Vitamin E Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: vitamin-e
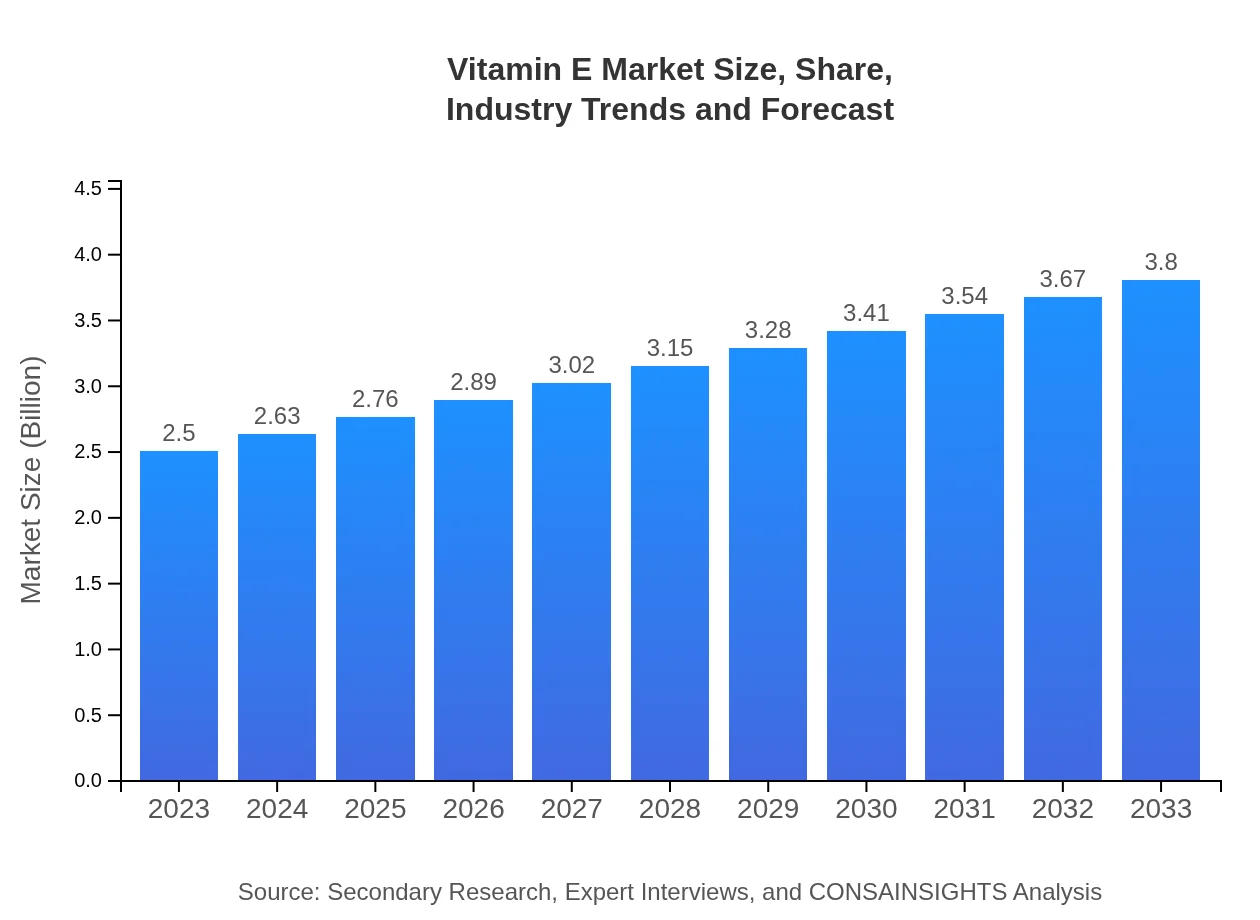
Vitamin E Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Vitamin E market from 2023 to 2033, detailing market size, growth trends, segmentation, regional insights, technology advancements, and key players impacting the industry.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $2.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 4.2% |
| 2033 Market Size | $3.80 Billion |
| Top Companies | BASF SE, Evonik Industries AG, Nutraceutics, Archer Daniels Midland Company |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Vitamin E Market Overview
Customize Vitamin E Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Vitamin E market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Vitamin E's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Vitamin E
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Vitamin E market in 2023?
