Zero Trust Security Market Report
Published Date: 31 January 2026 | Report Code: zero-trust-security
Zero Trust Security Market Size, Share, Industry Trends and Forecast to 2033
This report offers an in-depth analysis of the Zero Trust Security market, focusing on forecasts from 2023 to 2033. It provides insights into market size, growth metrics, regional analysis, industry trends, and key players shaping the future of cybersecurity in an increasingly digital world.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2023 - 2033 |
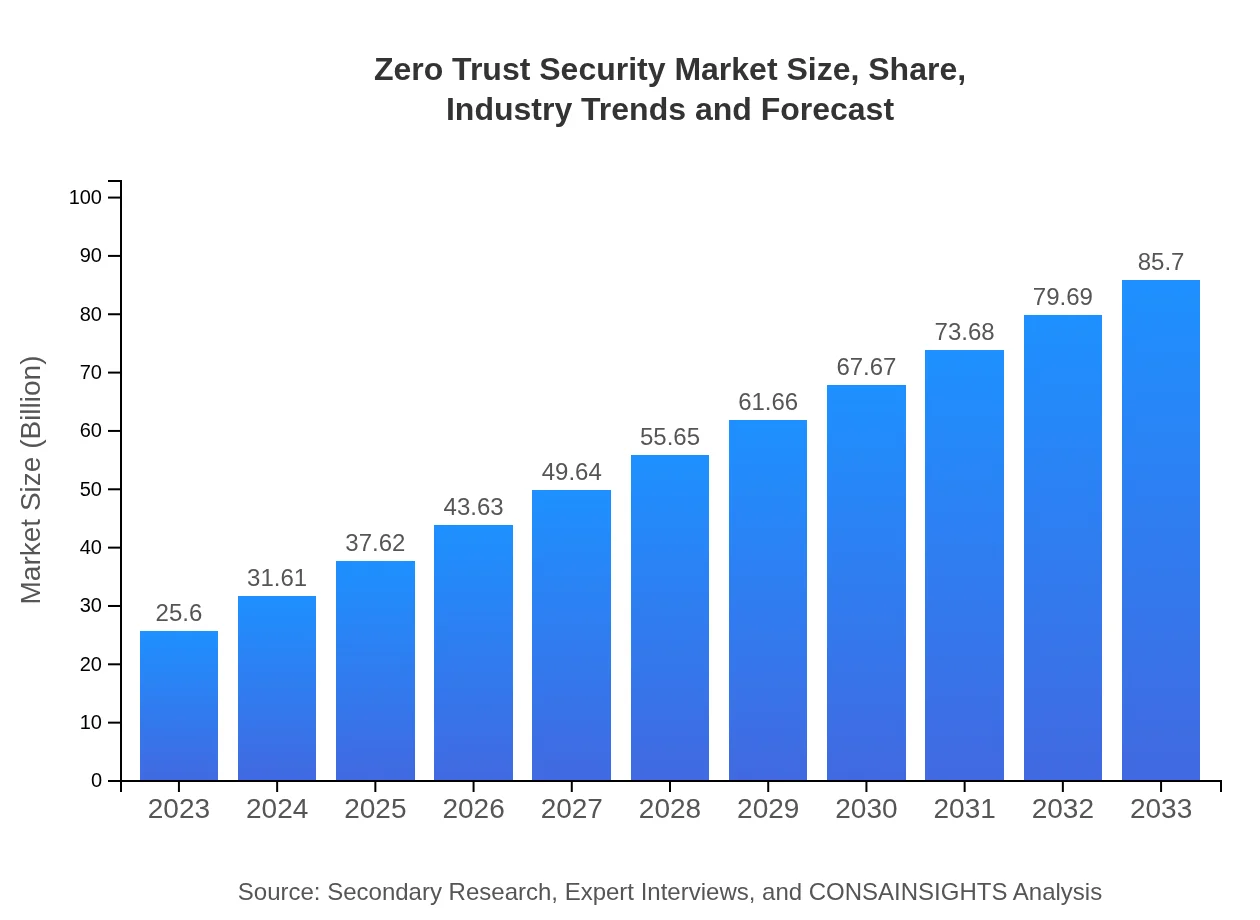
| 2023 Market Size | $25.60 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2033) | 12.3% |
| 2033 Market Size | $85.70 Billion |
| Top Companies | Cisco Systems, Inc., Palo Alto Networks, Inc., Zscaler, Inc., Symantec (Broadcom Inc.), Okta, Inc. |
| Last Modified Date | 31 January 2026 |
Zero Trust Security Market Overview
Customize Zero Trust Security Market Report market research report
- ✔ Get in-depth analysis of Zero Trust Security market size, growth, and forecasts.
