Thin Wafer Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: thin-wafer
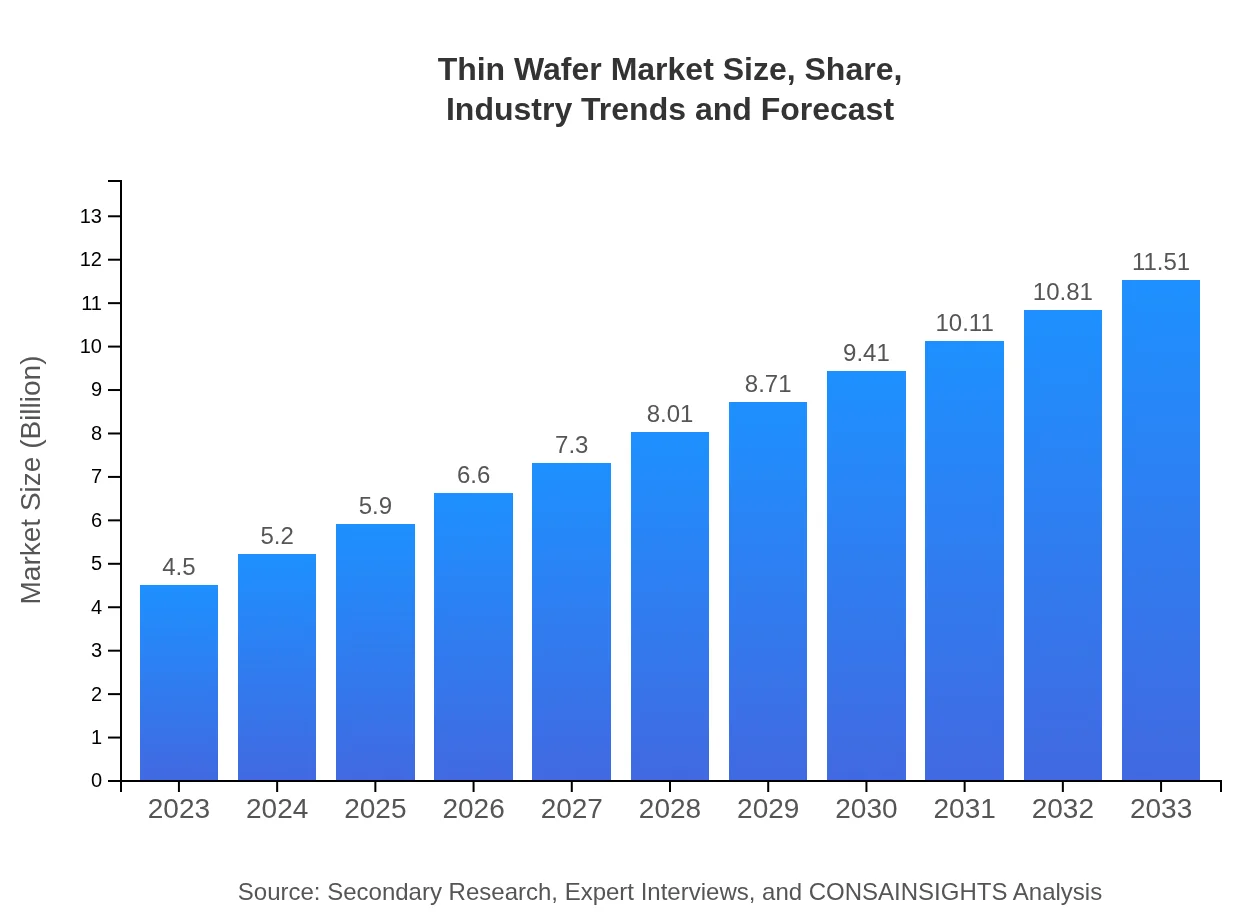
Thin Wafer Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This comprehensive market report covers the Thin Wafer market, detailing key insights from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth projections, industry analysis, segmentation, and regional dynamics. It aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the market landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $4.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 9.5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $11.51 Billion |
| Top Companies | Wafers Inc., Global Semiconductor Technologies, Silicon Solutions LLC |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Thin Wafer Market Overview
Customize Thin Wafer Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Thin Wafer market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Thin Wafer's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Thin Wafer
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Thin Wafer market in 2023?
