Vaccine Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: vaccine
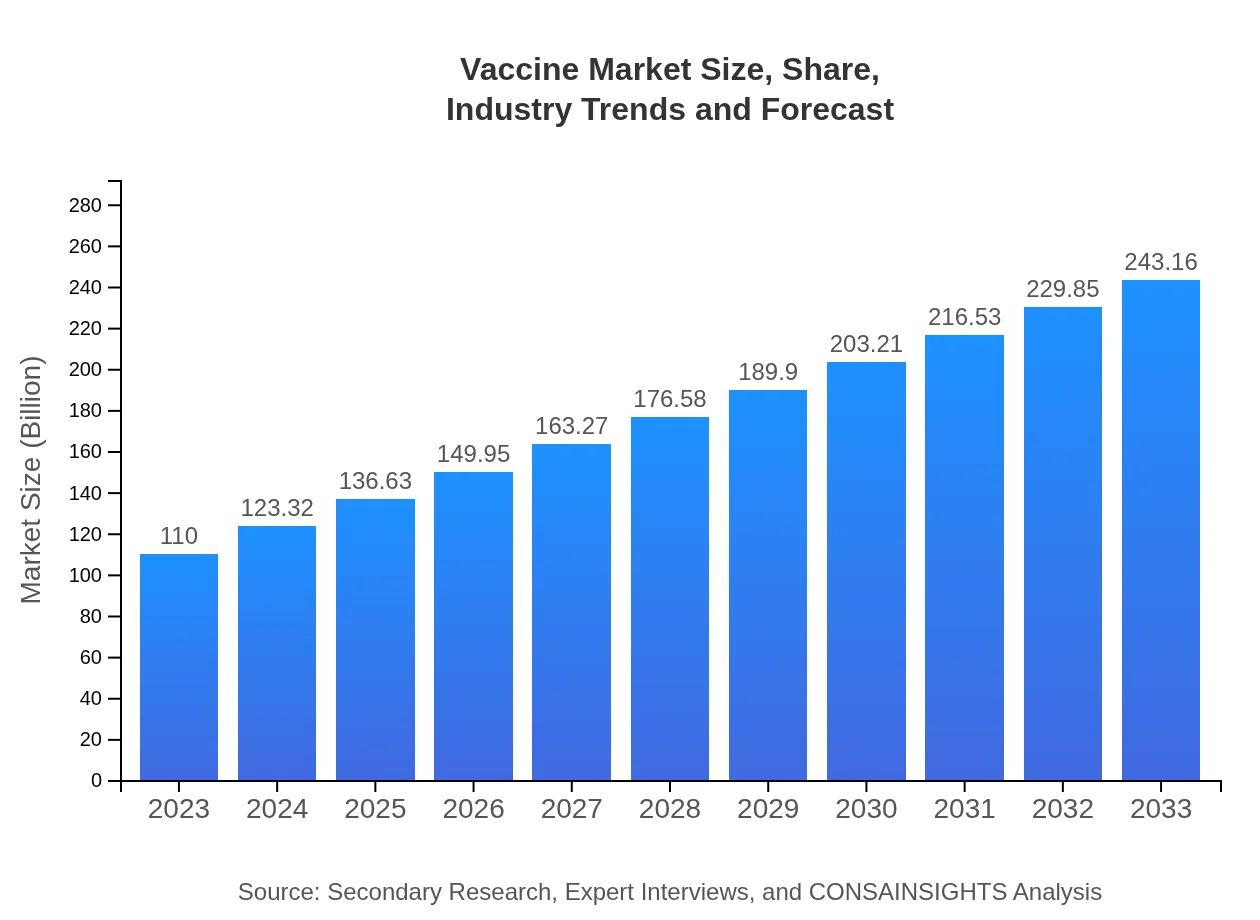
Vaccine Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global vaccine market, showcasing current conditions, market size, and growth forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It covers various market segments, regional insights, technological advancements, and key players impacting the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $110.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 8.0% |
| 2033 Market Size | $243.16 Billion |
| Top Companies | Pfizer , Sanofi, Merck & Co., Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Vaccine Market Overview
Customize Vaccine Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Vaccine market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Vaccine's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Vaccine
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Vaccine market in 2023?