Vitamin E Industry Analysis
Vitamin E Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Vitamin E Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Vitamin E Market Report:
Europe is expected to see growth from USD 0.73 billion in 2023 to USD 1.11 billion by 2033, largely influenced by regulatory support for health claims on Vitamin E products and a robust demand in clean beauty products.Asia Pacific Vitamin E Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to witness significant growth, with the market size expected to grow from USD 0.51 billion in 2023 to USD 0.77 billion by 2033. Factors such as rising health consciousness, increased disposable income, and demand for natural products drive the market.North America Vitamin E Market Report:
North America's market is projected to grow from USD 0.80 billion in 2023 to USD 1.22 billion by 2033, driven by strong consumer awareness about health benefits and the growing use of Vitamin E in the food and cosmetics industries.South America Vitamin E Market Report:
In South America, the Vitamin E market is anticipated to expand from USD 0.19 billion in 2023 to USD 0.29 billion by 2033, fueled by an increasing demand for supplements and a larger focus on nutrition and health, especially in Brazil and Argentina.Middle East & Africa Vitamin E Market Report:
The Middle East and Africa region is forecasted to grow from USD 0.26 billion in 2023 to USD 0.40 billion by 2033. Growth drivers include increasing health and wellness trends combined with a rise in product availability in both urban and rural markets.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
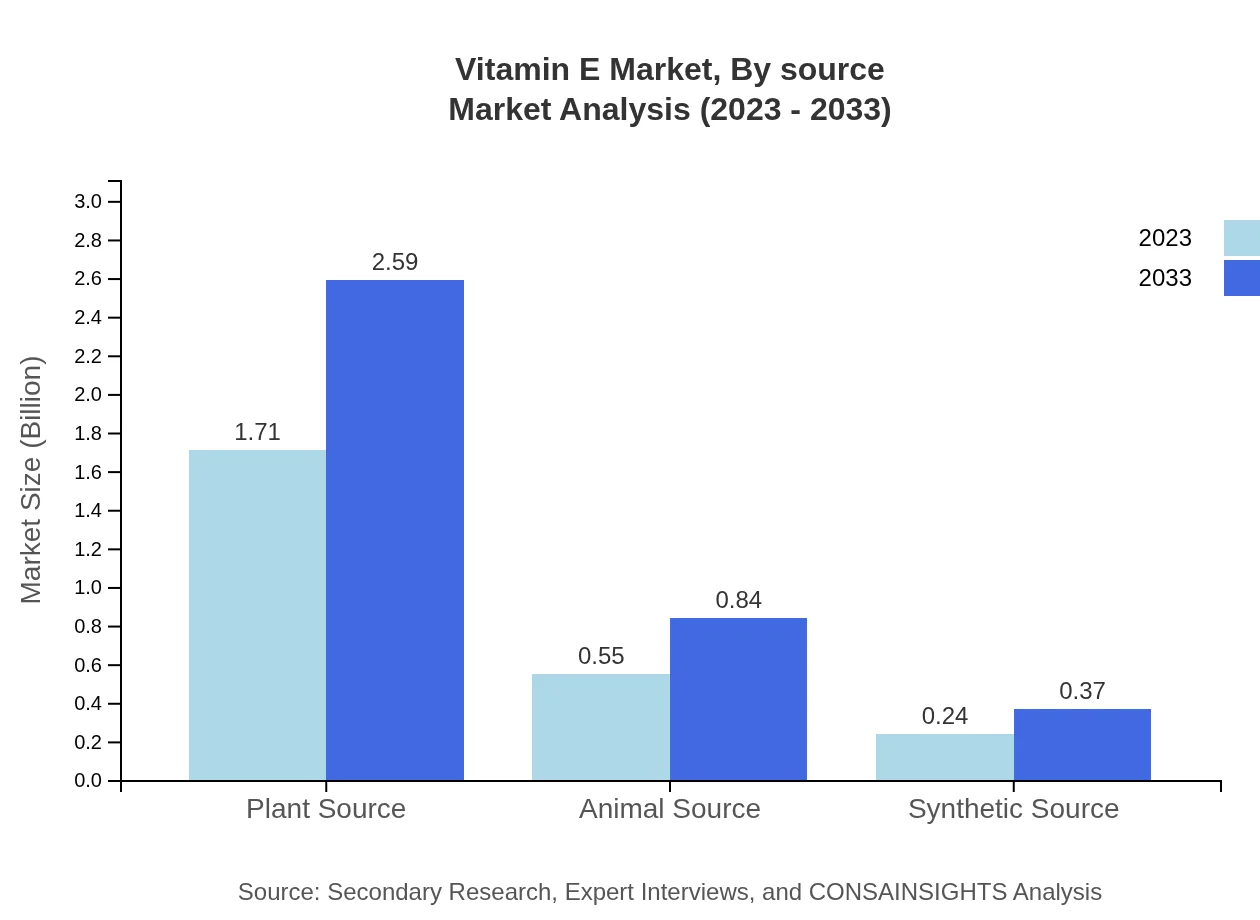
Vitamin E Market Analysis By Source
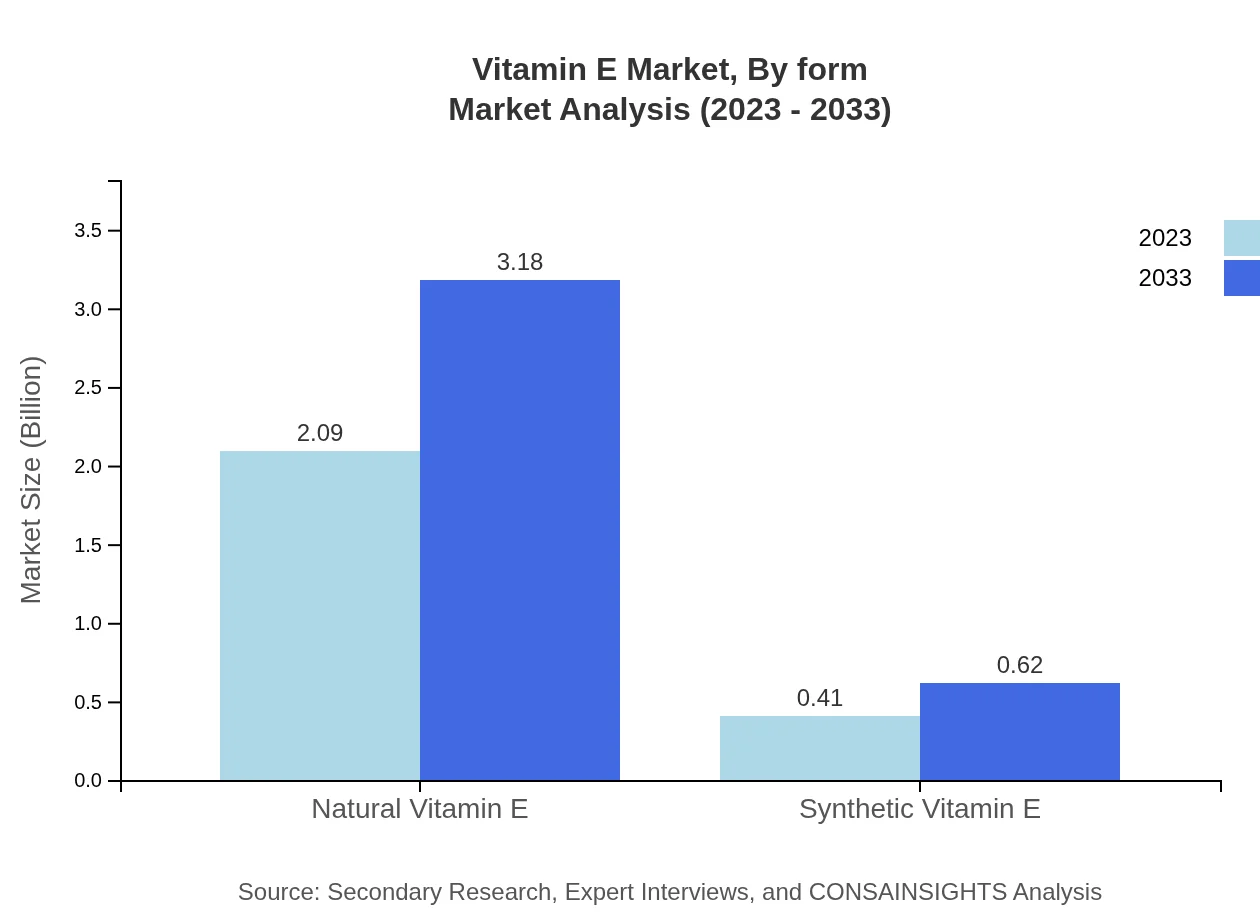
The market is primarily segmented into Natural Vitamin E and Synthetic Vitamin E. Natural Vitamin E is anticipated to grow from USD 2.09 billion in 2023 to USD 3.18 billion by 2033, holding the majority share at 83.66%. Synthetic Vitamin E, with a lower share of 16.34%, is also rising, growing from USD 0.41 billion in 2023 to USD 0.62 billion in 2033.
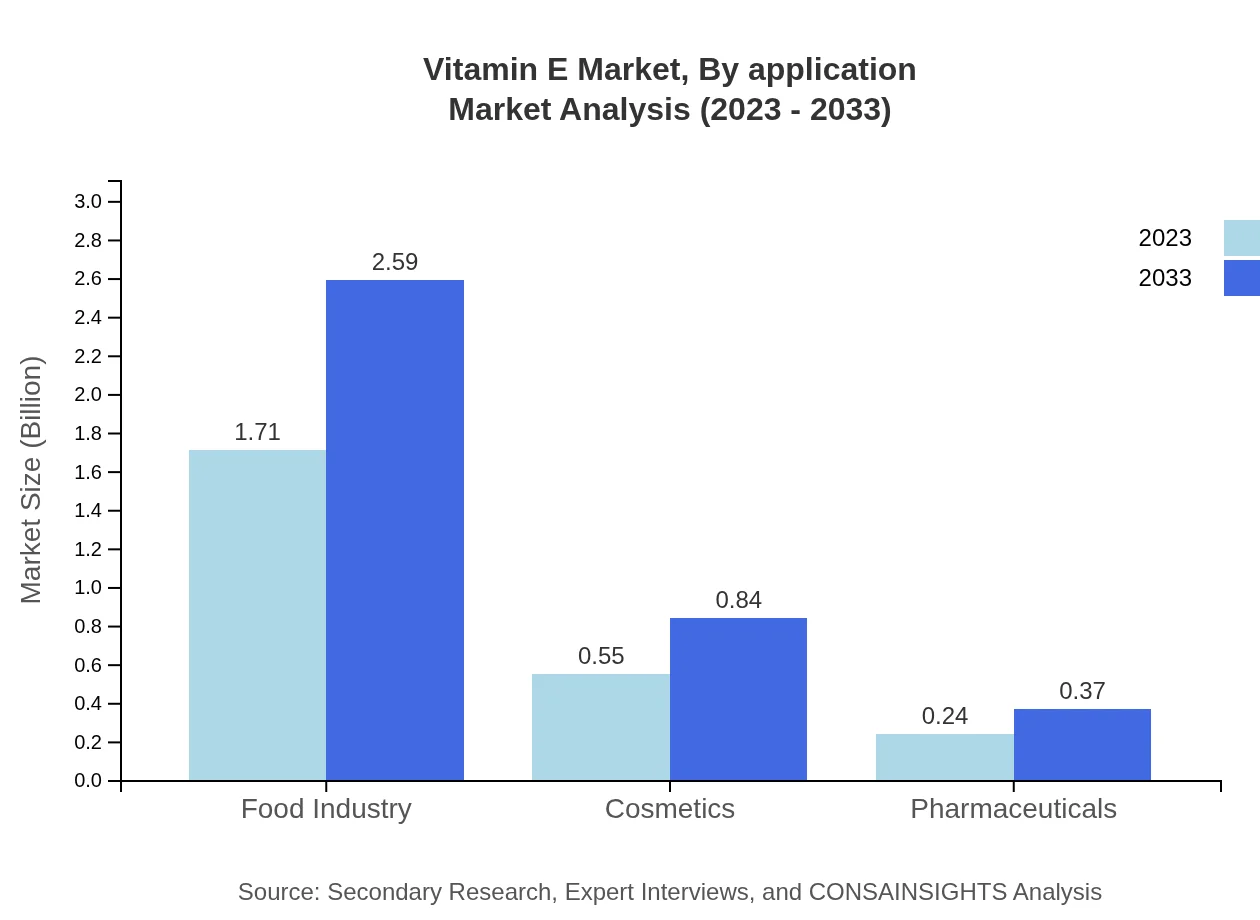
Vitamin E Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, the Food Industry segment is anticipated to hold the largest market share at 68.24%, growing from USD 1.71 billion in 2023 to USD 2.59 billion by 2033. The Cosmetics segment also shows promising growth, expected to increase from USD 0.55 billion in 2023 to USD 0.84 billion by 2033.
Vitamin E Market Analysis By Form
