Urea Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: urea
Urea Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Urea market from 2023 to 2033, covering market trends, size, growth insights, industry dynamics, and forecasts for regional performances. Valuable data and insights are presented for stakeholders to leverage in strategic planning.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
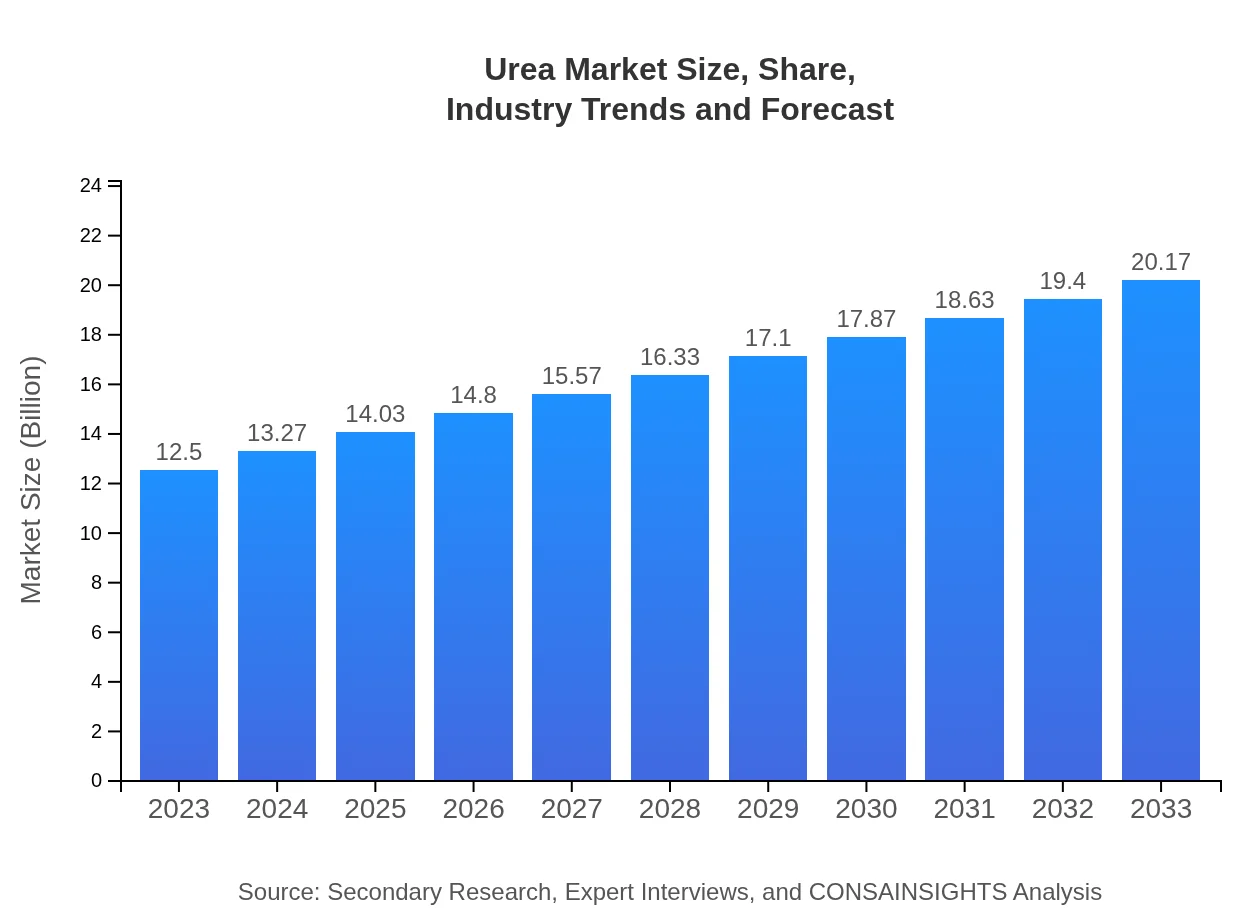
| 2023 Market Size | $12.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.8% |
| 2033 Market Size | $20.17 Billion |
| Top Companies | Yara International, CF Industries, Nutrien Ltd., OCI N.V. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Urea Market Overview
Customize Urea Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Urea market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Urea's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Urea
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Urea market in 2023?
