Vertical Farming Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: vertical-farming
Vertical Farming Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Vertical Farming market, covering market size, segmentation, competitive landscape, regional insights, and emerging trends from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
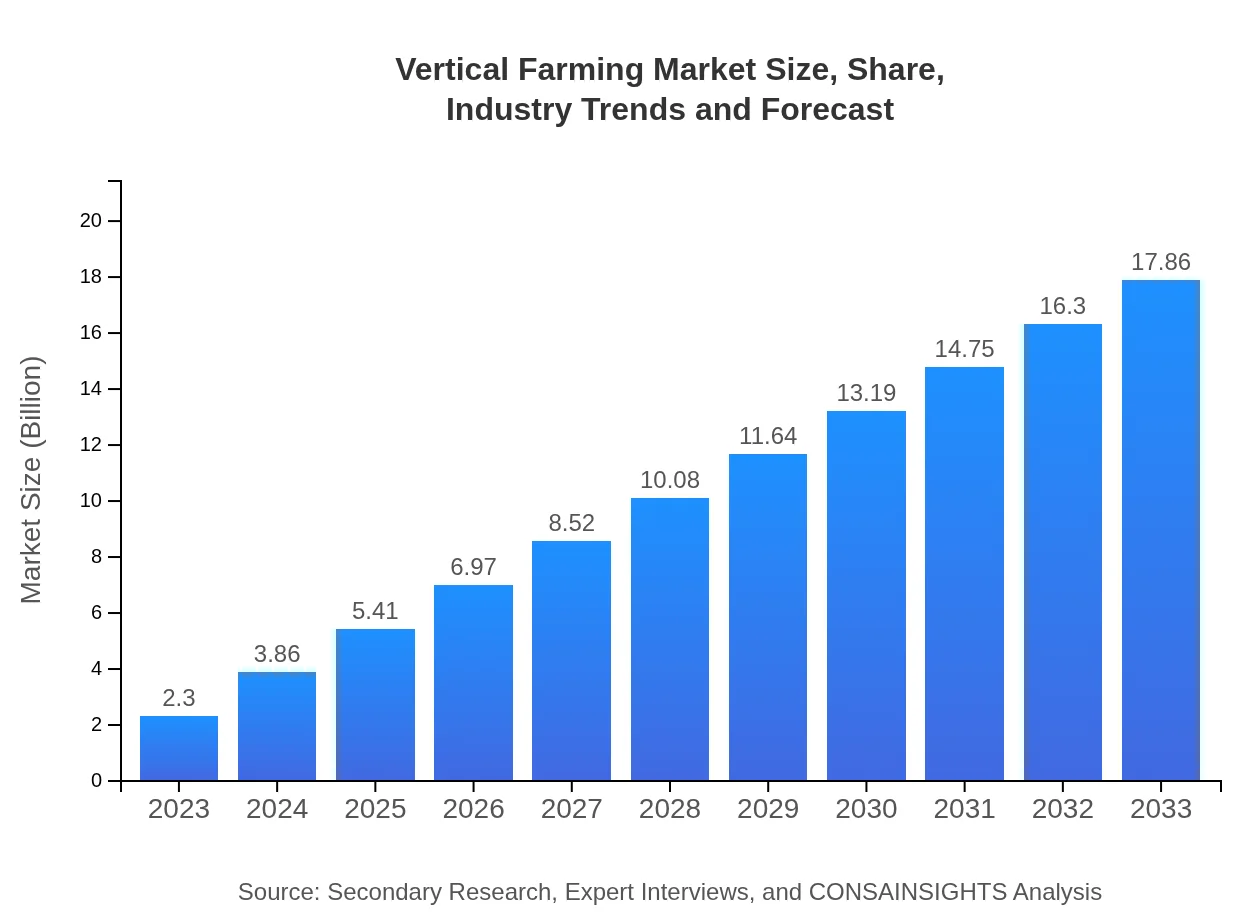
| 2023 Market Size | $2.30 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 21.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $17.86 Billion |
| Top Companies | AeroFarms, Plenty Unlimited, Vertical Harvest, Green Spirit Farms, Gotham Greens |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Vertical Farming Market Overview
Customize Vertical Farming Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Vertical Farming market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Vertical Farming's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Vertical Farming
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Vertical Farming market in 2023 and 2033?
