Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report
Published Date: 03 February 2026 | Report Code: synthetic-aperture-radar
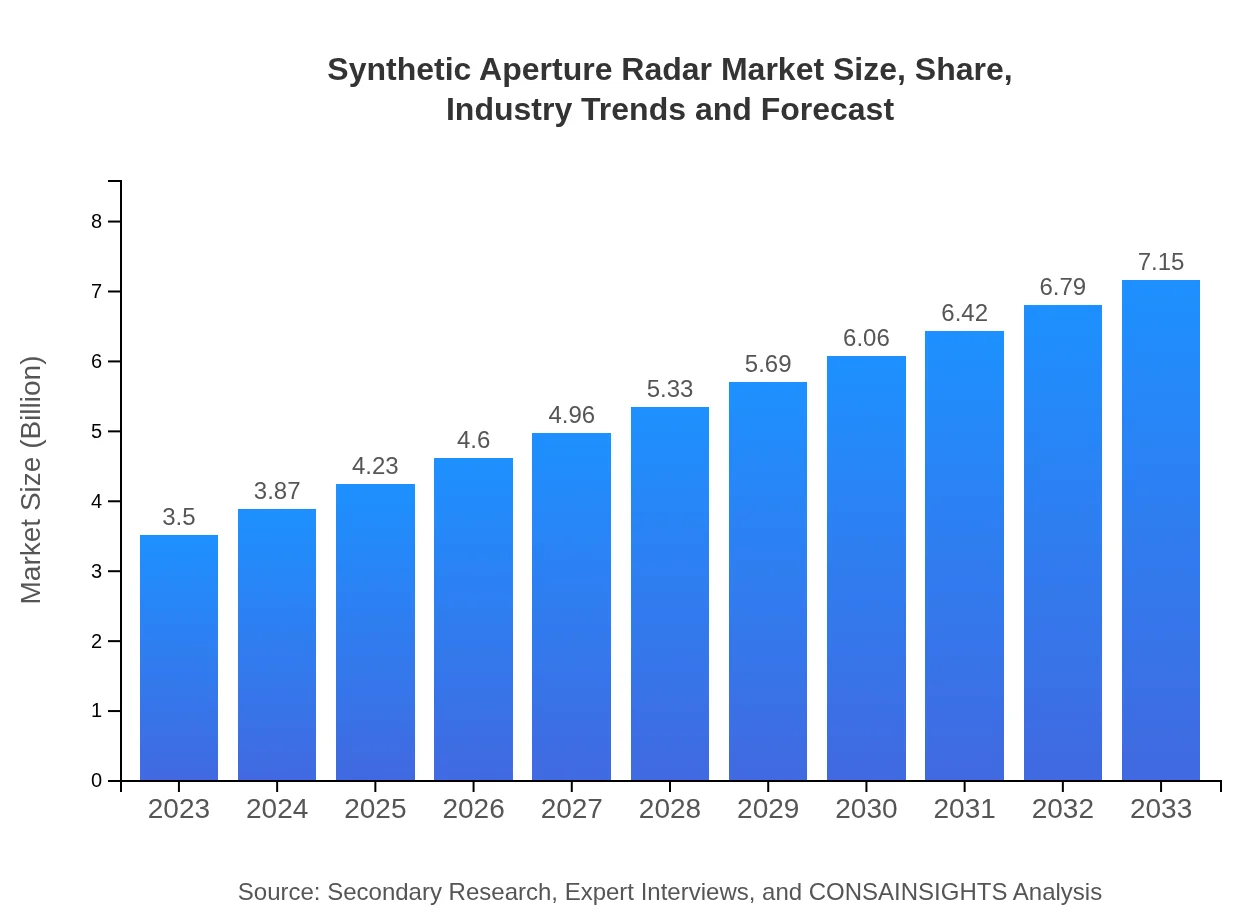
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) market, including key insights on market size, growth trends, and regional dynamics from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $3.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $7.15 Billion |
| Top Companies | Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Group |
| Last Modified Date | 03 February 2026 |
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Overview
Customize Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Synthetic Aperture Radar market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Synthetic Aperture Radar's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Synthetic Aperture Radar
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Synthetic Aperture Radar market in 2023?
