Wheat Seed Market Report
Published Date: 02 February 2026 | Report Code: wheat-seed
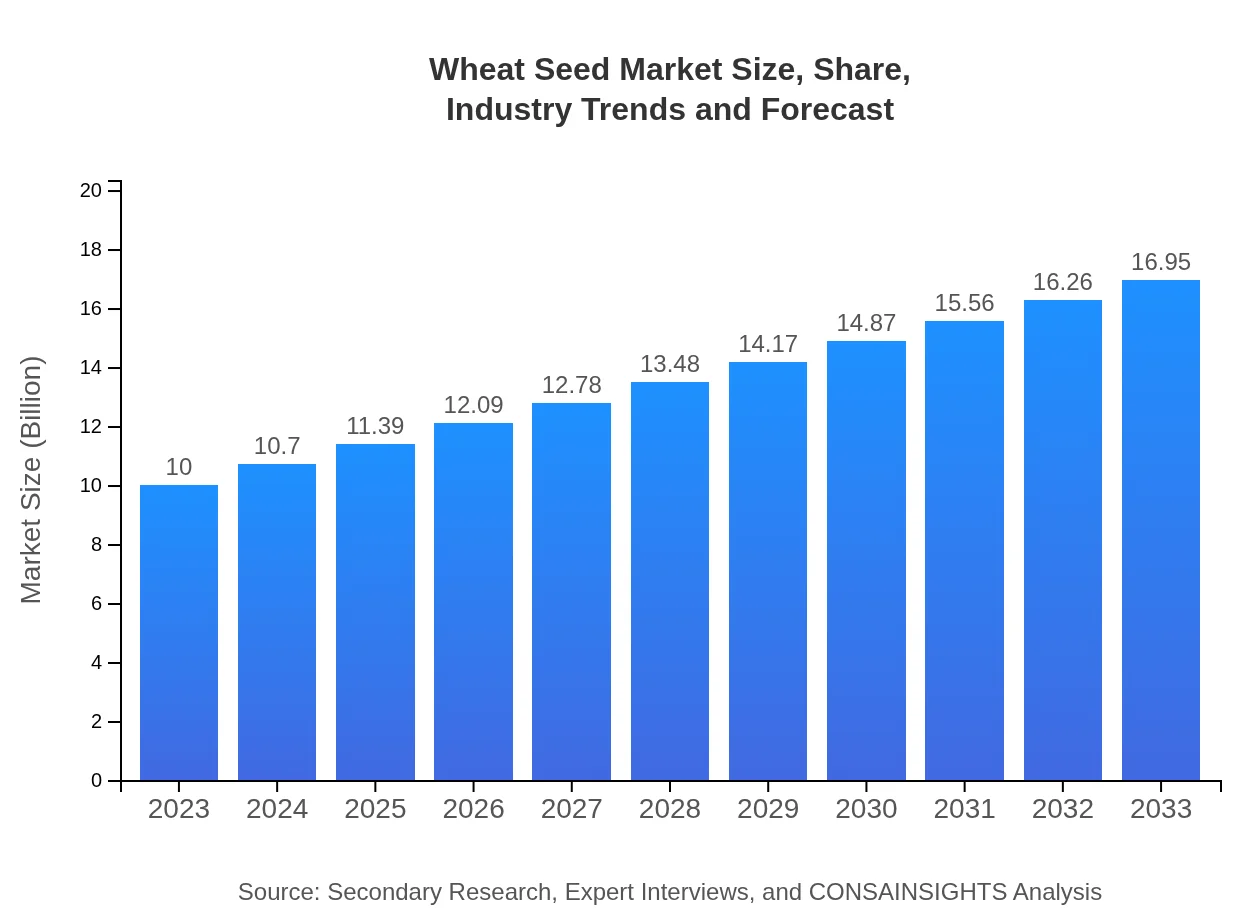
Wheat Seed Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the Wheat Seed market from 2023 to 2033, including insights on market size, growth trends, regional performance, technology developments, and key industry players.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
| 2023 Market Size | $10.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 5.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $16.95 Billion |
| Top Companies | BASF SE, Monsanto (Bayer AG), Syngenta, Corteva Agriscience |
| Last Modified Date | 02 February 2026 |
Wheat Seed Market Overview
Customize Wheat Seed Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Wheat Seed market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Wheat Seed's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Wheat Seed
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Wheat Seed market in 2023?
