Vegetable Farming Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: vegetable-farming
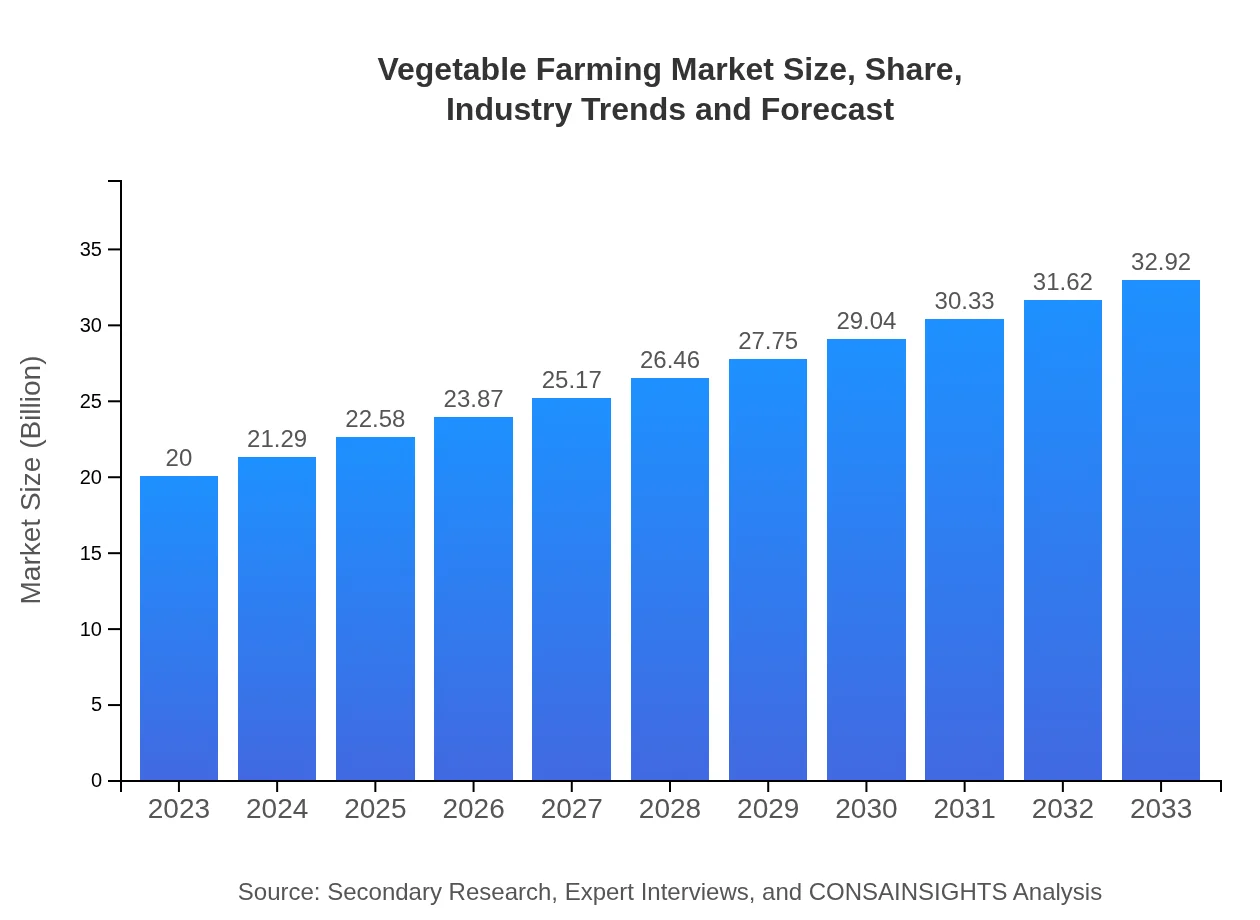
Vegetable Farming Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report delves into the global Vegetable Farming market, exploring insights and data on market trends, size, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It highlights the innovations, segmentation, regional analysis, and key players shaping the industry landscape.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $20.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $32.92 Billion |
| Top Companies | Dole Food Company, Fresh Del Monte Produce, Bayer AG, Ceres Global Ag Corp. |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Vegetable Farming Market Overview
Customize Vegetable Farming Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Vegetable Farming market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Vegetable Farming's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Vegetable Farming
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Vegetable Farming market in 2023?
