Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: whole-exome-sequencing
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) market, including market size, segmentation, regional insights, technological advancements, and forecasts from 2023 to 2033.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
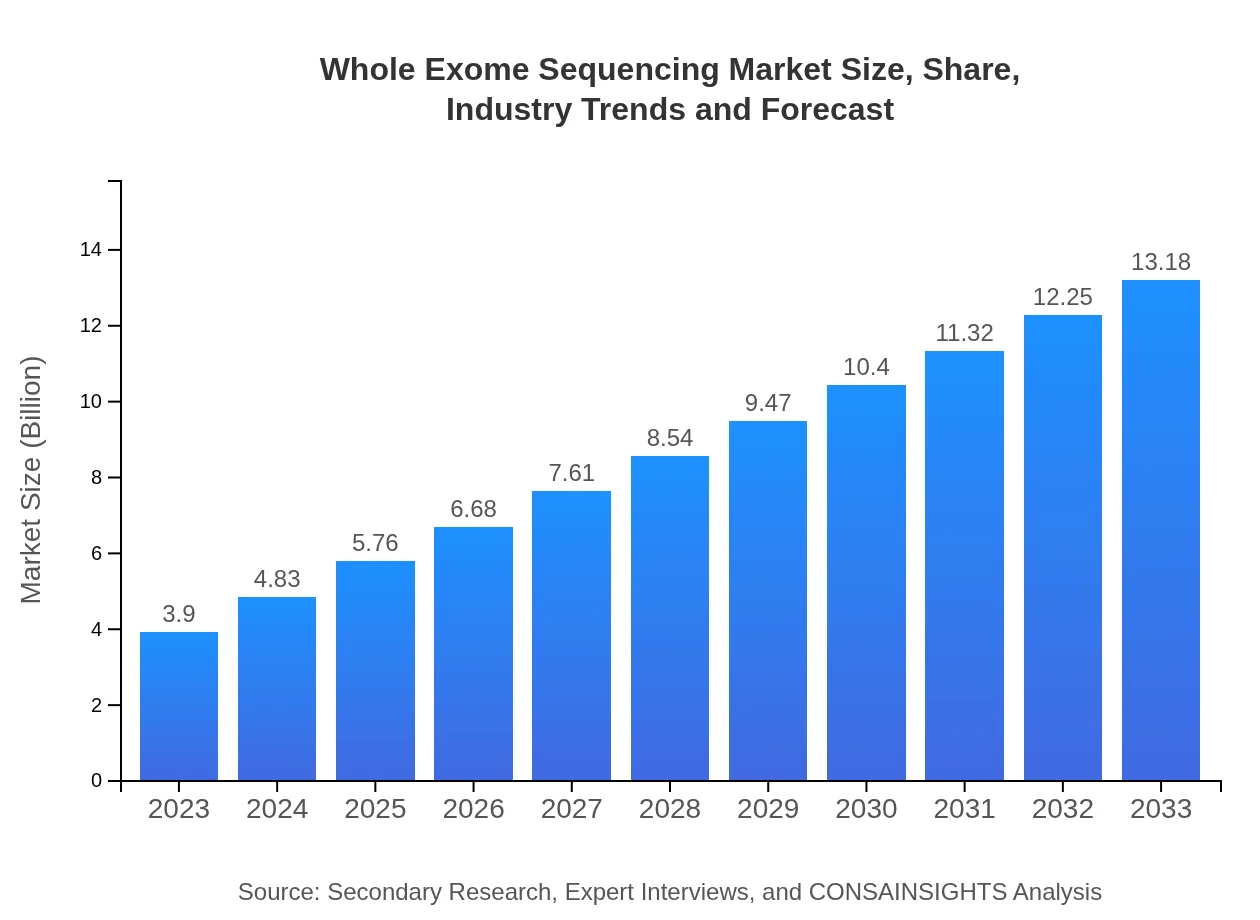
| 2023 Market Size | $3.90 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.4% |
| 2033 Market Size | $13.18 Billion |
| Top Companies | Illumina, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Roche Sequencing Solutions, Pacific Biosciences, BGI Genomics |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Overview
Customize Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Whole Exome Sequencing market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Whole Exome Sequencing's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Whole Exome Sequencing
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Whole Exome Sequencing market in 2023?