Urea Industry Analysis
Urea Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Urea Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Urea Market Report:
Europe is projected to grow from a market size of $3.77 billion in 2023 to $6.08 billion by 2033. Strict regulations demanding sustainable farming practices and intensified agricultural production techniques are significant factors contributing to this growth.Asia Pacific Urea Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is one of the largest consumers of Urea, with a market size of $2.37 billion in 2023, projected to grow to $3.83 billion by 2033. Factors driving this growth include high population density leading to increased food demand, advancements in agricultural practices, and government subsidies for fertilizer usage.North America Urea Market Report:
North America’s Urea market was valued at $4.49 billion in 2023 and is expected to rise to $7.24 billion by 2033. This is attributed to rising corn and soybean production, environmental regulations enhancing fertilizer efficiency, and technology integration in farming.South America Urea Market Report:
In South America, the Urea market is anticipated to grow from $1.21 billion in 2023 to $1.95 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are significant contributors, driven by extensive agricultural lands and the need for high-yield crop productivity.Middle East & Africa Urea Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is anticipated to increase from $0.66 billion in 2023 to $1.06 billion by 2033, driven by increasing agricultural investments and the necessity to improve food security in the region.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Urea Market Analysis By Type
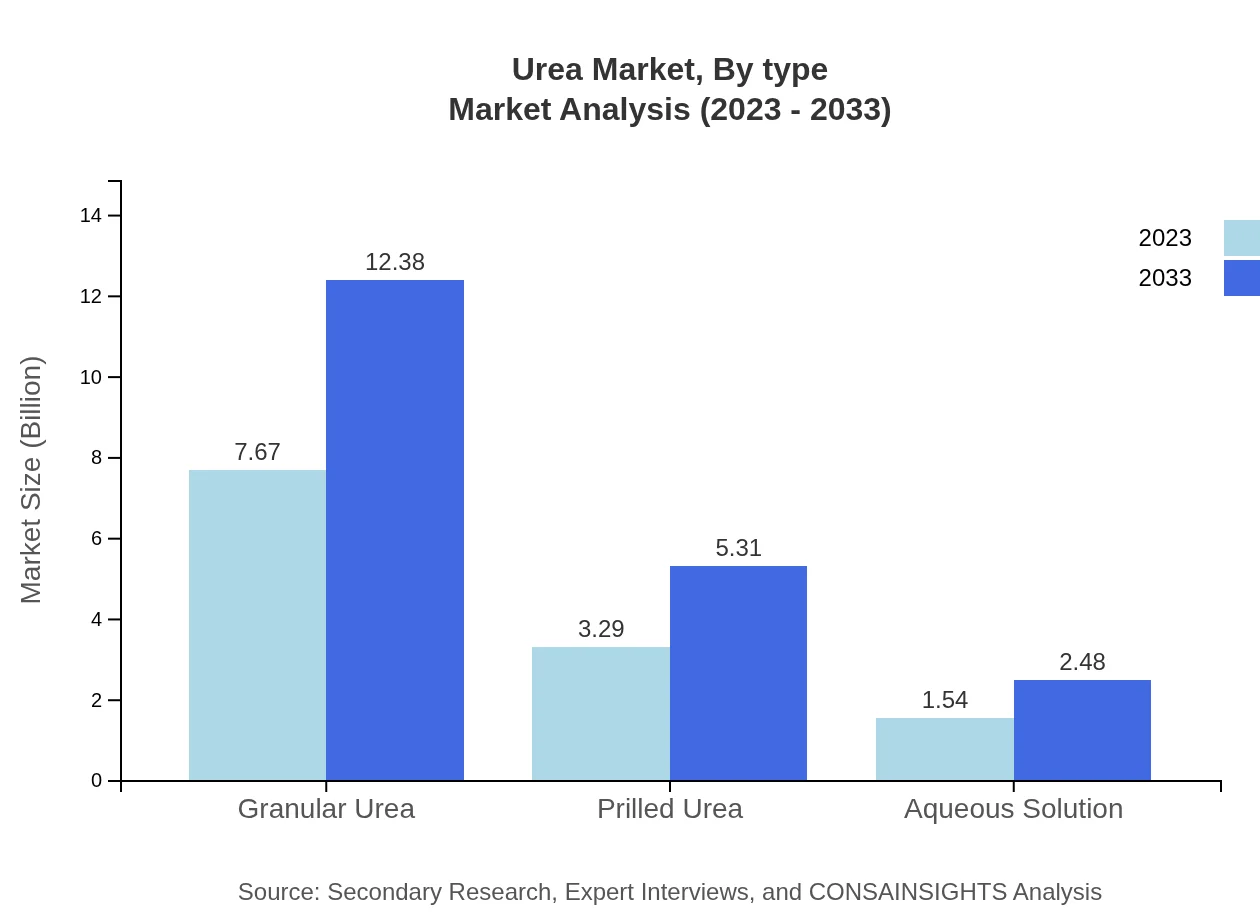
The Urea market is segmented by type into Granular Urea, Prilled Urea, and Aqueous Solutions. Granular Urea dominates the market with a size of $7.67 billion in 2023, expected to reach $12.38 billion by 2033, holding 61.36% market share. Prilled Urea, with a revenue of $3.29 billion in 2023, is anticipated to grow to $5.31 billion. Aqueous Solutions account for a slightly smaller segment, with a market size of $1.54 billion to reach $2.48 billion recognizing a 12.3% share.