Vertical Farming Industry Analysis
Vertical Farming Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vertical Farming Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Vertical Farming Market Report:
With a market value of USD 0.84 billion in 2023, Europe is anticipated to expand to USD 6.56 billion by 2033, supported by increasing consumer demand for local produce and sustainability initiatives across EU member states.Asia Pacific Vertical Farming Market Report:
In 2023, the Asia Pacific market is valued at USD 0.38 billion and is projected to reach USD 2.92 billion by 2033, driven by a rise in urbanization and population density. Countries like Japan and Singapore are leading in implementing vertical farming, focusing on technology and sustainability.North America Vertical Farming Market Report:
North America accounts for a market size of USD 0.75 billion in 2023, expected to reach USD 5.84 billion by 2033, fueled by the U.S.'s interest in sustainable practices and governmental support for agricultural technologies.South America Vertical Farming Market Report:
The South American market stands at USD 0.03 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow to USD 0.20 billion by 2033. Brazil is emerging as a hub for innovative agricultural practices, although lower investments and market adoption pose constraints.Middle East & Africa Vertical Farming Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa market is expected to grow from USD 0.30 billion in 2023 to USD 2.34 billion by 2033, as water scarcity urges nations to adopt efficient farming techniques. The UAE and Israel are leading the charge in this transformative agricultural shift.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
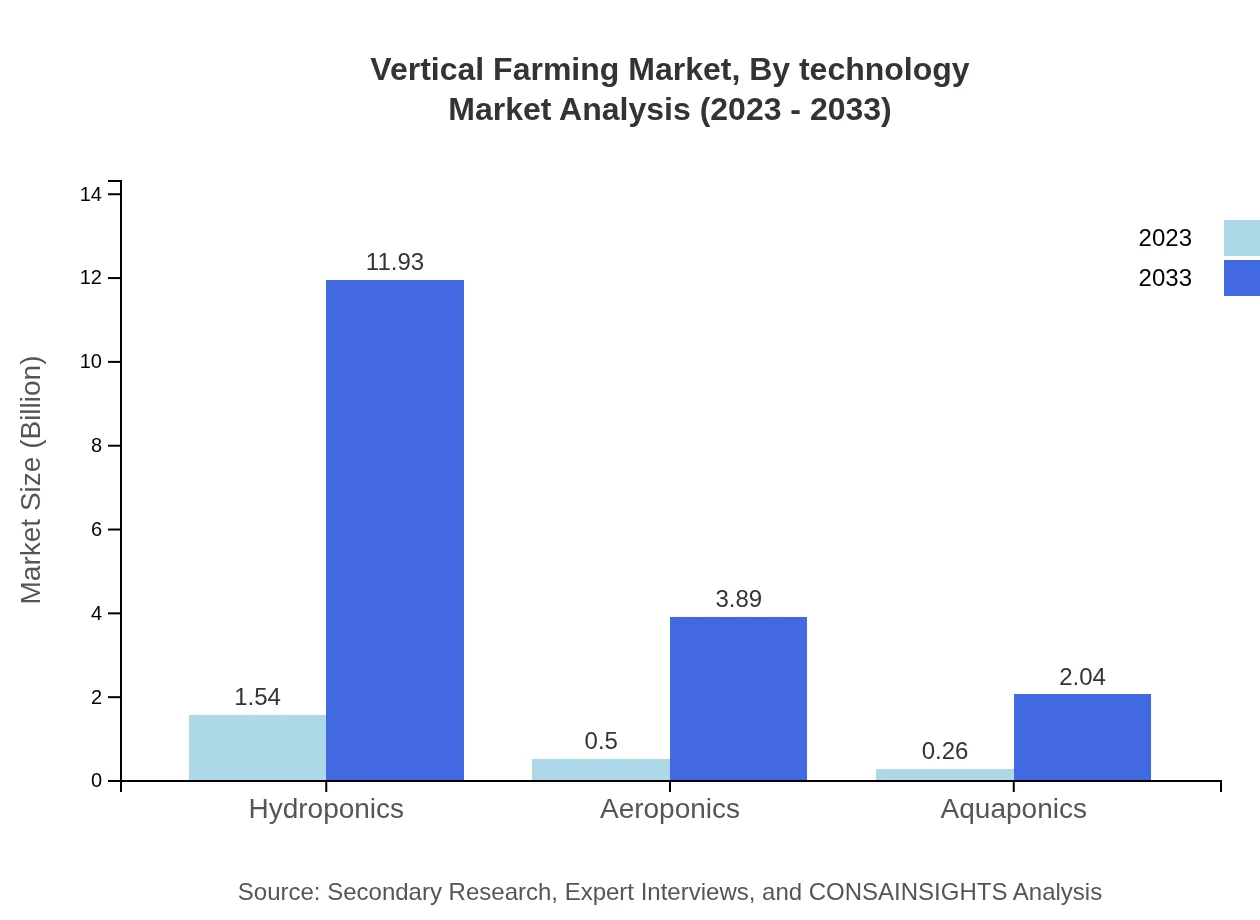
Vertical Farming Market Analysis By Technology
The Vertical Farming market is primarily divided into key technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. Hydroponics leads the market with a size of USD 1.54 billion in 2023 and is expected to rise to USD 11.93 billion by 2033. Aeroponics and aquaponics follow closely, with sizes of USD 0.50 billion and USD 0.26 billion in 2023, reaching USD 3.89 billion and USD 2.04 billion respectively by 2033.