- ✔ Understand Zero Trust Security's regional dynamics and industry-specific trends.
- ✔ Identify potential applications, end-user demand, and growth segments in Zero Trust Security
What is the Market Size & CAGR of Zero Trust Security market in 2023?
Zero Trust Security Industry Analysis
Zero Trust Security Market Segmentation and Scope
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis Report by Region
Europe Zero Trust Security Market Report:
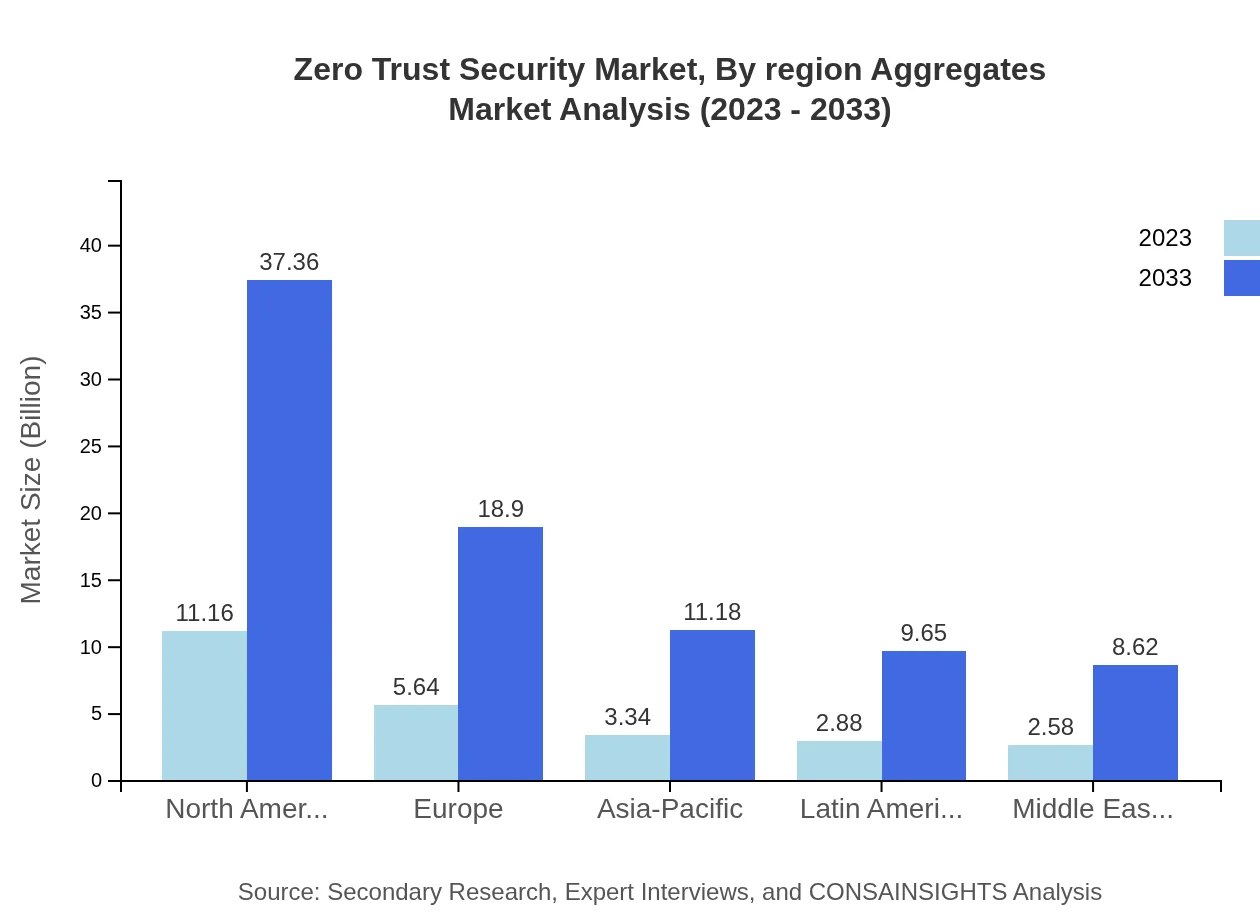
The European market is currently valued at 8.67 billion USD in 2023, expected to reach 29.03 billion USD by 2033. Stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR are motivating organizations to implement Zero Trust Security to protect sensitive data.Asia Pacific Zero Trust Security Market Report:
In the Asia Pacific region, the Zero Trust Security market was valued at 4.75 billion USD in 2023 and is projected to grow to 15.89 billion USD by 2033. The rise is driven by increasing digitalization and investments in cybersecurity infrastructure to combat heightened cyber threats.North America Zero Trust Security Market Report:
North America leads the market with a valuation of 9.21 billion USD in 2023, anticipated to rise to 30.83 billion USD by 2033. This growth is propelled by the presence of major technology firms and increasing regulatory compliance that drive the demand for Zero Trust solutions.South America Zero Trust Security Market Report:
Conversely, the South American region is observed to experience a decline, with market values of -0.52 billion USD in 2023 and projected further to -1.76 billion USD by 2033. This decline may be attributed to economic constraints and lower adoption rates of advanced cybersecurity measures.Middle East & Africa Zero Trust Security Market Report:
In the Middle East and Africa, the market stands at 3.50 billion USD in 2023 and is projected to grow to 11.72 billion USD by 2033. Growth in this region is fueled by an increasing focus on digital transformation and a rising need for robust data protection strategies.Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
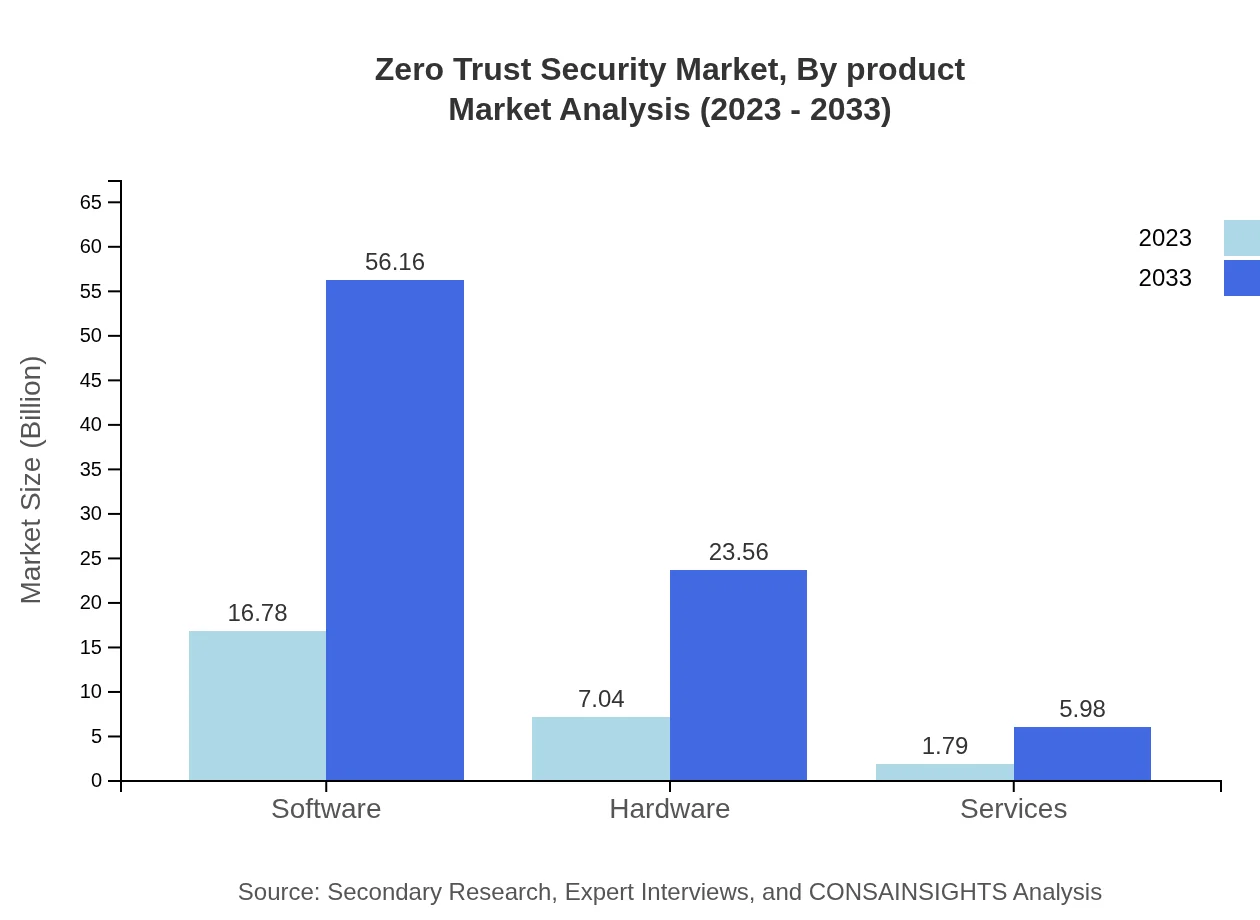
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis By Product
The Zero Trust Security market, by product, will see significant advancements in both software and hardware solutions over the forecast period. Software is expected to remain the largest segment, growing from 16.78 billion USD in 2023 to 56.16 billion USD by 2033, due to the increasing demand for effective access management and threat detection solutions. Hardware solutions, although smaller, are also vital for securing networks, predicted to reach 23.56 billion USD by 2033 from 7.04 billion USD in 2023.
