Substation Automation Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: substation-automation
Substation Automation Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Substation Automation market from 2023 to 2033, covering market size, trends, segmentation, regional insights, and forecasts to equip stakeholders with valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
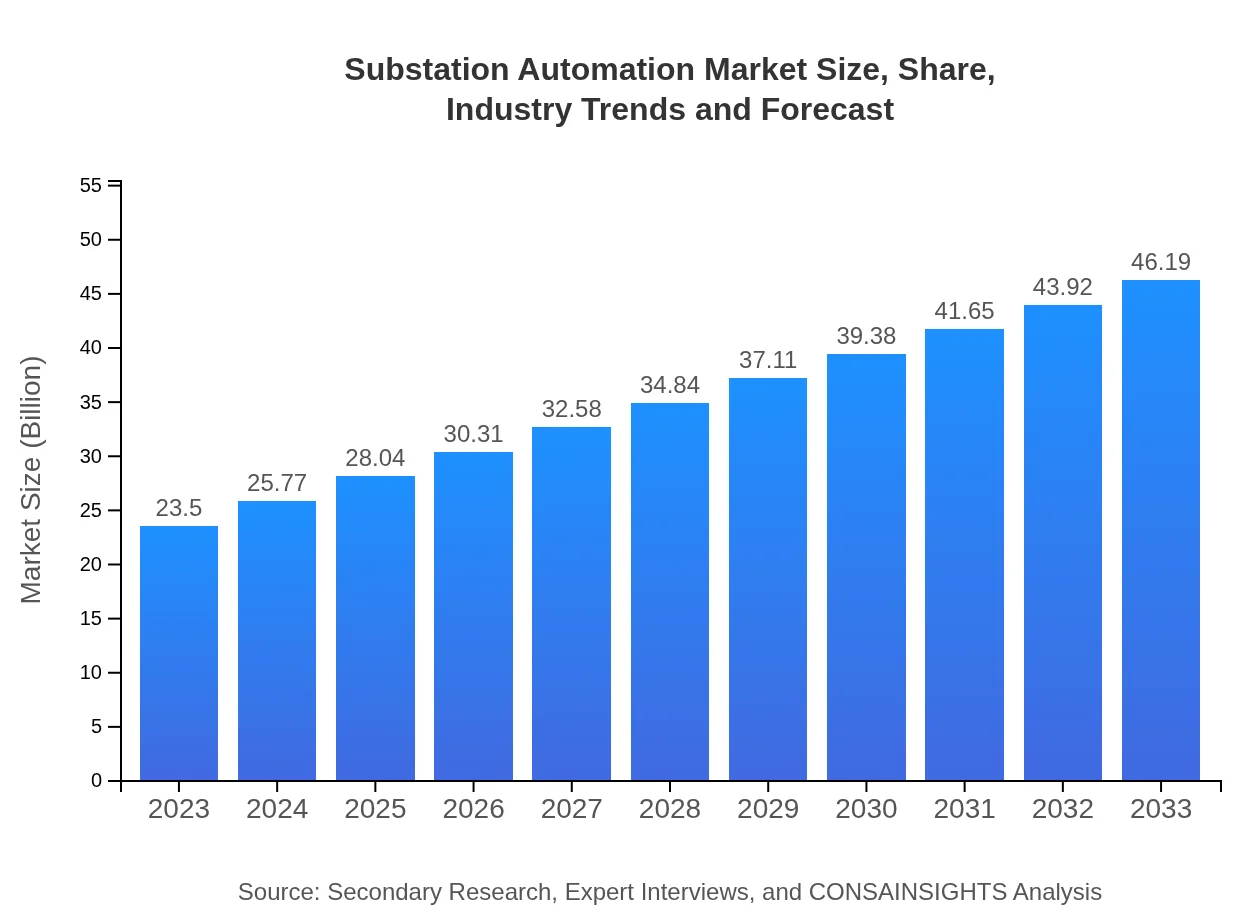
| 2023 Market Size | $23.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $46.19 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd., GE Grid Solutions, Emerson Electric Co. |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Substation Automation Market Overview
Customize Substation Automation Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Substation Automation market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Substation Automation's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Substation Automation
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Substation Automation market in 2023?
