Underground Garbage Cans Market Report
Published Date: 22 January 2026 | Report Code: underground-garbage-cans
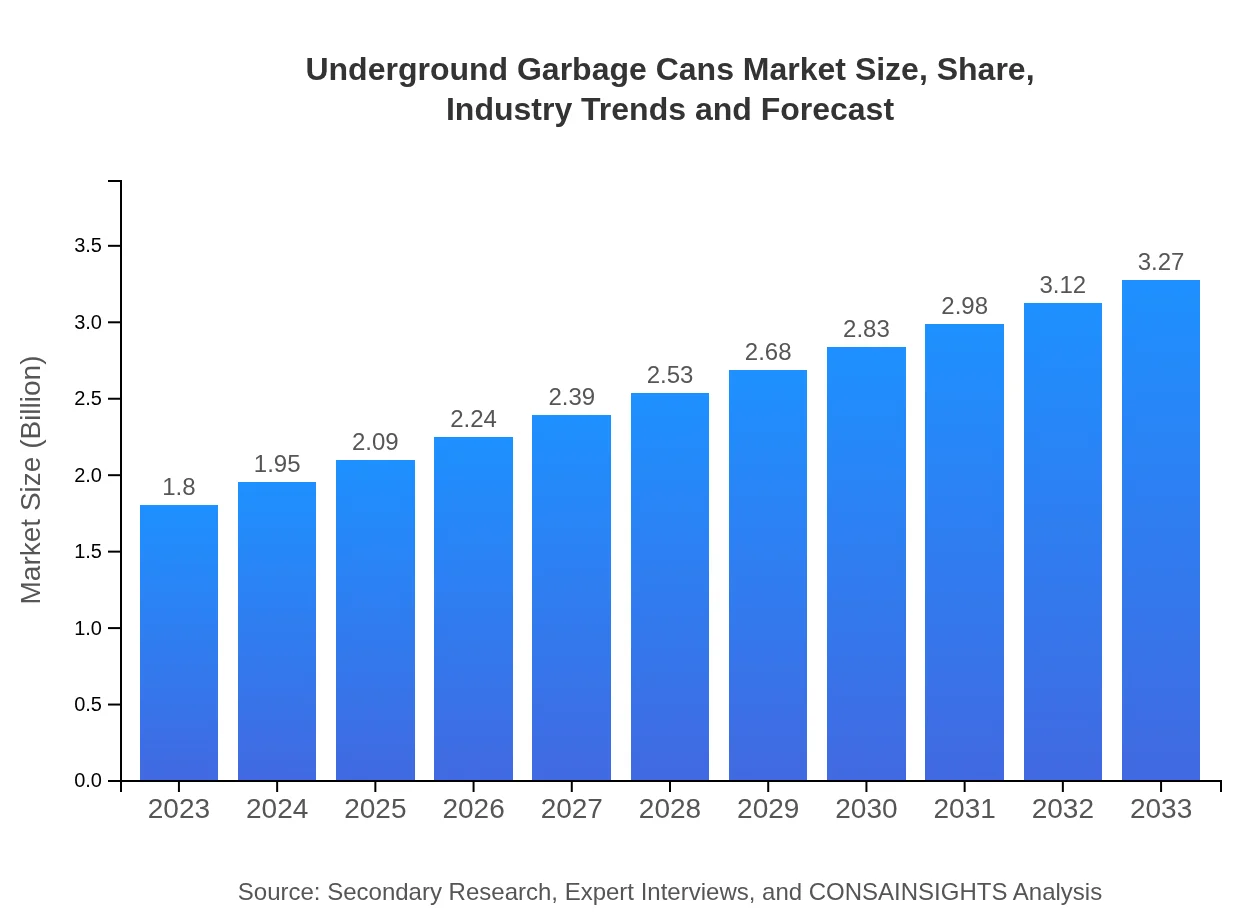
Underground Garbage Cans Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive insight into the Underground Garbage Cans market, including market size, growth trends, segmentation, regional analysis, and future forecasts for the years 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $1.80 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $3.27 Billion |
| Top Companies | Waste Management, Inc., SUEZ, Veolia |
| Last Modified Date | 22 January 2026 |
Underground Garbage Cans Market Overview
Customize Underground Garbage Cans Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Underground Garbage Cans market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Underground Garbage Cans's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Underground Garbage Cans
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Underground Garbage Cans market in 2023?
