Used Cooking Oil Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: used-cooking-oil
Used Cooking Oil Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Used Cooking Oil market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, growth rates, trends, and insights across various regions and segments.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
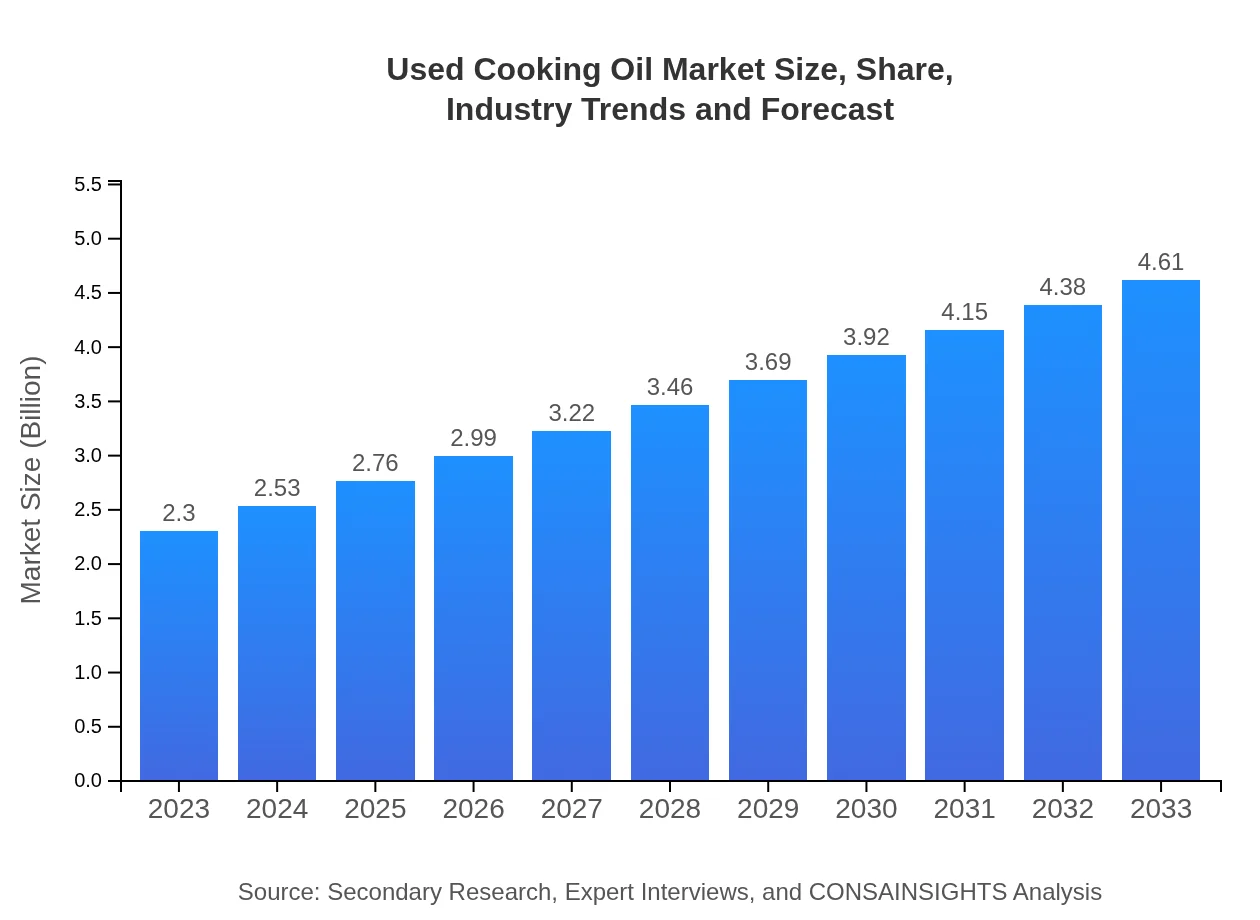
| 2023 Market Size | $2.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 7.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $4.61 Billion |
| Top Companies | Waste Management, Inc., Biox Corporation, Green Fuels Ltd., Ecovia Renewables, UCO Recycling, LLC |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Used Cooking Oil Market Overview
Customize Used Cooking Oil Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Used Cooking Oil market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Used Cooking Oil's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Used Cooking Oil
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Used Cooking Oil market in 2023?