Substation Automation Industry Analysis
Substation Automation Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Substation Automation Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Substation Automation Market Report:
Europe is one of the largest markets for Substation Automation, expected to grow from $6.18 billion in 2023 to $12.15 billion by 2033. The region benefits from rigorous regulatory frameworks aimed at promoting renewable energy and energy efficiency. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are actively investing in smart grid technologies.Asia Pacific Substation Automation Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region showcases a significant growth potential in the Substation Automation market, with a projected increase from $4.79 billion in 2023 to $9.41 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization, industrialization, and investments in smart grid infrastructure are key drivers of this growth. Countries like India and China are at the forefront, focusing on enhancing electrical infrastructure.North America Substation Automation Market Report:
North America, currently valued at $7.60 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $14.93 billion by 2033. The strong market performance is driven by technological advancements, increasing utility investments in grid modernization, and a shift towards sustainable energy practices in the United States and Canada.South America Substation Automation Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to grow from $2.06 billion in 2023 to $4.04 billion by 2033. The main drivers include increasing electricity demand, government initiatives towards energy efficiency, and the integration of renewable energy sources. Brazil and Argentina are leading the charge in adopting advanced automation technologies.Middle East & Africa Substation Automation Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is poised to grow from $2.88 billion in 2023 to $5.66 billion by 2033. The growth is fueled by increasing investments in power infrastructure, rising energy demand, and the integration of renewable energy solutions in the GCC nations, especially Saudi Arabia and the UAE.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Substation Automation Market Analysis By Product
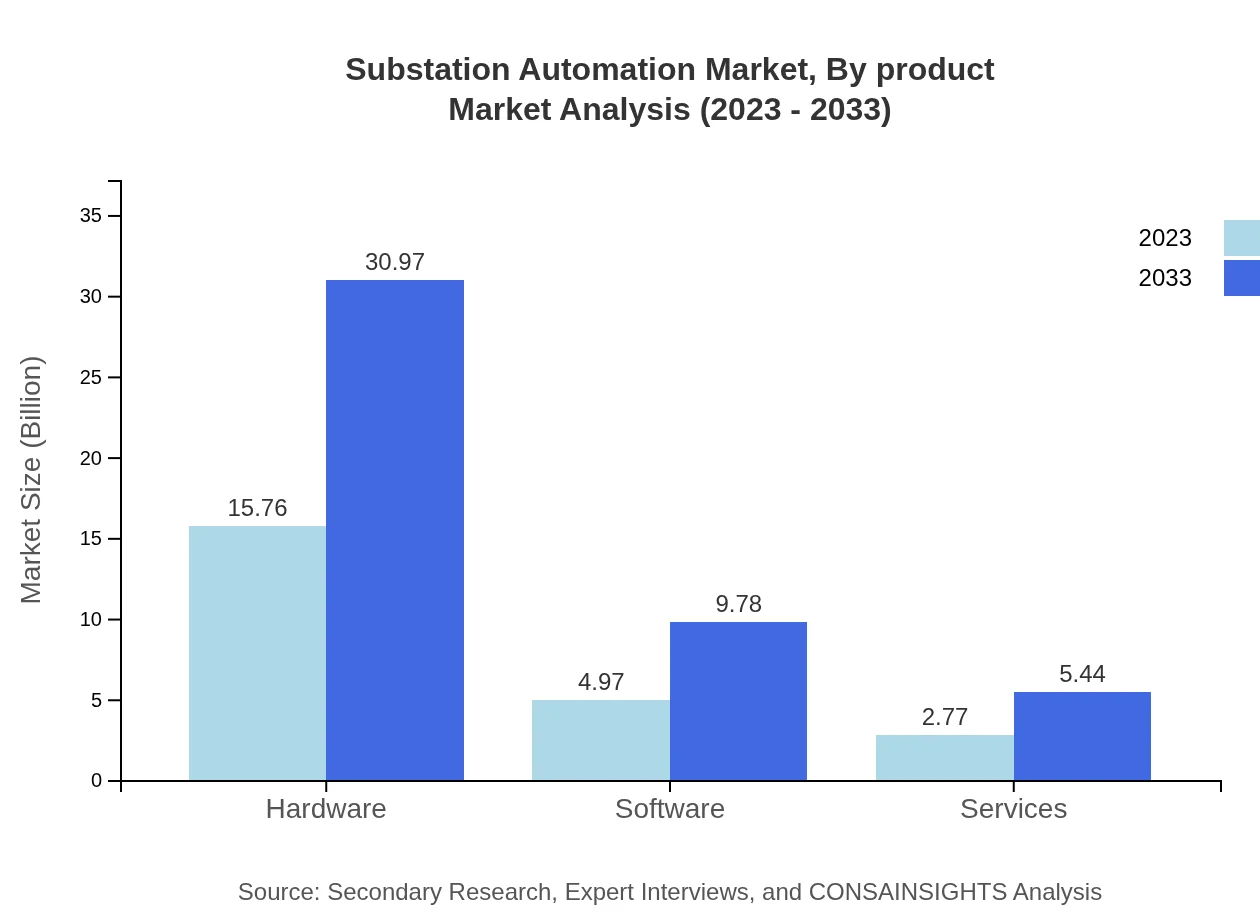
The Substation Automation market is divided into hardware, software, and services. In 2023, the hardware segment dominates with a market size of $15.76 billion, expected to reach $30.97 billion by 2033, representing a 67.05% market share. The software segment, valued at $4.97 billion in 2023, will also grow to $9.78 billion, capturing 21.17% share. The services segment, although smaller at $2.77 billion, will grow to $5.44 billion, reaching an 11.78% share.