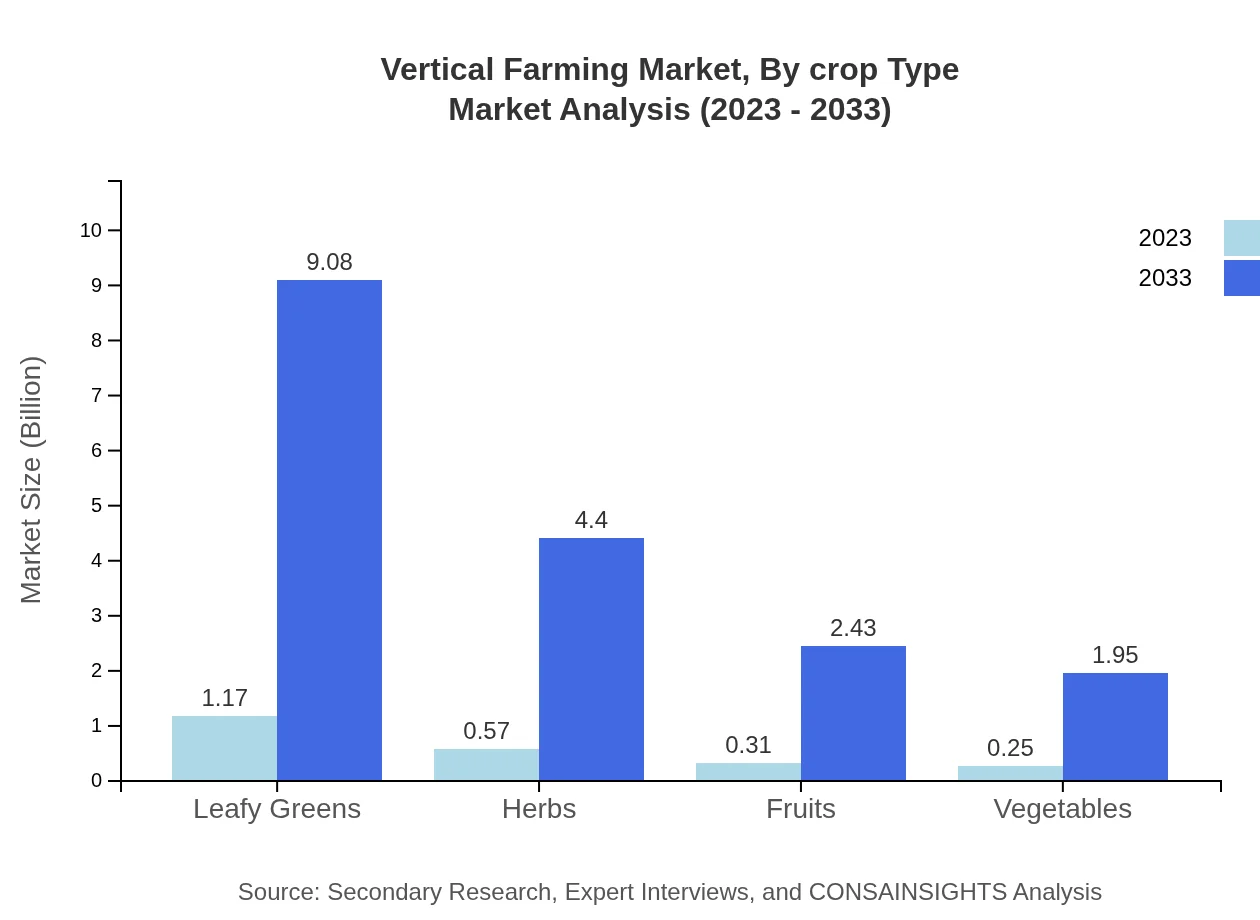
Vertical Farming Market Analysis By Crop Type
In crop types, leafy greens dominate with USD 1.17 billion in 2023 and forecasted to grow to USD 9.08 billion by 2033, holding a significant market share. Herbs, fruits, and vegetables follow, expected to grow at impressive rates, indicating the potential for diversified agricultural production within vertical farming.
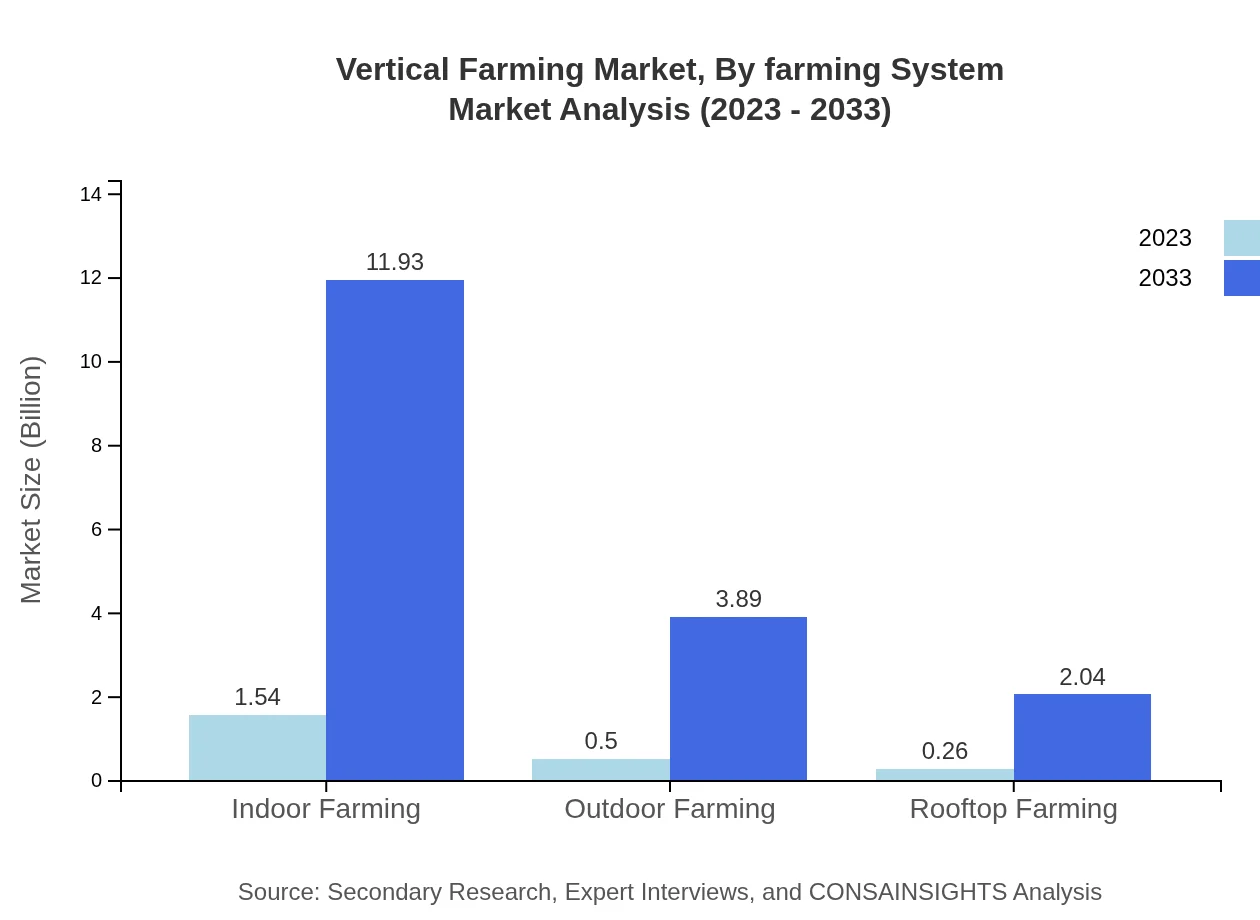
Vertical Farming Market Analysis By Farming System
The market is segmented into indoor and outdoor farming systems. Indoor farming dominates the segment with a size of USD 1.54 billion in 2023, forecasted to rise to USD 11.93 billion by 2033, reflecting increasing urban agriculture trends supported by technological integration.
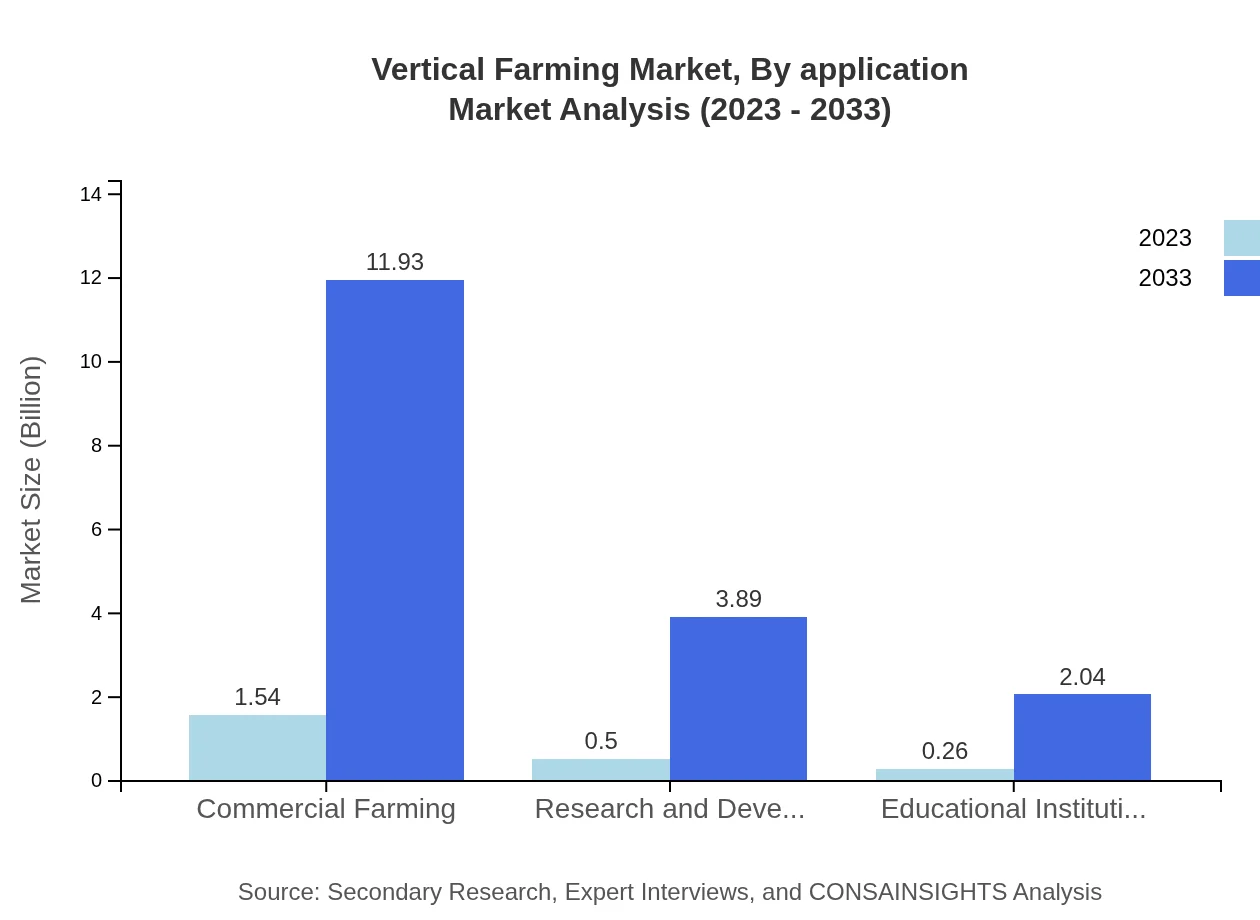
Vertical Farming Market Analysis By Application
Applications in commercial farming hold significant market share, valued at USD 1.54 billion in 2023 and projected to reach USD 11.93 billion by 2033. Educational institutions and R&D projects are also quintessential in pushing innovation and education in sustainable practices, with anticipated growth in their respective segments.