Whole Exome Sequencing Industry Analysis
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report:
The European market for Whole Exome Sequencing is set to expand from $1.23 billion in 2023 to $4.17 billion by 2033. Factors such as increasing investments in genomics and an effective regulatory framework for genetic testing propel this growth.Asia Pacific Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report:
The Asia Pacific region is projected to grow from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $2.03 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 13.3%. The increase is attributed to growing healthcare investments, rising incidences of genetic disorders, and improvements in healthcare infrastructure.North America Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report:
North America holds a significant share of the WES market, growing from $1.49 billion in 2023 to $5.02 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by the high prevalence of genetic diseases, supportive government policies, and a well-established healthcare system.South America Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report:
In South America, the market is expected to increase from $0.04 billion in 2023 to $0.14 billion by 2033, driven by increasing awareness of genetic testing and improved access to genomic services.Middle East & Africa Whole Exome Sequencing Market Report:
For the Middle East and Africa, the market is forecasted to grow from $0.54 billion in 2023 to $1.82 billion by 2033, backed by expanding healthcare initiatives and collaborative research projects in genomics.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
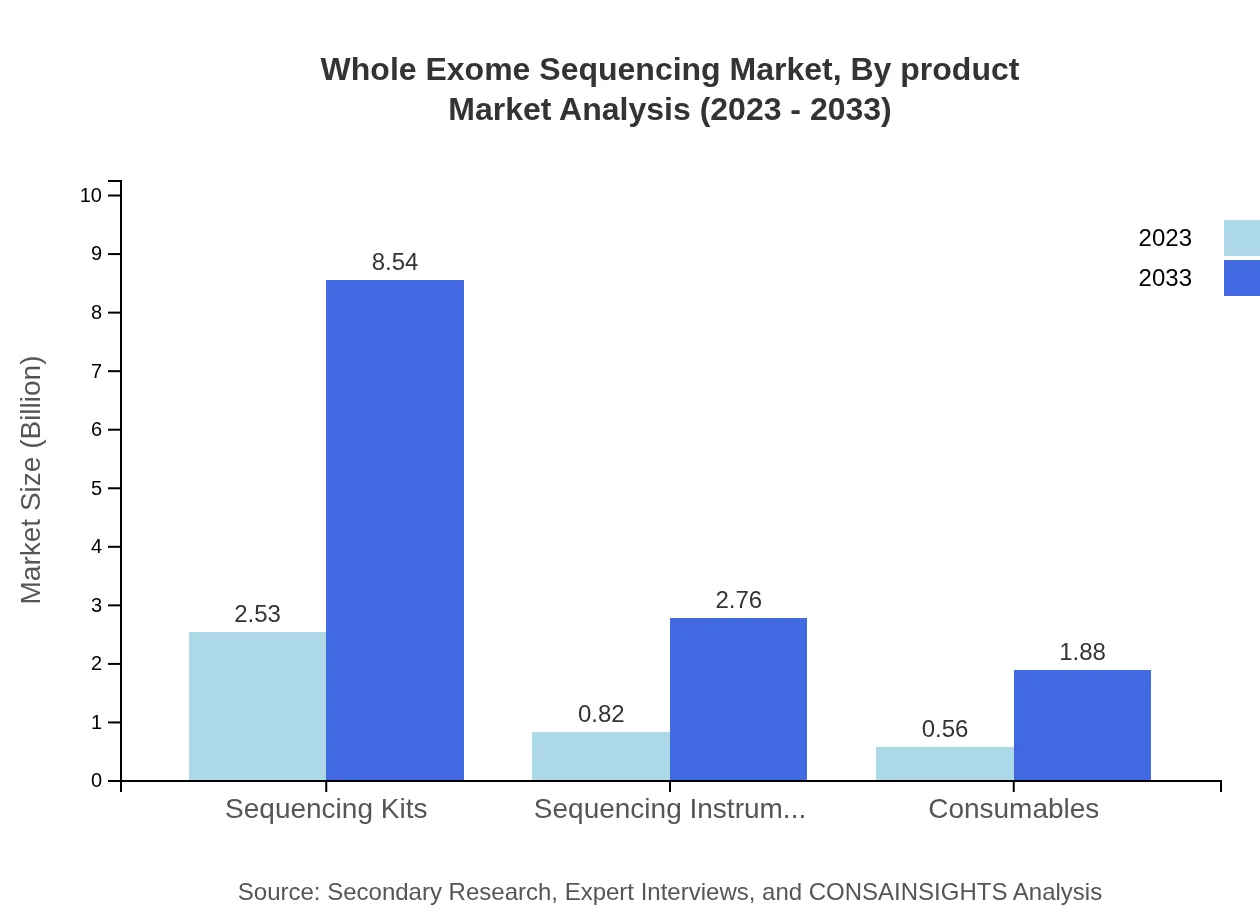
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis By Product
The Whole Exome Sequencing market by product reveals a diverse range of offerings. Key product types include Sequencing Kits, which are expected to grow from $2.53 billion in 2023 to $8.54 billion by 2033, and Sequencing Instruments, poised to increase from $0.82 billion in 2023 to $2.76 billion by 2033. The prominence of these products is driven by the requirement for advanced tools in genomic research.
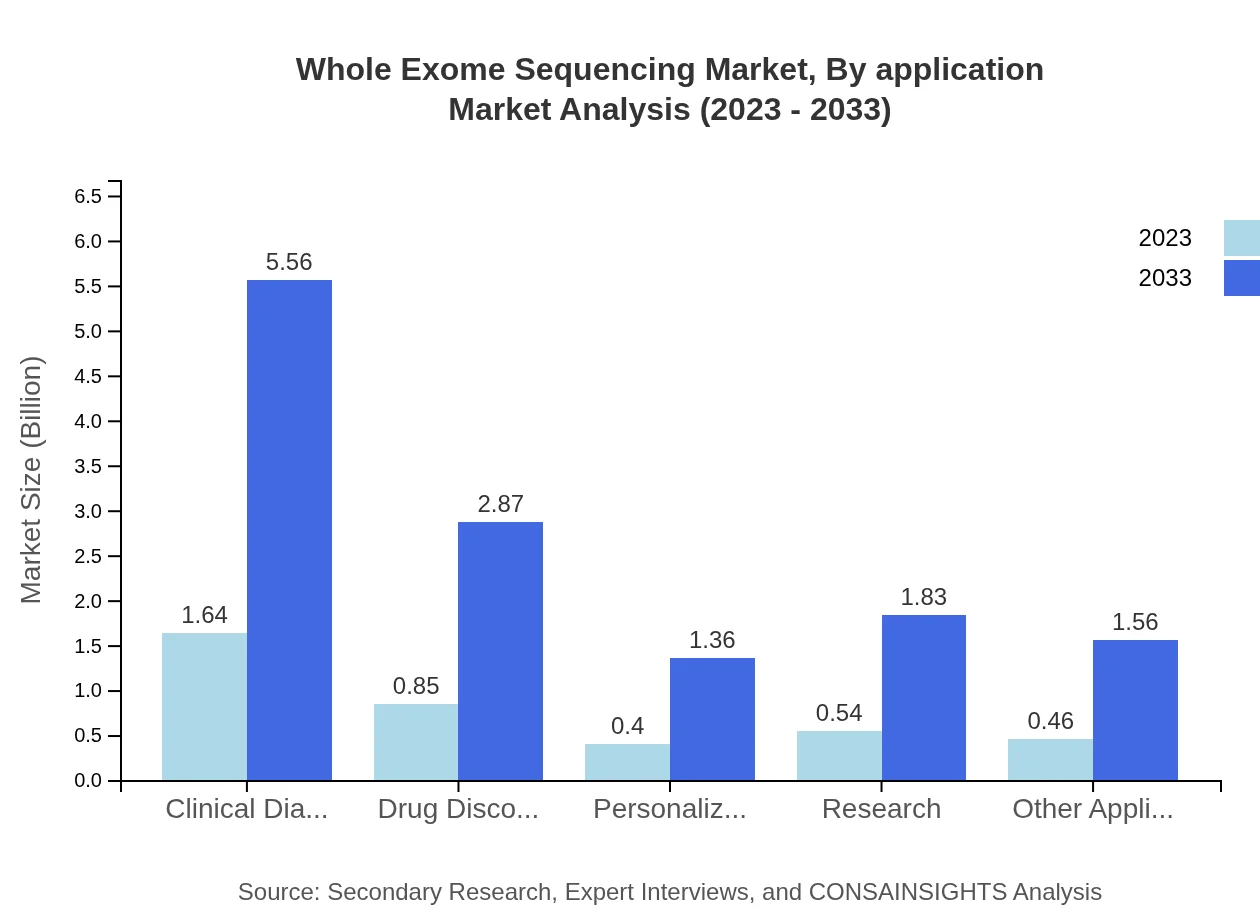
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis By Application