Urea Market Analysis By Application
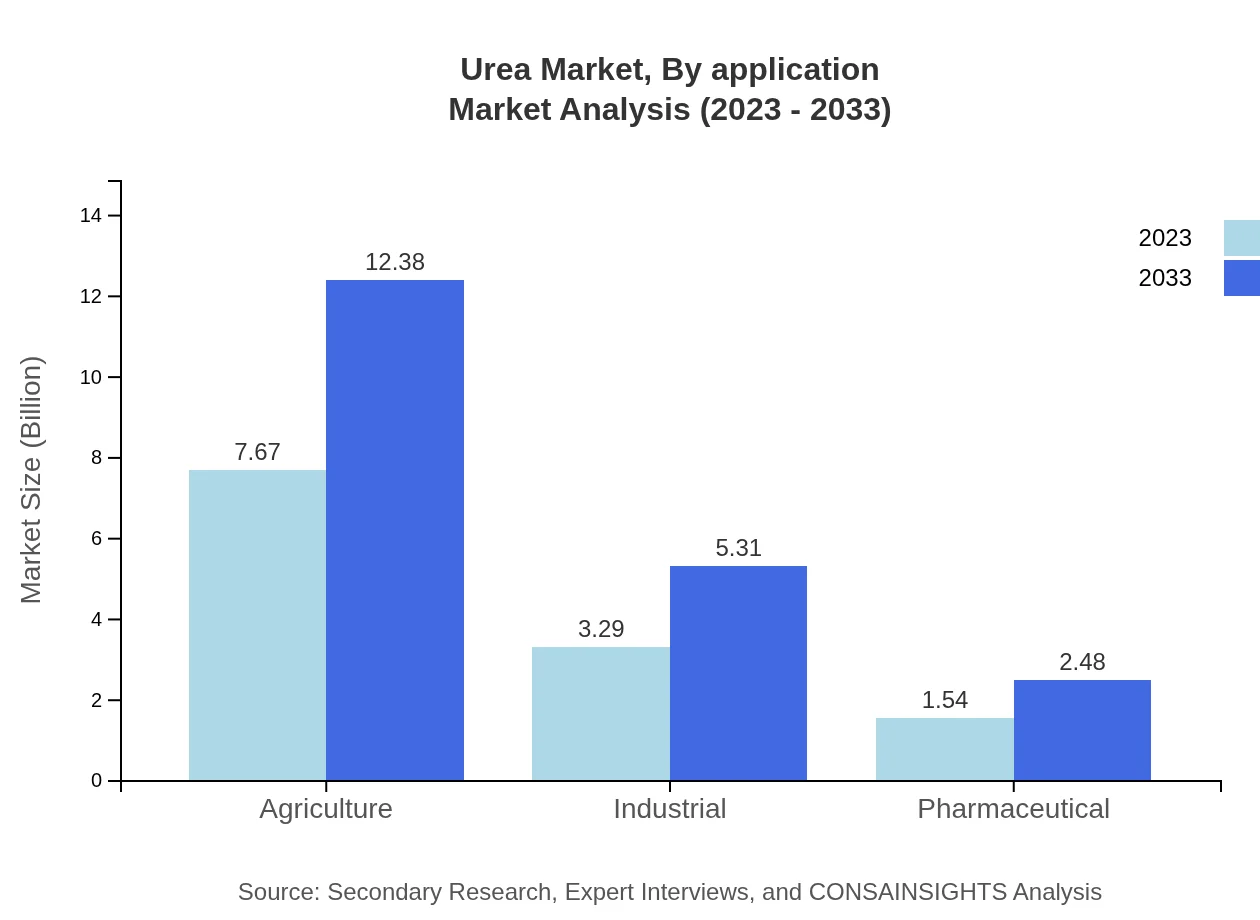
Key applications within the Urea market include Agriculture and Chemical Industries. The agricultural sector holds a commanding market share of 61.36% with a size of $7.67 billion in 2023, projected to grow significantly. Meanwhile, the chemical industry also plays a crucial role, growing from $3.29 billion to $5.31 billion over the next decade.
Urea Market Analysis By End User
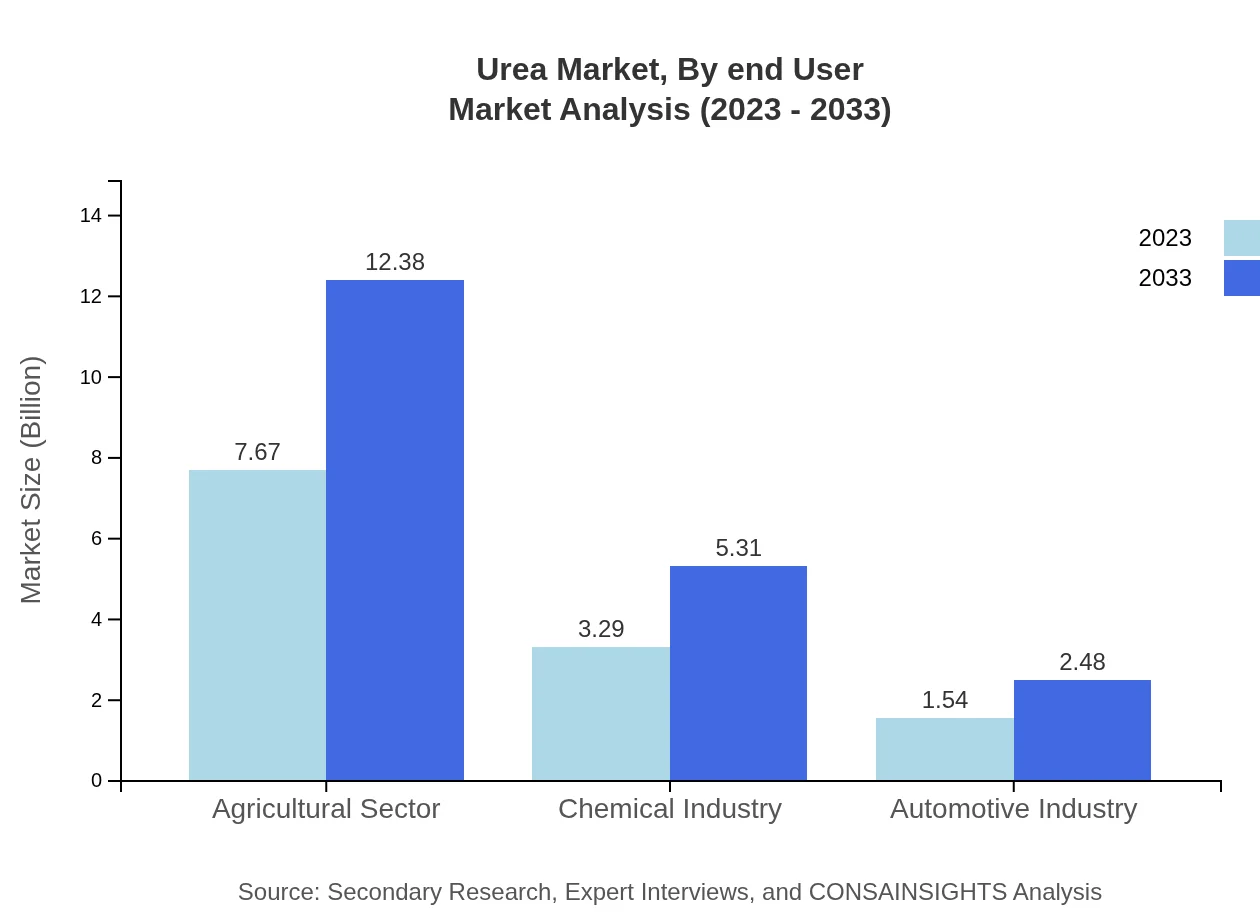
The Urea market serves various end-user industries, prominently Agriculture, Industrial, and Pharmaceutical sectors. Agricultural applications dominate the market with a significant growth trajectory while industrial applications ensure stability in demand due to Urea's use in production processes.
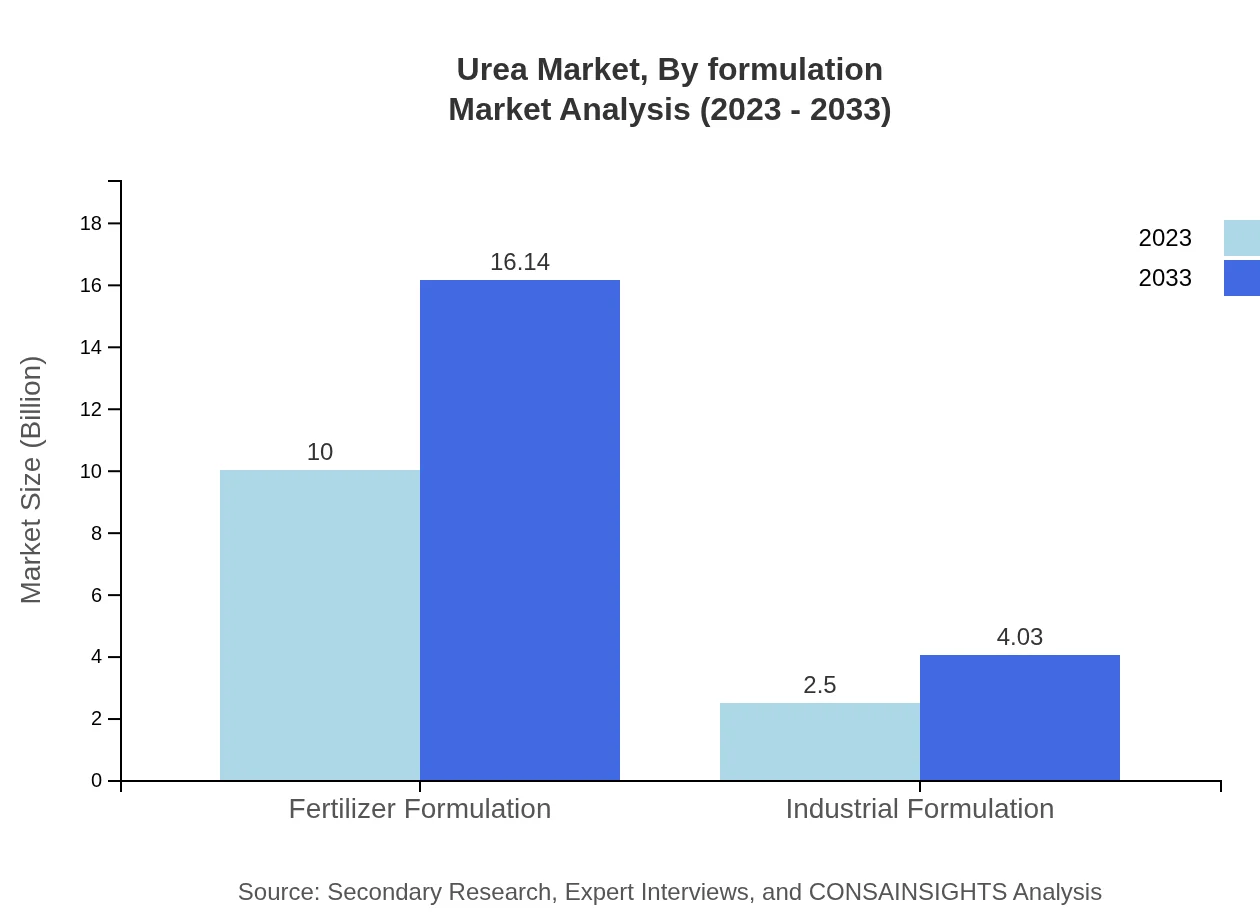
Urea Market Analysis By Formulation