Underground Garbage Cans Industry Analysis
Underground Garbage Cans Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Underground Garbage Cans Market Report:
Europe's Underground Garbage Can market is projected to grow from $0.47 billion in 2023 to $0.85 billion by 2033. The European Union's policies on waste reduction and recycling and increasing eco-conscious consumers bolster demand for underground options.Asia Pacific Underground Garbage Cans Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market size in 2023 is valued at $0.35 billion, projected to grow to $0.64 billion by 2033. Urban areas' growing population and increased focus on advanced waste management practices are major drivers of this growth.North America Underground Garbage Cans Market Report:
The North American market for Underground Garbage Cans is estimated at $0.60 billion in 2023, with projections to reach $1.10 billion by 2033. High levels of urbanization and stringent waste management regulations contribute significantly to this growth.South America Underground Garbage Cans Market Report:
The South American market is relatively smaller but shows significant potential, with an expected increase from $0.18 billion in 2023 to $0.32 billion by 2033. Increasing investment in municipal infrastructure and urban sustainability projects are anticipated to spur growth.Middle East & Africa Underground Garbage Cans Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa's market has the lowest valuation at $0.20 billion for 2023, expected to rise to $0.37 billion by 2033. Rapid urbanization and an increasing focus on cleanliness and sanitation will drive future growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
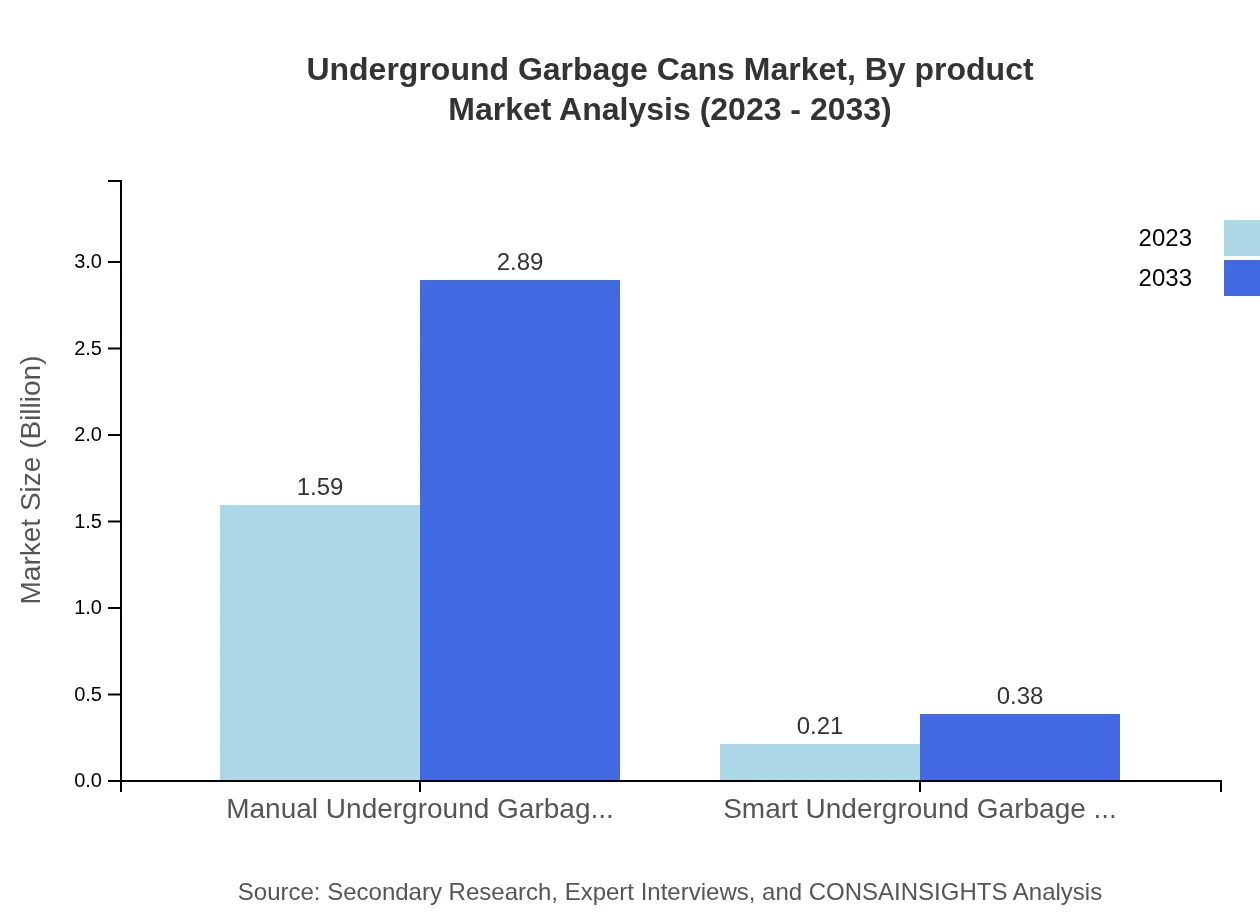
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis By Product
The market is dominated by Manual Underground Garbage Cans, which account for a significant share. In 2023, their market size is estimated at $1.59 billion, with a stable share of 88.3%, rising to a projected size of $2.89 billion by 2033. Smart Underground Garbage Cans are also emerging, increasing from $0.21 billion in 2023 with a market share of 11.7% to $0.38 billion in 2033.
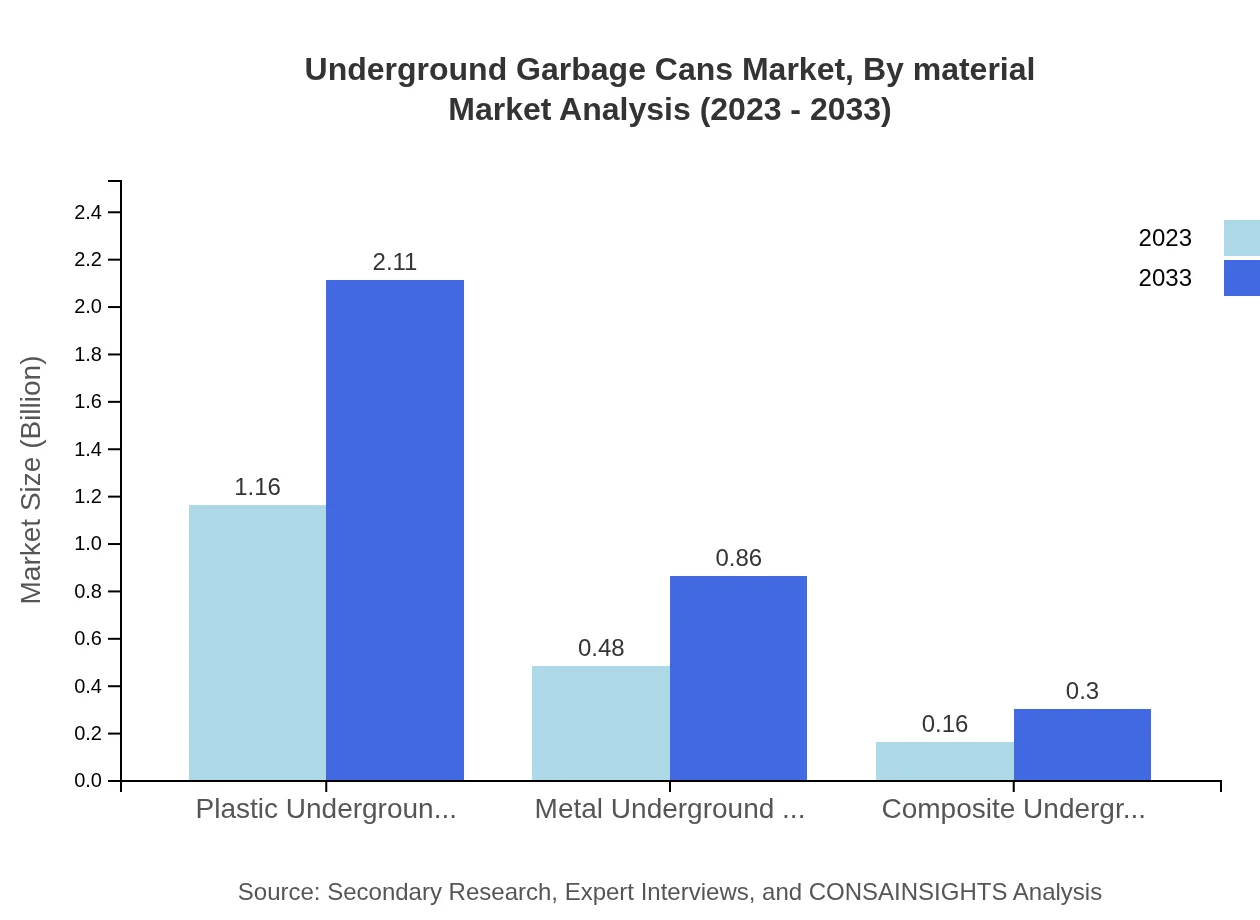
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis By Material