The Vitamin E market is further segmented by form into natural and synthetic types. Natural Vitamin E is experiencing significant demand for its perceived health benefits and is projected to grow significantly within the forecast period.
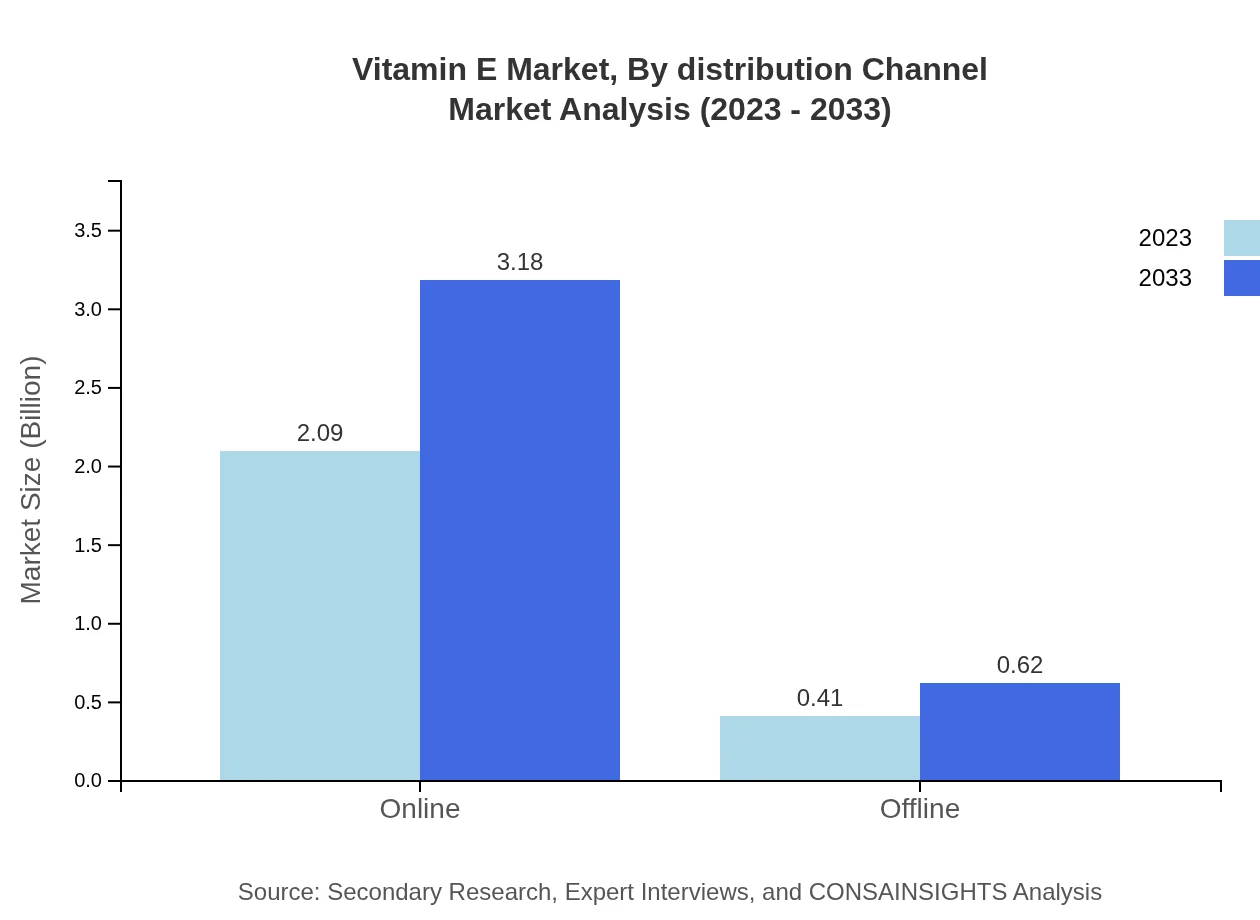
Vitamin E Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
The distribution channels are primarily categorized into online and offline sales. Online sales hold a huge share at about 83.66%, with growth anticipated from USD 2.09 billion in 2023 to USD 3.18 billion by 2033, driven by increasing trends in e-commerce and direct-to-consumer business models.
Vitamin E Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Vitamin E Industry
BASF SE:
BASF SE is one of the leading manufacturers of Vitamin E, known for its strong investment in R&D and innovative products aimed at diverse applications including cosmetics and dietary supplements.Evonik Industries AG:
Evonik Industries AG specializes in health and nutrition sectors, focusing on high-quality, sustainable Vitamin E production to meet increasing market demands.Nutraceutics:
Nutraceutics emphasizes natural Vitamin E products, targeting health-conscious consumers while ensuring quality and efficacy in their product line.Archer Daniels Midland Company:
ADM plays an important role in the Vitamin E market and focuses on food and beverage applications, emphasizing its role in enhancing product quality and nutritional value.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of Vitamin E?
The global Vitamin E market is valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2023, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2%. By 2033, this market size is anticipated to increase significantly, reflecting the growing demand in various sectors.
What are the key market players or companies in the Vitamin E industry?
Key players in the Vitamin E market include major global companies specializing in nutritional supplements, cosmetic ingredients, and food additives. These companies are recognized for their strong market presence and innovative product offerings, contributing significantly to the industry's growth.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the Vitamin E industry?
The growth of the Vitamin E industry is driven by increasing consumer awareness regarding health and wellness, rising demand in the cosmetics and food industries, and advancements in manufacturing techniques. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of vitamin deficiencies supports market expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the Vitamin E market?
The North American region is projected to be the fastest-growing market for Vitamin E, with a market size of $0.80 billion in 2023, expected to reach $1.22 billion by 2033. Regions such as Europe and Asia Pacific also show significant growth potential.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the Vitamin E industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data tailored to the specific needs of businesses in the Vitamin E industry. This includes insights on market size, growth trends, and competitive analysis to help organizations make informed decisions.
What deliverables can I expect from this Vitamin E market research project?
Deliverables from the Vitamin E market research project include comprehensive reports detailing market size, growth projections, competitive analysis, and segment data. Clients will receive actionable insights to guide their strategic planning and investment decisions.
What are the market trends of Vitamin E?
Current trends in the Vitamin E market include a shift towards natural sources, increased demand in the food industry, and a rise in online sales. Segment data reveals that natural Vitamin E is gaining popularity due to its health benefits and consumer preference for organic products.