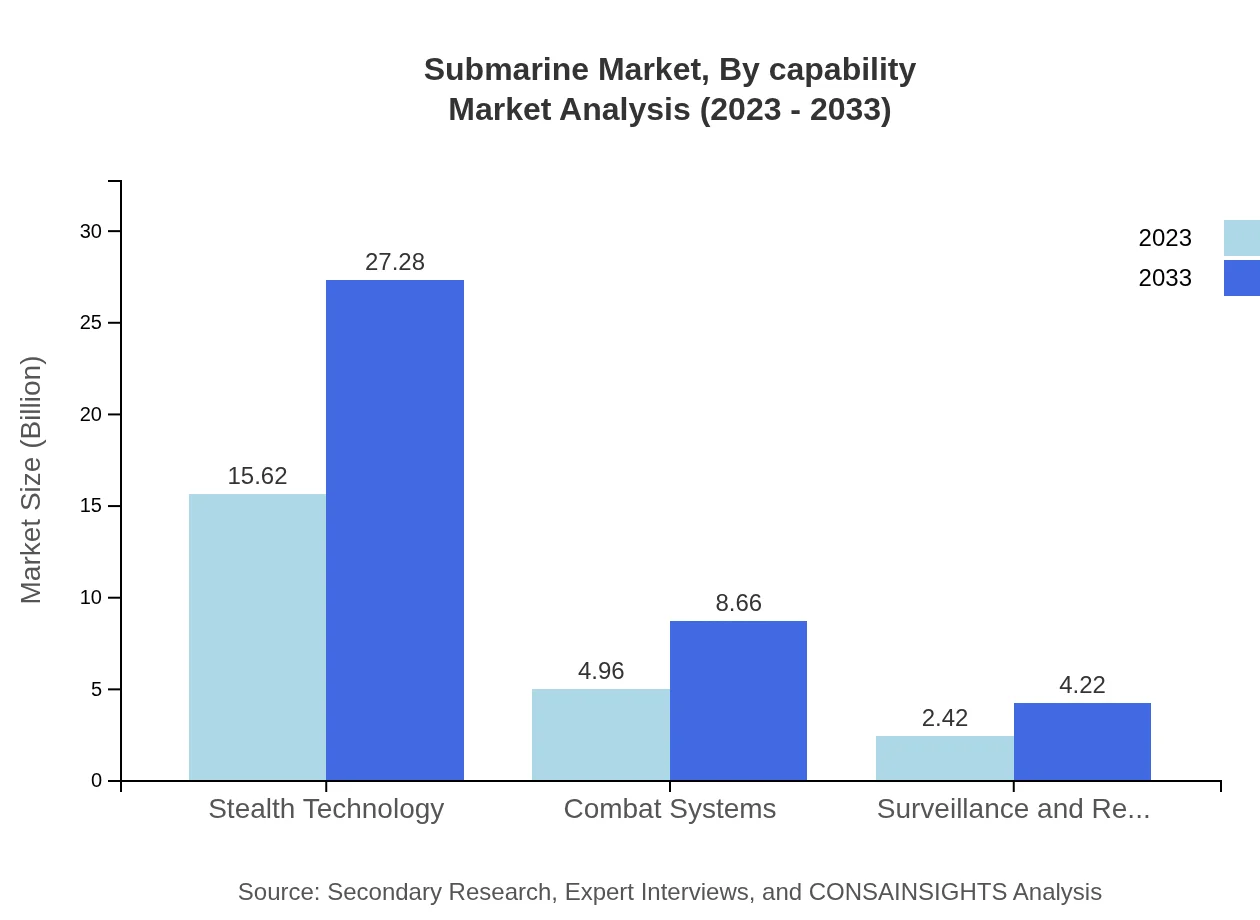
Submarine Market Analysis By Capability
Considering capabilities, the submarine market segments into stealth technology, automated systems, combat systems, and more. Stealth technology leads with a 67.92% market share, growing from USD 15.62 billion in 2023 to USD 27.28 billion in 2033. Automation systems, combat systems, and surveillance technologies reflect growing trends in operational efficiency and combat readiness.