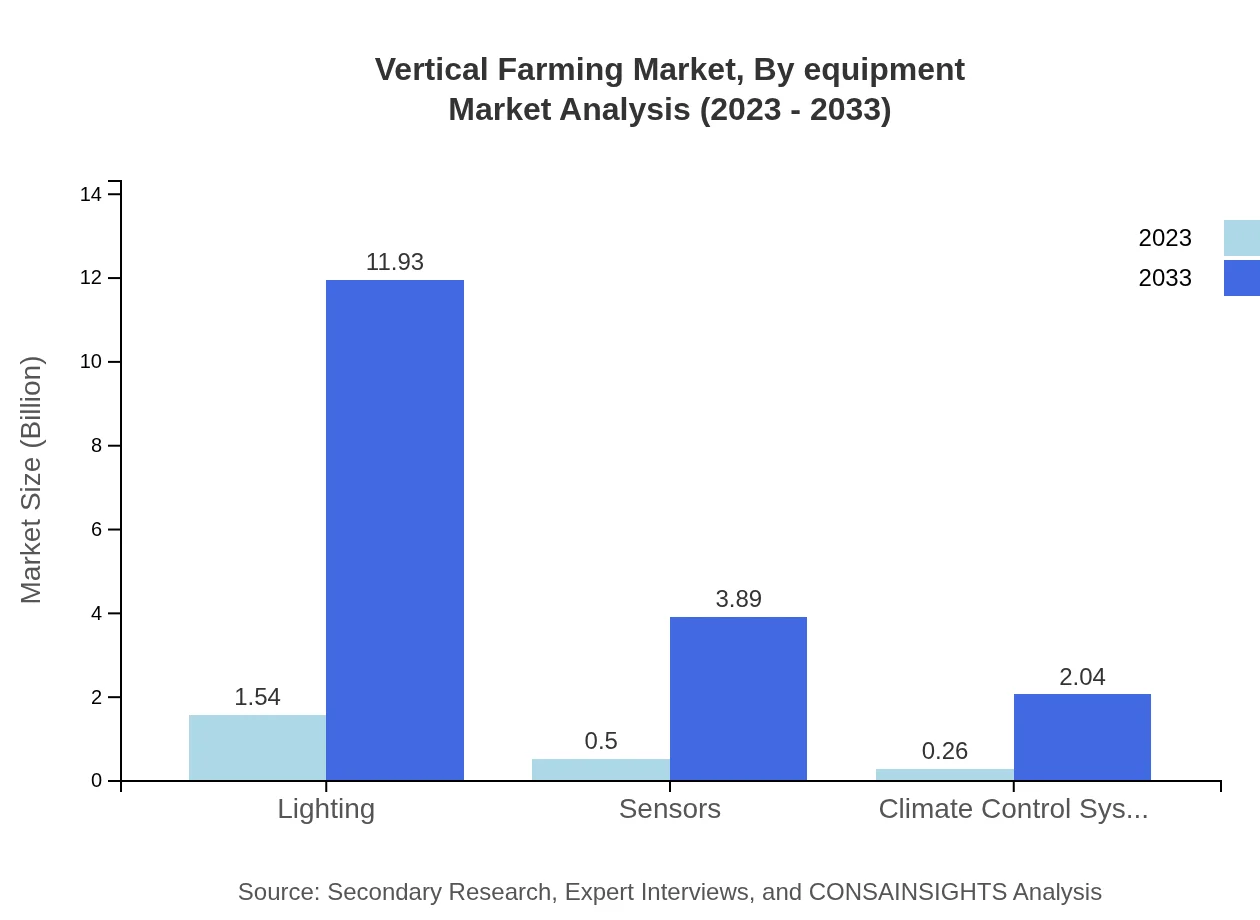
Vertical Farming Market Analysis By Equipment
The equipment segment includes lighting, sensors, and climate control systems. The lighting segment alone is expected to grow from USD 1.54 billion in 2023 to USD 11.93 billion by 2033, as energy-efficient solutions become paramount in vertical farming aesthetics and functionalities.
Vertical Farming Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Vertical Farming Industry
AeroFarms:
A leading player in aeroponics technology, AeroFarms is known for its innovative practices and sustainable farming methods that significantly reduce water usage and land requirements.Plenty Unlimited:
Specializing in vertical farming, Plenty Unlimited employs advanced robotics and artificial intelligence to optimize growing conditions and streamline food production.Vertical Harvest:
Vertical Harvest utilizes innovative farming technologies to create year-round access to fresh produce while providing employment opportunities to the community.Green Spirit Farms:
Focusing on sustainability, Green Spirit Farms implements energy-efficient practices within their vertical farming operations to maximize output while minimizing ecological impact.Gotham Greens:
Renowned for its rooftop farms and hydroponic systems, Gotham Greens emphasizes local production and distribution of fresh leafy greens throughout urban environments.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of vertical Farming?
The global vertical farming market is currently valued at approximately $2.3 billion, showing significant growth potential with a projected CAGR of 21.4% from 2023 to 2033.
What are the key market players or companies in the vertical Farming industry?
Key players in the vertical farming market include AeroFarms, Plenty, and Swisslog. These firms are leaders in technology and innovation, contributing to strong market competition and growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the vertical farming industry?
Growth is largely driven by urbanization, the increasing demand for fresh produce, and advancements in agricultural technology. Sustainable practices and climate change concerns enhance interest in vertical farming solutions.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the vertical farming?
Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region, with market size increasing from $0.38 billion in 2023 to $2.92 billion by 2033, reflecting a strong CAGR as urban farms expand.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the vertical Farming industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers tailored market report data for the vertical farming industry, allowing clients to access specific insights relevant to their operational needs and strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this vertical Farming market research project?
Expected deliverables include comprehensive market analysis, segmentation data, growth forecasts, competitive landscape assessments, and actionable insights to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of vertical farming?
Current market trends highlight increased investment in technology, the rise of automated farming solutions, and a shift towards local food production driven by sustainability and health-conscious consumers.