Vegetable Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: vegetable-seed
Vegetable Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Vegetable Seed market from 2023 to 2033, including market size, CAGR, trends, regional insights, and key players. It aims to offer valuable insights for stakeholders and investors in the agricultural sector.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
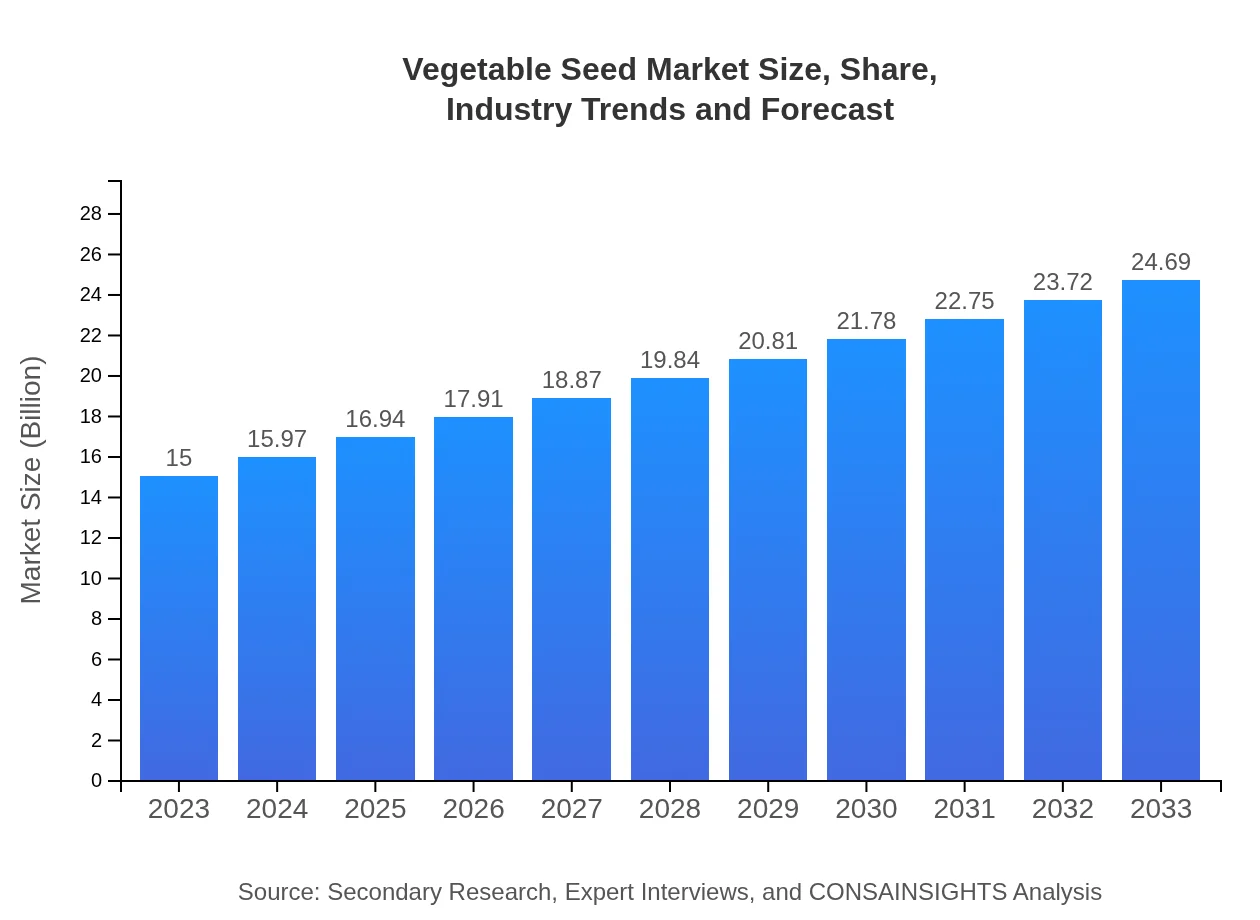
| 2023 Market Size | $15.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5% |
| 2033 Market Size | $24.69 Billion |
| Top Companies | Monsanto Company, BASF SE, Syngenta AG, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Vegetable Seed Market Overview
Customize Vegetable Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Vegetable Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Vegetable Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Vegetable Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Vegetable Seed market in 2023?