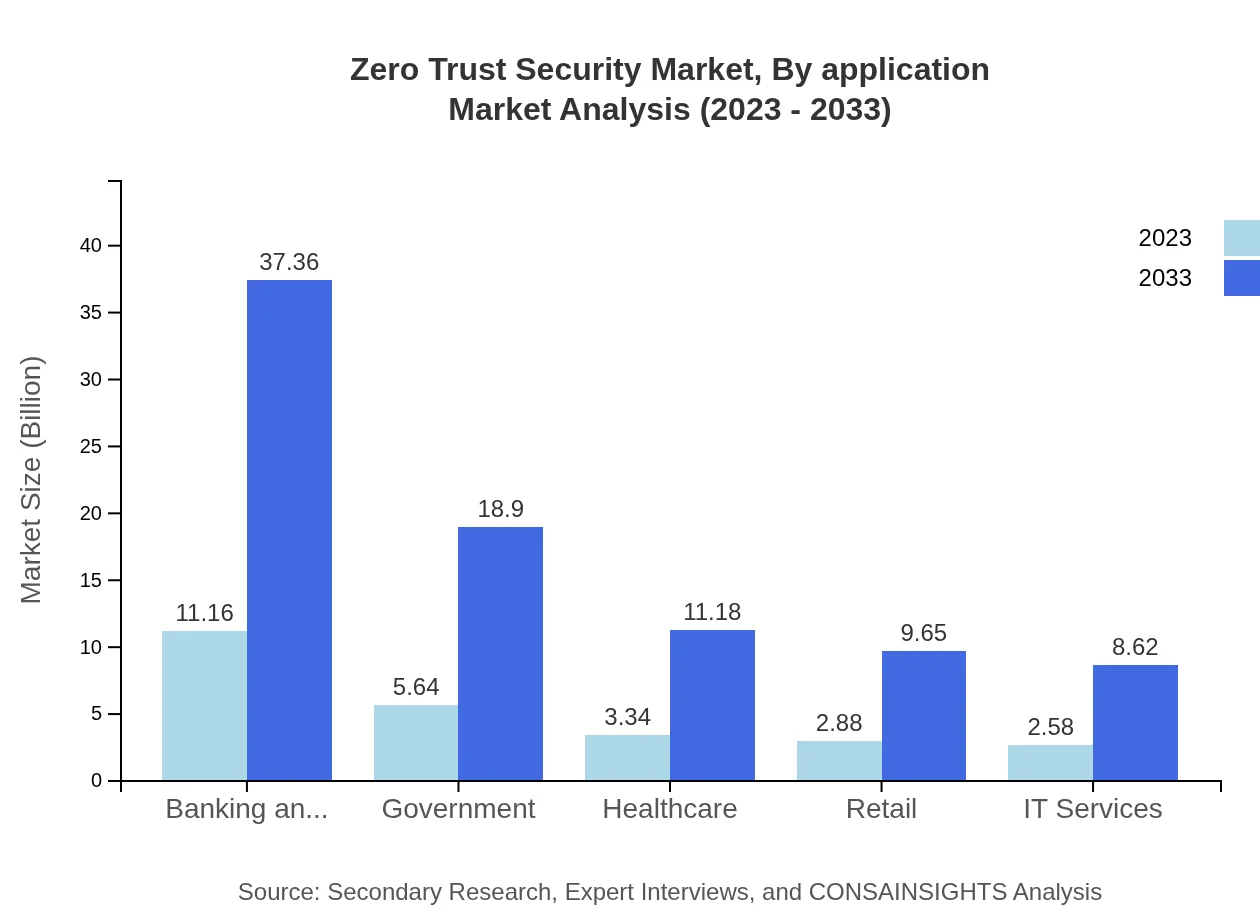
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis By Application
Applications of Zero Trust Security span across diverse sectors such as Banking (11.16 billion USD in 2023 to 37.36 billion USD in 2033), Financial Services, Healthcare, Education, and Government. Banking is the highest market share holder, driven by the critical need to protect sensitive financial data, representing 43.59% in 2023 and sustaining its share by 2033.
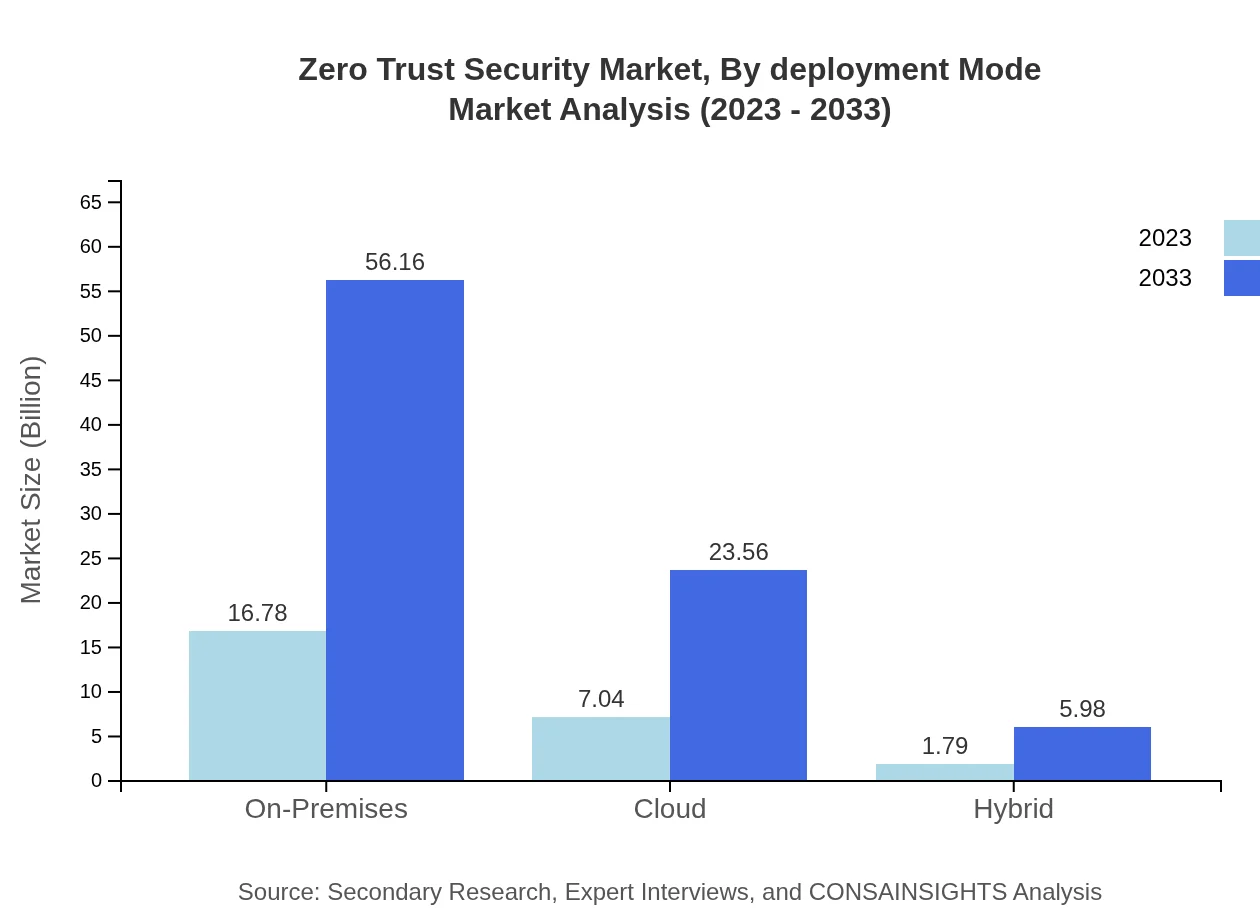
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis By Deployment Mode
Market segmentation by deployment mode highlights that On-Premises solutions will maintain a significant market presence, growing from 16.78 billion USD in 2023 to 56.16 billion USD by 2033, ensuring organizations retain control over their security measures. Cloud-based solutions are also seeing increased traction, reflected in projections of 23.56 billion USD by 2033, as companies shift towards more flexible, scalable security options.
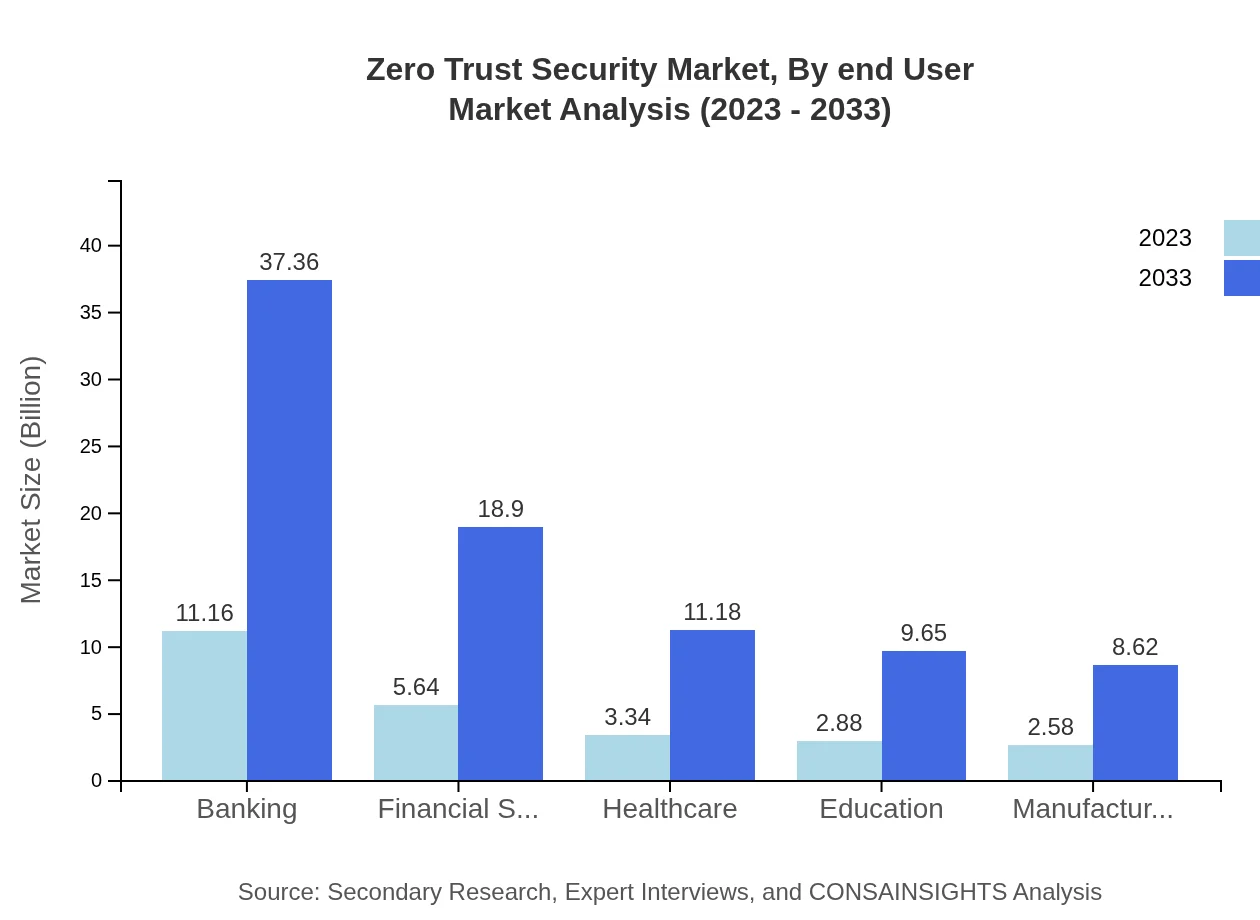
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis By End User