Wheat Seed Industry Analysis
Wheat Seed Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Wheat Seed Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Wheat Seed Market Report:
Europe's Wheat Seed market reached $2.62 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $4.44 billion by 2033. The region emphasizes sustainability and organic farming, with countries like France and Germany leading advancements in wheat cultivation techniques.Asia Pacific Wheat Seed Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Wheat Seed market was valued at $2.14 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $3.63 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to rising wheat consumption, particularly in countries like China and India, alongside advancements in agricultural practices and government support for seed production.North America Wheat Seed Market Report:
North America boasts a Wheat Seed market valued at $3.64 billion in 2023, forecasted to grow to $6.18 billion by 2033. The United States is a major contributor, with technological innovations and extensive arable land facilitating increased yields and effective supply chain operations.South America Wheat Seed Market Report:
For South America, the market size in 2023 stood at $0.31 billion, with projections estimating $0.53 billion by 2033. Brazil and Argentina are significant players in wheat production, leveraging improved seed varieties and their agricultural exports to drive growth.Middle East & Africa Wheat Seed Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the Wheat Seed market was valued at $1.28 billion in 2023, expected to rise to $2.17 billion by 2033. The increasing population and changing dietary needs are driving wheat consumption, while initiatives aimed at enhancing irrigation and agricultural practices are also impacting market growth.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
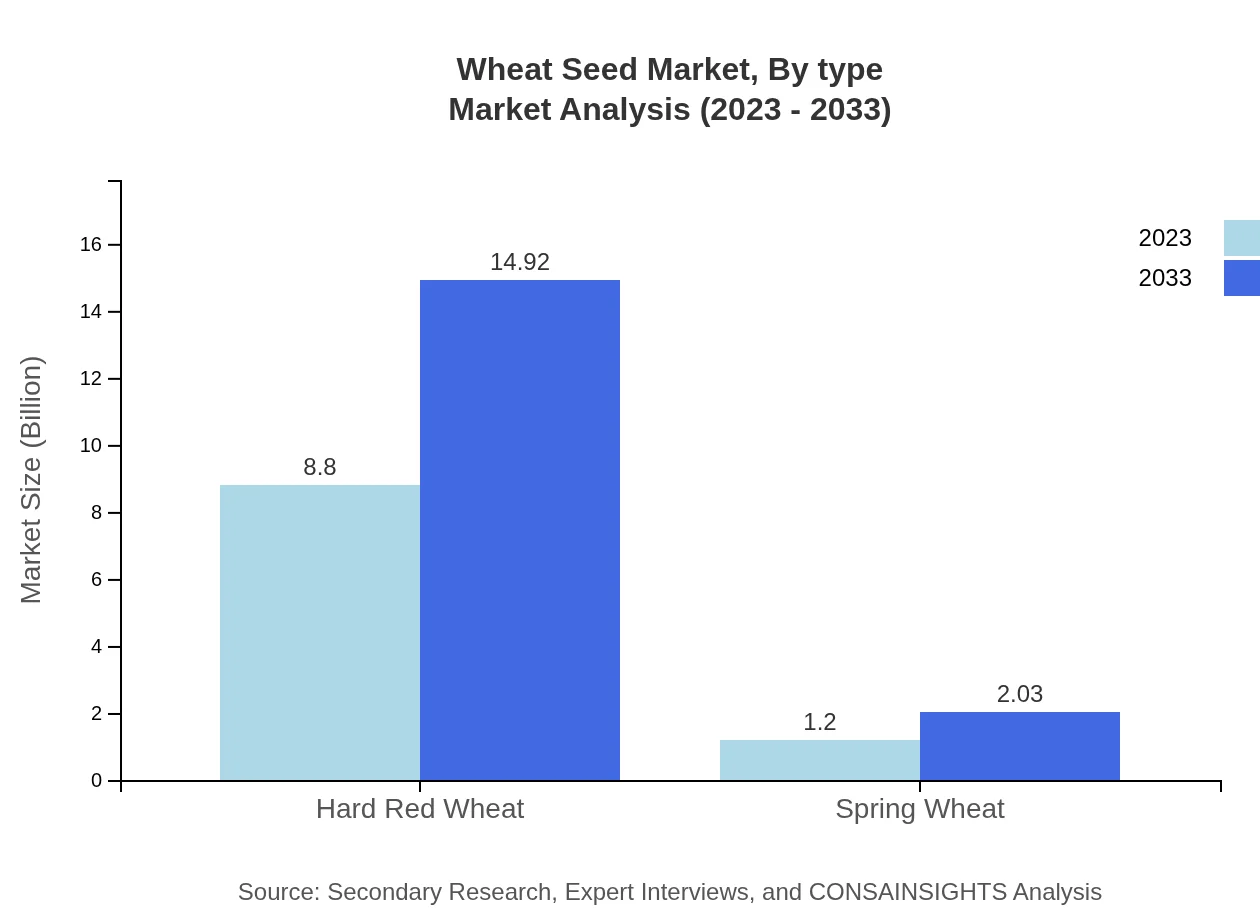
Wheat Seed Market Analysis By Type
The Hard Red Wheat segment accounted for a market size of $8.80 billion in 2023, with expectations of reaching $14.92 billion by 2033, maintaining a market share of 88.01%. In contrast, Spring Wheat is projected to grow from $1.20 billion in 2023 to $2.03 billion in 2033, representing 11.99% of the market share.