Used Cooking Oil Industry Analysis
Used Cooking Oil Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Used Cooking Oil Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Used Cooking Oil Market Report:
Europe’s UCO market is estimated at 0.71 billion USD in 2023 and expected to reach 1.41 billion USD by 2033. Stringent EU regulations on waste management and biomass energy production underpin this growth. Countries like Germany and France are key players, promoting UCO usage in renewable energy sectors.Asia Pacific Used Cooking Oil Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Used Cooking Oil market is projected to grow from approximately 0.41 billion USD in 2023 to 0.83 billion USD by 2033. Countries like China and India are driving this growth through increased oil consumption and rising demand for biodiesel. Additionally, initiatives aimed at enhancing waste management practices further bolster the UCO industry.North America Used Cooking Oil Market Report:
North America has the largest Used Cooking Oil market, valued at 0.87 billion USD in 2023, and anticipated to expand to 1.75 billion USD by 2033. The U.S. leads the way in biodiesel manufacturing and strict waste disposal regulations which promote UCO collection and recycling initiatives. This trend is further enhanced by consumer awareness of sustainability.South America Used Cooking Oil Market Report:
In South America, the UCO market is relatively small, expected to grow from 0.07 billion USD in 2023 to 0.15 billion USD by 2033. The focus on sustainable agriculture and biofuels, particularly in Brazil, is expected to drive growth in the region, leveraging its existing biodiesel production frameworks.Middle East & Africa Used Cooking Oil Market Report:
The UCO market in the Middle East and Africa is anticipated to grow from 0.24 billion USD in 2023 to 0.47 billion USD by 2033, spurred by the advancing biodiesel sector and the need for improved waste management systems.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
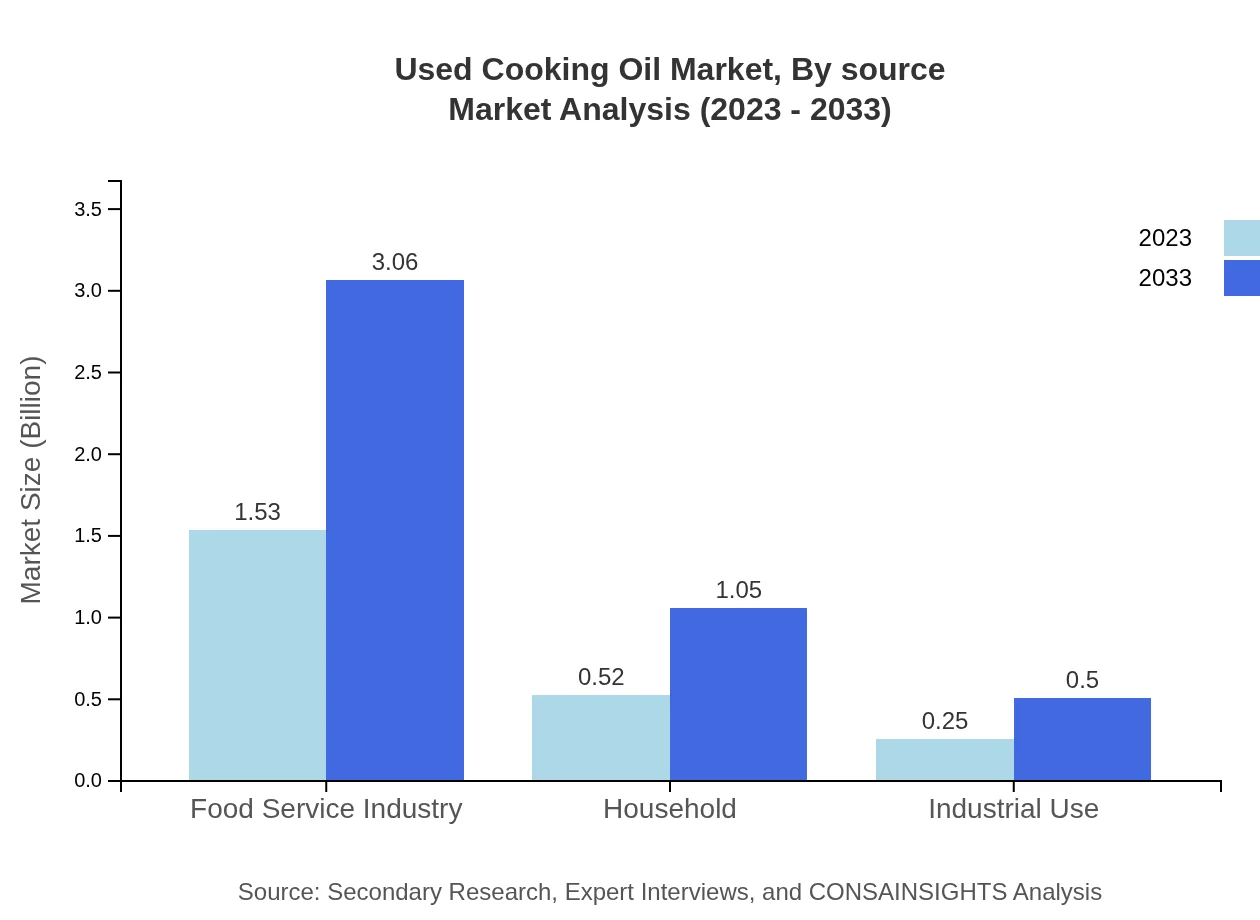
Used Cooking Oil Market Analysis By Source
The Used Cooking Oil market is largely dominated by the food service industry, with a market size of 1.53 billion USD in 2023 expected to double by 2033. Households contribute significantly, reflecting a value of 0.52 billion USD in 2023, which is projected to increase by 100% over the period. Industrial usage remains smaller at 0.25 billion USD, yet shows consistency with expected growth. Recycling of UCO into biodiesel primarily drives these figures.
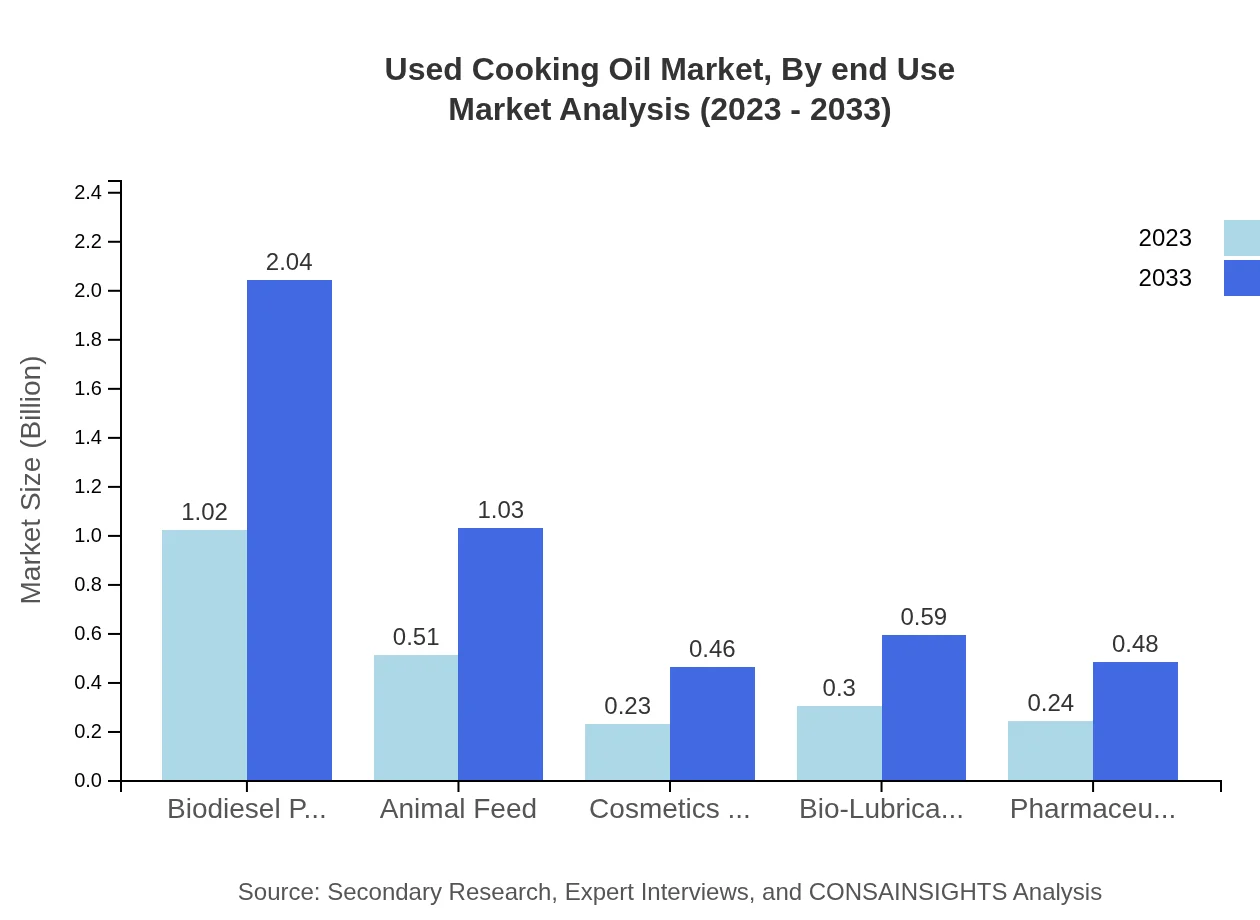
Used Cooking Oil Market Analysis By End Use
The end-use segment is prominently driven by biodiesel production, which represents 44.33% of the market share in 2023. The food service sector accounts for a substantial portion at 66.45%, supported by various applications in animal feed and cosmetics. Notably, animal feed employs about 22.39% of UCO. Other growing segments include cosmetics, with anticipated growth owing to the rise in bio-lubricants and pharmaceutical applications.
