Transgenic Seeds Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: transgenic-seeds
Transgenic Seeds Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This market report offers an in-depth analysis of the transgenic seeds industry, providing critical insights into market size, growth forecasts, segmentation, regional dynamics, and technology trends for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
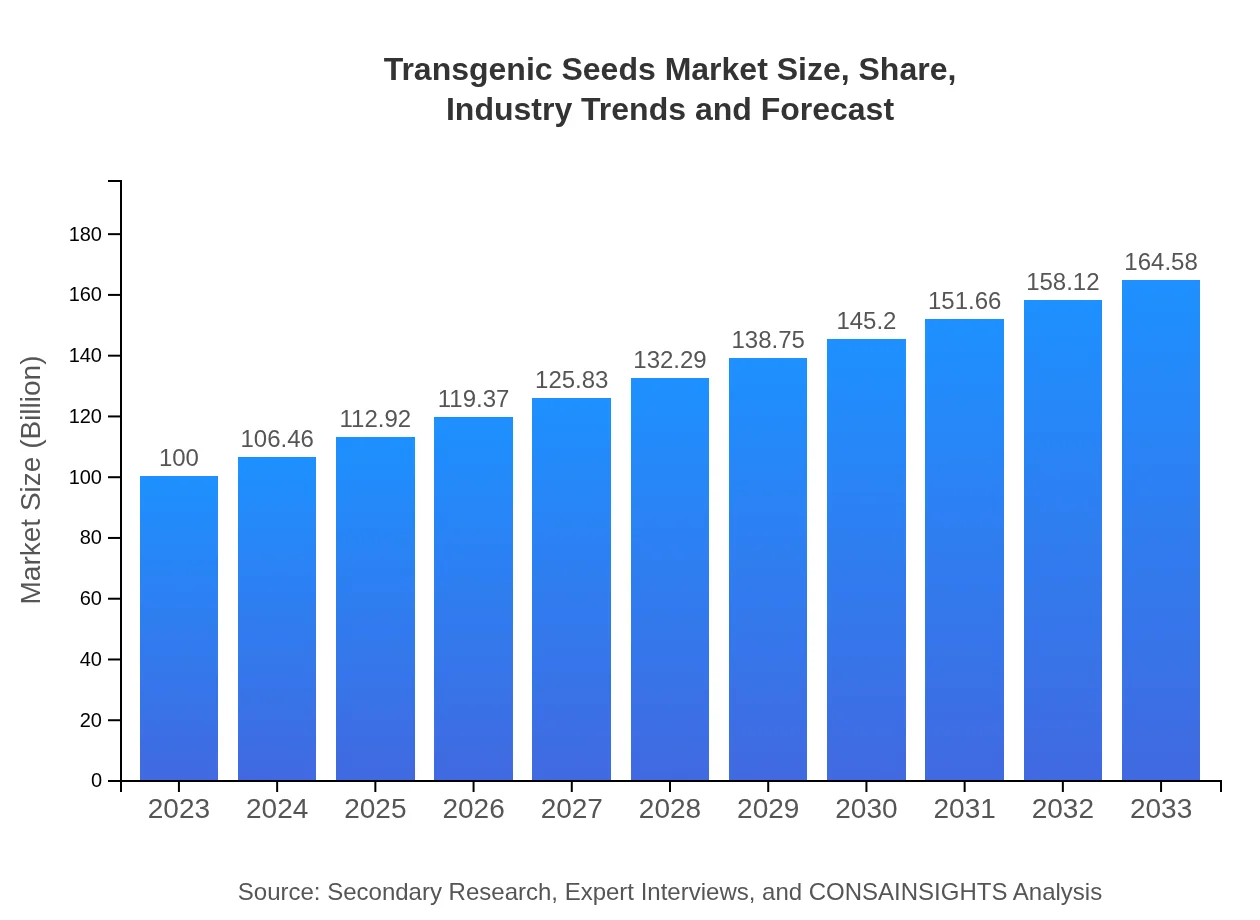
| 2023 Market Size | $100.00 Million |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $164.58 Million |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Transgenic Seeds Market Overview
Customize Transgenic Seeds Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Transgenic Seeds market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Transgenic Seeds's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Transgenic Seeds
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Transgenic Seeds market in 2023?