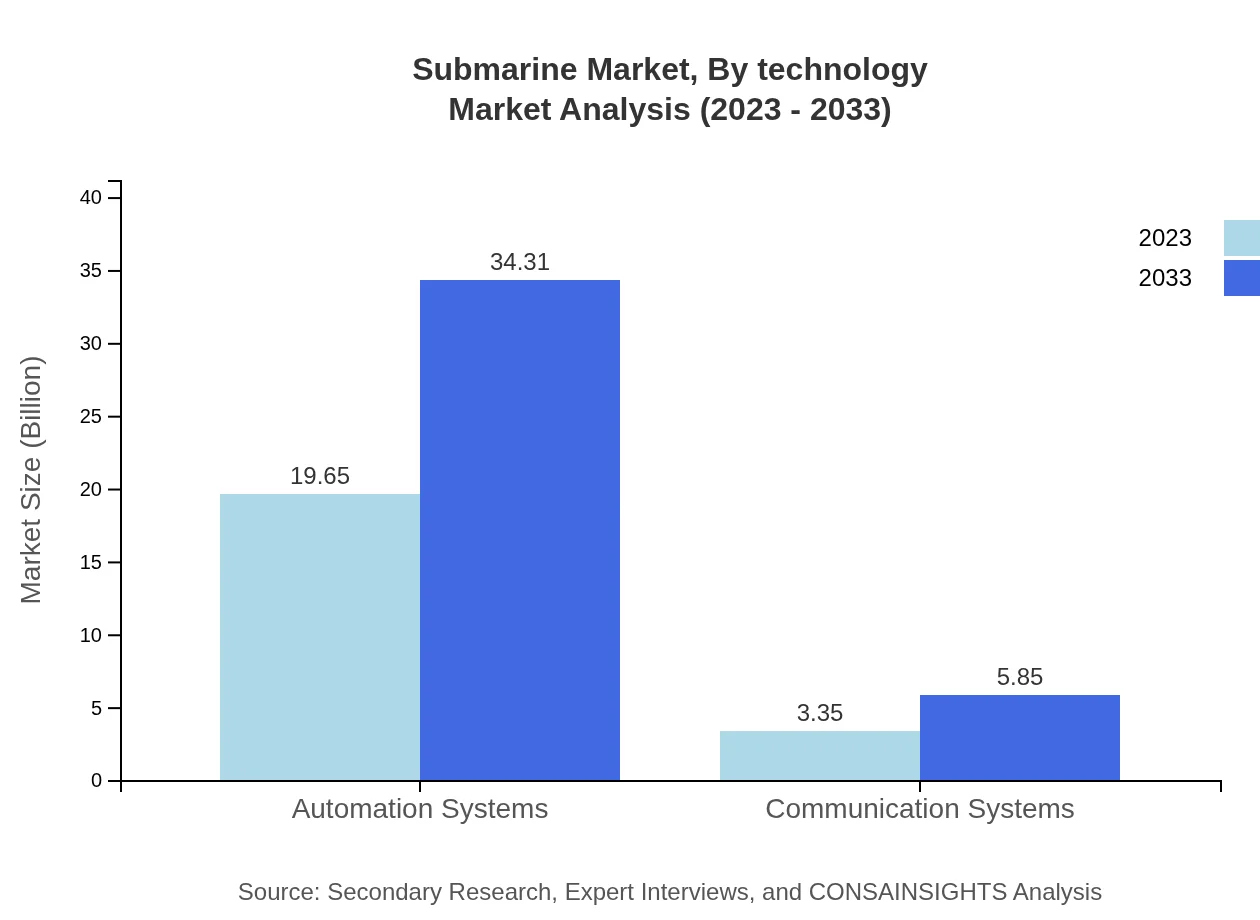
Submarine Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements are significantly affecting the submarine market, with automation and communication systems becoming essential for modern naval operations. In 2023, automation systems were valued at USD 19.65 billion, projected to grow to USD 34.31 billion by 2033, whereas communication systems will increase from USD 3.35 billion to USD 5.85 billion.