Vegetable Seed Industry Analysis
Vegetable Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Vegetable Seed Market Report:
Europe’s market for Vegetable Seeds is $4.99 billion in 2023, expected to expand to $8.21 billion by 2033. Stringent regulations on agricultural practices and a strong emphasis on sustainability influence the growth trajectory, with consumers increasingly favoring organic and non-GMO options.Asia Pacific Vegetable Seed Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia-Pacific region holds a market value of $2.41 billion, projected to reach $3.96 billion by 2033. The region benefits from a large agricultural base, increased consumption of vegetables, and a trend towards modern farming practices, including precision agriculture, driving the demand for high-quality seeds.North America Vegetable Seed Market Report:
In 2023, North America’s Vegetable Seed market is valued at $5.40 billion and is forecasted to reach $8.89 billion by 2033. This growth is led by advancements in seed technology, high adoption rates of hybrid seeds, and a significant market focus on organic produce.South America Vegetable Seed Market Report:
The South American Vegetable Seed market is valued at $1.19 billion in 2023, with expectations of growth to $1.96 billion by 2033. The growth is driven by rising agricultural exports, focused efforts towards sustainable agriculture, and a growing population demanding fresh produce.Middle East & Africa Vegetable Seed Market Report:
Market analysis in the Middle East and Africa shows a value of $1.01 billion in 2023, growing to $1.66 billion by 2033. Key factors include transformation in agricultural practices and increasing imports of high-quality seeds to boost local vegetable production.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis By Type
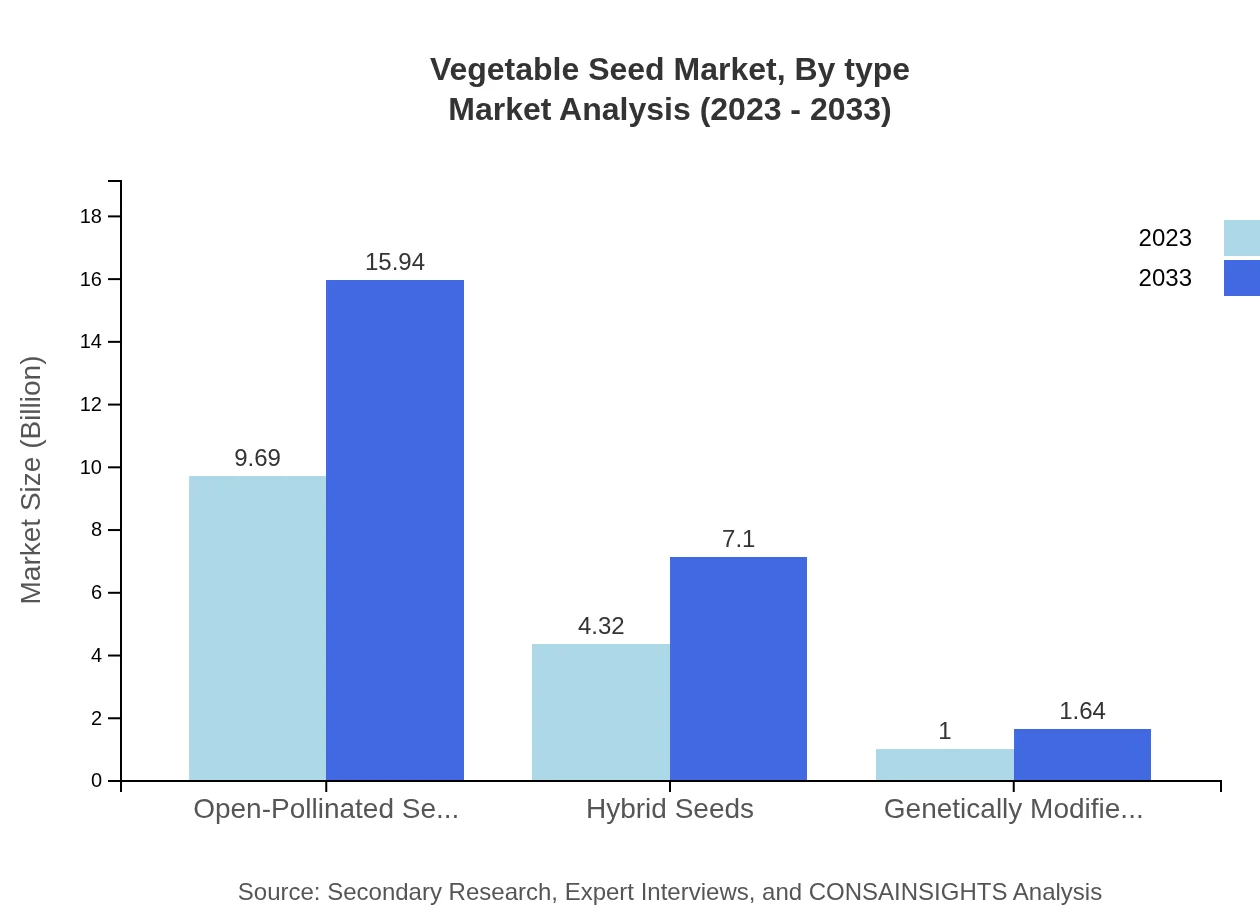
The Vegetable Seed market by type is categorized into Open-Pollinated Seeds, Hybrid Seeds, and Genetically Modified Seeds. Open-pollinated seeds dominate with a market size of $9.69 billion in 2023, growing to $15.94 billion by 2033, maintaining a 64.59% market share. Hybrid seeds, valued at $4.32 billion in 2023, are projected to grow to $7.10 billion, holding 28.77% market share, driven by commercial farmers seeking high yields. Genetically modified seeds represent the smallest segment but are expected to grow from $1.00 billion in 2023 to $1.64 billion by 2033.
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis By Crop Type