Vegetable Farming Industry Analysis
Vegetable Farming Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Vegetable Farming Market Report:
In Europe, the market is expected to increase from $5.24 billion in 2023 to $8.62 billion by 2033. The European market's focus on sustainable agricultural practices, coupled with a strong demand for organic vegetables, is significantly driving market trends. EU regulations and consumer preferences are pushing for more sustainable vegetable farming practices.Asia Pacific Vegetable Farming Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Vegetable Farming market is projected to grow from $3.99 billion in 2023 to $6.56 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a vast agricultural base, with countries like China and India being key players in vegetable production due to favorable climatic conditions and extensive arable land. Additionally, increasing urbanization and dietary transitions towards more vegetable intake are propelling market growth.North America Vegetable Farming Market Report:
North America's Vegetable Farming market is forecasted to surge from $7.38 billion in 2023 to $12.14 billion by 2033. The United States is the largest contributor due to advanced farming technologies and a strong consumer focus on organic produce. Market growth is further enhanced by the increasing preference for locally sourced vegetables.South America Vegetable Farming Market Report:
The South American market is expected to expand from $1.13 billion in 2023 to $1.87 billion by 2033, led by Brazil and Argentina. Home to diverse vegetable crops, the region's market growth is anticipated due to rising export opportunities and a growing domestic demand for fresh produce, augmented by supportive agricultural policies.Middle East & Africa Vegetable Farming Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is projected to grow from $2.26 billion in 2023 to $3.73 billion by 2033. Rising investments in agro-tech and climate-adaptive agricultural solutions are vital for growth in this region, where vegetable production is often challenged by arid climates. Enhanced irrigation systems and innovative farming models are crucial for improving yield.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
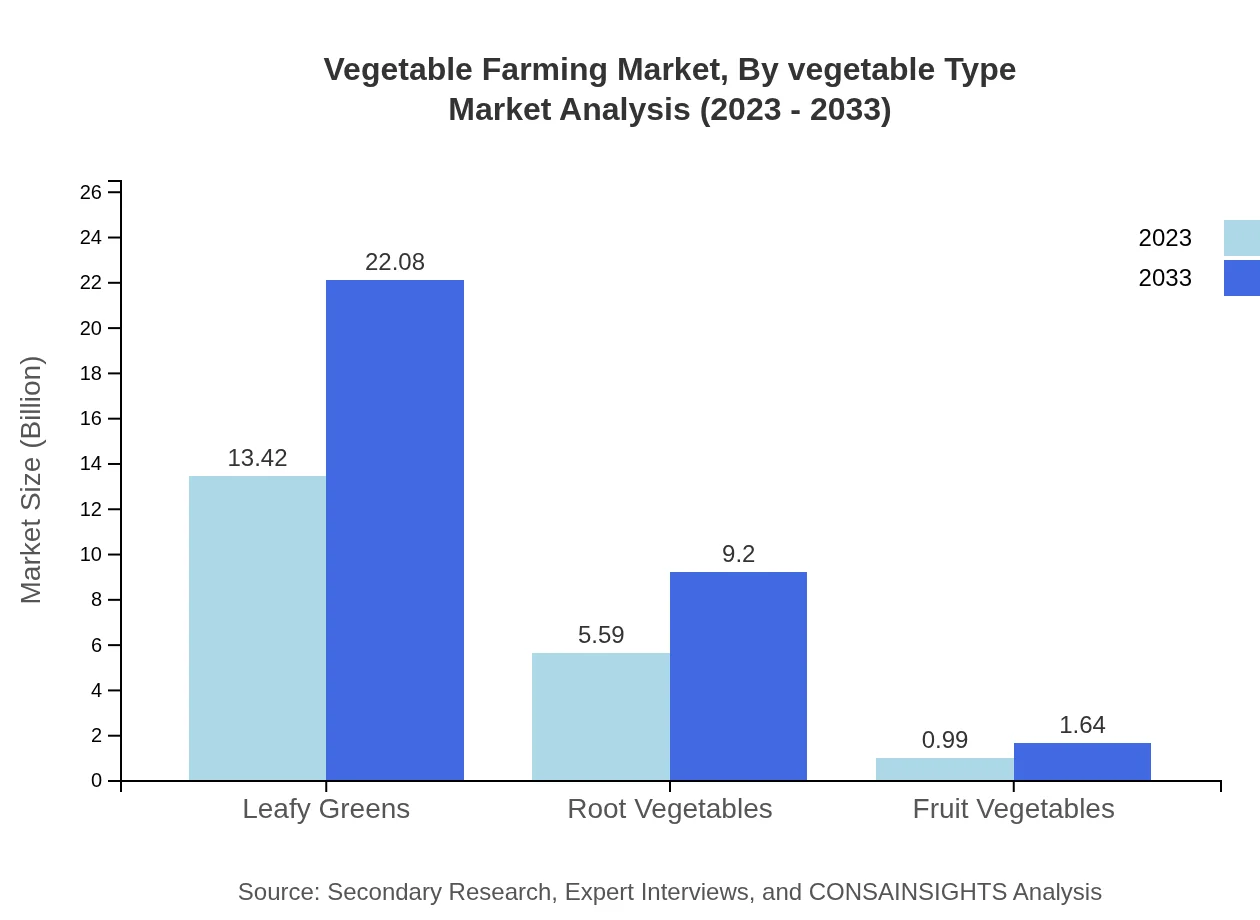
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis By Vegetable Type
The Vegetable Farming market is primarily segmented by vegetable type which includes leafy greens, root vegetables, and fruit vegetables. Leafy greens exhibit strong demand due to trends in health and diet-conscious consumers, leading the segment with a market value expected to grow significantly from $13.42 billion in 2023 to $22.08 billion by 2033. Root vegetables follow closely, anticipated to increase from $5.59 billion to $9.20 billion due to their persistent market presence in nutrition. Fruit vegetables like tomatoes and peppers are also witnessing growth driven by culinary uses.