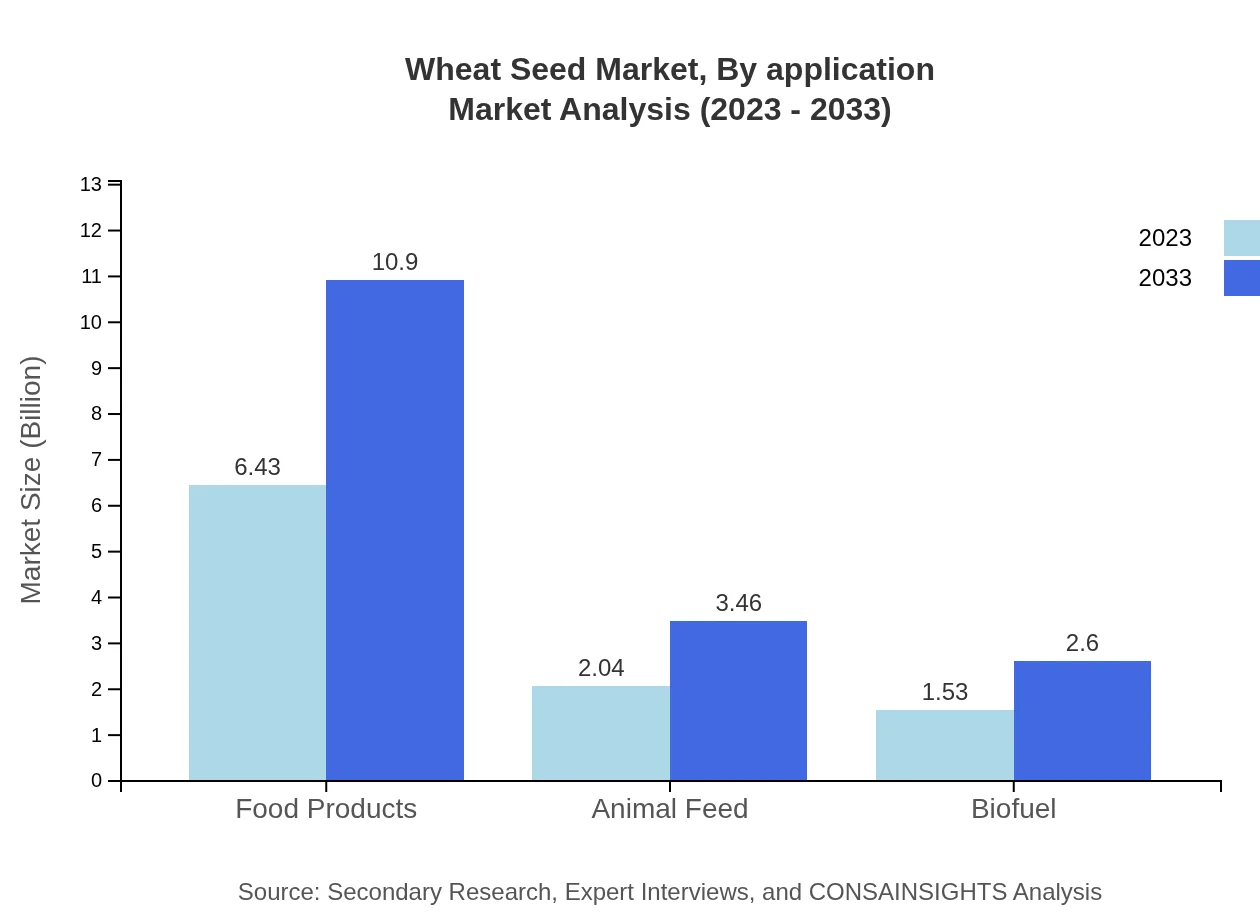
Wheat Seed Market Analysis By Application
In terms of application, Food Products dominate the segment, valued at $6.43 billion in 2023, growing to $10.90 billion by 2033, with a 64.27% market share. Animal Feed and Biofuel applications also show promise with sizes of $2.04 billion and $1.53 billion respectively, growing significantly over the forecast period.
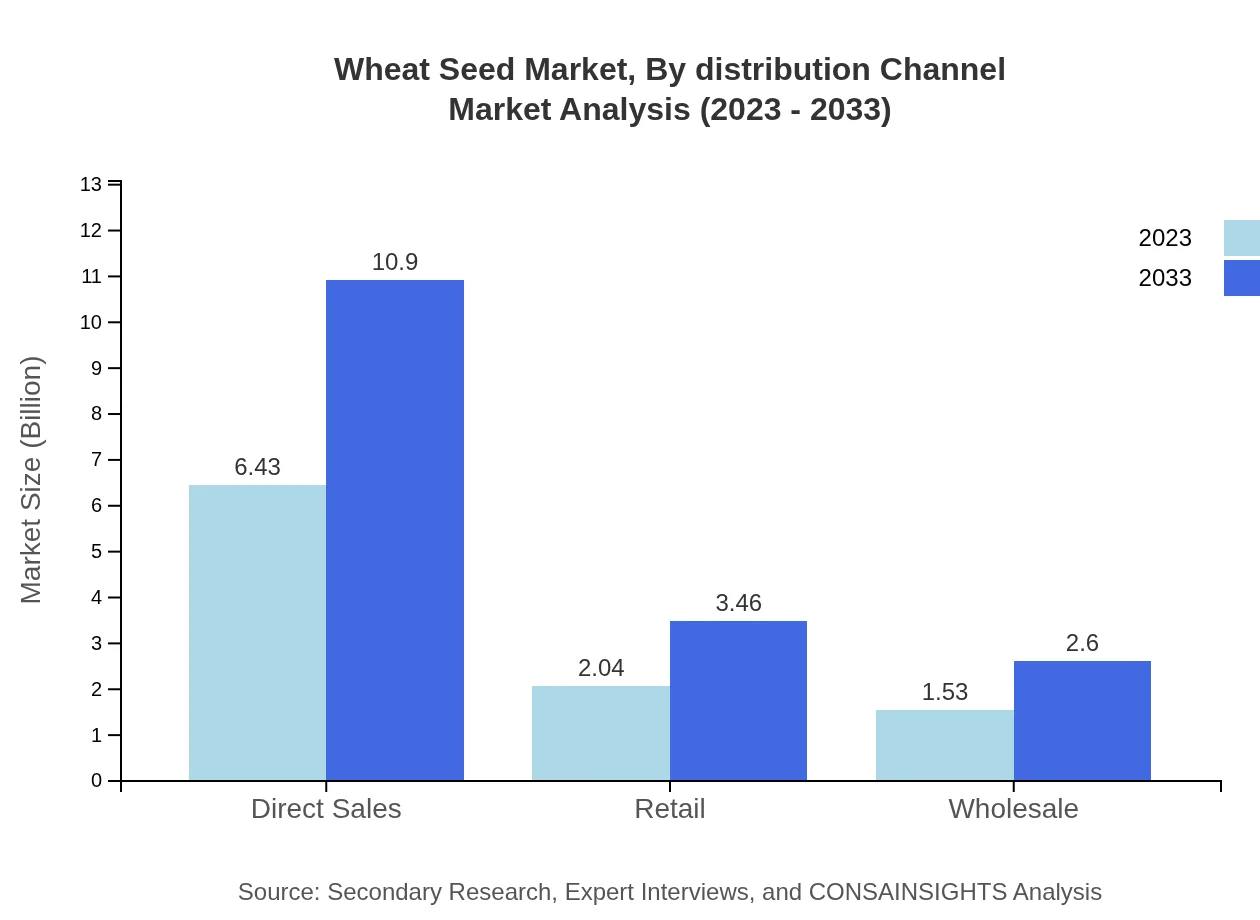
Wheat Seed Market Analysis By Distribution Channel
Direct Sales is the leading distribution channel, with a size of $6.43 billion in 2023, expected to grow to $10.90 billion by 2033, representing 64.27% market share. Retail and Wholesale channels follow closely behind, showing steady growth as the need for accessibility increases.
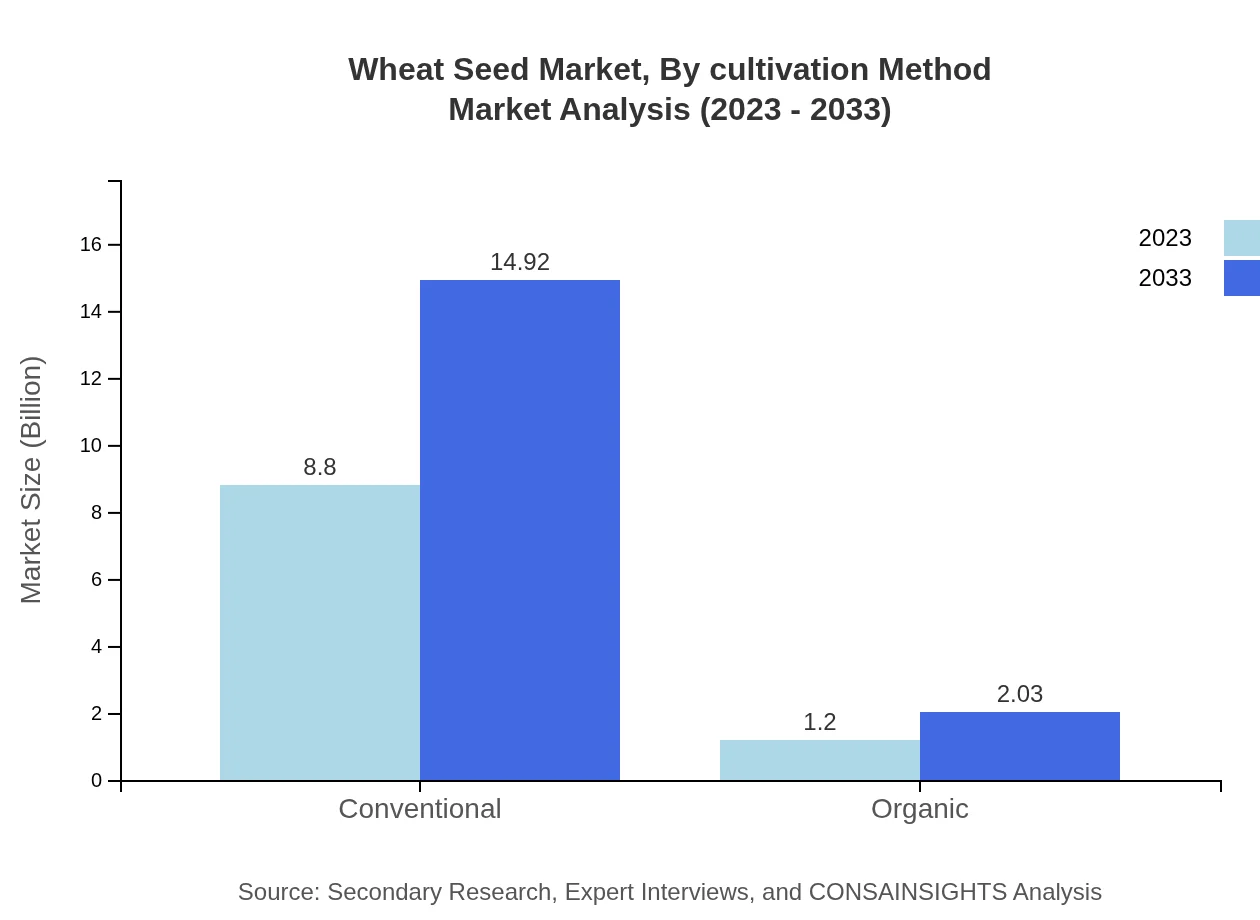
Wheat Seed Market Analysis By Cultivation Method
Conventional methods dominate with a market size of $8.80 billion in 2023, growing to $14.92 billion by 2033, while Organic cultivation, valued at $1.20 billion in 2023, is expected to reach $2.03 billion, indicating a growing trend toward sustainable practices.