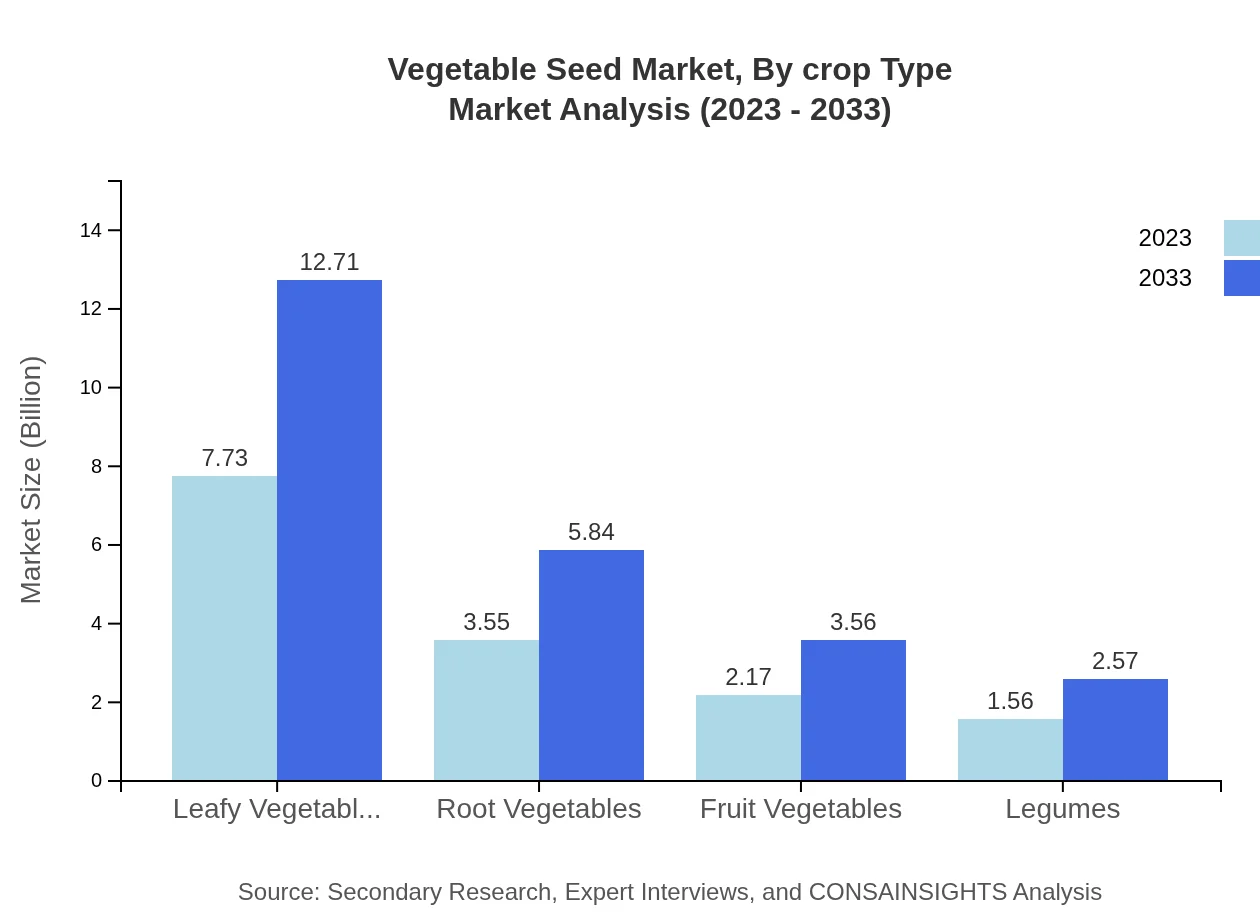
The market segmentation by crop type includes Leafy Vegetables, Root Vegetables, Fruit Vegetables, and Legumes. Leafy vegetables are the largest segment, valued at $7.73 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $12.71 billion by 2033, capturing a 51.5% market share. Root vegetables account for $3.55 billion with projections of $5.84 billion by 2033 (23.65% share). Fruit vegetables and legumes are valued at $2.17 billion and $1.56 billion, respectively, showing steady growth aligned with rising consumer health consciousness.
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
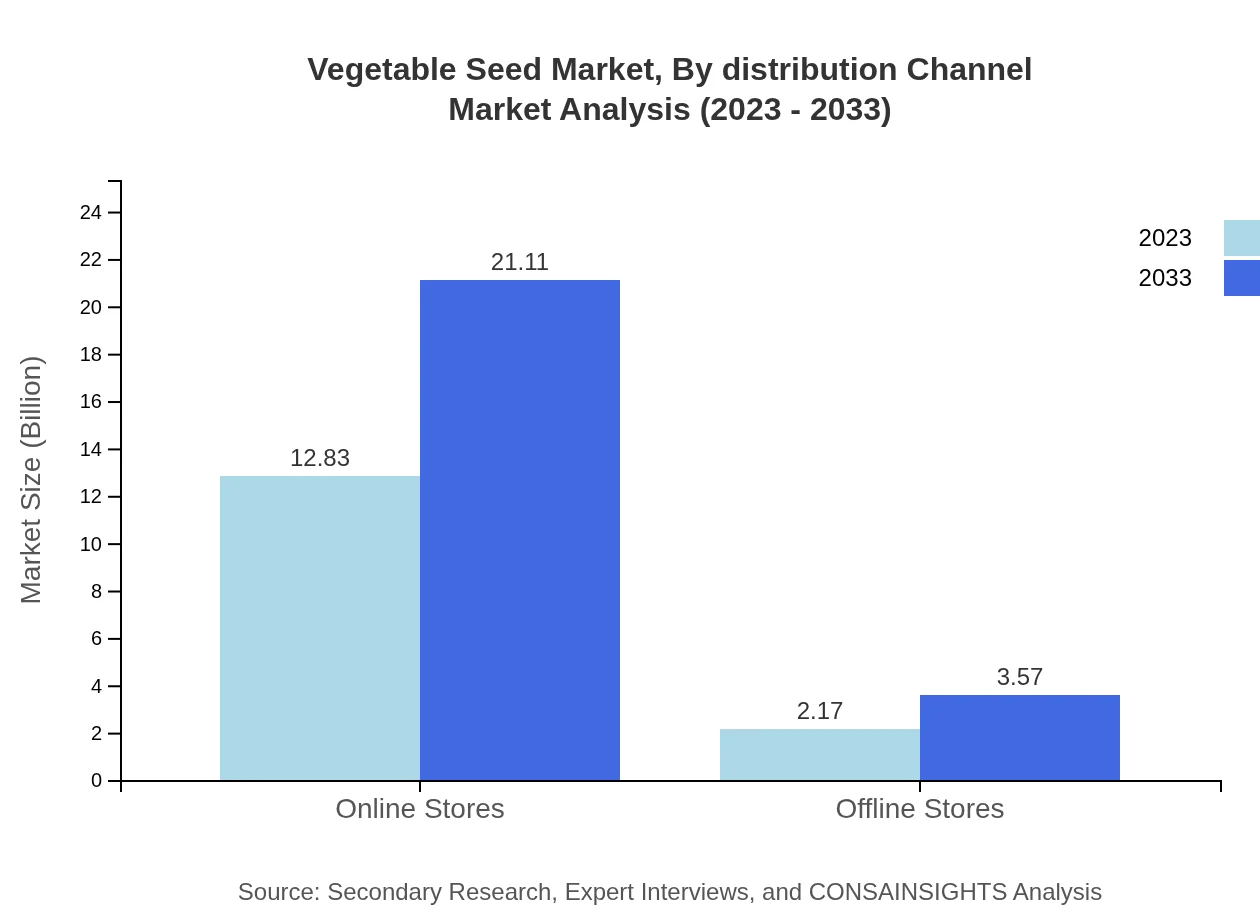
The Vegetable Seed market distribution channels are divided into Online and Offline sales. Online stores currently command a market size of $12.83 billion, projected to reach $21.11 billion by 2033, capturing 85.52% of the market share due to the ease of access and growing e-commerce trends. In contrast, offline stores remain at $2.17 billion in 2023 and are projected to grow to $3.57 billion, holding 14.48%, as traditional farming practices continue but at a slower pace.
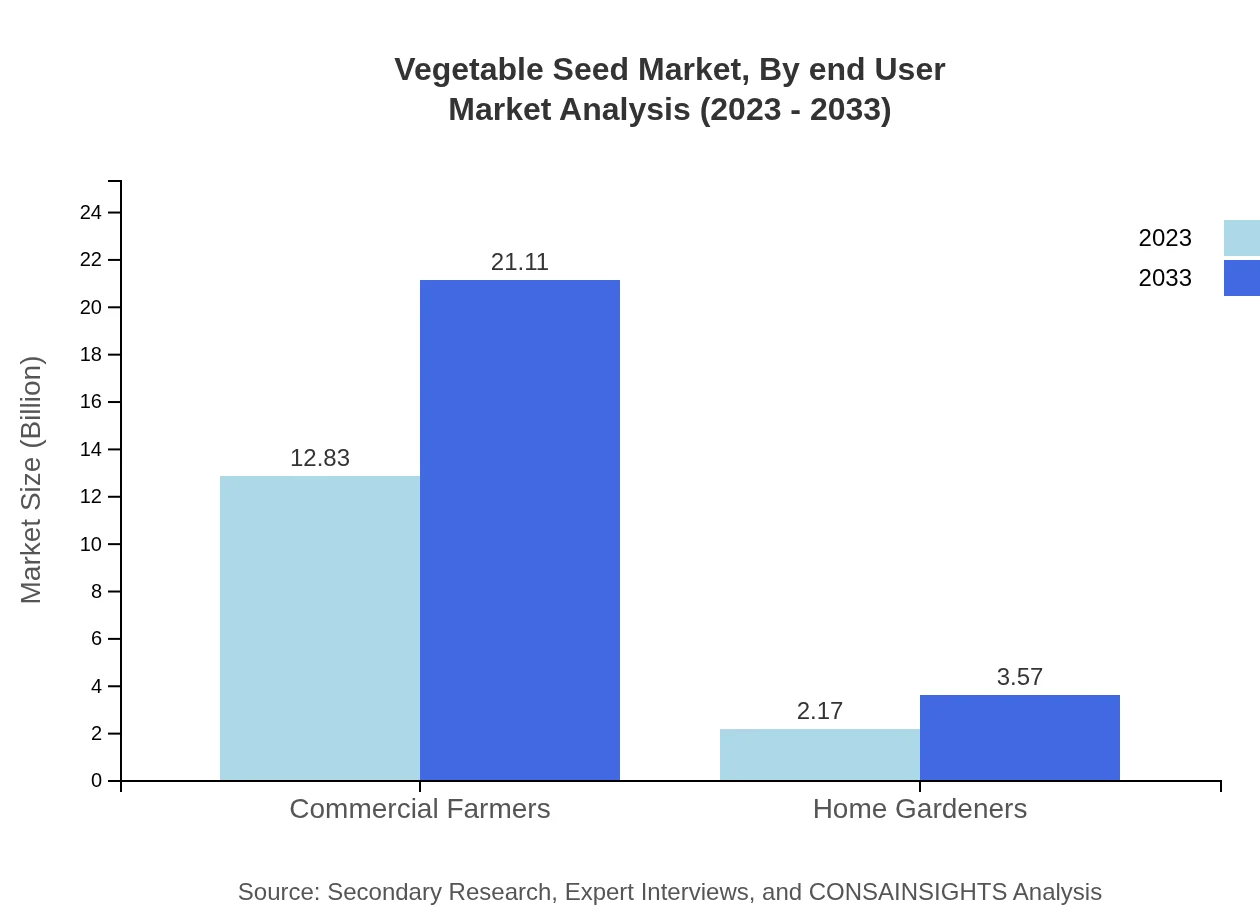
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis By End User