Synthetic Aperture Radar Industry Analysis
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report:
Europe presents a sizable market for SAR technology, initially valued at $1.24 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $2.53 billion by 2033, largely influenced by governmental defense initiatives and environmental monitoring policies.Asia Pacific Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region shows a growing SAR market, valued at approximately $0.66 billion in 2023, expected to reach $1.35 billion by 2033, driven by rising investments in defense and environmental monitoring programs by countries like China and India.North America Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report:
North America continues to lead the SAR market with a value of $1.14 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $2.32 billion by 2033, attributed to high military spending and advancements in remote sensing technologies.South America Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report:
In South America, the SAR market is projected to grow from $0.31 billion in 2023 to $0.63 billion in 2033. The increasing need for agricultural monitoring and disaster management solutions are key drivers in this region.Middle East & Africa Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa SAR market is anticipated to grow from $0.16 billion in 2023 to approximately $0.32 billion by 2033, fueled by regional security concerns and urban development projects.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
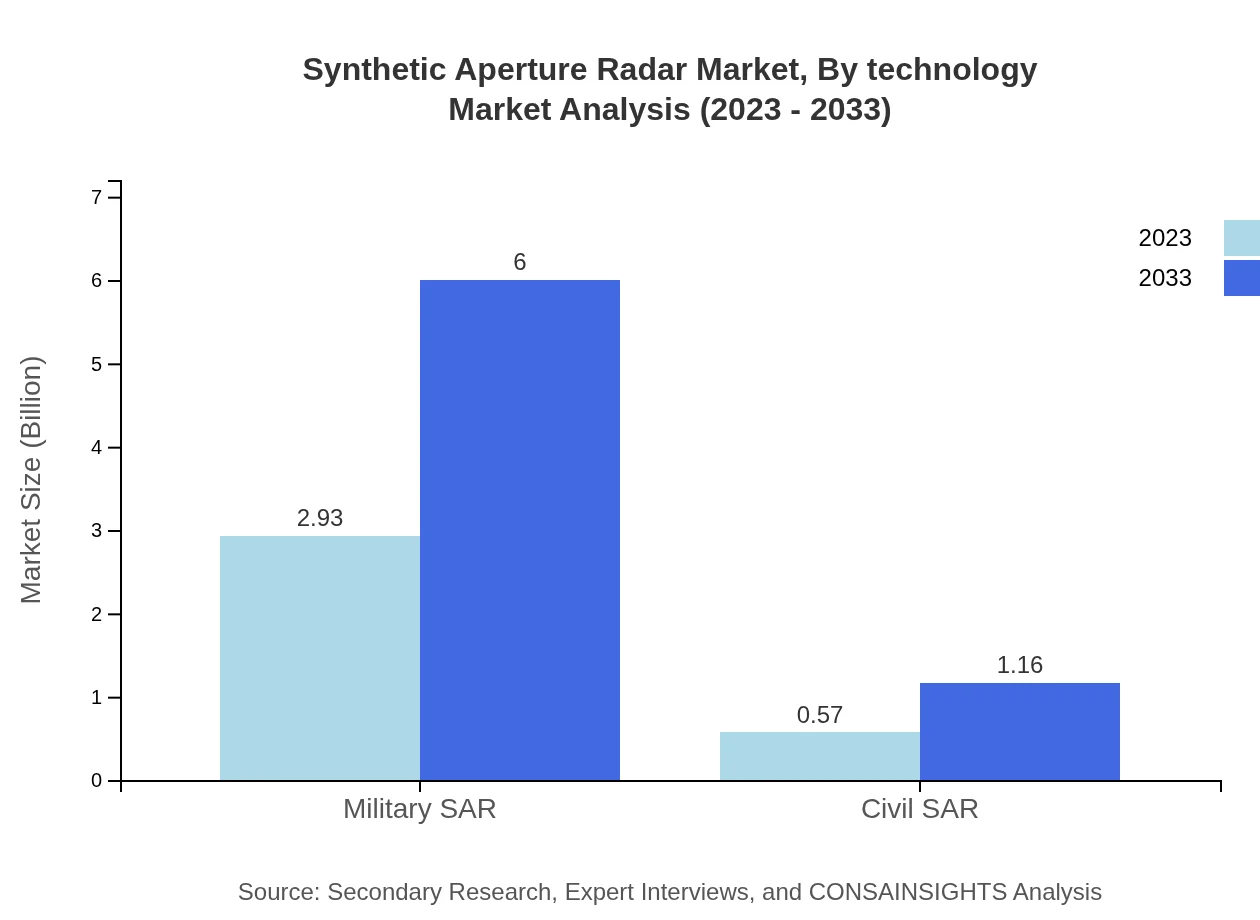
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Analysis By Technology
The SAR market, segmented by technology, indicates advanced interactive systems in radar development. Technologies include both hardware components like antennas and software solutions improving image resolution and signal processing capabilities. As SAR becomes more integrated with AI technologies, systems are equipped to manage and analyze data more efficiently.