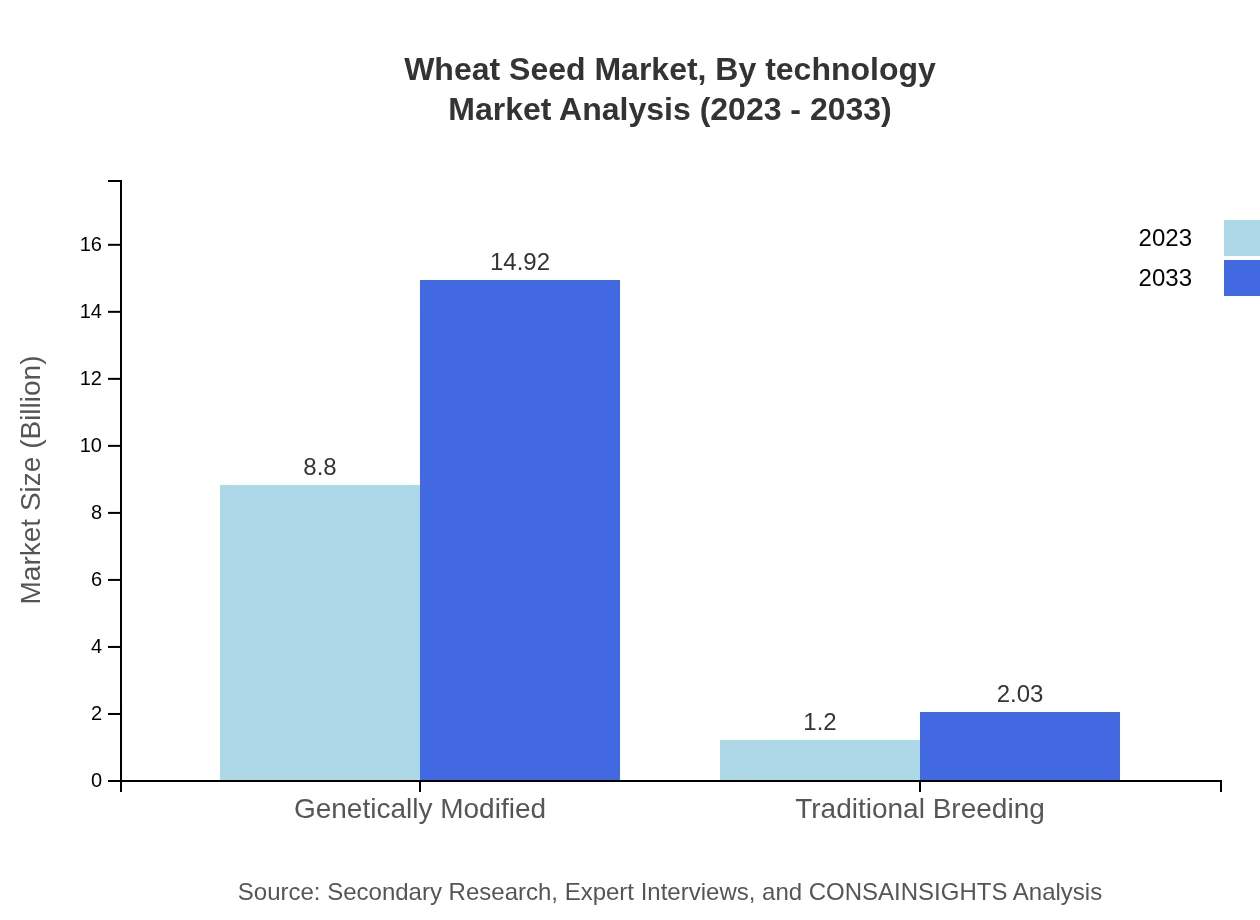
Wheat Seed Market Analysis By Technology
The Genetically Modified segment leads the market with a valuation of $8.80 billion in 2023, expected to increase to $14.92 billion by 2033, holding an 88.01% share. Traditional Breeding methods account for $1.20 billion with projections of $2.03 billion, showcasing ongoing importance in crop production.
Wheat Seed Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Wheat Seed Industry
BASF SE:
BASF operates in agricultural solutions, providing innovative crop protection products and seeds including wheat. The company's R&D efforts focus on enhancing seed traits and sustainability.Monsanto (Bayer AG):
Monsanto, now part of Bayer, is a leader in seeds and traits, developing genetically modified wheat varieties that improve yield potential and pest resistance.Syngenta:
Syngenta is dedicated to agronomy and developing high-quality seeds, including wheat, with substantial investment in research and technology.Corteva Agriscience:
Corteva specializes in seed technologies and is actively involved in the development of innovative wheat seed products aimed at improving productivity and sustainability.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of wheat Seed?
The wheat seed market is currently valued at approximately 10 billion dollars, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2033. This growth is driven by increasing demand for wheat products globally.
What are the key market players or companies in the wheat Seed industry?
Key players in the wheat seed market include major agricultural biotechnology companies, seed manufacturers, and distributors. These companies play a crucial role in the development and commercialization of innovative wheat seed varieties.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the wheat seed industry?
The growth of the wheat seed market is primarily driven by rising population demands, advancements in seed technology, and increased awareness regarding food security. Additionally, government initiatives and agricultural subsidies also support the market's expansion.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the wheat seed market?
The fastest-growing region in the wheat seed market is North America, projected to grow from 3.64 billion in 2023 to 6.18 billion by 2033. This growth is attributed to advanced agricultural practices and a strong demand for wheat products.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the wheat seed industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the wheat seed industry. Clients can request specific insights, data segmentation, and tailored analysis to suit their business needs.
What deliverables can I expect from this wheat seed market research project?
Deliverables from the wheat seed market research project include detailed market size reports, growth forecasts, segmentation analysis, competitive landscape, and insights into regional trends, tailored to support strategic decision-making.
What are the market trends of wheat seed?
Current trends in the wheat seed market include the increasing adoption of genetically modified seeds, rising focus on sustainable agriculture, and a shift towards organic seed production. These trends are shaping the future of wheat cultivation.