Applications of Whole Exome Sequencing include Clinical Diagnostics, which reflects a significant market share. This application is projected to grow from $1.64 billion in 2023 to $5.56 billion by 2033. The focus on personalized medicine drives the demand within clinical diagnostics, as practitioners increasingly rely on genomic data for treatment decisions.
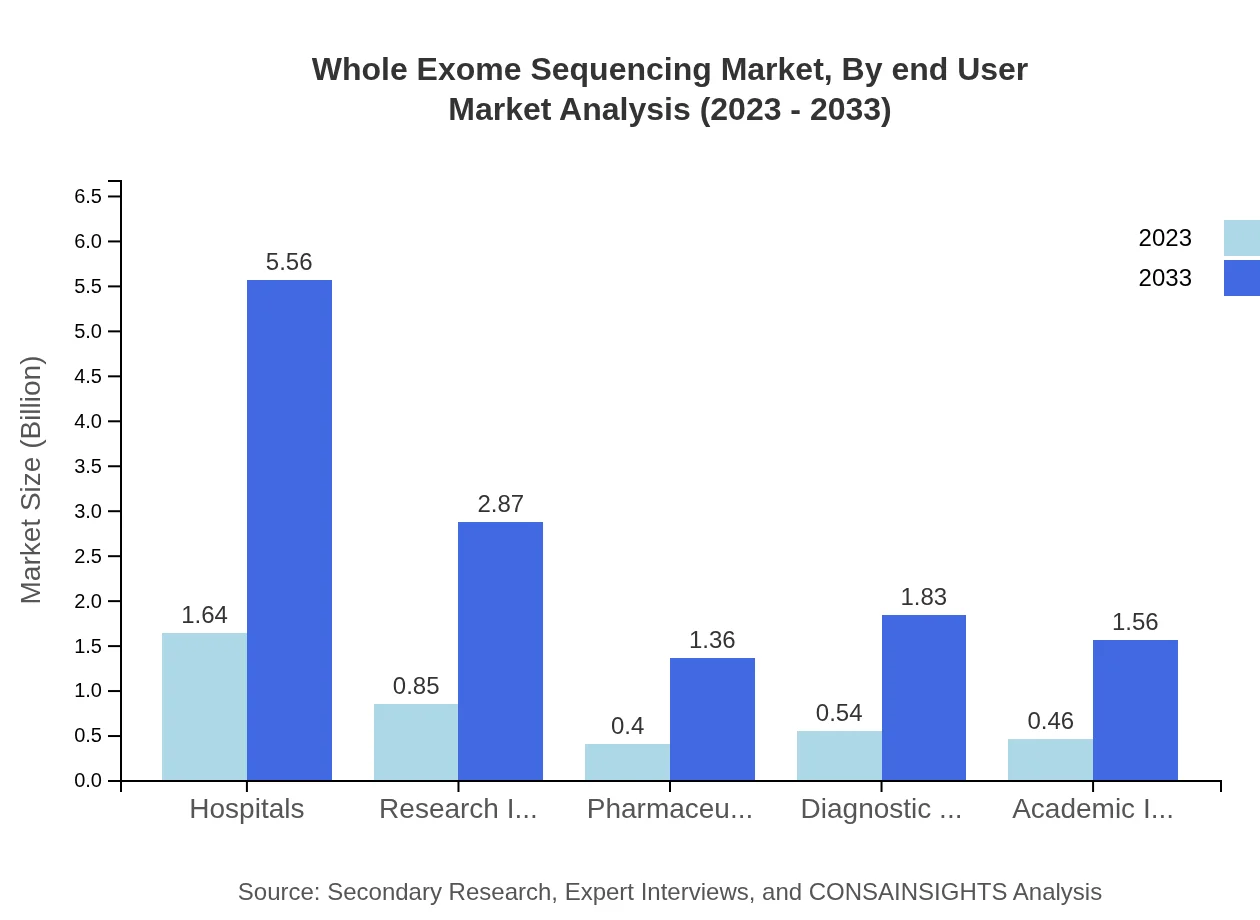
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis By End User
In terms of end-users, Hospitals and Research Institutes lead the market. Hospitals are anticipated to grow from $1.64 billion in 2023 to $5.56 billion by 2033, accounting for a substantial share due to the increasing adoption of genomic testing. Research Institutes are also expected to see significant growth as they leverage WES in various initiatives.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis By Region
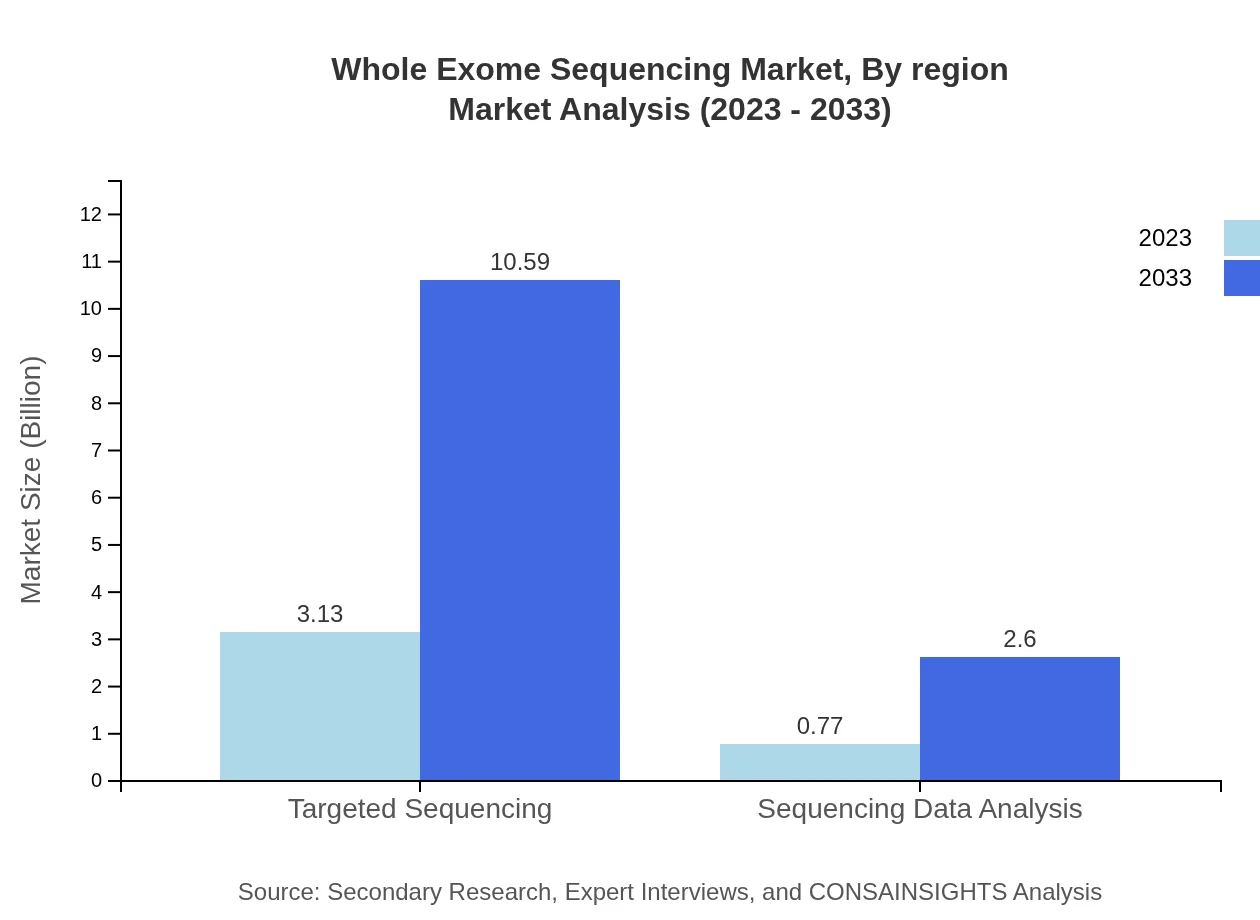
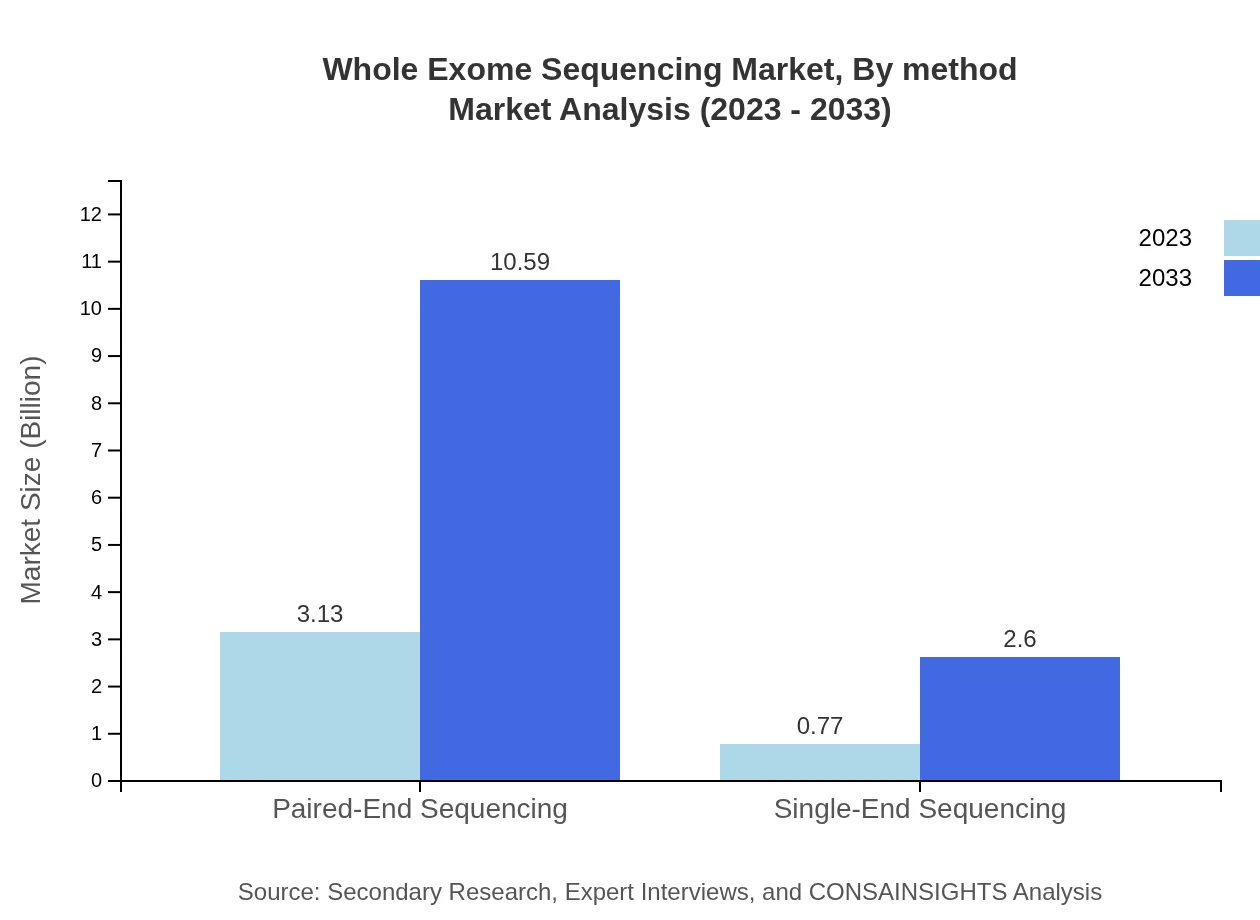
When analyzing by technology, Paired-End Sequencing dominates the market. This technology is expected to grow from $3.13 billion in 2023 to $10.59 billion by 2033, capturing a significant share at 80.31%. Single-End Sequencing is also noted, although it holds a smaller market share.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Analysis By Method