Substation Automation Market Analysis By Application
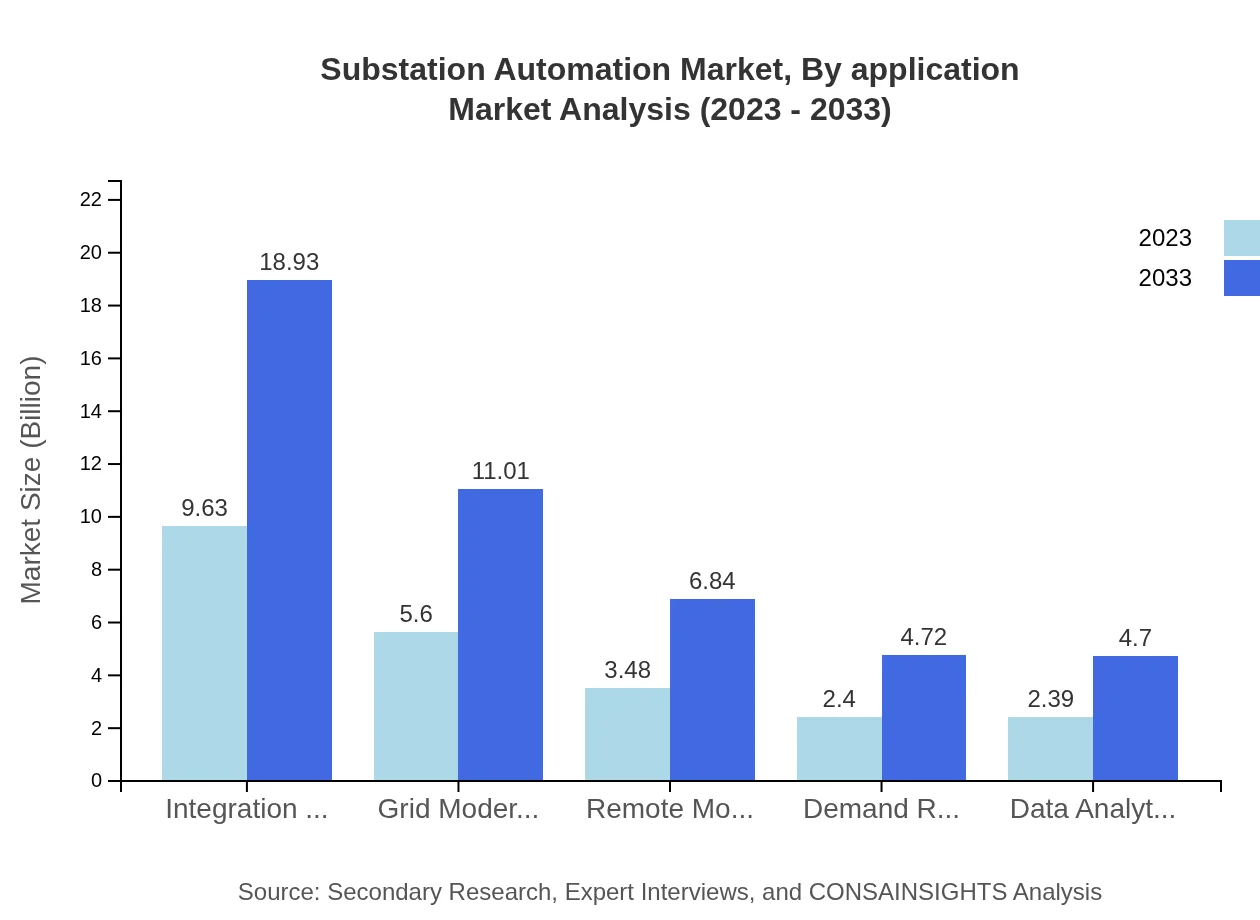
Segmentation by application shows that utilities account for the largest share in the market. Utility applications will see growth from $15.76 billion in 2023 to $30.97 billion by 2033 (67.05% share). Furthermore, commercial and industrial sectors also significantly contribute, with the industrial sector expected to grow from $4.97 billion to $9.78 billion (21.17%), and the commercial sector from $2.77 billion to $5.44 billion (11.78%).
Substation Automation Market Analysis By Technology
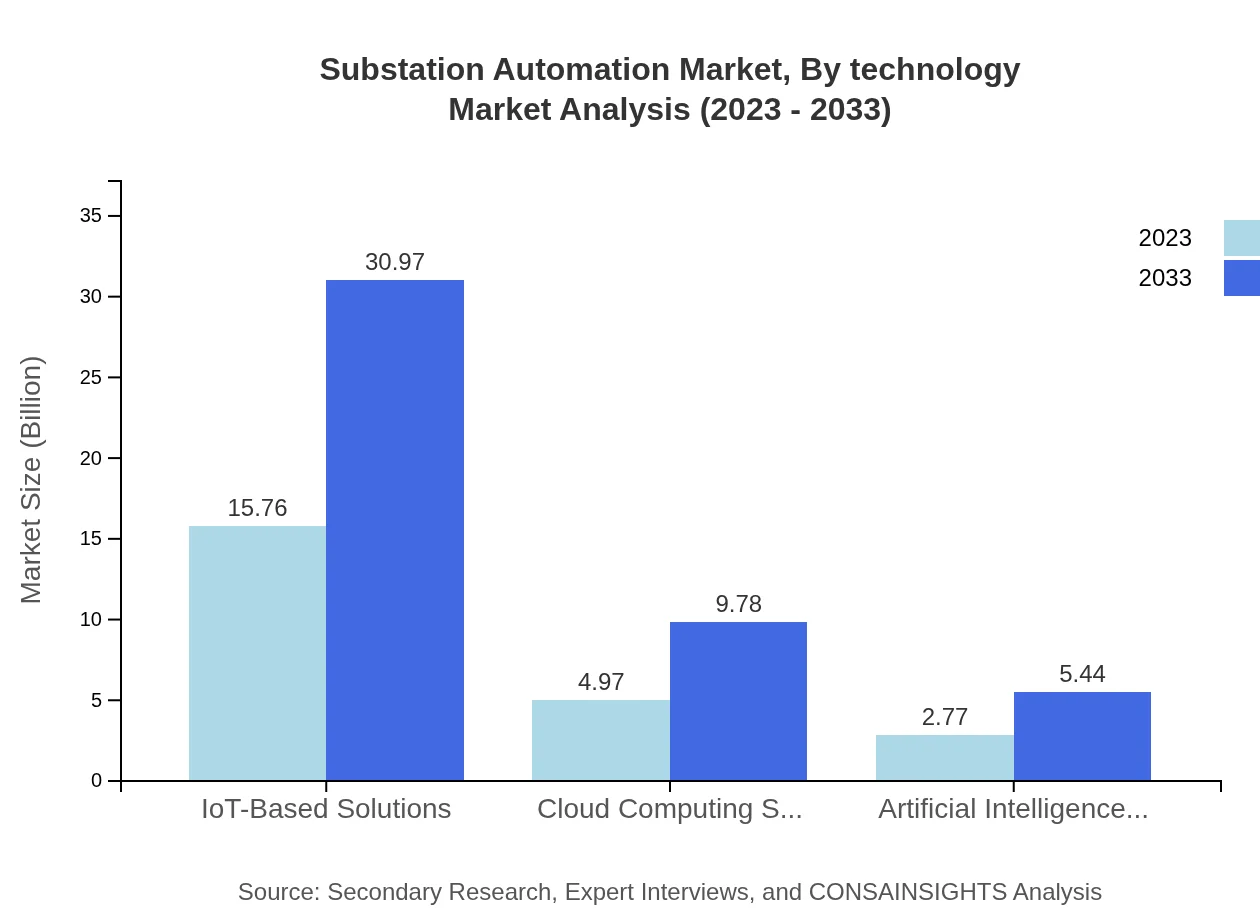
The technology segment shows significant importance for the market with IoT-based solutions growing from $15.76 billion to $30.97 billion (67.05% share). Cloud computing solutions will expand from $4.97 billion to $9.78 billion (21.17%), and applications for artificial intelligence are projected to rise from $2.77 billion to $5.44 billion (11.78%).
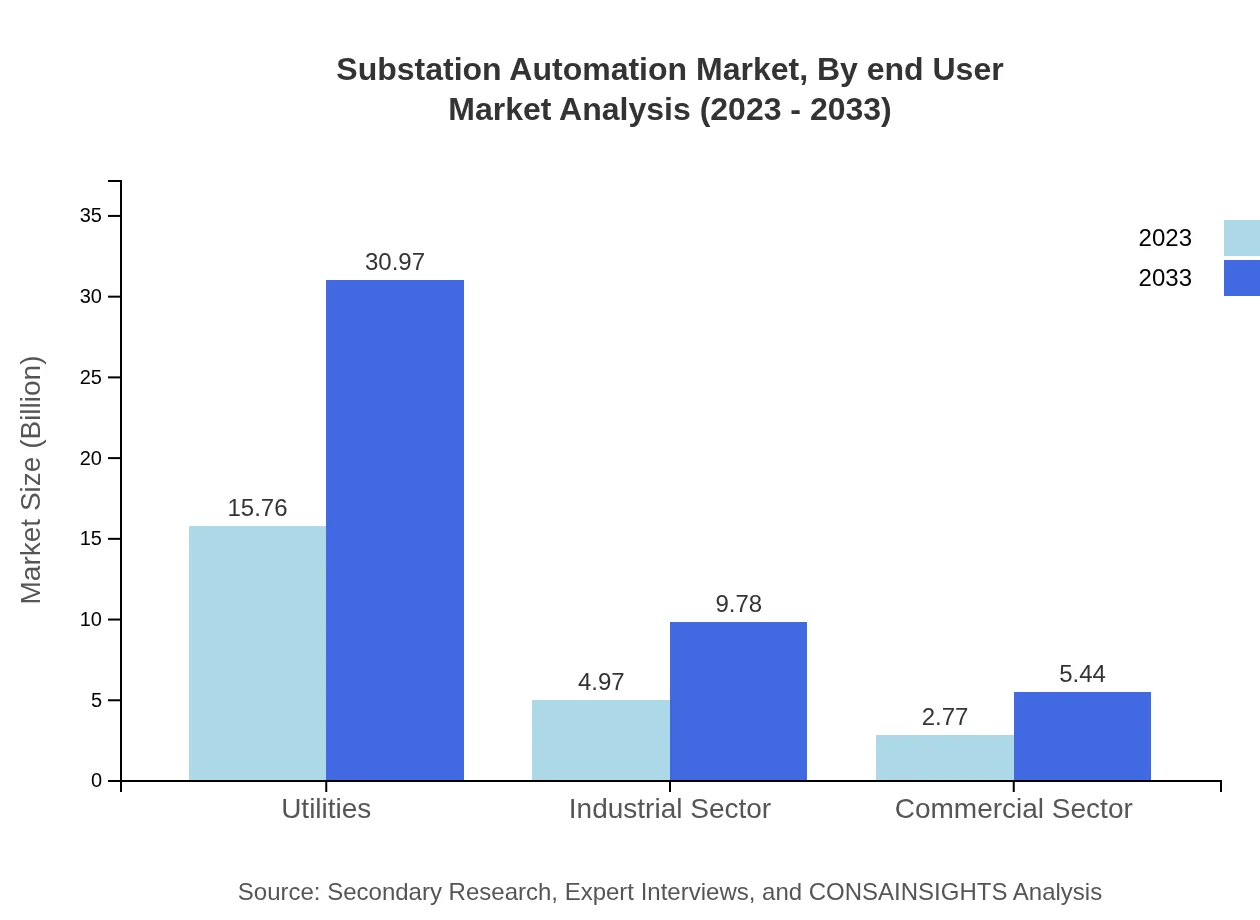
Substation Automation Market Analysis By End User