End-user analysis underlines the adoption of Zero Trust Security by sectors such as Government, Healthcare, and IT Services, where the forecast value ranges significantly from 11.26 billion USD in retail to 18.90 billion USD for government by 2033. The pervasive need for compliance and data protection aligns investments from various verticals toward Zero Trust methodologies.
Zero Trust Security Market Analysis By Region Aggregates
Overall, regional aggregates show North America will hold a leading position in market share while Europe follows closely due to stringent data protection policies. Key investments and market growth will predominantly occur in North America and Europe, while other regions such as Asia-Pacific gain momentum from increased digital transformation.
Zero Trust Security Market Trends and Future Forecast
Tell us your focus area and get a customized research report.
Global Market Leaders and Top Companies in Zero Trust Security Industry
Cisco Systems, Inc.:
A pioneer in the cybersecurity space, Cisco offers a wide range of Zero Trust solutions integrating hardware and software to secure networks and endpoints against evolving threats.Palo Alto Networks, Inc.:
Renowned for its advanced firewall solutions, Palo Alto Networks provides extensive Zero Trust security frameworks that facilitate identity and access management.Zscaler, Inc.:
Blending cloud security with a Zero Trust architecture, Zscaler enables secure access to applications and data regardless of device or location.Symantec (Broadcom Inc.):
Symantec contributes to the Zero Trust domain with innovative cybersecurity solutions, focusing on endpoint security and advanced threat protection.Okta, Inc.:
Okta specializes in identity management solutions, empowering organizations to implement Zero Trust strategies effectively through centralized access control.We're grateful to work with incredible clients.









FAQs
What is the market size of zero Trust Security?
The zero trust security market is projected to reach a size of $25.6 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.3%. This growth is driven by increasing cyber threats and the need for secure access management.
What are the key market players or companies in the zero Trust Security industry?
Key players in the zero trust security market include major companies like Microsoft, Cisco, Palo Alto Networks, and Zscaler. These firms are at the forefront of developing innovative security solutions aligned with zero trust principles.
What are the primary factors driving the growth in the zero Trust Security industry?
The growth of the zero trust security market is primarily driven by rising concerns over data breaches, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and regulatory compliance requirements demanding stronger data protection measures.
Which region is the fastest Growing in the zero Trust Security?
North America is the fastest-growing region in the zero trust security market, expected to grow from $9.21 billion in 2023 to $30.83 billion by 2033, reflecting significant investments in cybersecurity initiatives.
Does ConsaInsights provide customized market report data for the zero Trust Security industry?
Yes, ConsaInsights offers customized market report data for the zero-trust security industry, allowing businesses to access tailored insights that fit their specific requirements and strategic goals.
What deliverables can I expect from this zero Trust Security market research project?
From this market research project, expect comprehensive deliverables including detailed market analysis, competitive landscape assessments, and forecasts of market size, share, and growth trends tailored to your business needs.
What are the market trends of zero Trust Security?
Key trends in the zero trust security market include a shift towards cloud-based solutions, increased adoption of identity-based security platforms, and the integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning for threat detection.