Materials such as Plastic, Metal, and Composite each play a pivotal role in the market. Plastic Underground Garbage Cans hold the largest market share at 64.43% in 2023, with expected growth from $1.16 billion to $2.11 billion by 2033. Metal bins are projected to grow from $0.48 billion to $0.86 billion within the same period, maintaining a share of 26.45%.
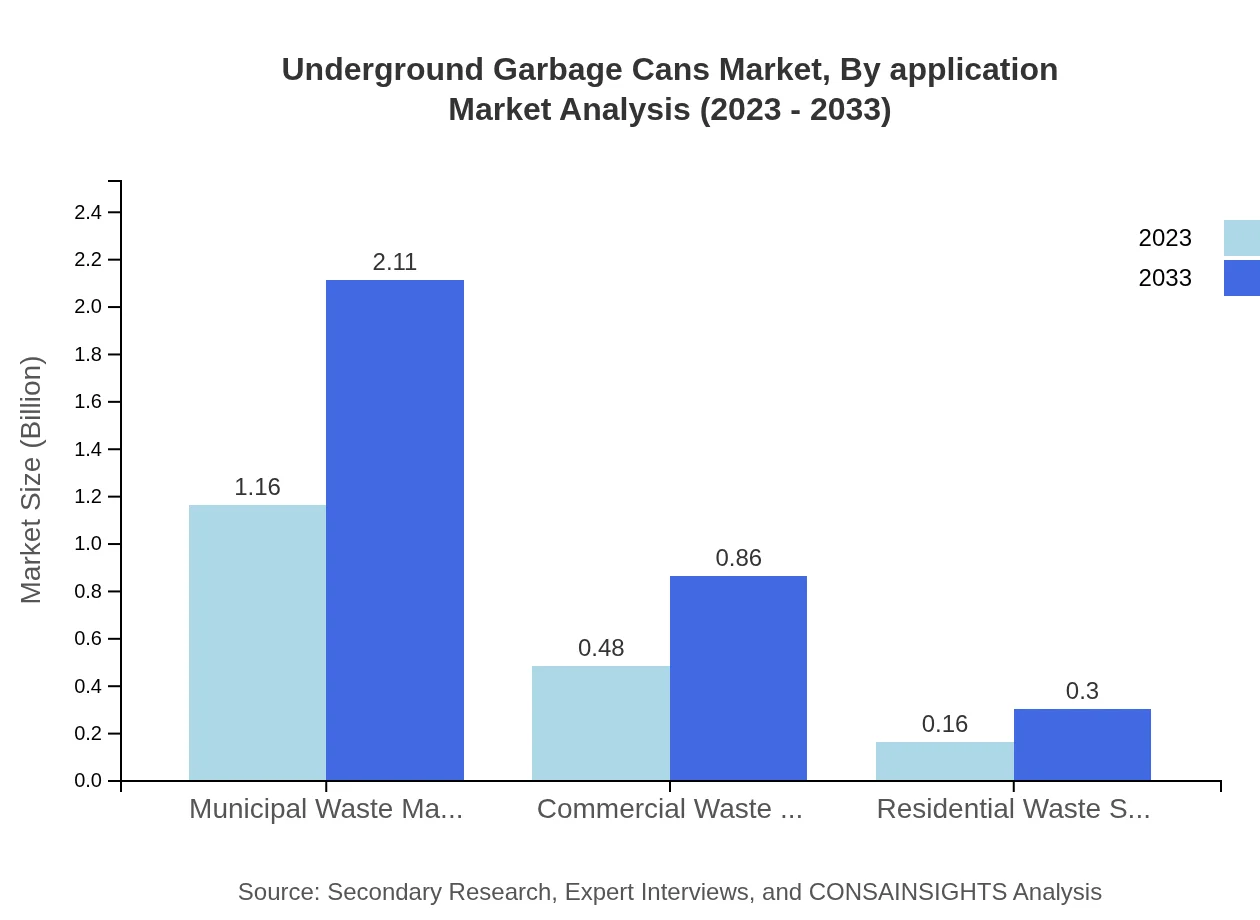
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis By Application
The applications of Underground Garbage Cans include Municipal Waste Management, with a size of $1.16 billion in 2023 and a growth trajectory to $2.11 billion by 2033, holding a market share of 64.43%. Commercial and Residential waste solutions also show promise, though they account for smaller portions of the overall market.
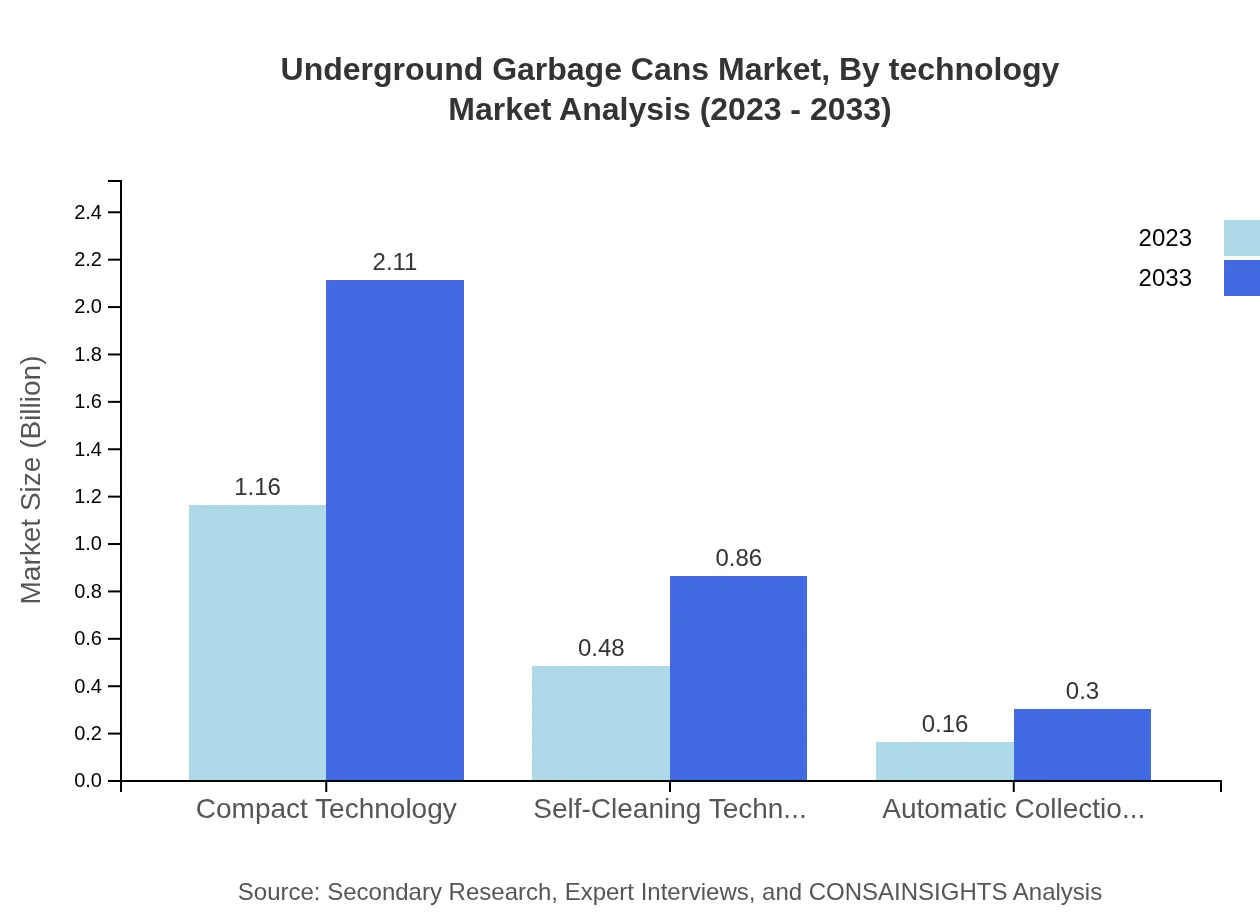
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis By Technology
In terms of technology, Compact Technology leads the market with a size of $1.16 billion and a share of 64.43% in 2023, expected to rise to $2.11 billion by 2033. Self-Cleaning and Automatic Collection technologies are growing but capture smaller portions of the market, each at 26.45% and 9.12% respectively.