The market reflects diverse methodologies with Sequencing Data Analysis growth projected from $0.77 billion to $2.60 billion between 2023 and 2033. The focus on data interpretation within the WES workflow supports the proliferation of dedicated analytics solutions.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Whole Exome Sequencing Industry
Illumina, Inc.:
Illumina is a leader in genomic sequencing and array-based solutions and plays a crucial role in advancing WES technologies, making genetic insights more accessible.Thermo Fisher Scientific:
Thermo Fisher Scientific offers robust whole exome sequencing kits and instruments, leading the development of innovative solutions for genomics research.Roche Sequencing Solutions:
Roche provides comprehensive sequencing solutions that include whole exome sequencing, enhancing accuracy in diagnostics and research.Pacific Biosciences:
Pacific Biosciences focuses on providing advanced sequencing platforms that support long-read capabilities, complementing traditional WES methods.BGI Genomics:
BGI Genomics is known for its cost-effective sequencing services and extensive library preparation methods, catering to diverse research demands.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of whole Exome Sequencing?
The global whole-exome sequencing market is projected to grow from approximately $3.9 billion in 2023 to significantly higher valuations by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4%, indicating robust growth in this sector.
What are the key market players or companies in the whole Exome Sequencing industry?
Key players in the whole-exome sequencing market include major biotechnology firms, leading genomic analysis companies, and diagnostic laboratories that specialize in genetic testing, contributing significantly to market advancements and innovation.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the whole Exome Sequencing industry?
Key growth drivers include increasing demand for personalized medicine, technological advancements in sequencing methods, declining costs of sequencing, and the rising prevalence of genetic disorders prompting demand for genetic testing.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the whole Exome Sequencing?
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the whole-exome sequencing market, projected to expand from $0.60 billion in 2023 to $2.03 billion by 2033, showcasing increased investment and technological adoption in genomic research.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the whole Exome Sequencing industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market reports for the whole-exome sequencing industry, allowing clients to obtain tailored insights and data relevant to their specific interests and requirements.
What deliverables can I expect from this whole Exome Sequencing market research project?
Expected deliverables include a comprehensive market analysis, growth projections, segmented data insights, competitive landscape assessment, and customized recommendations based on the latest market trends.
What are the market trends of whole Exome Sequencing?
Current trends in the whole-exome sequencing market include increased focus on personalized healthcare, advancements in exome capturing technologies, and growing application in various fields such as clinical diagnostics, research, and drug discovery.