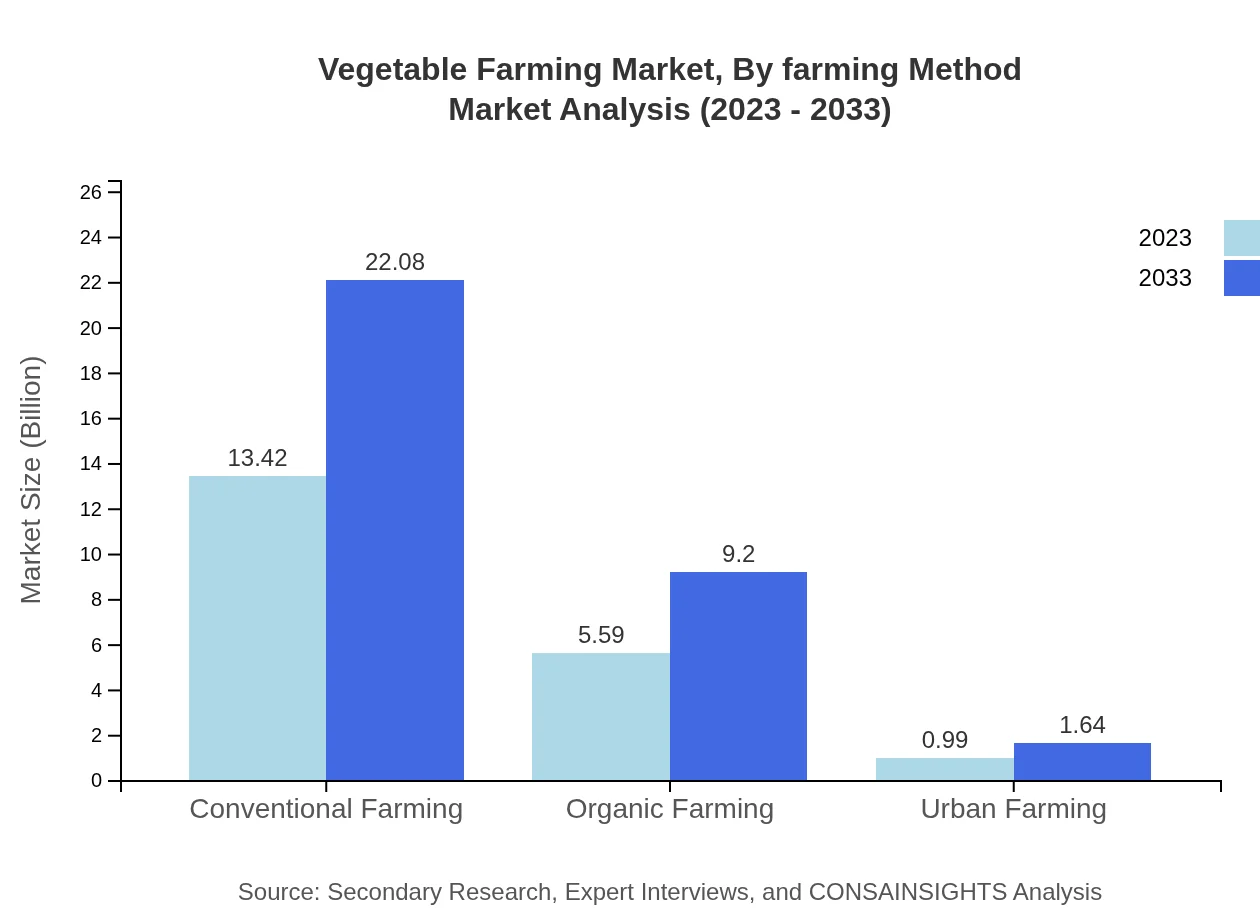
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis By Farming Method
The segment by farming method reveals a transition towards organic practices. In 2023, conventional farming holds significant market share valued at $13.42 billion with stable growth towards $22.08 billion by 2033. However, organic farming is gaining traction, with a current market size of $5.59 billion expected to rise to $9.20 billion, driven by changing consumer preferences towards sustainably sourced vegetables. Urban farming is also emerging as a noteworthy method, growing in both size and interest, predicted to grow from $0.99 billion to $1.64 billion.
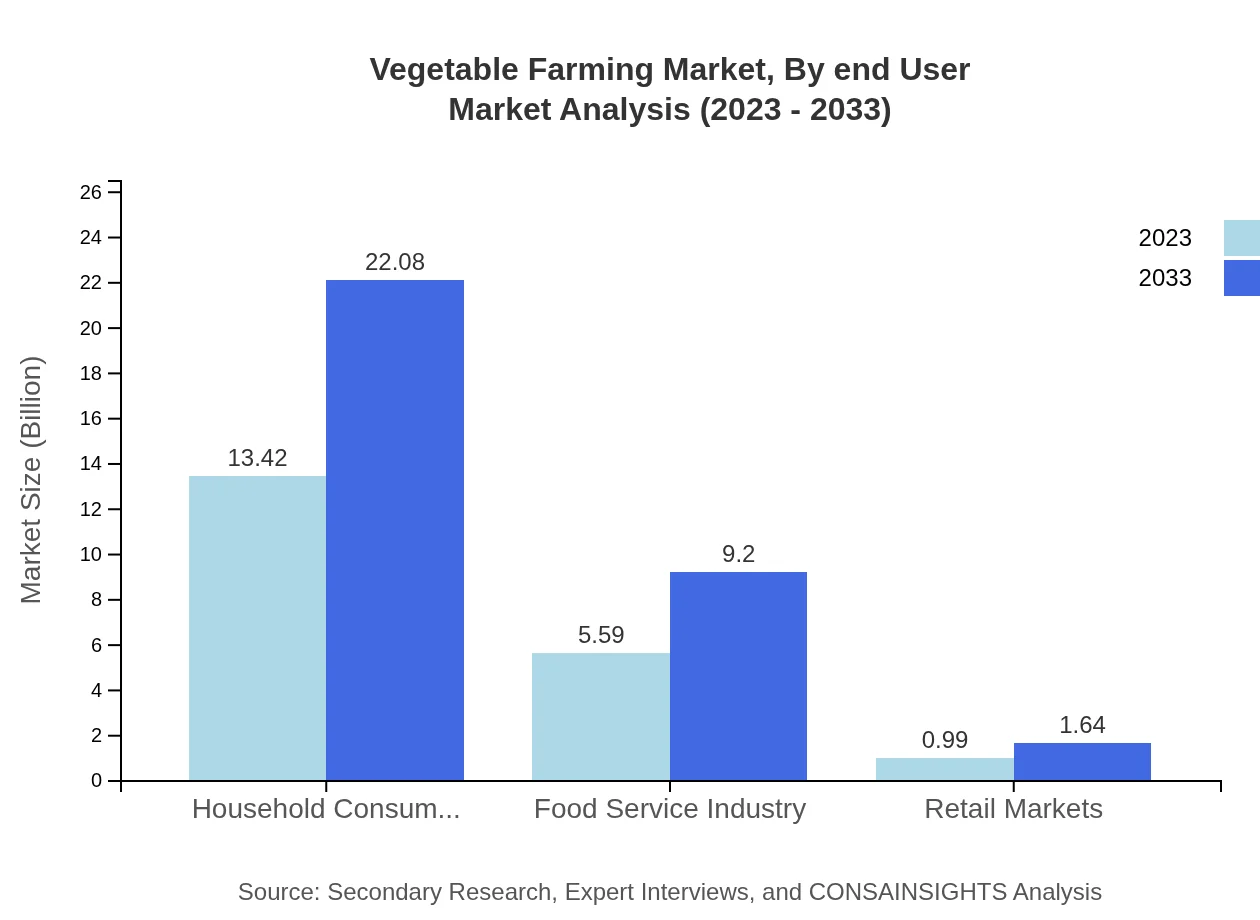
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis By End User
The Vegetable Farming market by end-user segments shows household consumers leading the market, with anticipated growth from $13.42 billion in 2023 to $22.08 billion by 2033, capturing over 67% market share. The food service industry, closely following, is projected to expand from $5.59 billion to $9.20 billion as restaurants increasingly source fresh, local produce. Retail markets contribute significantly but remain less than 5%, growing from $0.99 billion to $1.64 billion in the same period.