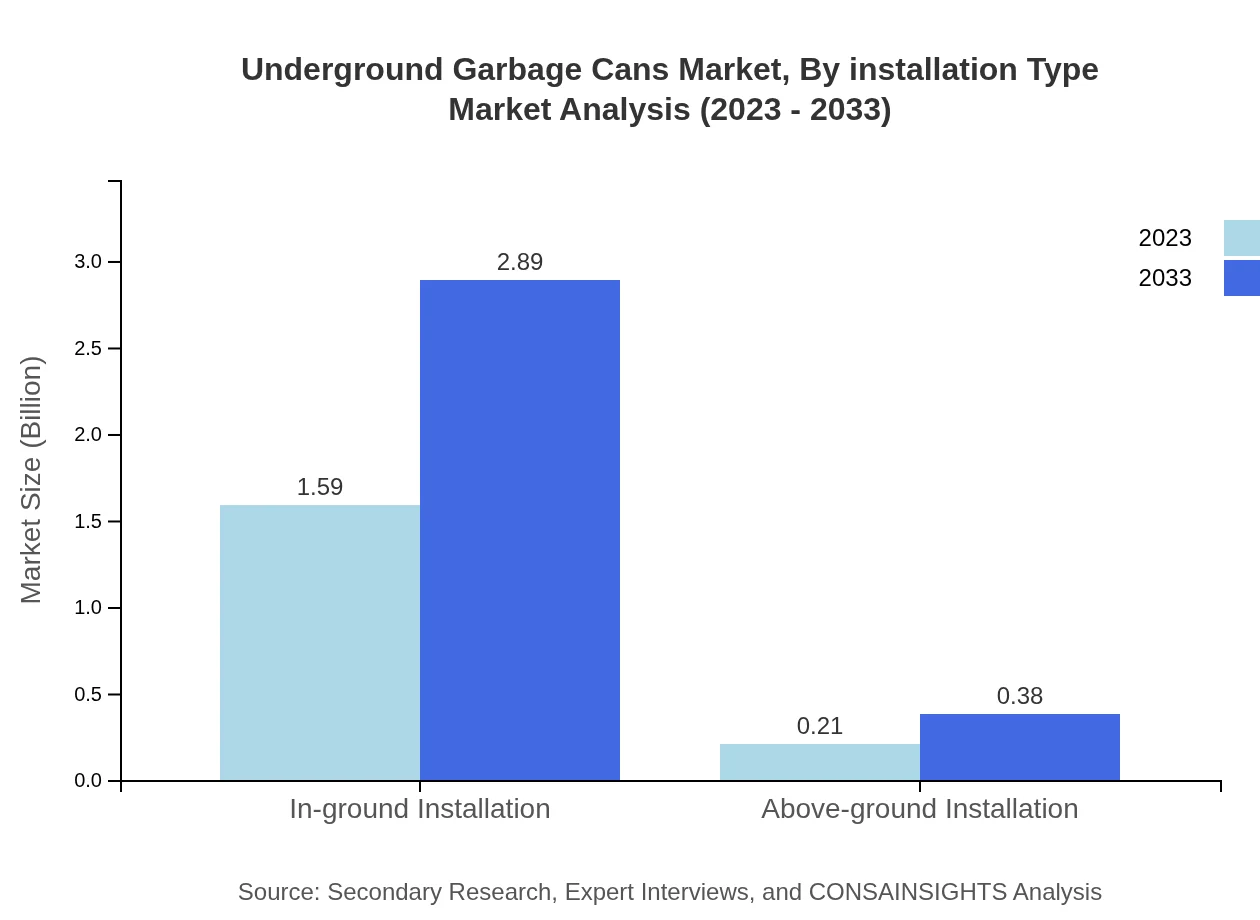
Underground Garbage Cans Market Analysis By Installation Type
Most Underground Garbage Cans are installed in-ground, holding a significant share of 88.3% with a size of $1.59 billion in 2023, anticipated to grow to $2.89 billion by 2033. Above-ground installations are gaining traction but represent only 11.7% of the market.
Underground Garbage Cans Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Underground Garbage Cans Industry
Waste Management, Inc.:
A leading provider of comprehensive waste management services, Waste Management is at the forefront of integrating sustainable solutions including underground systems to enhance urban waste management.SUEZ:
SUEZ offers waste management and recycling services, focusing on smart waste solutions that leverage technology to improve efficiency and environmental sustainability.Veolia:
Veolia is a global leader in optimized resource management, providing innovative underground waste solutions while supporting sustainable urban development.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of underground garbage cans?