Thin Wafer Industry Analysis
Thin Wafer Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Thin Wafer Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Thin Wafer Market Report:
The European Thin Wafer market is projected to grow from 1.39 billion USD in 2023 to 3.56 billion USD by 2033. The European market is characterized by a focus on sustainability and renewable technologies, leading to increased adoption of thin wafers in energy solutions.Asia Pacific Thin Wafer Market Report:
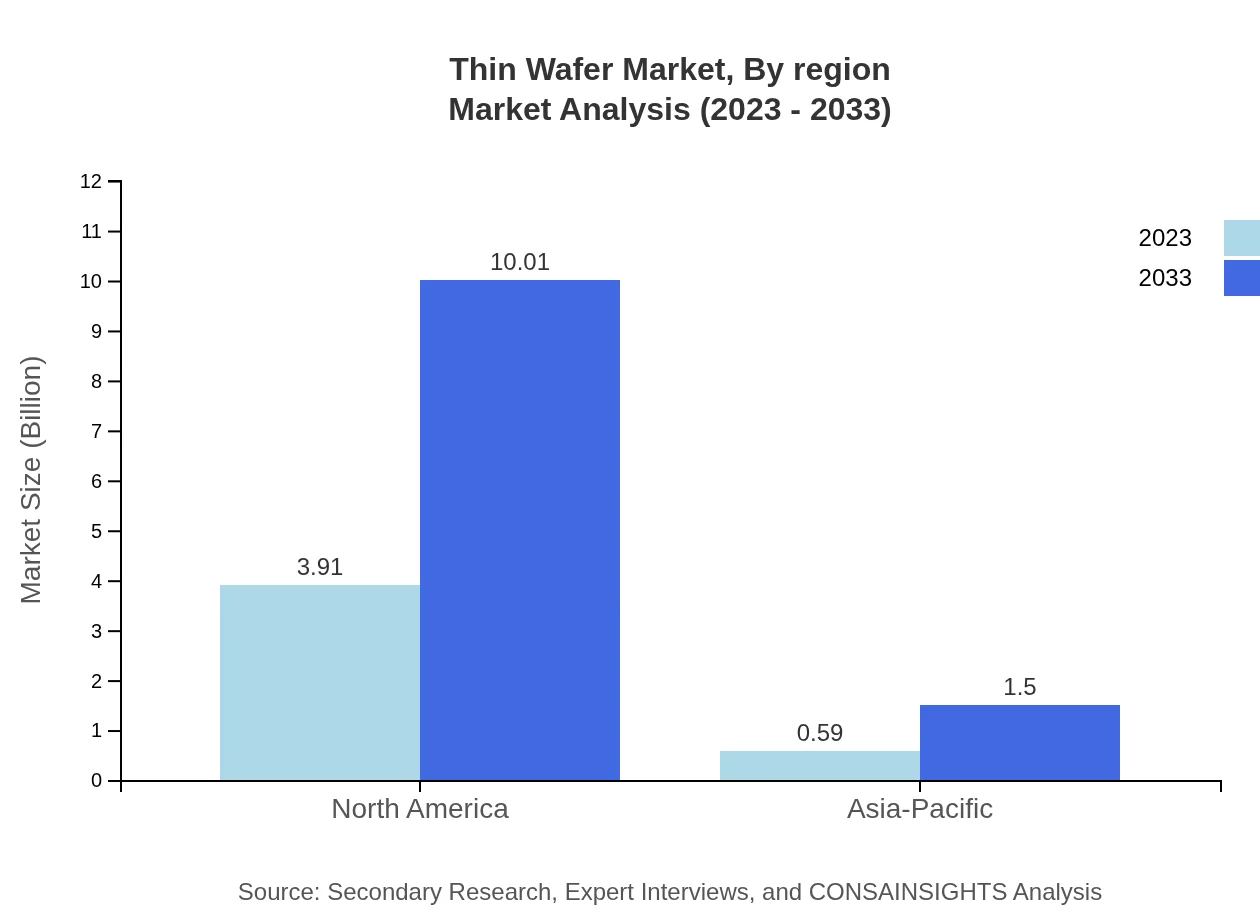
In 2023, the Thin Wafer market in the Asia Pacific region is valued at 0.86 billion USD, with projections reaching 2.19 billion USD by 2033. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront of semiconductor manufacturing, significantly driving market growth due to their extensive electronic industries.North America Thin Wafer Market Report:
Valued at 1.56 billion USD in 2023, the North American market is expected to grow to 3.98 billion USD by 2033. The region is home to major semiconductor companies and innovative technology firms that leverage thin wafer technology for advanced electronics.South America Thin Wafer Market Report:
The South American Thin Wafer market is valued at 0.23 billion USD in 2023, with an anticipated increase to 0.58 billion USD by 2033. This growth is primarily driven by rising investments in renewable energy, particularly solar, fostering demand for thin wafers in photovoltaic applications.Middle East & Africa Thin Wafer Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market stands at 0.47 billion USD in 2023 with expectations of reaching 1.19 billion USD by 2033. The market growth in this region is fueled by increasing infrastructure developments and technological advancements in mobile and telecommunications sectors.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
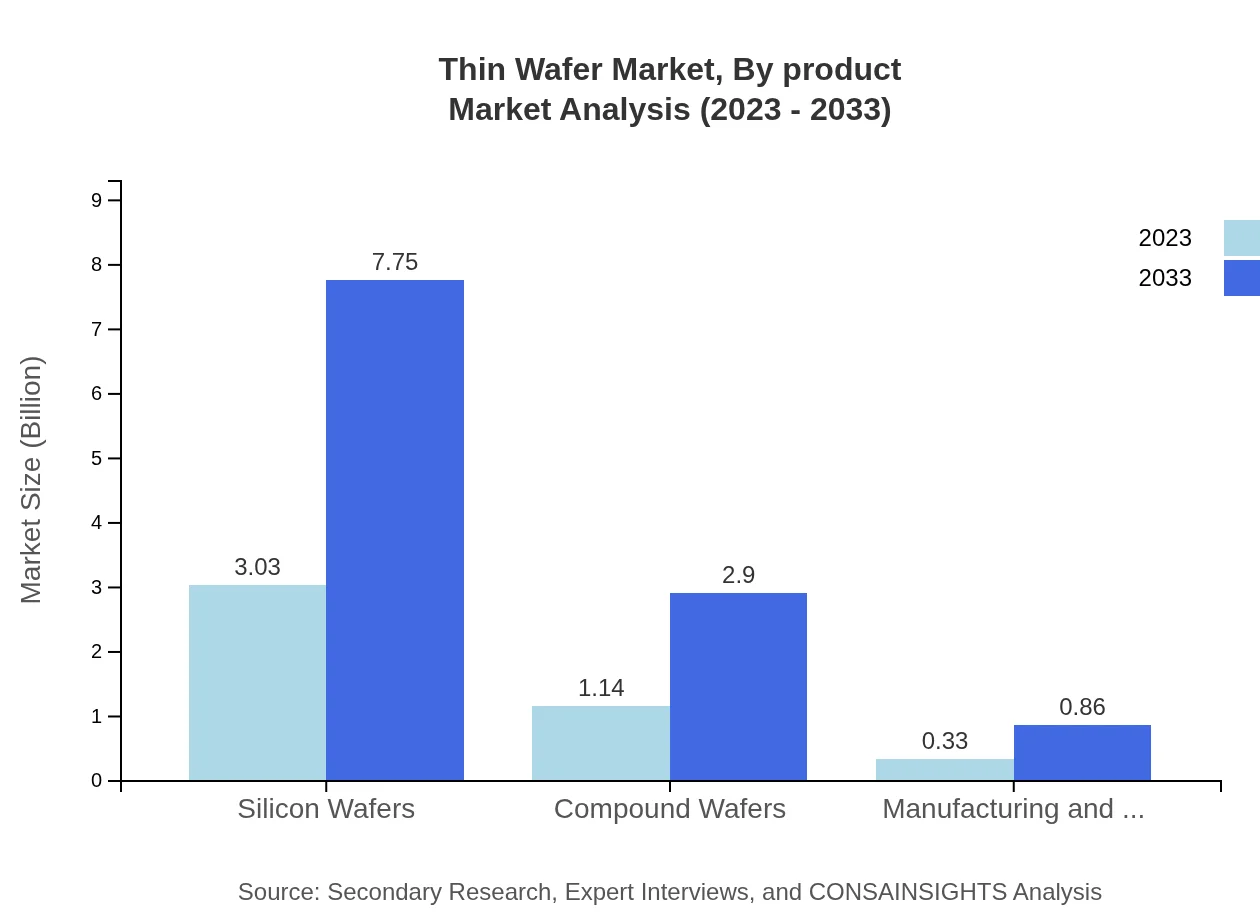
Thin Wafer Market Analysis By Product
Thin wafers segment, particularly silicon wafers, dominate the market due to their wide applications in semiconductor manufacturing and photovoltaic cells. The market for compound wafers is also significant, growing steadily as applications diversify.