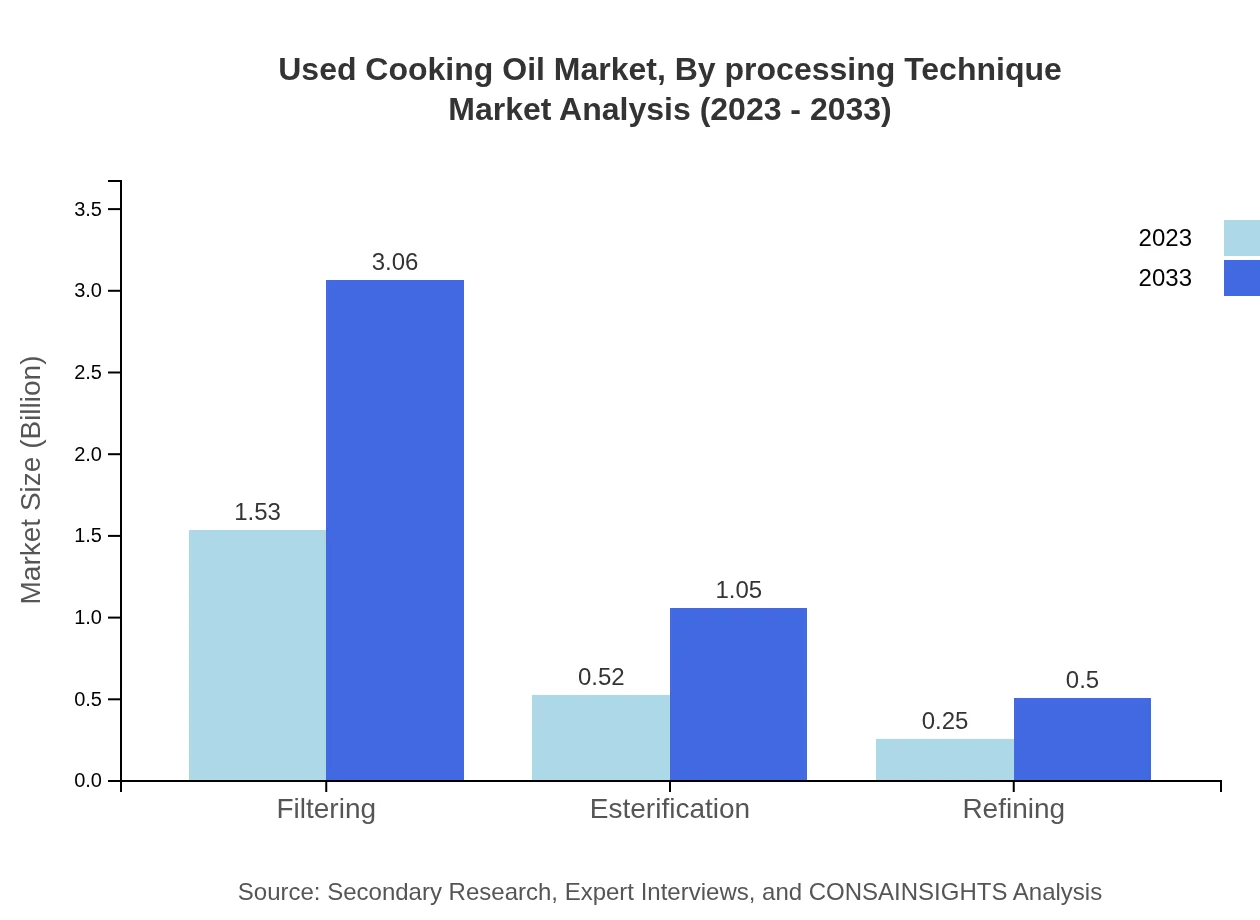
Used Cooking Oil Market Analysis By Processing Technique
In processing techniques, filtering constitutes the largest segment at 1.53 billion USD, driven by the need for quality UCO for biodiesel production. Esterification is significant, expected to reach a market size of 0.52 billion USD in 2023. Refining processes hold a vital share, but are expected to experience slower growth relative to filtering and esterification.
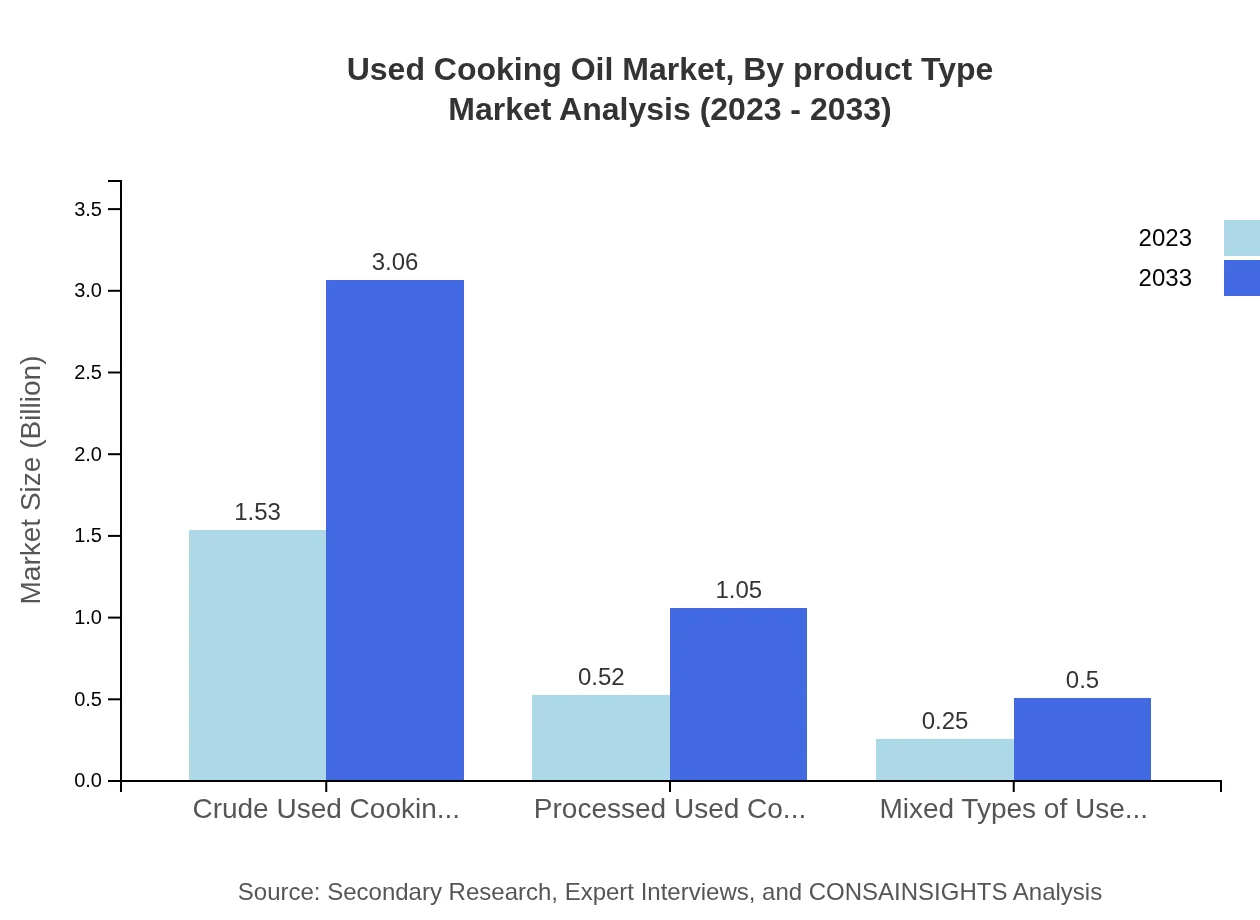
Used Cooking Oil Market Analysis By Product Type
The product types primarily include crude used cooking oil, which dominates with a market size of 1.53 billion USD in 2023. Processed used cooking oil trails behind in market size, while mixed types account for 0.25 billion USD. The emphasis on crude oil for biodiesel production significantly boosts its prominence, while secondary products like processed UCO are growing steadily.
Used Cooking Oil Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Used Cooking Oil Industry
Waste Management, Inc.:
A leader in waste disposal and recycling services, Waste Management is heavily involved in the collection and processing of Used Cooking Oil for biodiesel production.Biox Corporation:
A prominent player in the biodiesel sector utilizing Used Cooking Oil, Biox Corporation focuses on sustainable energy solutions and recycling of used oils.Green Fuels Ltd.:
A pioneer in biodiesel technology, Green Fuels demonstrates extensive expertise in converting Used Cooking Oils into biodiesel products.Ecovia Renewables:
Specializing in the production of biodiesel from feedstock sources including Used Cooking Oil, Ecovia is committed to promoting renewable energy.UCO Recycling, LLC:
A notable company in the UCO collection and recycling industry, UCO Recycling focuses on sustainable practices for waste cooking oils.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of used cooking oil?
The used cooking oil market is expected to reach $2.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.0%. This growth trajectory indicates increasing demands across various applications, enhancing market viability over the next decade.
What are the key market players or companies in the used cooking oil industry?
Key players in the used cooking oil industry include large chemical manufacturers, biodiesel producers, and waste oil recyclers. They are crucial to establishing sustainable supply chains and improving conversion technologies for used cooking oil.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the used cooking oil industry?
Growth factors in the used cooking oil industry include rising biodiesel demand, increased environmental awareness, and stringent regulations on waste disposal. Additionally, advancements in processing technologies contribute to enhanced oil recovery and recycling.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the used cooking oil market?
North America is slated to be the fastest-growing region, with the market increasing from $0.87 billion in 2023 to $1.75 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by rising consumer awareness and government incentives for recycling.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the used cooking oil industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports tailored to specific needs. These reports provide in-depth sector analysis, trends, and regional insights for clients looking to make informed decisions in the used cooking oil industry.
What deliverables can I expect from this used cooking oil market research project?
Deliverables include comprehensive market analysis reports, growth forecasts, competitive landscape insights, and consumer behavior studies. Clients also receive data visualization charts for better interpretation of trends and market dynamics.
What are the market trends of used cooking oil?
Current trends in the used cooking oil market include increasing adoption in biodiesel production, a shift towards sustainability in the food service sector, and rising innovations in refining processes that enhance end-product quality.