Formulation-wise, the Urea market qualifies as Direct Sales and Online Sales segments. Both channels are increasingly favored due to advancements in distribution efficiency, ensuring better reaches of Urea products to farmers and industrial users alike.
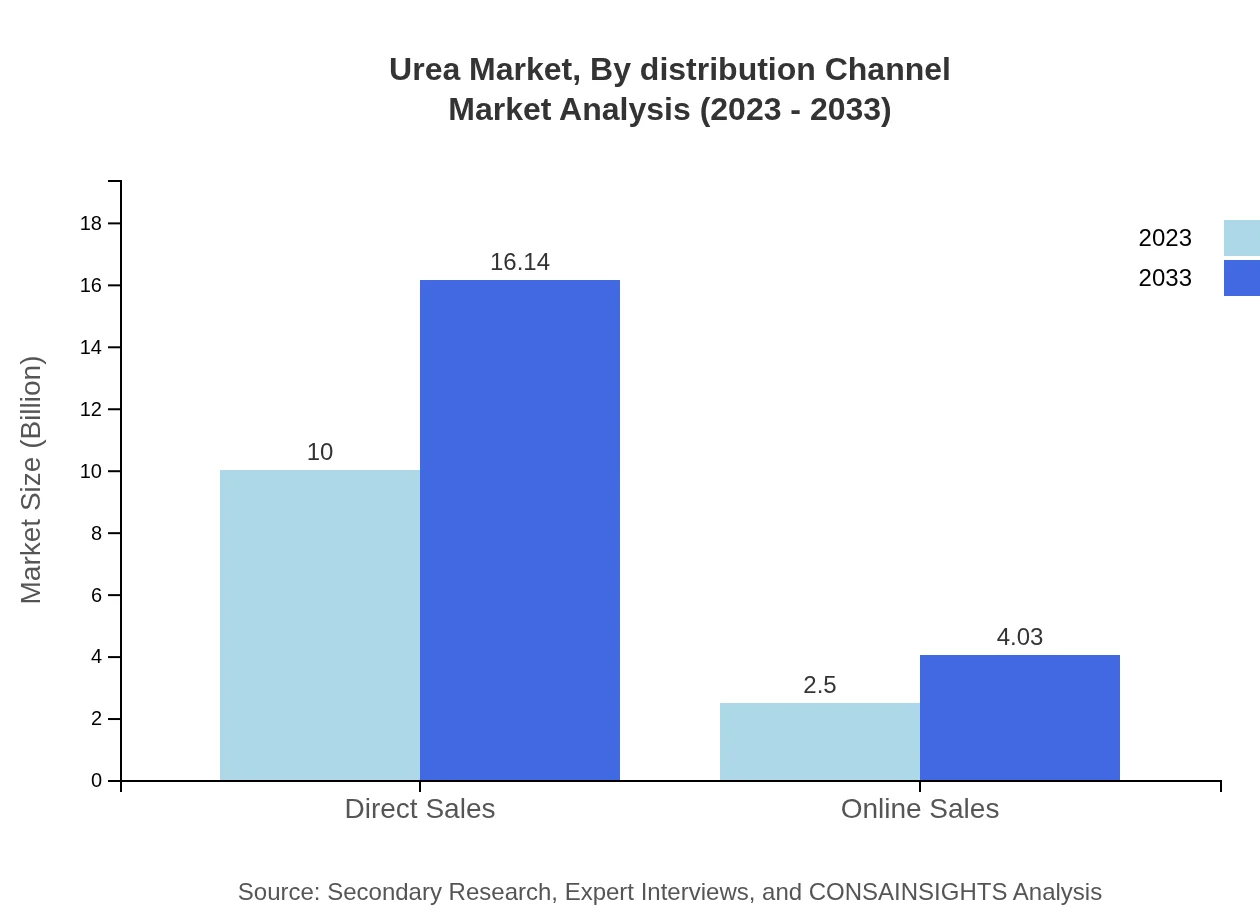
Urea Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels for Urea encompass Direct and Online sales. Direct sales account for the largest segment with a market size of $10 billion in 2023, while online sales continue gaining momentum, projected to reach $4.03 billion by 2033 as digitalization reshapes market access.
Urea Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Urea Industry
Yara International:
Yara is a leading global fertilizer company specializing in the production of nitrogen fertilizers, particularly Urea. Yara focuses on sustainable agricultural practices and innovative solutions aiding farmers globally.CF Industries:
CF Industries is a major manufacturer and distributor of nitrogen and phosphate-based fertilizers. Their production capabilities and strategic positions enhance their contributions significantly in the Urea market.Nutrien Ltd.:
As one of the largest providers of crop inputs and services globally, Nutrien plays a key role in the Urea market. Their extensive distribution networks provide essential products to various end-users.OCI N.V.:
OCI N.V. is recognized for its production of Urea fertilizers through innovative and efficient methodologies, focusing on optimizing output and promoting environmental stewardship.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of urea?
The global urea market is valued at approximately $12.5 billion in 2023, with a projected CAGR of 4.8%, indicating steady growth through 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this urea industry?
Key players in the urea market include major producers and suppliers focused on efficient production and distribution across various regions, enhancing their market presence.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the urea industry?
Growth in the urea market is driven by increasing agricultural demand, advancements in fertilizer technology, and rising global food consumption necessitating higher yields.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the urea market?
North America is expected to exhibit the fastest growth in the urea market from 2023 to 2033, with a market size increasing from $4.49 billion to $7.24 billion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the urea industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market reports to address specific client needs within the urea industry, ensuring relevant and actionable insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this urea market research project?
From the urea market research project, expect detailed reports, market sizing data, trends, competitive analysis, and actionable recommendations to support decision-making.
What are the market trends of urea?
Current trends in the urea market include a shift towards sustainable agricultural practices, increased efficiency in urea production, and growing demand in emerging economies.