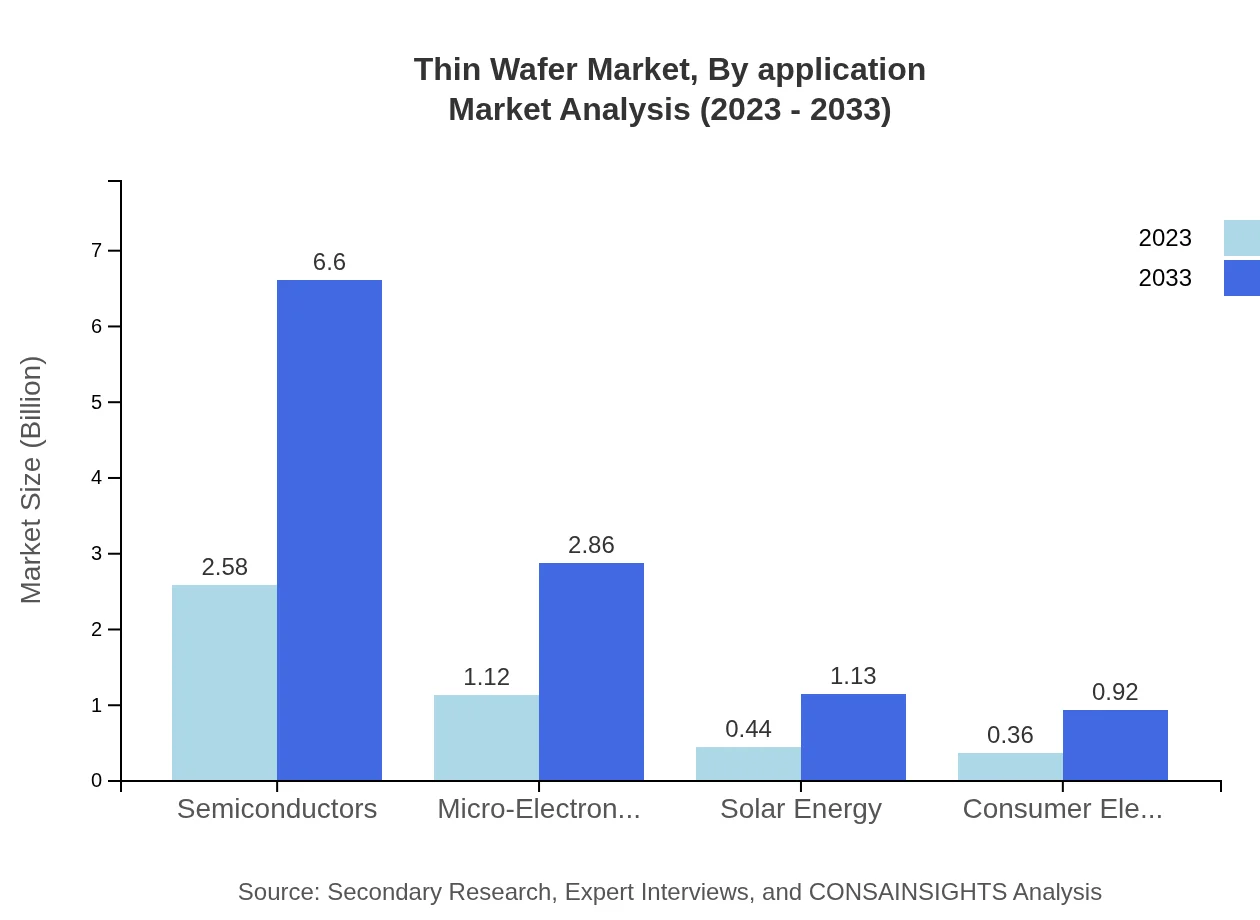
Thin Wafer Market Analysis By Application
The Thin Wafer market, by application, finds major demand in semiconductors, automotive, telecommunications, and solar cells. The semiconductor segment particularly leads in market share, accelerating the demand for efficient and miniaturized solutions.
Thin Wafer Market Analysis By Region
The market distribution reveals North America and Europe holding substantial shares, while Asia Pacific showcases rapid growth dynamics due to manufacturing hub establishment and technological advancements in the region.
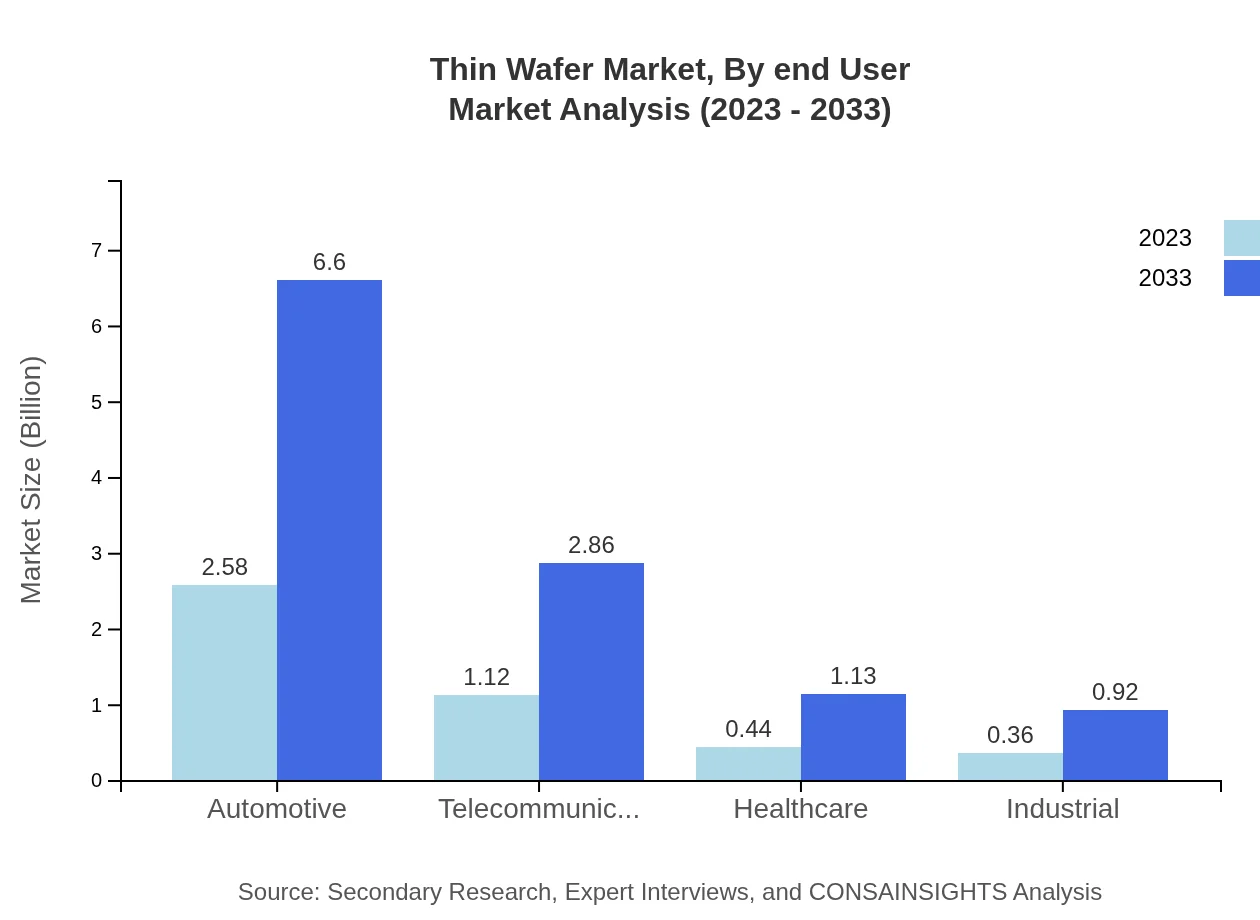
Thin Wafer Market Analysis By End User
End-user industries such as automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics significantly contribute to the Thin Wafer market growth, focusing on the need for advanced technologies in integration and energy efficiency.
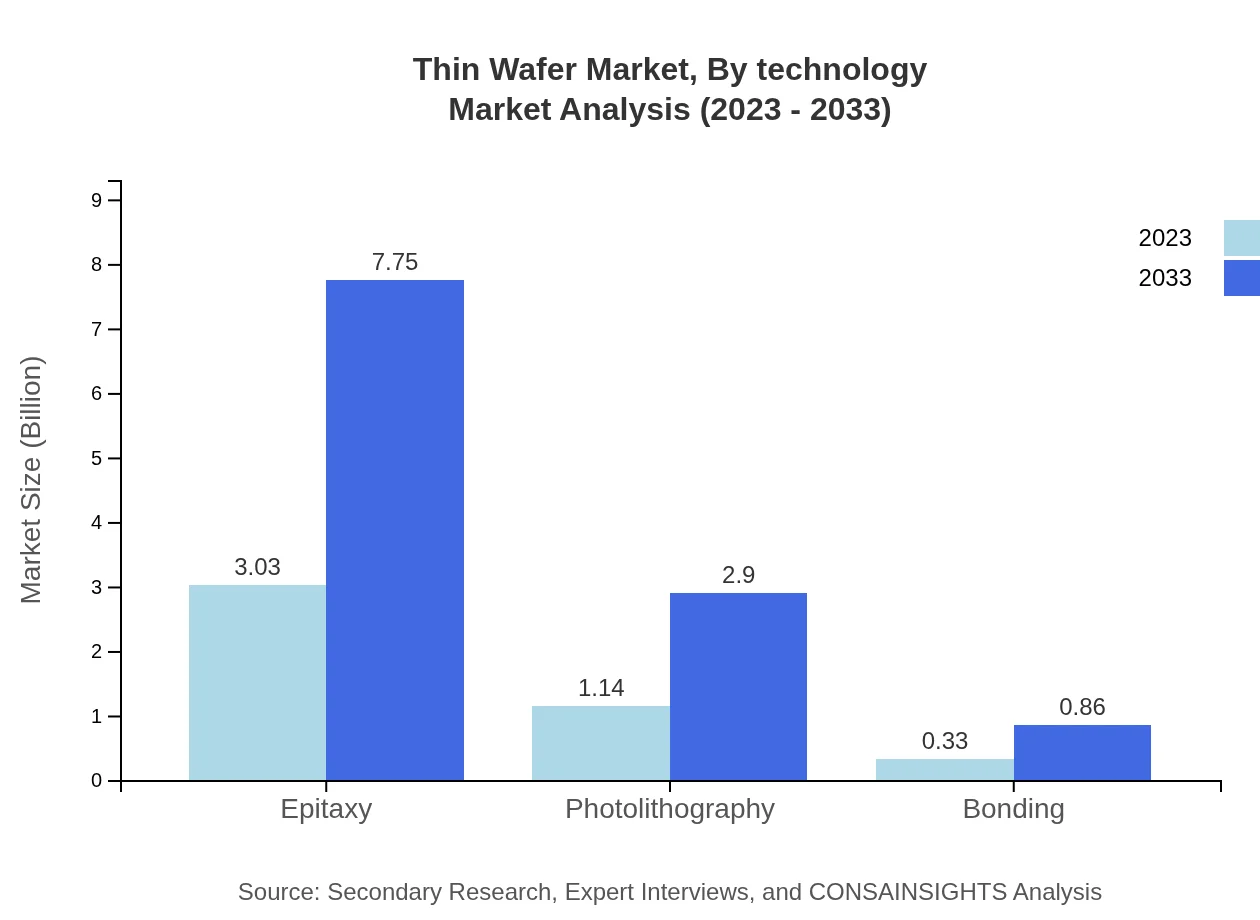
Thin Wafer Market Analysis By Technology