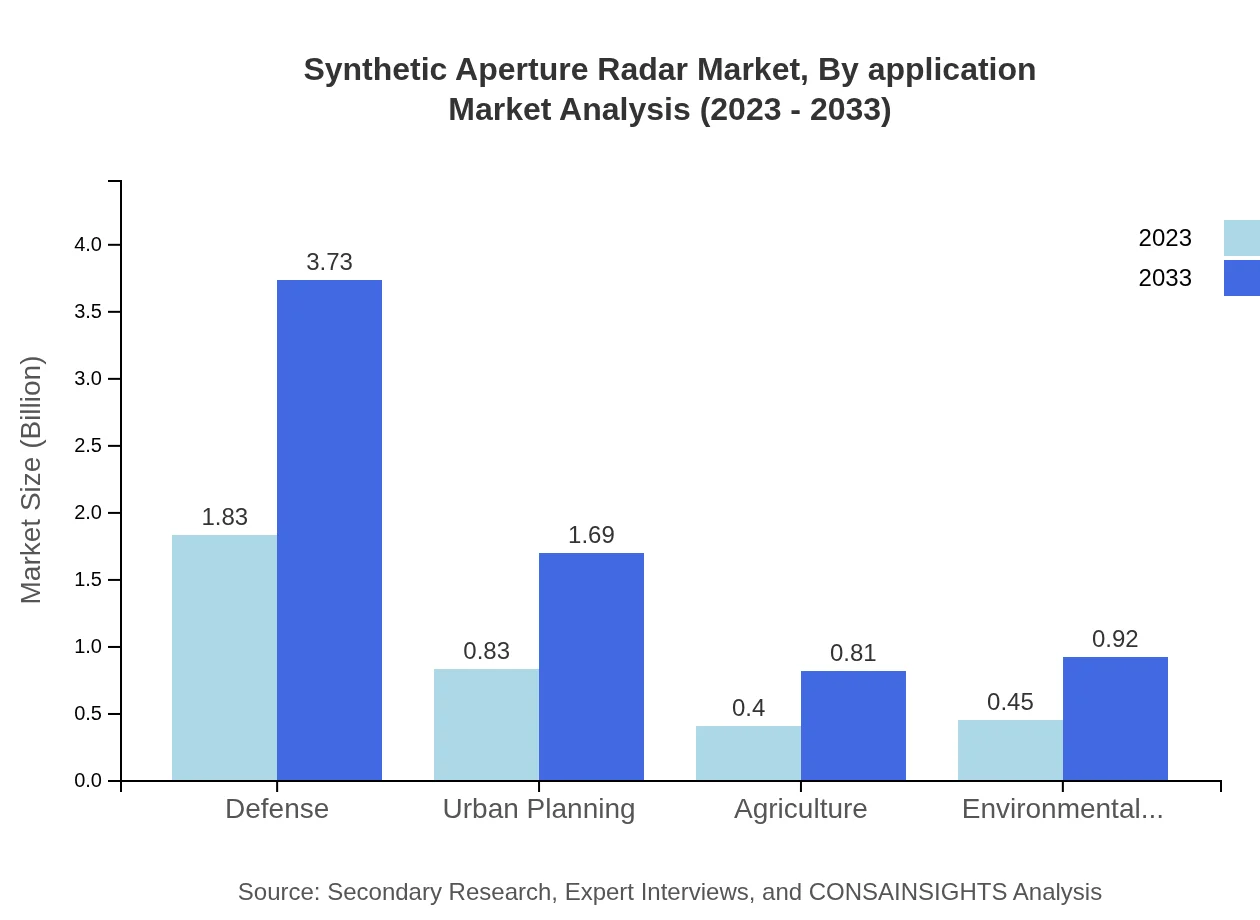
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the defense sector continues to dominate the SAR market due to heightened demands for surveillance and reconnaissance. Additionally, sectors such as agriculture, environmental monitoring, and urban planning are increasingly leveraging SAR for decision-making and policy development.