The underground garbage cans market is valued at approximately $1.8 billion in 2023, with an expected CAGR of 6.0% from 2023 to 2033. This growth indicates a rising demand for innovative waste management solutions.
What are the key market players or companies in this underground garbage cans industry?
Key players in the underground garbage cans industry include major manufacturers and technology providers focusing on sustainability and efficiency. Their commitment to innovation drives competition and enhances product offerings in the market.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the underground garbage cans industry?
Growth factors for the underground garbage cans industry include increasing urbanization, the need for sustainable waste management solutions, and advancements in smart technology that facilitate efficient garbage collection and reduce environmental impact.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the underground garbage cans?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the underground garbage cans market, projected to expand from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $1.10 billion by 2033. Europe and Asia Pacific also show significant growth potential during this period.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the underground garbage cans industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the needs of clients in the underground garbage cans industry. Clients can receive specific insights and trends that cater directly to their business interests.
What deliverables can I expect from this underground garbage cans market research project?
Deliverables from the underground garbage cans market research project include detailed market analyses, growth projections, competitive landscape assessments, segment breakdowns, and actionable insights to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of underground garbage cans?
Trends in the underground garbage cans market highlight a shift towards smart technology integrations, increased demand for sustainable materials, and innovative waste management strategies that enhance efficiency and promote environmental responsibility.