Vaccine Industry Analysis
Vaccine Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vaccine Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Vaccine Market Report:
Europe holds a significant share of the vaccine market, projected to increase from USD 31.43 billion in 2023 to USD 69.47 billion by 2033. Stringent health policies and a growing trend towards preventive healthcare are pivotal in enhancing vaccine uptake.Asia Pacific Vaccine Market Report:
The Asia-Pacific region, valued at USD 23.74 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 52.47 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by increased investments in healthcare infrastructure, rising awareness regarding vaccination, and government initiatives to improve immunization rates across various age groups.North America Vaccine Market Report:
North America is set to lead the vaccine market, rising from USD 36.86 billion in 2023 to USD 81.48 billion by 2033. High R&D investments, strong regulatory frameworks, and advanced healthcare systems contribute to this dynamic growth in the region.South America Vaccine Market Report:
In South America, the vaccine market is projected to grow from USD 2.72 billion in 2023 to USD 6.01 billion by 2033. Challenges such as economic instability and access to vaccines persist, yet concerted efforts by governments and NGOs are expected to enhance vaccination coverage and market growth.Middle East & Africa Vaccine Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa vaccine market, valued at USD 15.26 billion in 2023, is expected to climb to USD 33.73 billion by 2033. With rising healthcare expenditure and the need for improved disease management, both regions are accelerating their vaccination programs.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
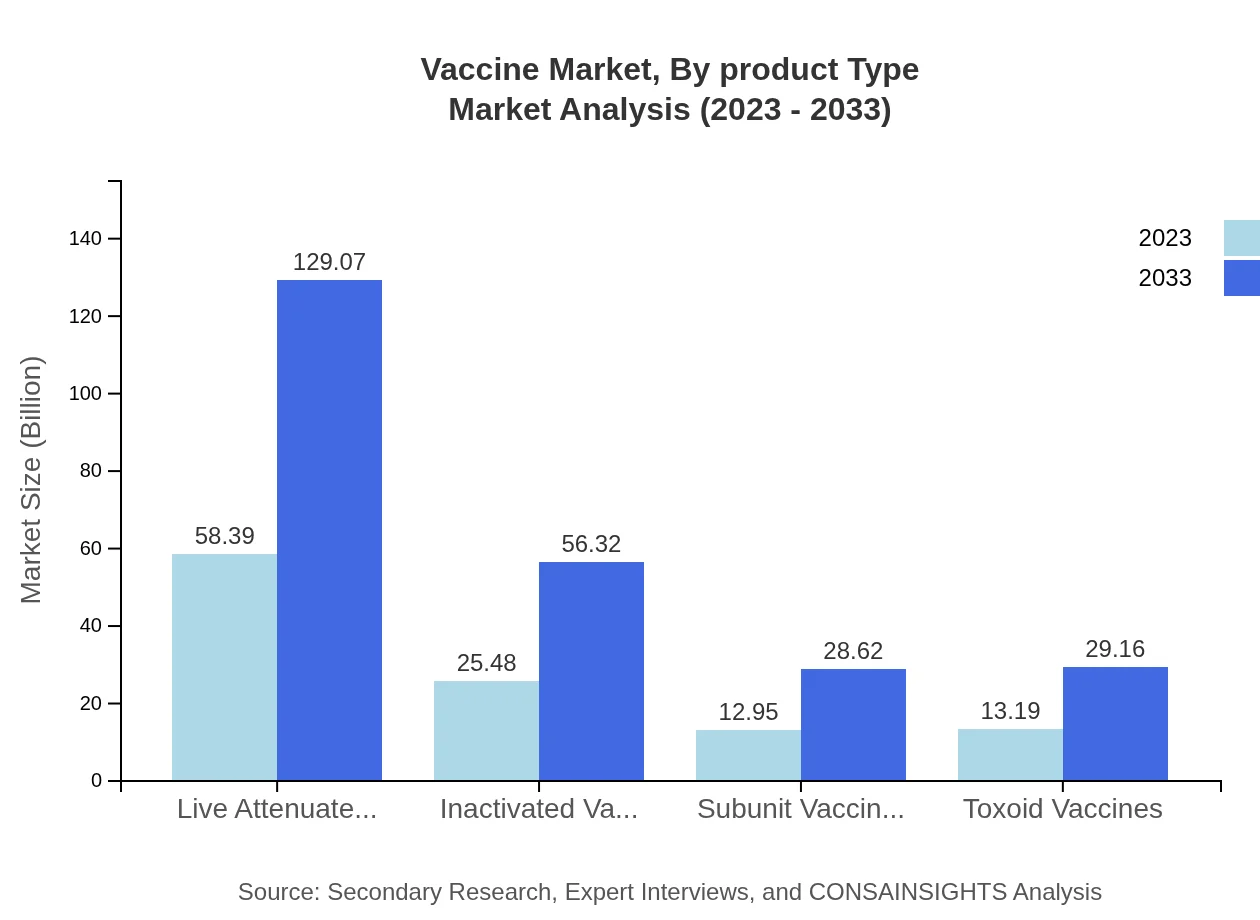
Vaccine Market Analysis By Product Type
In 2023, the vaccine market by product type is dominated by live attenuated vaccines with a market size of USD 58.39 billion, expected to grow to USD 129.07 billion by 2033, holding a 53.08% market share. Other significant segments include inactivated vaccines at USD 25.48 billion and subunit vaccines at USD 12.95 billion, reflecting the diverse needs for various immunization strategies.
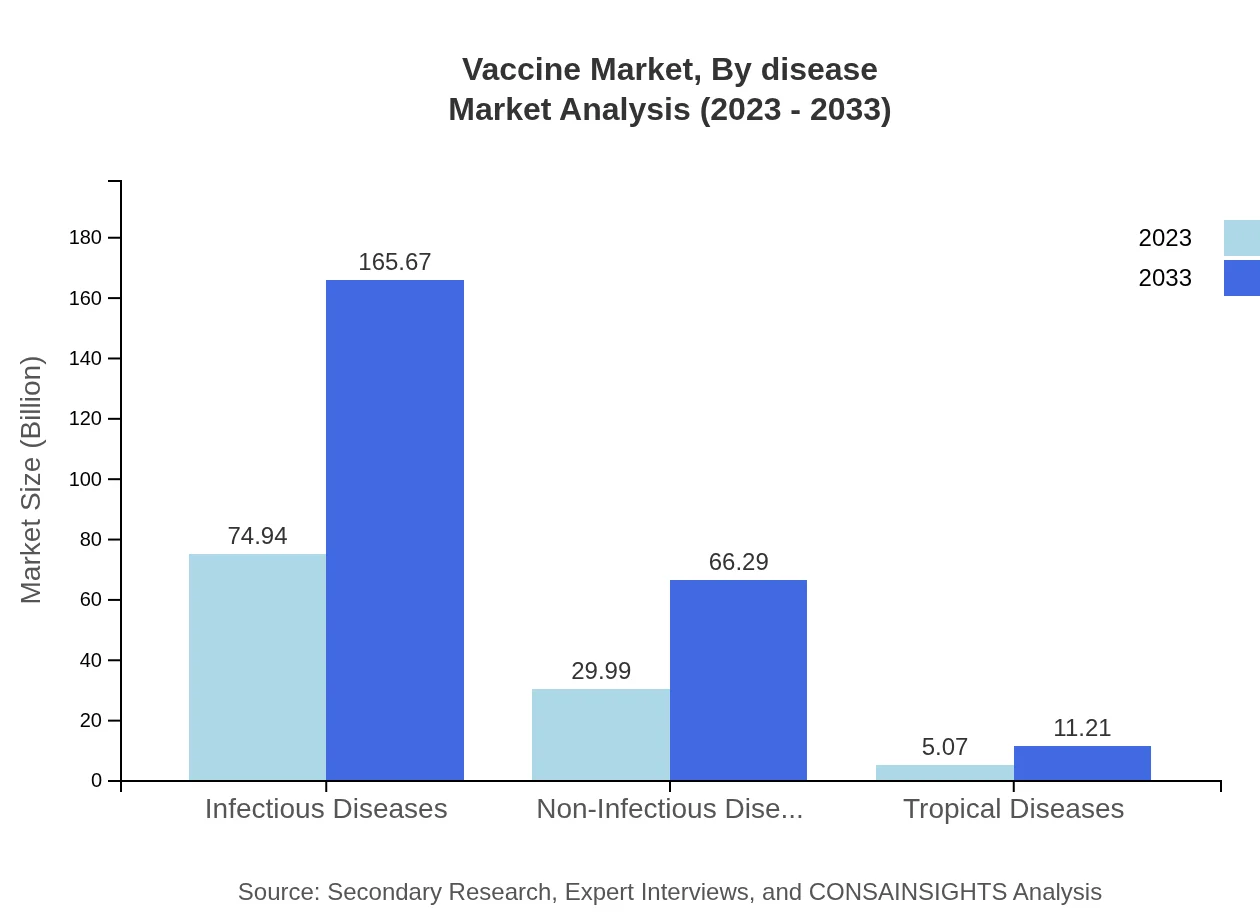
Vaccine Market Analysis By Disease
Focusing on infectious diseases, this segment is projected to expand from USD 74.94 billion in 2023 to USD 165.67 billion by 2033, capturing 68.13% of the market share. Conversely, non-infectious diseases, while currently smaller at USD 29.99 billion in 2023, are forecasted to grow significantly to USD 66.29 billion, highlighting the emerging focus on preventing chronic illnesses through vaccination.
