Utilities Security Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: utilities-security
Utilities Security Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report explores the Utilities Security market, providing detailed insights into its size, growth forecasts, and future trends from 2023 to 2033. It covers regional analysis, market segmentation, and key industry players, offering a comprehensive understanding of the factors driving market evolution.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
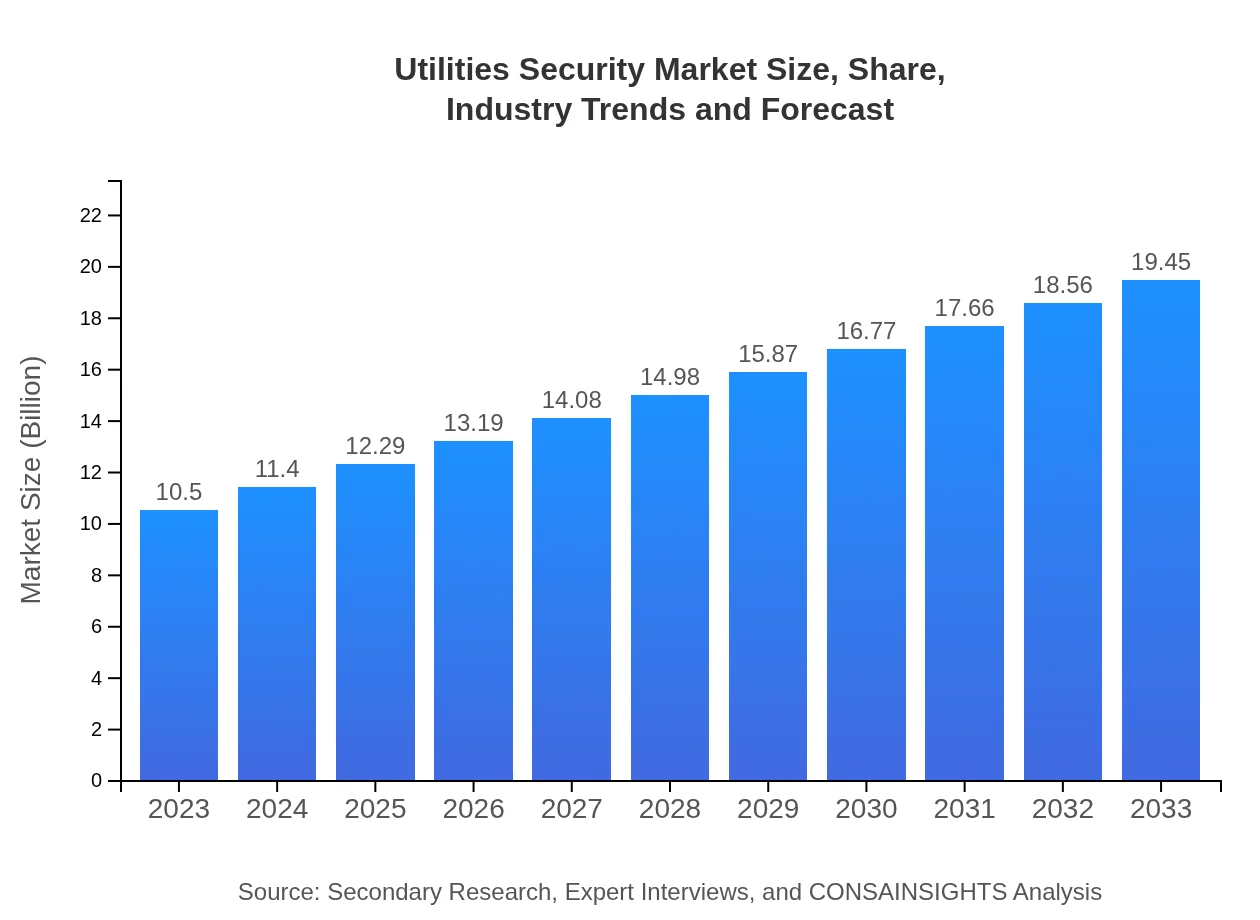
| 2023 Market Size | $10.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 6.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $19.45 Billion |
| Top Companies | Siemens AG, Honeywell International Inc., Schneider Electric, ABB Ltd. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Utilities Security Market Overview
Customize Utilities Security Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Utilities Security market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Utilities Security's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Utilities Security
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Utilities Security market in 2023?