Transgenic Seeds Industry Analysis
Transgenic Seeds Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Transgenic Seeds Market Report:
In Europe, the transgenic seeds market was valued at $24.47 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $40.27 billion by 2033. The market is characterized by stricter regulations and varied acceptance of GMOs across different countries, with Germany and Spain being more receptive to transgenic crops.Asia Pacific Transgenic Seeds Market Report:
In 2023, the transgenic seeds market in the Asia Pacific is valued at $20.00 billion and is expected to grow to $32.92 billion by 2033. Key countries in this region include India and China, where increasing agricultural productivity is vital to support the rapidly growing population. The adoption of transgenic crops is facilitated by rising incomes and changing consumer preferences.North America Transgenic Seeds Market Report:
North America holds a prominent share of the transgenic seeds market, valued at $33.90 billion in 2023, expected to reach $55.79 billion by 2033. The United States is a leader in transgenic crop adoption, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and extensive agricultural technologies that promote high efficiency in planting and harvesting.South America Transgenic Seeds Market Report:
The South American market for transgenic seeds was valued at $9.04 billion in 2023, projecting an increase to $14.88 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina lead in the cultivation of GM crops, particularly soybeans, driven by significant investments in biotechnology and strong agricultural exports.Middle East & Africa Transgenic Seeds Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region recorded a market size of $12.59 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $20.72 billion in 2033. Growth is driven by an increasing focus on improving food security and agricultural productivity, although it remains affected by cultural perceptions regarding genetic modification.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
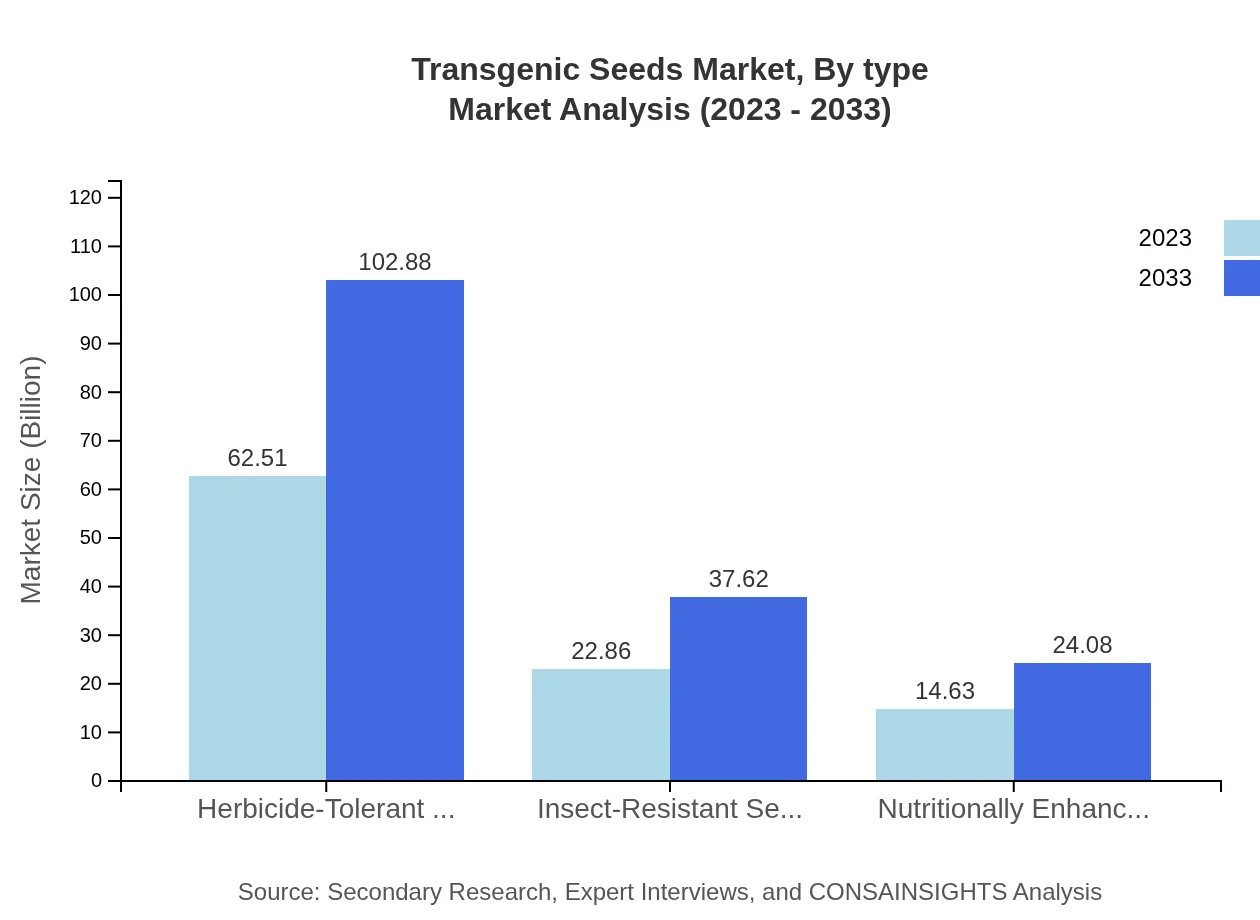
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis By Type
The transgenic seeds market is segmented by type into herbicide-tolerant seeds, insect-resistant seeds, and nutritionally enhanced seeds. As of 2023, herbicide-tolerant seeds dominate, valued at $62.51 billion, and are projected to grow to $102.88 billion by 2033. Insect-resistant seeds follow, currently valued at $22.86 billion and expected to rise to $37.62 billion. Nutritionally enhanced seeds hold a market value of $14.63 billion, with a forecasted growth to $24.08 billion.