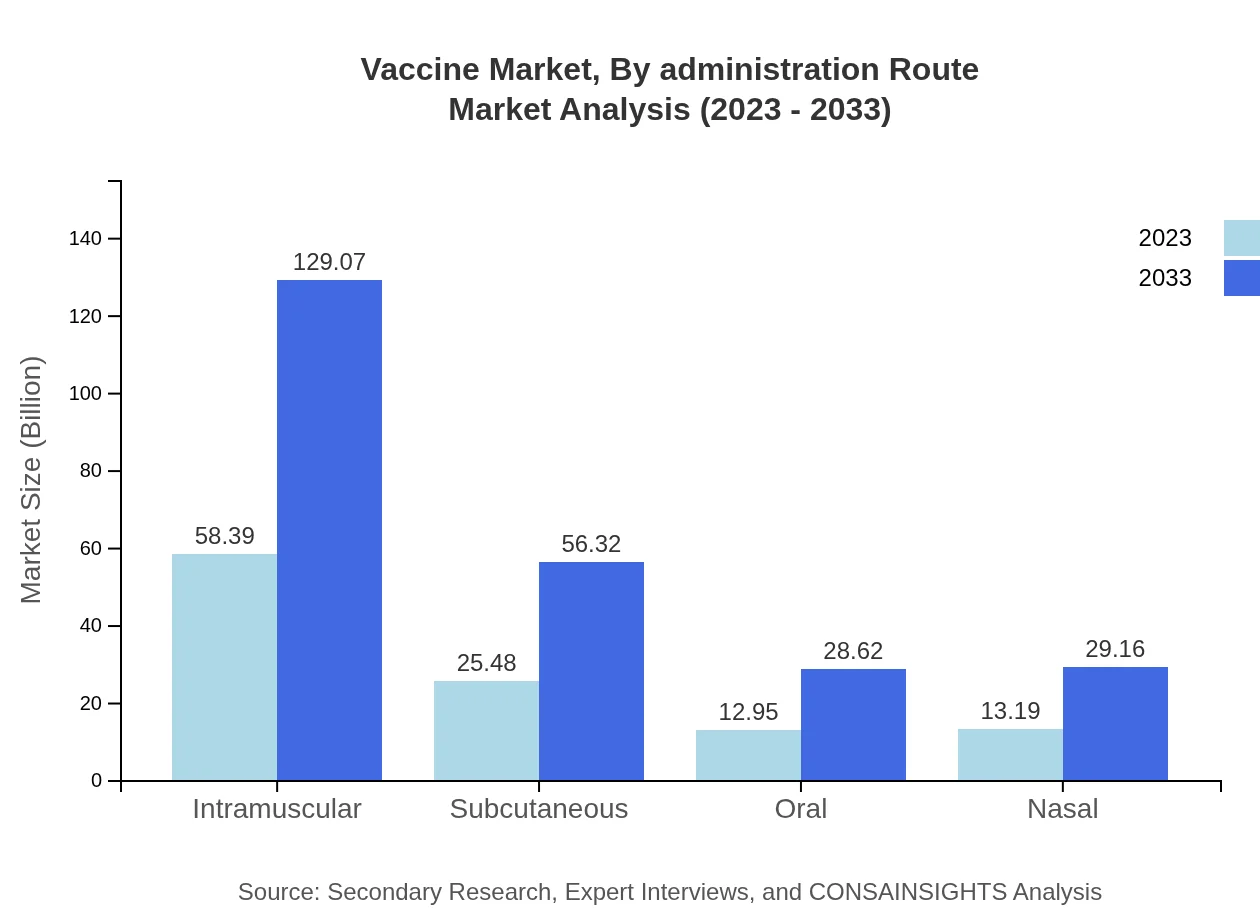
Vaccine Market Analysis By Administration Route
The vaccine administration route analysis reveals intramuscular injections commanding a significant share with USD 58.39 billion in 2023, likely reaching USD 129.07 billion by 2033. Subcutaneous and oral administration routes are also critical segments, reflecting varied preferences and delivery methods for vaccine administration.
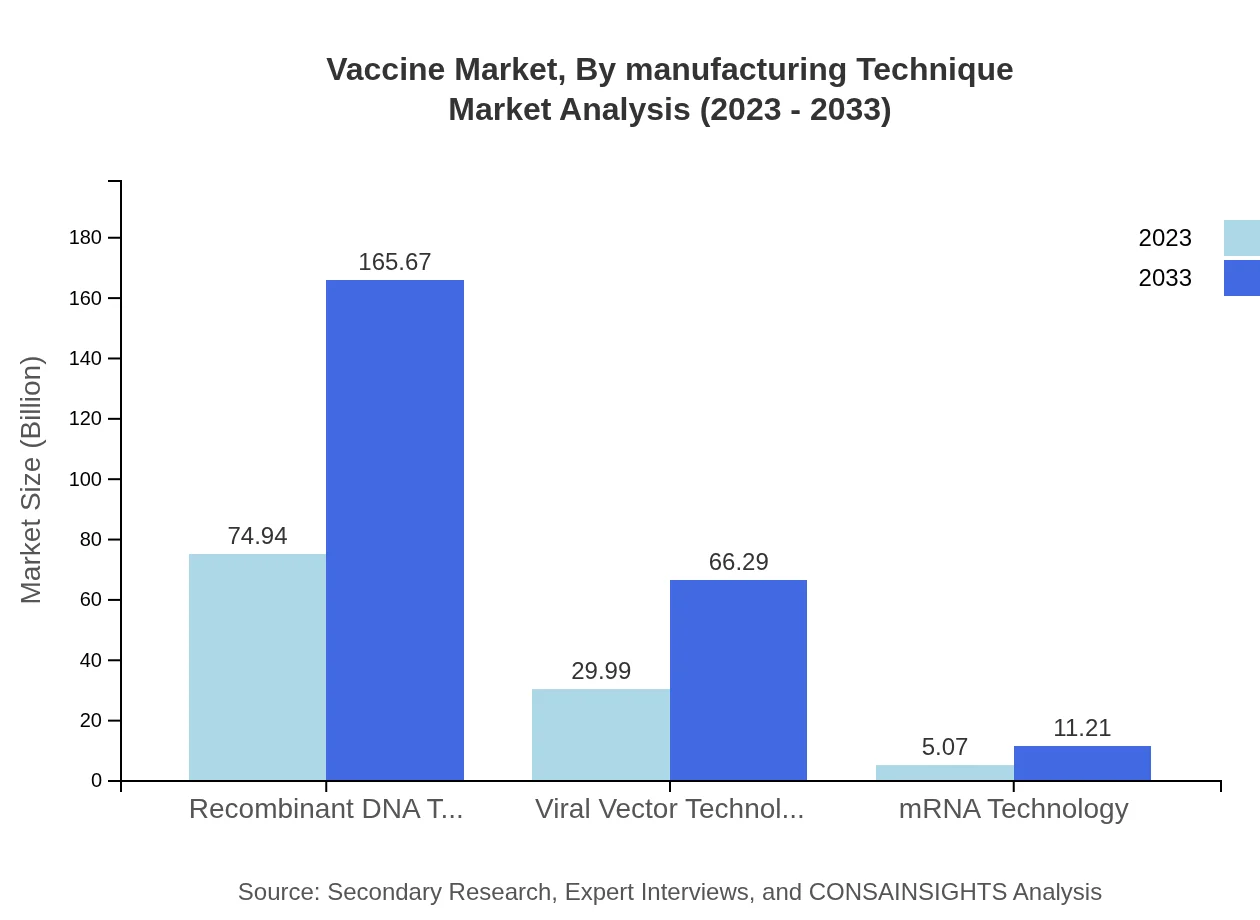
Vaccine Market Analysis By Manufacturing Technique
Advancements in manufacturing techniques have led to noteworthy segments in the vaccine market. The recombinant DNA technology segment, as of 2023, is valued at USD 74.94 billion and is expected to double by 2033. Viral vector technology is also seeing significant growth, increasing from USD 29.99 billion to USD 66.29 billion over the same period, emphasizing the innovation driving this industry forward.
Vaccine Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Vaccine Industry
Pfizer :
Pfizer is a leading biopharmaceutical company engaged in the development and manufacturing of a broad range of vaccines, including its widely-known COVID-19 vaccine. They invest heavily in R&D to sustain their market leadership and innovate for future health challenges.Sanofi:
Sanofi, a global healthcare leader, has a strong foothold in the vaccine sector, particularly in pediatric vaccines. Their commitment to public health and continuous innovation plays a crucial role in maintaining their market position.Merck & Co.:
Merck & Co. is recognized for its comprehensive portfolio of vaccines and commitment to infectious disease prevention. They focus on innovative technologies to enhance vaccine efficacy and broaden their market presence.Johnson & Johnson:
Johnson & Johnson is known for its terrestrial vaccine production, including the development of vaccines targeting viral diseases. Their diversified healthcare strategies facilitate their strong position in the global vaccine market.AstraZeneca:
AstraZeneca has emerged as a vital contributor to the global vaccination effort, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with its vaccine becoming a leading option in many countries.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of the vaccine industry?
The global vaccine market is projected to reach approximately $110 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0% from its current value.
What are the key market players or companies in the vaccine industry?
Key players in the vaccine industry include significant pharmaceutical companies that focus on immunization products, biologics, and vaccine development, contributing substantially to market growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the vaccine industry?
Growth drivers include increasing vaccination rates, rising awareness of infectious diseases, and advancements in vaccine technology, catering to a global demand for effective immunization.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the vaccine market?
North America leads as the fastest-growing region, with its market expected to rise from $36.86 billion in 2023 to $81.48 billion by 2033, owing to strong healthcare infrastructure.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the vaccine industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market research reports, adapting to specific needs and queries related to the vaccine industry, ensuring relevant insights.
What deliverables can I expect from this vaccine market research project?
Deliverables typically include comprehensive reports, market forecasts, segment analyses, and data visualizations that showcase growth trends and competitive landscapes.
What are the market trends of the vaccine industry?
Current trends include the rise of mRNA vaccines, increased demand for immunization in emerging economies, and a focus on personalized vaccine development for various diseases.