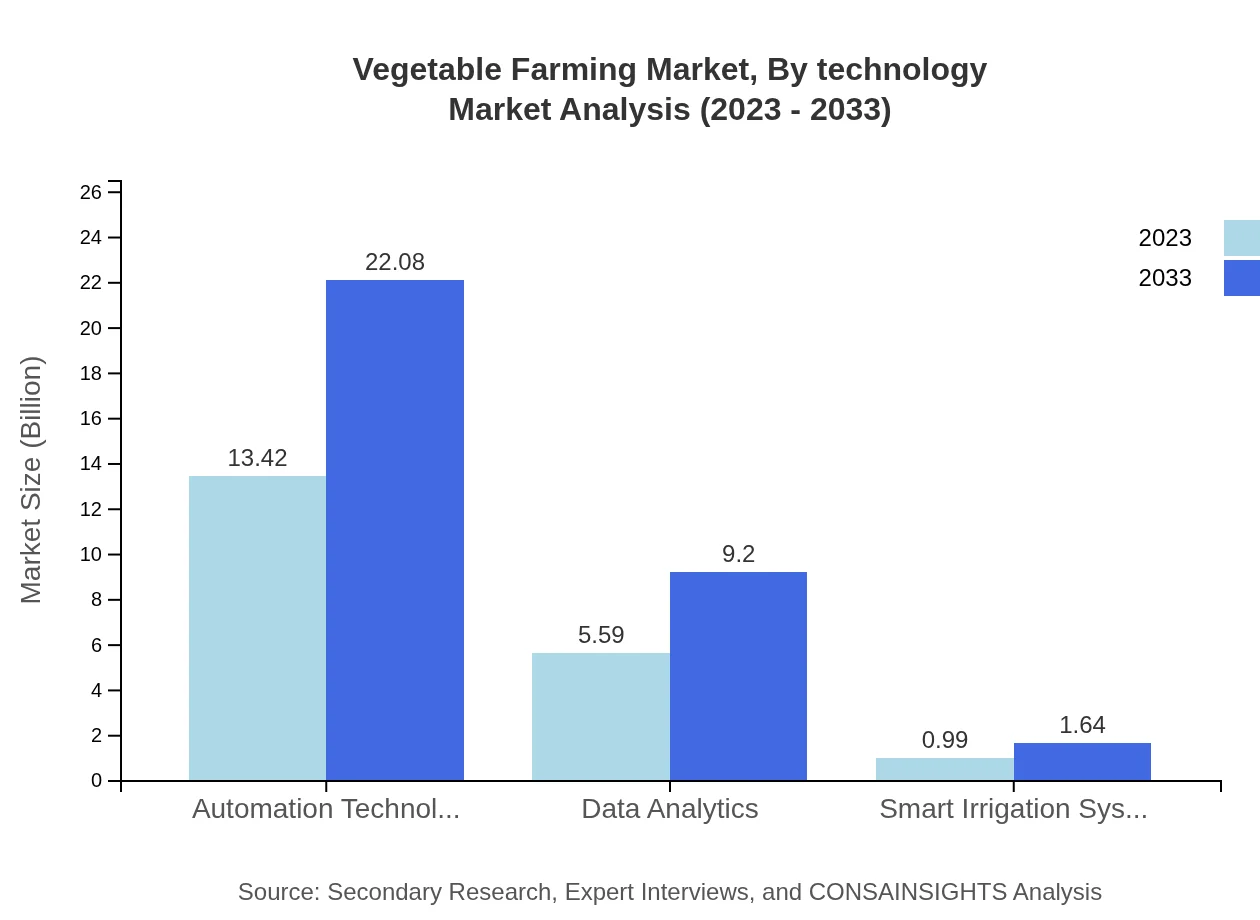
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis By Technology
Technology's role in enhancing operational efficiencies in vegetable farming is profound. Automation technology segment is valued at $13.42 billion with a dominant share of 67% projected growth to $22.08 billion by 2033. Strategies employing data analytics show promising growth from $5.59 billion to $9.20 billion, reflecting the increasing reliance on data-driven decisions in farming practices. Smart irrigation systems are also vital, projected to increase from $0.99 billion to $1.64 billion, addressing water-related challenges in arid areas.
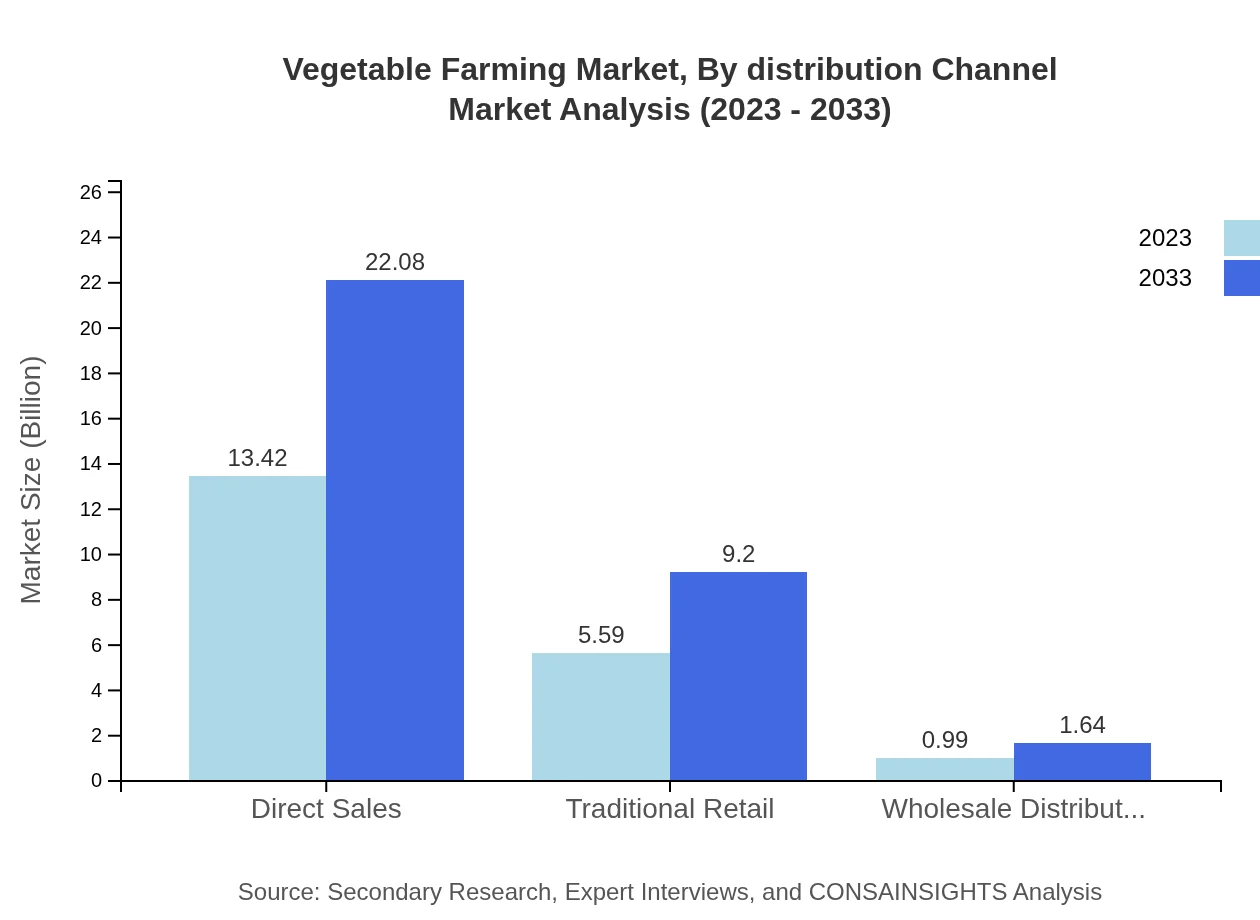
Vegetable Farming Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
By distribution channel, the Vegetable Farming market is primarily driven by direct sales, valued at $13.42 billion in 2023 with a projected increase to $22.08 billion by 2033, associated with farmers' market trends focusing on fresh produce. Traditional retail holds a solid share, from $5.59 billion to $9.20 billion, while wholesale distributors are projected for modest growth increasing from $0.99 billion to $1.64 billion due to the need for bulk supply across various channels.
Vegetable Farming Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Vegetable Farming Industry
Dole Food Company:
Dole is a leading producer and marketer of fresh fruits and vegetables. They focus on sustainability and incorporate advanced technologies in agriculture to enhance yield.Fresh Del Monte Produce:
Fresh Del Monte is a global supplier of fresh and packaged produce, operating with significant investments in sustainable agriculture practices and product innovation.Bayer AG:
Bayer operates in the agricultural domain dealing with seeds, crop protection, and biotechnology to improve agricultural efficiencies, including vegetable farming.Ceres Global Ag Corp.:
Ceres engages in the sourcing and marketing of agricultural products, emphasizing logistics and supply chain efficiency for produce distribution.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of vegetable farming?
The vegetable farming market is currently valued at approximately $20 billion, with a projected CAGR of 5% from 2023 to 2033. This growth is indicative of increasing consumer demand and advancements in farming technologies.
What are the key market players or companies in the vegetable farming industry?
Key players in the vegetable farming industry include major agricultural companies and local farms engaged in innovative farming practices. These players leverage technology to optimize yields and meet the rising demand for fresh produce.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the vegetable farming industry?
Growth in the vegetable farming industry is driven by increasing population, rising health consciousness among consumers favoring vegetables, technological advancements in farming practices, and the expansion of organic and local food markets.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the vegetable farming?
The fastest-growing region in vegetable farming is predicted to be North America, with a market size of $12.14 billion projected by 2033, reflecting a significant increase from $7.38 billion in 2023 due to high demand and technological advancements.
Does ConsainInsights provide customized market report data for the vegetable farming industry?
Yes, ConsainInsights offers tailored market report data for the vegetable farming industry, ensuring that clients receive insights and analyses that cater specifically to their needs and strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this vegetable farming market research project?
Deliverables from the vegetable farming market research project typically include comprehensive market analysis reports, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and insights on emerging trends and consumer preferences.
What are the market trends of vegetable farming?
Current market trends in vegetable farming include a shift towards organic produce, adoption of smart farming technologies, increased direct-to-consumer sales models, and a growing emphasis on sustainability within agricultural practices.