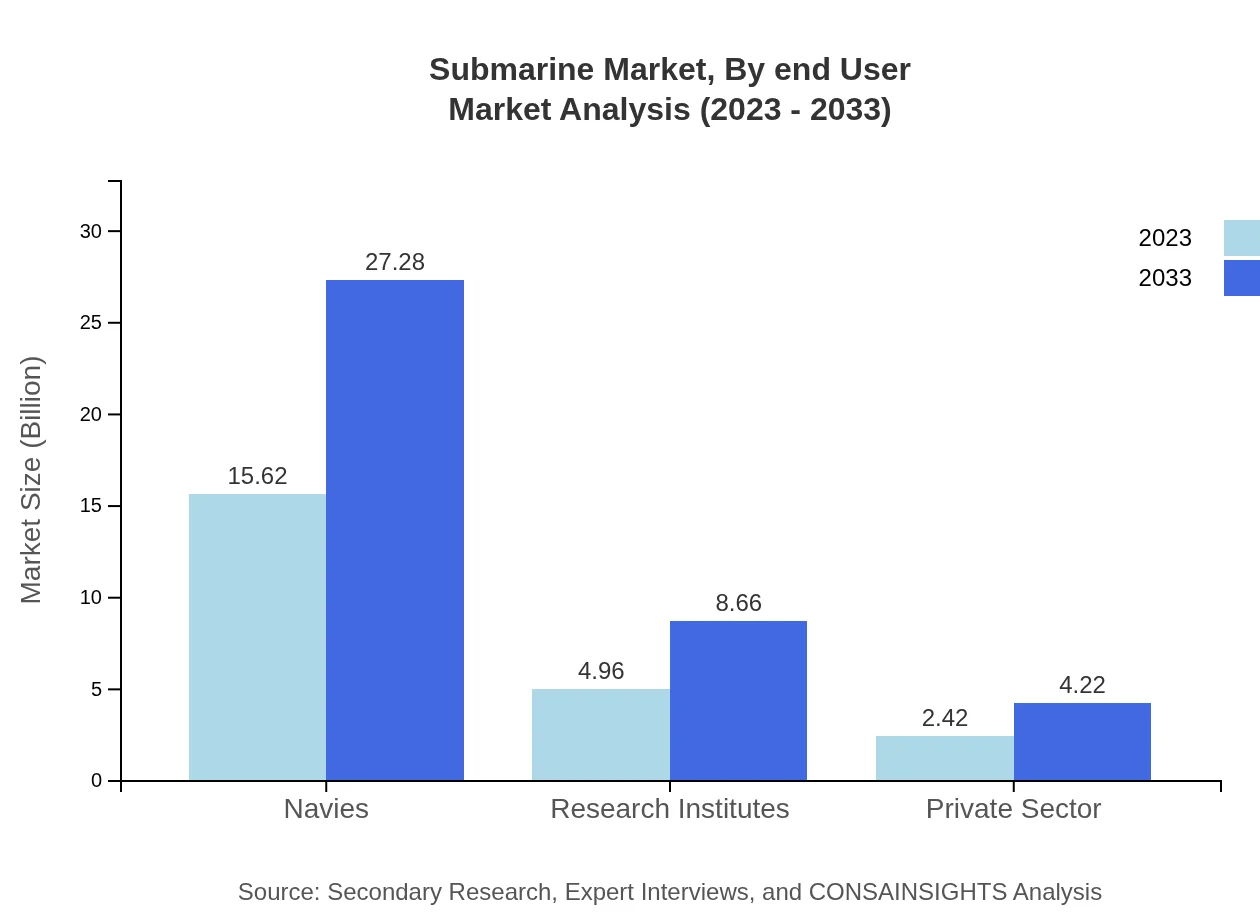
Submarine Market Analysis By End User
End-users of submarines include navies, research institutions, and the private sector. Navies captured a market size of USD 15.62 billion in 2023, expected to grow to USD 27.28 billion. Research institutes and the private sector are garnering attention for their expertise in advancing underwater technology and applications.
Submarine Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Submarine Industry
General Dynamics:
A leading defense contractor specializing in submarine construction and modernization, General Dynamics is known for its Virginia-class submarines which integrate cutting-edge technology.BAE Systems:
BAE Systems is a major player in the defense sector, recognized for its Astute-class submarines, which emphasize stealth and advanced combat systems.Thyssenkrupp Marine Systems:
The German company is noted for its design and construction of advanced conventional submarines, contributing to the modernization of naval forces across Europe.Huntington Ingalls Industries:
One of the largest naval shipbuilding companies in the U.S., it specializes in the design and construction of nuclear submarines and has substantial revenues from the defense sector.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of submarine?
The global submarine market is projected to grow from approximately $23 billion in 2023 to an estimated size in 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6%. This growth signifies increasing investments in military and defense capabilities globally.
What are the key market players or companies in this submarine industry?
Key players in the submarine market include prominent defense manufacturers and naval contractors that specialize in submarine production and technology. These companies are pivotal to advancing submarine capabilities and are focused on innovation in defense systems.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the submarine industry?
The growth of the submarine market is driven by increased military expenditure, geopolitical tensions necessitating enhanced naval security, and advancements in submarine technology such as stealth capabilities and automation systems.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the submarine market?
The fastest-growing region in the submarine market is projected to be Asia Pacific, with its market expected to grow from $4.60 billion in 2023 to $8.03 billion in 2033, reflecting significant investments in naval modernization.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the submarine industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the submarine industry, allowing for a detailed analysis of market dynamics, trends, and forecasts as per client requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this submarine market research project?
Deliverables from the submarine market research project include detailed market analysis reports, regional growth insights, competitive landscape information, trend analyses, and customized forecasts to aid strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of submarine?
Current market trends in the submarine sector include increasing focus on stealth technology, automation systems, and advanced combat and communication systems, reflecting the evolving needs of modern naval warfare and security.