Utilities Security Industry Analysis
Utilities Security Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Utilities Security Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Utilities Security Market Report:
The European market is forecasted to expand from USD 2.63 billion in 2023 to USD 4.86 billion by 2033, driven by a mix of regulatory frameworks and increasing emphasis on digital transformations in utility operations, further necessitating enhanced security protocols.Asia Pacific Utilities Security Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the market is projected to grow from USD 2.04 billion in 2023 to USD 3.78 billion by 2033, driven primarily by the increased adoption of smart grid technologies and rising cyber threats. Countries such as China and India are leading investments in utility infrastructure which enhances the need for robust security measures.North America Utilities Security Market Report:
North America remains a dominant player in the Utilities Security market, projected to grow from USD 3.91 billion in 2023 to USD 7.24 billion by 2033. The adoption of innovative technology solutions, along with stringent regulations around data protection and infrastructure security, largely drive this growth.South America Utilities Security Market Report:
The South American market is expected to see growth from USD 0.62 billion in 2023 to USD 1.15 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by increasing investments in water and energy sectors combined with regulatory initiatives aimed at improving infrastructure security.Middle East & Africa Utilities Security Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market is anticipated to grow from USD 1.31 billion in 2023 to USD 2.43 billion by 2033, driven by construction and enhancement of utility infrastructure and the demand for resilient power and water systems.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Utilities Security Market Analysis By Product
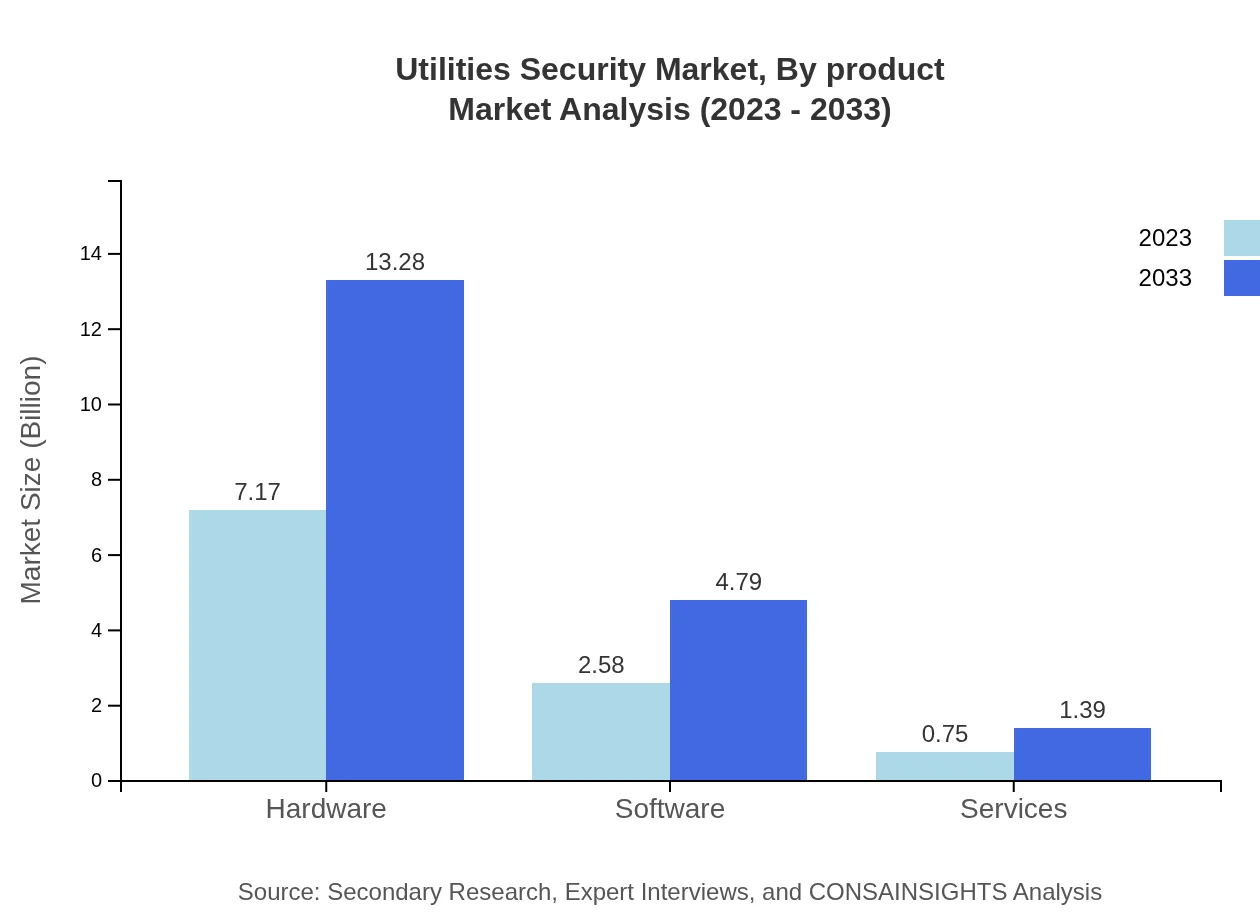
The Utilities Security market by product is dominated by Hardware, Software, and Services. Hardware holds the largest share with a market size projected at USD 7.17 billion in 2023, increasing to USD 13.28 billion by 2033, retaining a market share of 68.24%. Software revenues are projected to grow from USD 2.58 billion in 2023 to USD 4.79 billion, holding a 24.61% share. Services are projected to grow from USD 0.75 billion in 2023 to USD 1.39 billion, representing 7.15% of market share.
Utilities Security Market Analysis By Technology
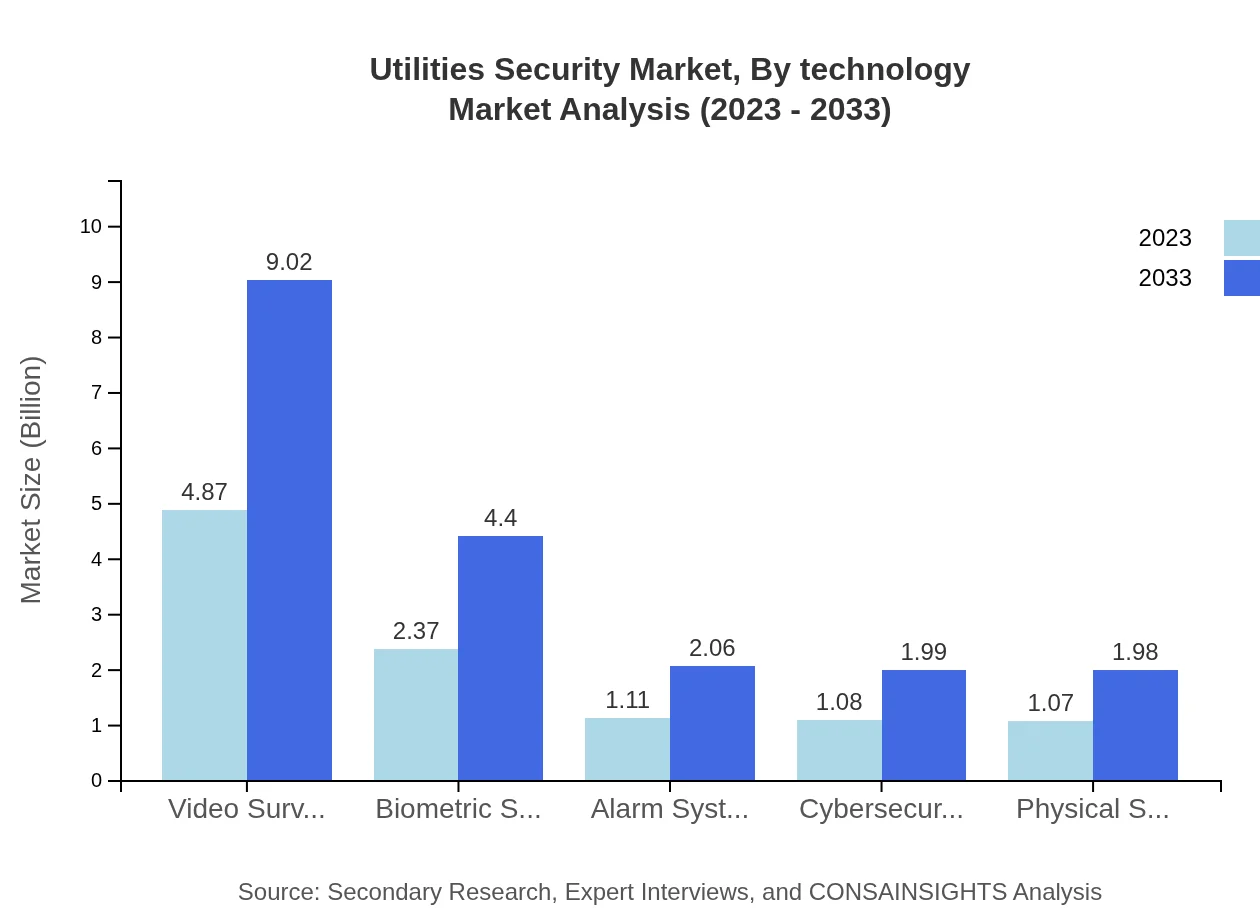
Within the Utilities Security market by technology, key advancements include Video Surveillance, Biometric Systems, the implementation of Alarm Systems, Cybersecurity Solutions, and Physical Security Systems. Video Surveillance