The Vegetable Seed market by end-user is primarily divided into Commercial Farmers and Home Gardeners. Commercial farmers dominate the segment with a size of $12.83 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $21.11 billion by 2033, holding an 85.52% market share driven by the need for high-yield crops. Home gardeners, while smaller in comparison, have a valued market of $2.17 billion in 2023, projected to reach $3.57 billion, reflecting a growing interest in home gardening initiatives.
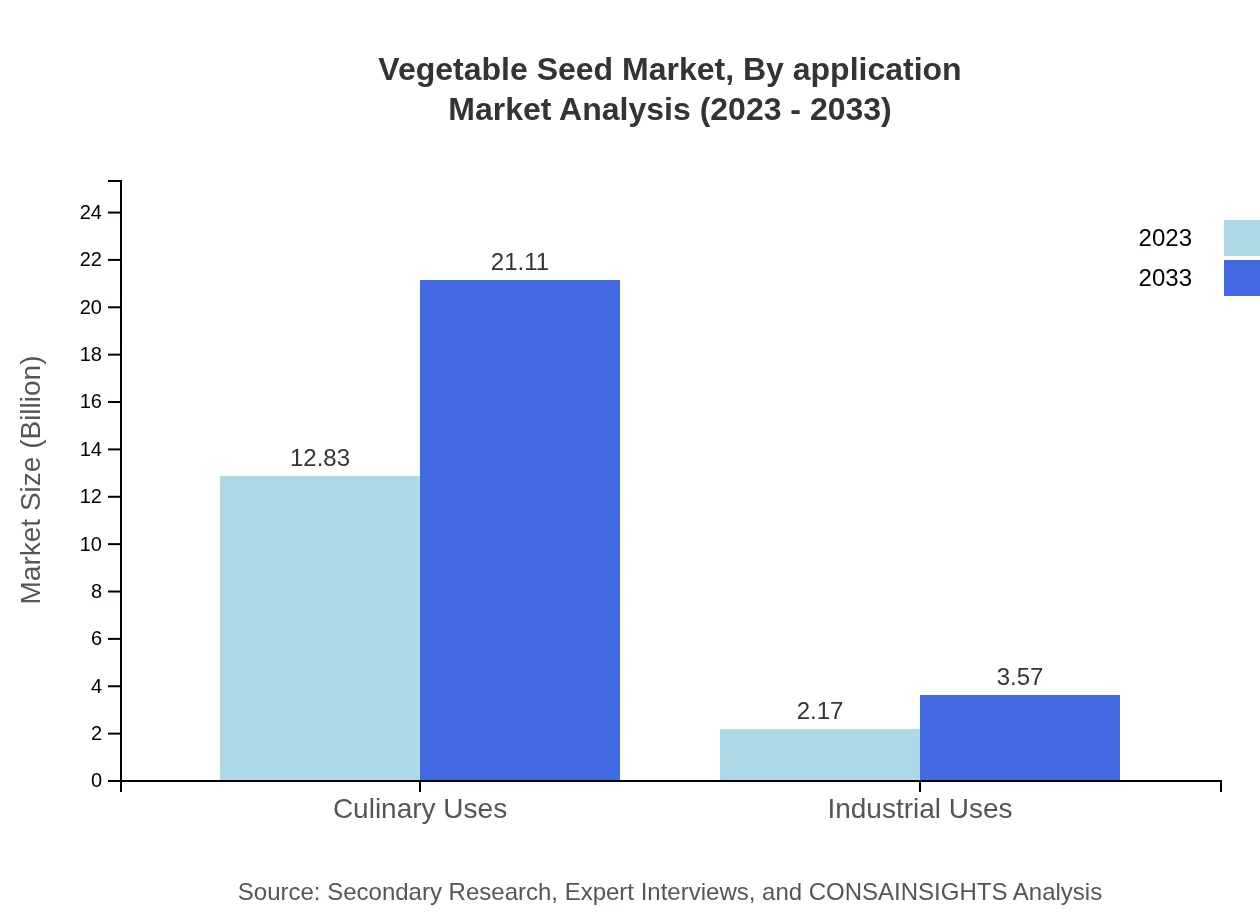
Vegetable Seed Market Analysis By Application
The Vegetable Seeds market is segmented by application into Culinary and Industrial Uses. The culinary uses segment is projected at $12.83 billion in 2023, growing to $21.11 billion by 2033 (85.52% share), reflecting the essential nature of fresh vegetables in daily diets. Industrial uses hold a value of $2.17 billion, expanding to $3.57 billion, representing 14.48% share as industries increasingly use vegetables in food processing and packaging.
Vegetable Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Vegetable Seed Industry
Monsanto Company:
A leading global player in agricultural biotechnology, Monsanto focuses on developing genetically modified seeds and sustainable farming solutions.BASF SE:
BASF is renowned for its innovation in agricultural solutions, including hybrid seed varieties and crop protection products.Syngenta AG:
Syngenta specializes in crop protection products and vegetable seeds, striving for sustainability and advanced agricultural solutions.DuPont de Nemours, Inc.:
DuPont is a key player in plant genetics, providing advanced seed varieties and innovative crop management solutions.Corteva Agriscience:
Corteva offers a range of seed products and crop protection solutions, focusing on enhancing productivity and sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of vegetable Seed?
The global vegetable seed market is projected to reach approximately $15 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5% from 2023. This growth indicates a robust demand for seeds across various regions and segments.
What are the key market players or companies in this vegetable Seed industry?
Key players in the vegetable seed industry include major agribusiness companies and seed manufacturers. These companies are focused on innovation, product quality, and market expansion to maintain their competitive edges.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the vegetable Seed industry?
Growth in the vegetable seed industry is driven by increased demand for high-yield crops, advancements in seed technology, and shifting consumer preferences towards organic produce and sustainable farming practices.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the vegetable Seed?
In the vegetable seed market, Europe is the fastest-growing region, with projections showing an increase from $4.99 billion in 2023 to $8.21 billion by 2033, indicating strong market expansion.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the vegetable Seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the needs of clients within the vegetable-seed industry, focusing on specific segments, regions, and product types.
What deliverables can I expect from this vegetable Seed market research project?
Deliverables from a vegetable-seed market research project typically include comprehensive reports covering market size, trends, key players, forecasts, and in-depth analyses of regional and segment data.
What are the market trends of vegetable Seed?
Market trends in the vegetable seed industry include rising demand for hybrid and genetically modified seeds, growing interest in sustainability, and increasing online sales channels for seed distribution.