Technological advancements in manufacturing processes, particularly epitaxy and photolithography, are pivotal in enhancing wafer performance and reducing production costs, thereby benefitting the overall Thin Wafer market.
Thin Wafer Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Thin Wafer Industry
Wafers Inc.:
A leader in wafer manufacturing, specializing in silicon and compound semiconductor wafers, Wafers Inc. is known for its high-quality products and sustainability initiatives.Global Semiconductor Technologies:
Global Semiconductor Technologies focuses on advanced materials and cutting-edge technologies in the production of thin wafers for various applications including electronics and renewable energy.Silicon Solutions LLC:
Silicon Solutions is recognized for its innovative approaches in wafer processing and is a key player in the thin wafer supply chain for solar and microelectronics sectors.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of thin Wafer?
The global thin wafer market is projected to reach $4.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.5% from 2023. In 2023, the market size is significant, indicating robust growth potential over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in this thin Wafer industry?
Key players in the thin wafer market include major semiconductor manufacturers and suppliers specializing in silicon and compound wafers. These companies drive innovation and production efficiencies, ensuring the industry's competitive landscape continues to evolve.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the thin Wafer industry?
The growth of the thin wafer market is driven by advancements in semiconductor technology, increasing demand for efficient electronics, and rising applications in automotive and telecommunications sectors. Additionally, the push for miniaturization in devices fuels this growth.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the thin Wafer?
The fastest-growing region in the thin wafer market is projected to be Asia-Pacific, where market size will expand from $0.86 billion in 2023 to $2.19 billion by 2033, reflecting a robust demand for semiconductors and electronics.
Does ConsInsights provide customized market report data for the thin Wafer industry?
Yes, ConsInsights offers customized market report data tailored to specific needs within the thin wafer industry. Clients can request detailed analyses that encompass market trends, forecasts, and segment breakdowns relevant to their interests.
What deliverables can I expect from this thin Wafer market research project?
From the thin wafer market research project, clients can expect comprehensive reports including market size data, CAGR insights, regional breakdowns, segment analyses, and emerging trends, all tailored to inform strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of thin Wafer?
Current trends in the thin wafer market include increased focus on wafer fabrication technologies, growing integration of IoT devices, and an emphasis on energy-efficient solutions in electronics. These trends indicate a shift toward more sustainable and effective manufacturing processes.