leads with a market of USD 4.87 billion in 2023, projected to reach USD 9.02 billion by 2033, while Biometric Systems contribute USD 2.37 billion in 2023, growing to USD 4.40 billion. Cybersecurity Solutions play an increasing role due to rising cyber threats, with a market of USD 1.08 billion projected in 2023, growing significantly in the coming years.
Utilities Security Market Analysis By Application
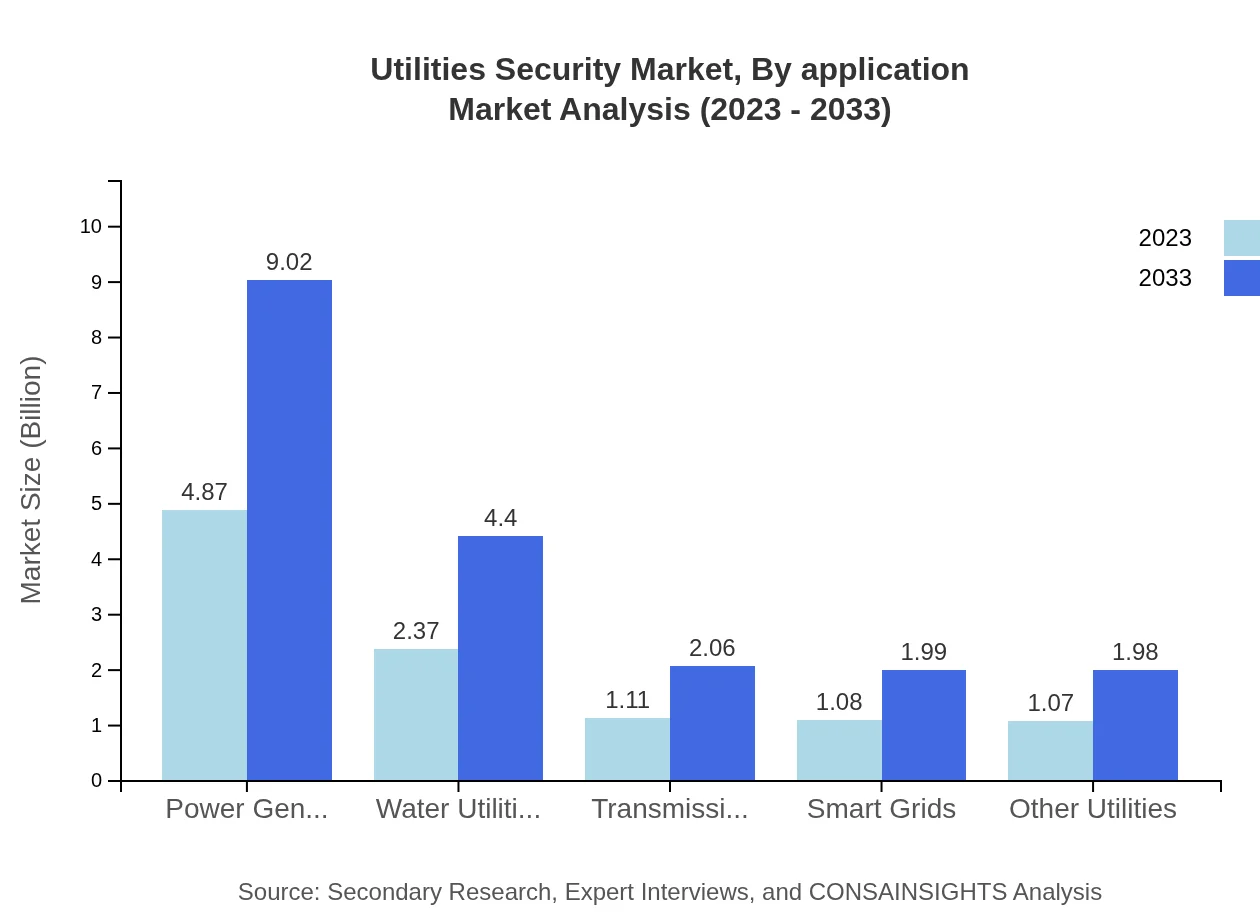
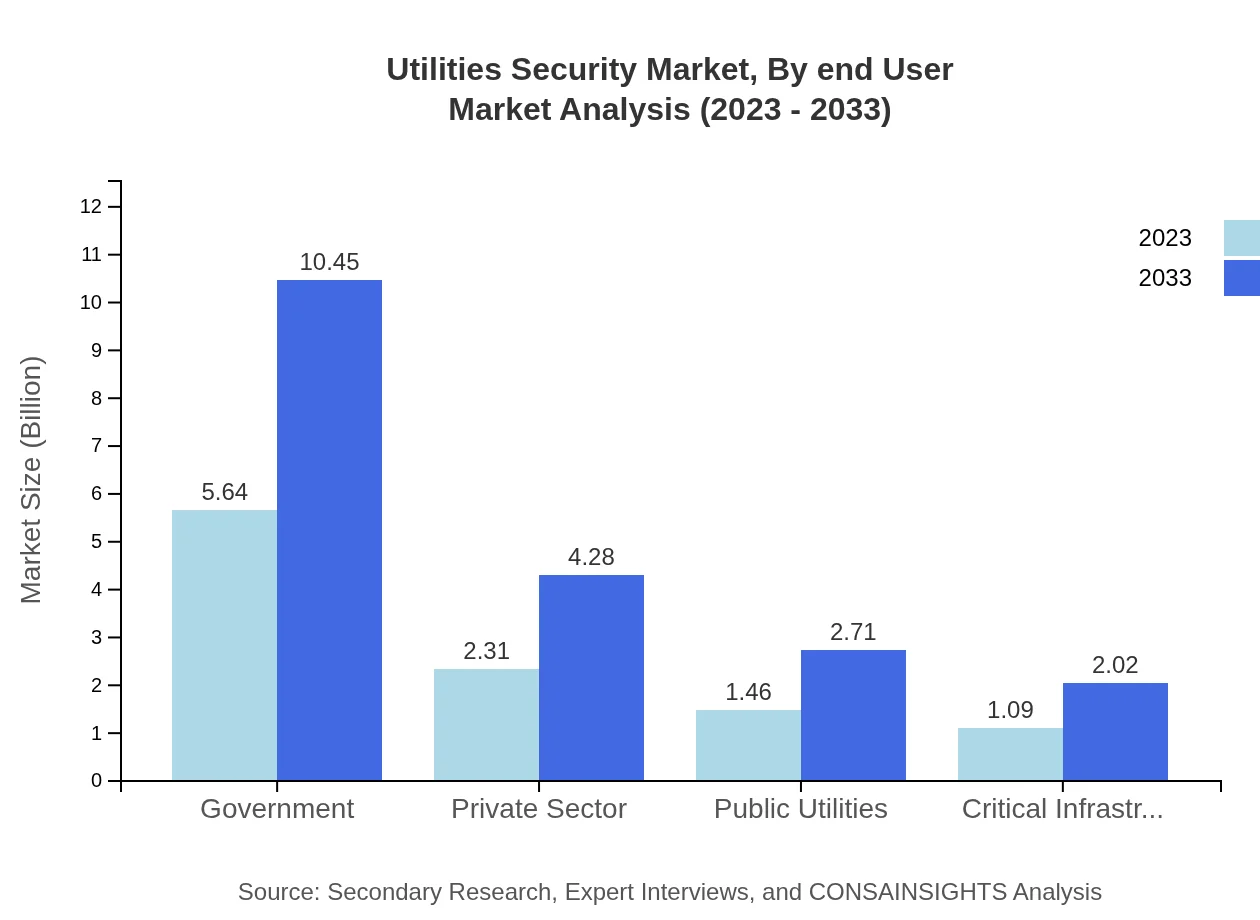
Applications within the Utilities Security sector are primarily categorized into two areas: Government and Private Sector, and Public Utilities. Government applications significantly impact the market, which accounts for a size of USD 5.64 billion in 2023, growing to USD 10.45 billion by 2033. Private sector applications are projected to grow from USD 2.31 billion in 2023 to USD 4.28 billion by 2033, while Public Utilities increase from USD 1.46 billion in 2023 to USD 2.71 billion.
Utilities Security Market Analysis By End User
The Utilities Security market by end-user includes Critical Infrastructure sectors alongside various utility services. The Critical Infrastructure segment holds significant stakes with market sizes projected to grow from USD 1.09 billion in 2023 to USD 2.02 billion by 2033, followed by other services increasing from USD 1.07 billion to USD 1.98 billion.