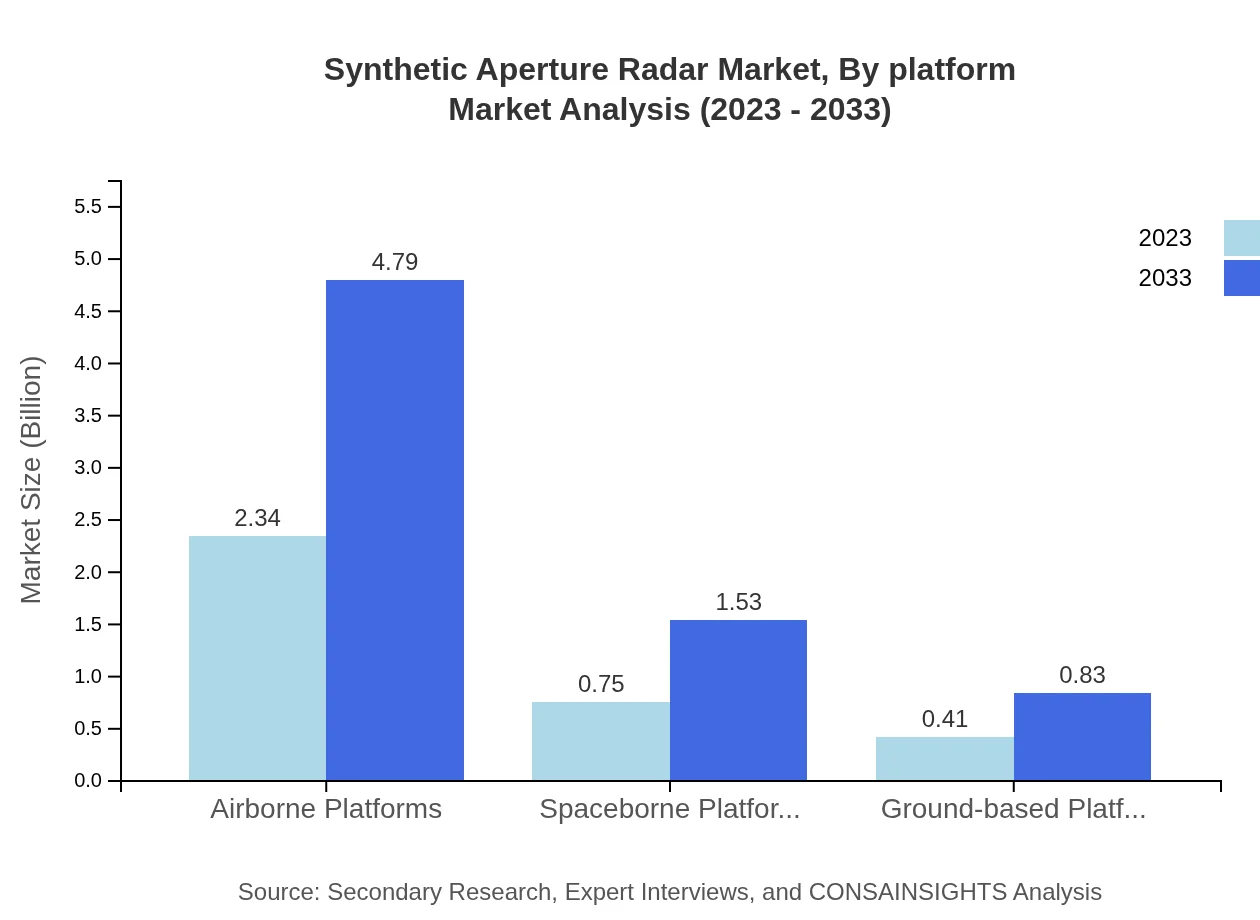
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Analysis By Platform
Regarding platforms, airborne SAR systems hold a significant share, providing rapid deployment and flexible operation capabilities. Spaceborne platforms are gaining traction as they offer comprehensive Earth observation data while ground-based systems enhance localized monitoring efforts.