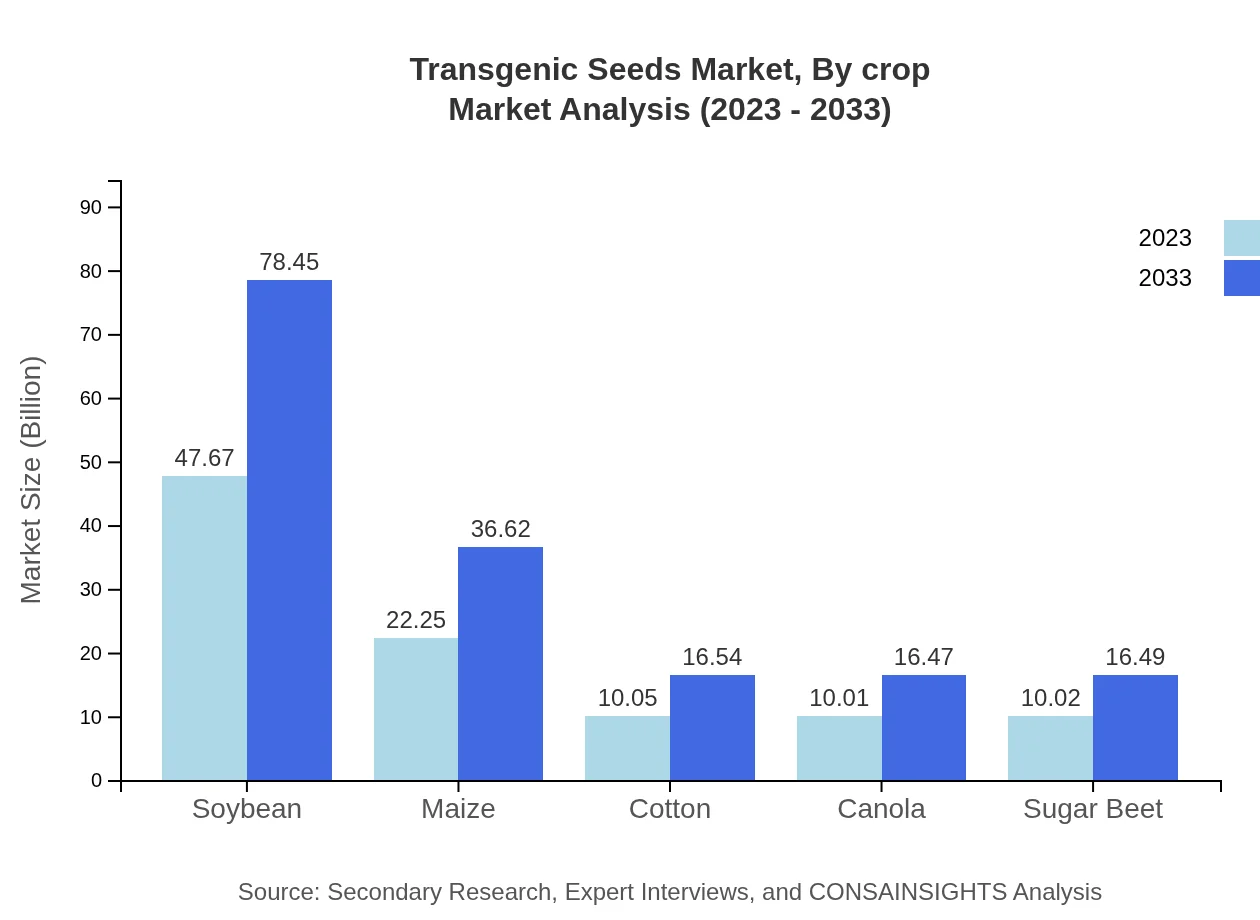
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis By Crop
Key crops in the transgenic seeds market include soybeans, maize, cotton, canola, and sugar beet. Soybeans lead the segment with a significant market size of $47.67 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $78.45 billion by 2033. Maize follows with a market size of $22.25 billion in 2023, anticipated to reach $36.62 billion. Notably, cotton holds $10.05 billion, canola stands at $10.01 billion, and sugar beet is valued at $10.02 billion, all showing promising growth.
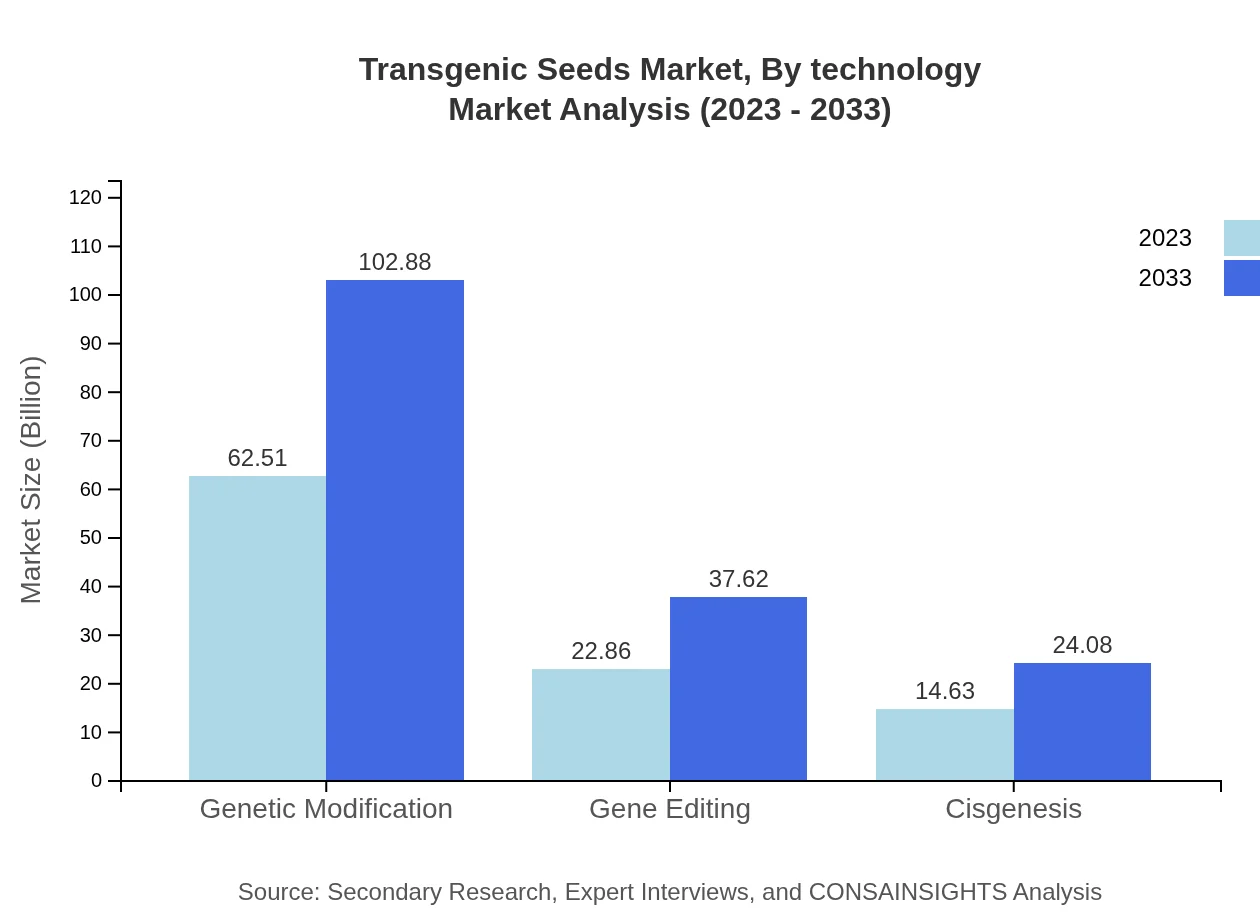
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis By Technology
The technologies adopted in the transgenic seeds market include genetic modification, gene editing, and cisgenesis. Genetic modification continues to dominate the market with a size of $62.51 billion in 2023, looking to hit $102.88 billion by 2033. Following this, gene editing holds $22.86 billion, with projections of $37.62 billion. Cisgenesis is currently valued at $14.63 billion, expected to rise to $24.08 billion.
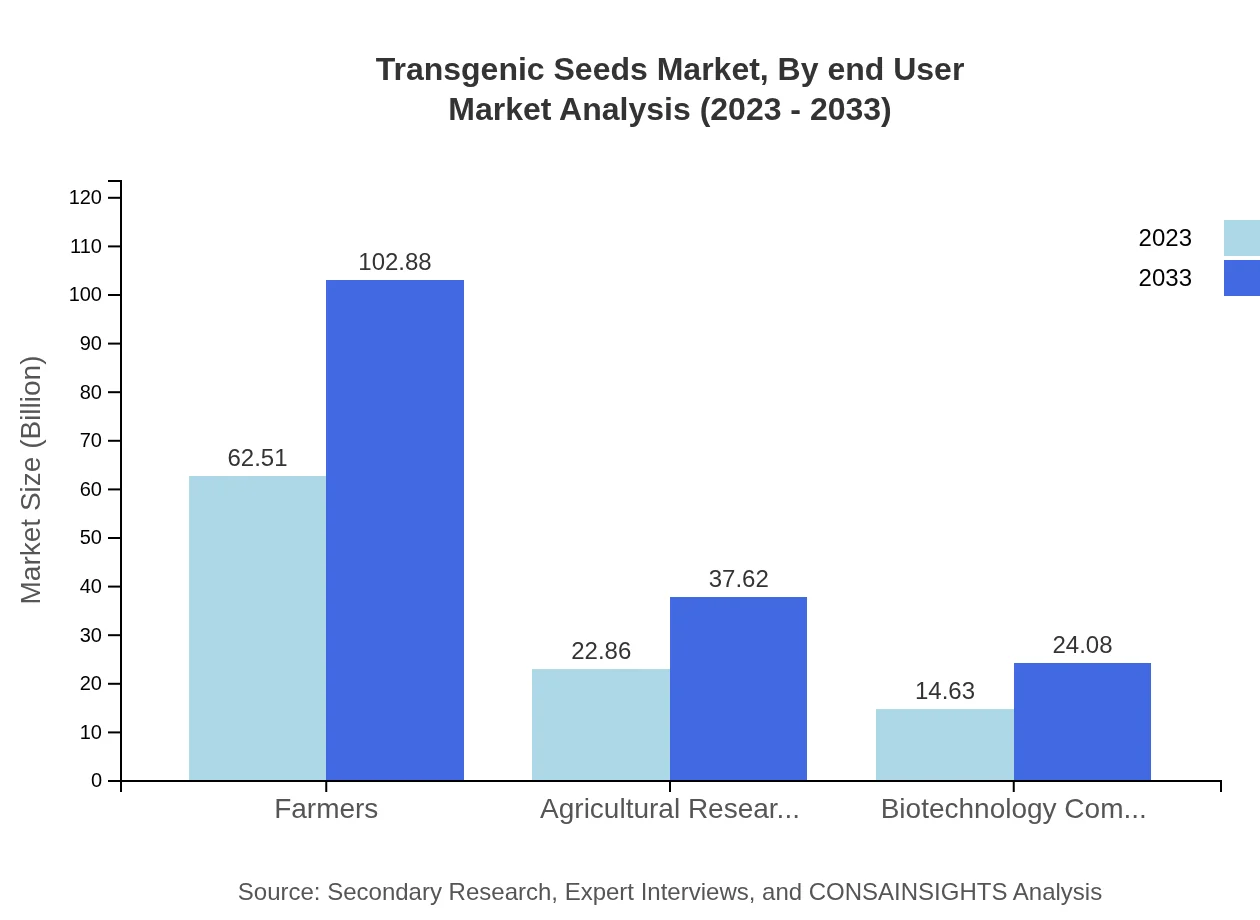
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis By End User