Utilities Security Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Utilities Security Industry
Siemens AG:
A global leader in electrical engineering and electronics, Siemens AG offers extensive solutions catering to the utilities sector, particularly in providing advanced protection systems and digital security.Honeywell International Inc.:
Honeywell is a diversified multinational technology company that is a key player in automation and control solutions, playing a prominent role in cybersecurity technologies for utility companies.Schneider Electric:
Focusing on energy management and automation solutions, Schneider Electric provides comprehensive security solutions aimed at ensuring operational resilience across utilities.ABB Ltd.:
ABB is specialized in electrification, robotics, and industrial automation. Its key contributions include enhancing physical and cyber security measures within utility infrastructures.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of utilities Security?
The utilities-security market is valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow with a CAGR of 6.2%, reaching significant milestones by 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in this utilities Security industry?
Key players include tech giants and security firms specializing in critical infrastructure protection, cybersecurity solutions, and physical security systems tailored for utilities, enhancing resilience against threats.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the utilities Security industry?
Growth is driven by increasing cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance demands, investment in critical infrastructure, and the adoption of advanced surveillance technologies and digital transformation initiatives.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the utilities Security?
The fastest-growing region is North America, expanding from $3.91 billion in 2023 to $7.24 billion by 2033, driven by advanced security solutions and heightened awareness of cybersecurity risks.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the utilities Security industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market reports for the utilities-security industry, allowing clients to receive market insights specific to their needs and strategic objectives.
What deliverables can I expect from this utilities Security market research project?
Expect comprehensive insights including market size, trends, regional analysis, segment data, and profiles of key players, alongside actionable recommendations for strategic planning.
What are the market trends of utilities Security?
Current trends include the rise in AI-based security solutions, integration of smart technologies in utilities, increased investments in cybersecurity infrastructure, and a growing focus on regulatory compliance.