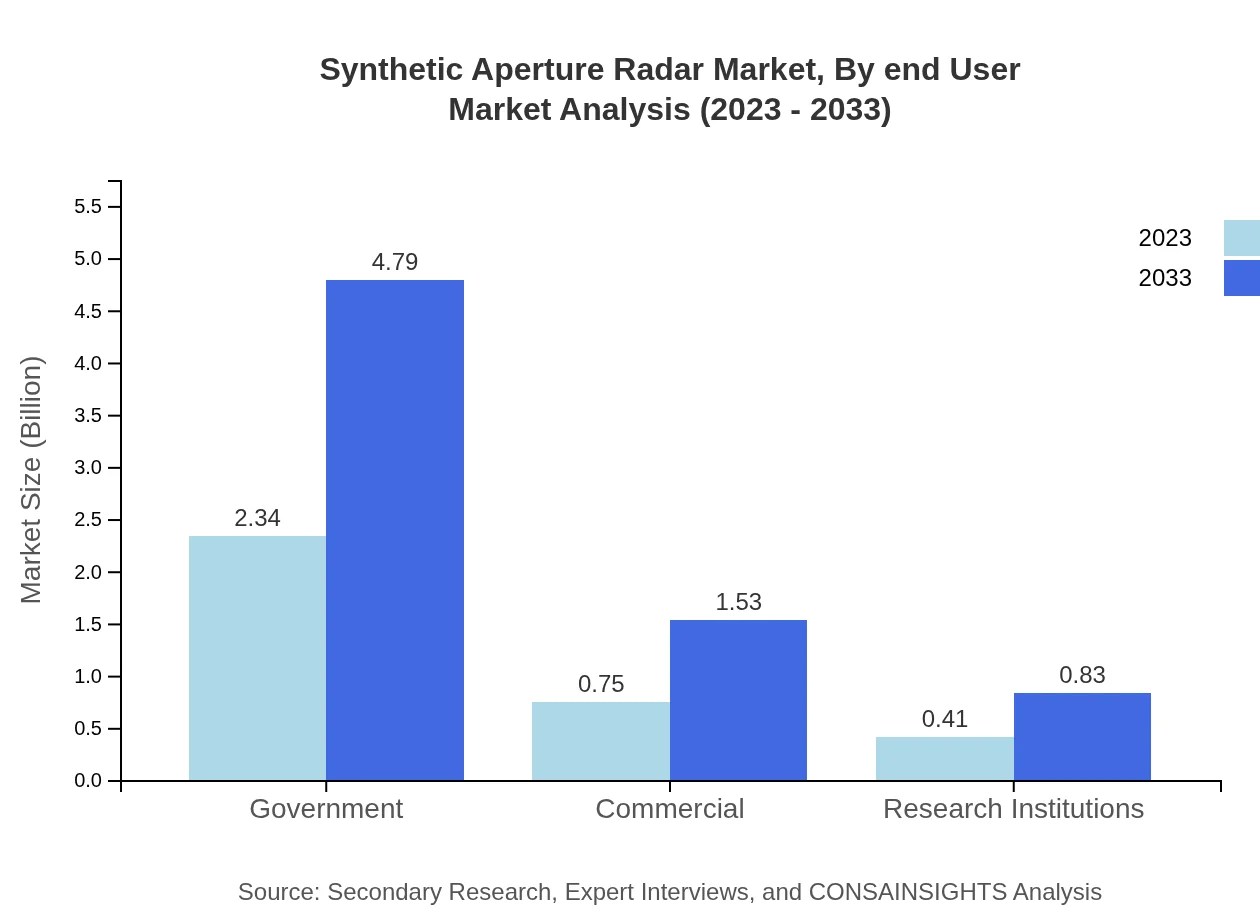
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Analysis By End User
The SAR market’s end-user segmentation reveals a stronghold in governmental entities and military organizations, focusing on defense. However, commercial and research institutions are increasingly adopting SAR for various applications, reflecting a diverse client base.
Synthetic Aperture Radar Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Synthetic Aperture Radar Industry
Lockheed Martin Corporation:
Lockheed Martin is a global aerospace and defense leader, producing advanced SAR systems used extensively in military applications for surveillance and reconnaissance.Northrop Grumman Corporation:
Northrop Grumman develops cutting-edge SAR solutions for both defense and commercial applications, focusing on innovation and high-resolution imaging capabilities.Thales Group:
Thales specializes in secure communication and surveillance technologies, offering innovative SAR solutions for environmental monitoring and national security.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of synthetic Aperture Radar?
The global synthetic aperture radar market is valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%, projecting significant expansion through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this synthetic Aperture Radar industry?
Key players in the synthetic aperture radar market include Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, Thales Group, Airbus Defence and Space, and Lockheed Martin. These companies dominate through continuous innovation and strategic partnerships.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the synthetic Aperture Radar industry?
Growth in the synthetic aperture radar industry is driven by increasing demand for advanced surveillance systems, technological advancements in radar technology, and rising applications in defense, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the synthetic Aperture Radar?
The fastest-growing region for synthetic aperture radar is Europe, expected to grow from $1.24 billion in 2023 to $2.53 billion by 2033, followed closely by North America and Asia Pacific, indicating robust demand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the synthetic Aperture Radar industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs in the synthetic aperture radar industry, ensuring relevant insights and analytics that cater to unique market circumstances.
What deliverables can I expect from this synthetic Aperture Radar market research project?
Deliverables from the synthetic aperture radar market research project include a comprehensive market analysis report, segmentation data, trends, forecasts, and actionable insights tailored to your business needs.
What are the market trends of synthetic Aperture Radar?
Trends in the synthetic aperture radar market include increasing integration with artificial intelligence, enhanced data processing capabilities, and expanded applications across military and civil sectors, fostering innovation and adoption.