The primary end-users in the transgenic seeds market are farmers, agricultural research institutions, and biotechnology companies. Farmers are the largest user group, reflecting a market size of $62.51 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $102.88 billion. Agricultural research institutions are valued at $22.86 billion and expected to grow alongside biotechnology companies, which currently stand at $14.63 billion.
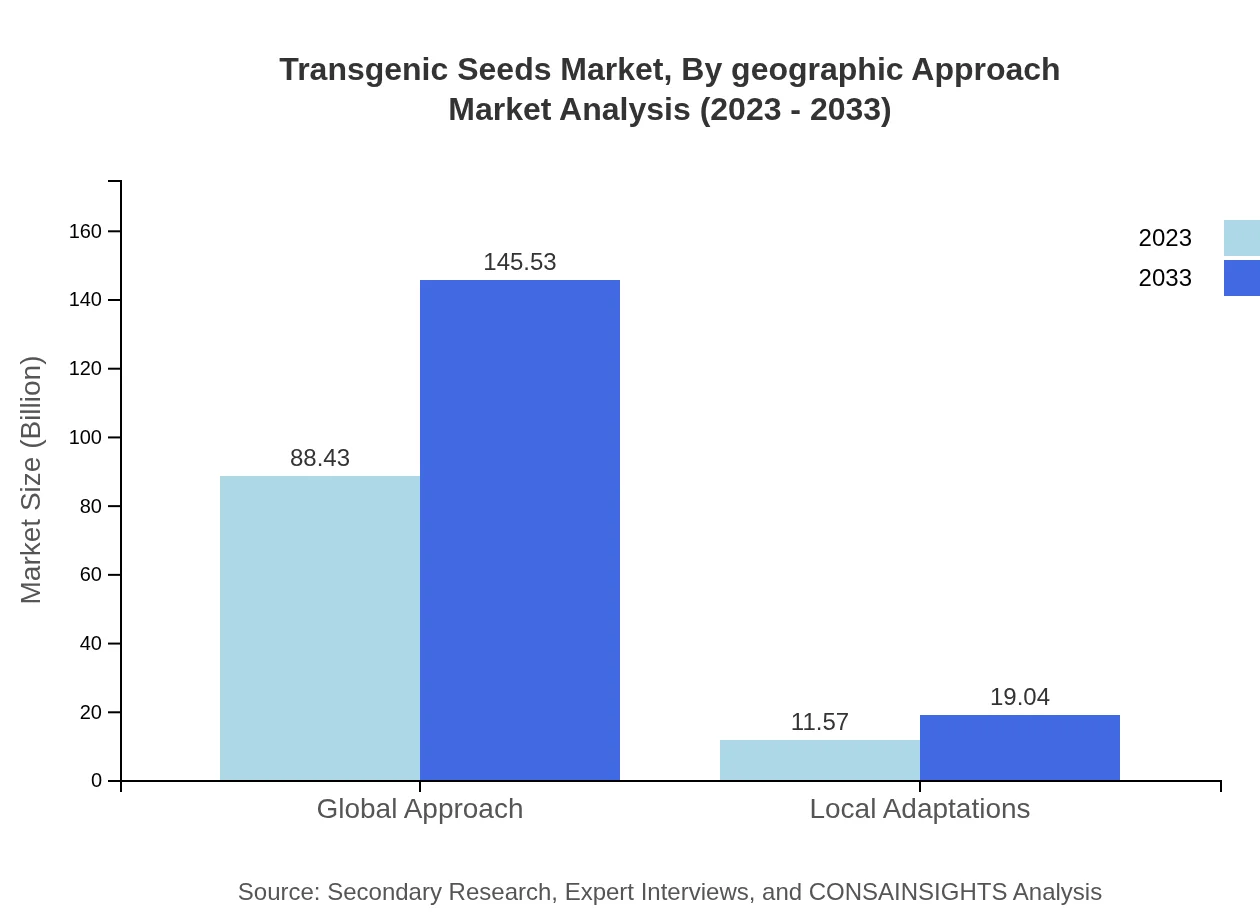
Transgenic Seeds Market Analysis By Geographic Approach
The transgenic seeds market can be divided into global and local adaptations. The global approach encompasses a market of $88.43 billion in 2023 to $145.53 billion by 2033, reflecting widespread acceptance. Conversely, local adaptations currently hold a market value of $11.57 billion, with a forecasted trajectory to $19.04 billion, highlighting the importance of region-specific crop development.
Transgenic Seeds Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Transgenic Seeds Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leading global agricultural company specializing in biotechnology and seed development, recognized for their innovations in herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant crops.Bayer AG:
A multinational company that has significantly expanded its agricultural product portfolio through the acquisition of Monsanto, focusing on sustainable agricultural solutions.Syngenta AG:
A prominent player in the transgenic seeds market, dedicated to innovation in crop protection and seeds that enhance productivity and resist pests.Corteva Agriscience:
A major seed and agricultural protection company known for its robust research in biotechnology aimed at developing high-performance seeds.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of transgenic Seeds?
The transgenic seeds market is projected to reach approximately $100 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5%. This growth reflects increasing adoption rates and technological advancements in agricultural biotechnology.
What are the key market players or companies in the transgenic Seeds industry?
Key players in the transgenic seeds market include multinational corporations such as Bayer AG, Syngenta AG, and Corteva Agriscience, which are recognized for their extensive research and development in genetic modifications.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the transgenic Seeds industry?
Factors driving growth include the need for higher crop yields, resistance to pests and diseases, and growing demand for sustainable agriculture practices. Technological advancements in biotechnology further bolster this market.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the transgenic Seeds market?
North America is currently the fastest-growing region in the transgenic seeds market, projected to increase from $33.90 million in 2023 to $55.79 million by 2033, highlighting its robust agricultural technology sector.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the transgenic Seeds industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data for the transgenic seeds industry, accommodating unique client needs based on specific regions, segments, or timeframes for a comprehensive market analysis.
What deliverables can I expect from this transgenic Seeds market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, regional and segment breakdowns, competitor analyses, trends forecasting, and actionable insights that can guide strategic decisions in the transgenic seeds sector.
What are the market trends of transgenic Seeds?
Current trends in the transgenic seeds market include an increasing focus on herbicide-tolerant and insect-resistant seeds. Additionally, nutritional enhancement and gene editing techniques are gaining traction, driven by consumer demands for healthier crop options.