With growing investments and technological advancements, the utility sector remains the primary end-user in the Substation Automation market. The market for utilities is anticipated to capture a substantial share with growth from $15.76 billion in 2023 to $30.97 billion in 2033. The industrial and commercial sectors will also progressively utilize automation technologies, with growth trajectories of $4.97 billion to $9.78 billion and $2.77 billion to $5.44 billion respectively.
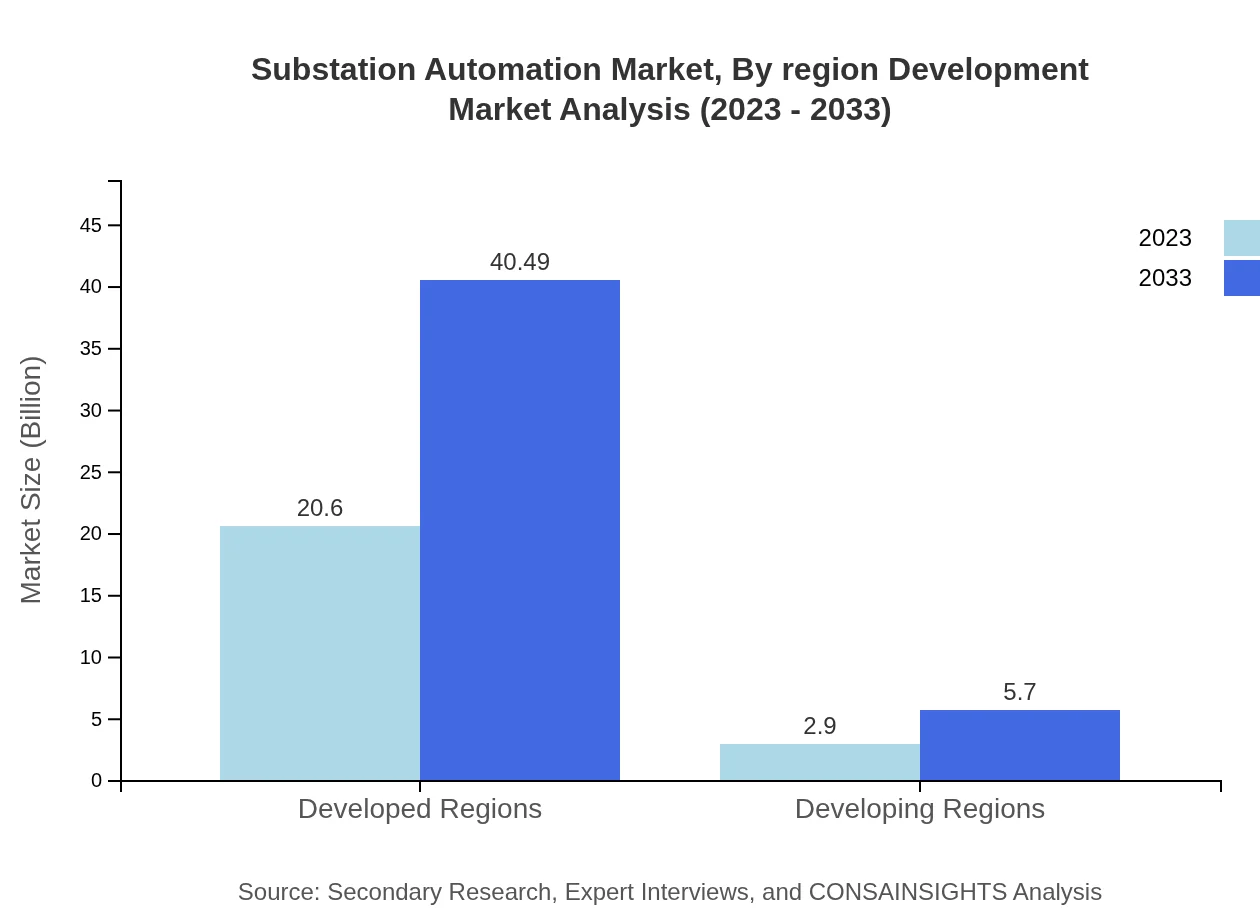
Substation Automation Market Analysis By Region Development
Developed regions are expected to maintain a dominant position in the Substation Automation market, growing from $20.60 billion to $40.49 billion (87.66% share) from 2023 to 2033. In contrast, developing regions show a burgeoning market growth from $2.90 billion to $5.70 billion (12.34% share) due to increasing investments in smart technologies and energy infrastructure.
Substation Automation Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Substation Automation Industry
Siemens AG:
Siemens AG is a leading global company specializing in electrical engineering and electronics, focusing on technology development for substation automation that enhances operational efficiency while integrating low-carbon energy sources.Schneider Electric:
Schneider Electric provides energy and automation digital solutions, leveraging IoT technologies for smarter and more sustainable energy management in substations.ABB Ltd.:
A pioneer in automation technology, ABB Ltd. offers innovative solutions for substation automation that bolster reliability, efficiency, and security in electrical grids.GE Grid Solutions:
GE Grid Solutions delivers modern technology for substation applications, focusing on developing comprehensive solutions that support utilities in their grid automation needs.Emerson Electric Co.:
Emerson Electric Co. specializes in advanced automation solutions, including software and services for substation automation, enhancing performance and security.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Substation Automation?
The global substation automation market was valued at approximately $23.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8%, reaching significant heights over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the Substation Automation industry?
Key players in the substation automation market include major companies like Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd., General Electric, and Mitsubishi Electric, among others, which contribute significantly to innovative solutions and technologies.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Substation Automation industry?
Several factors are driving growth in the substation automation market, including increasing demand for reliable power distribution, the integration of renewable energy sources, and advancements in smart grid technology that enhance efficiency and operational reliability.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Substation Automation market?
The Asia-Pacific region shows remarkable growth potential in the substation automation market, expected to expand from $4.79 billion in 2023 to $9.41 billion by 2033 due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Substation Automation industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market reports specifically designed to address unique client needs in the substation automation field, providing actionable insights and detailed analytics.
What deliverables can I expect from this Substation Automation market research project?
Deliverables from the substation automation market research project typically include comprehensive market analysis, regional insights, data segmentation, growth projections, and strategic recommendations to help clients make informed decisions.
What are the market trends of Substation Automation?
Current trends in substation automation include the rise of IoT-based solutions, increased focus on grid modernization, adoption of AI applications, and the integration of renewable energy, shaping the future landscape of the industry.